This chapter explains the process clustering in the WebLogic server to provide increased scalability and reliability.
Topics:
· Overview
· Configuration of OFS AAI in Clustered Environment
· Changes in Node Manager Configuration
· Configuring the Apache Proxy Plugin for WebLogic
· Domain Creation in HOST B from HOST A (Valid for Horizontal Clustering)
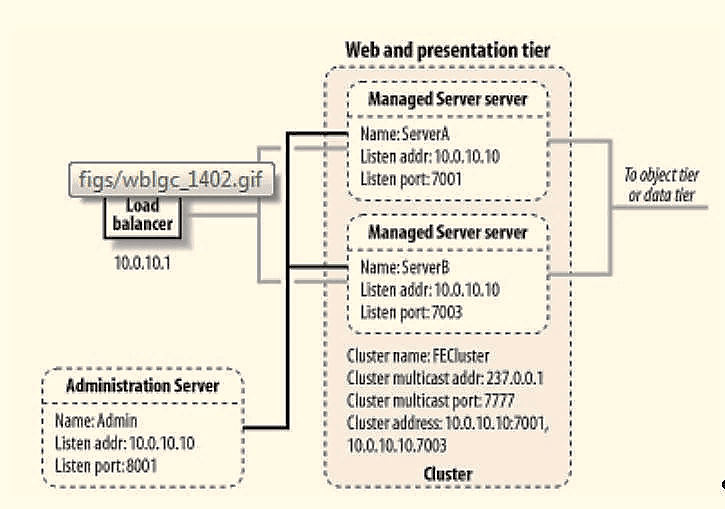
Cluster permits the deployment of application components and services to several machines while presenting only a single face to the client. This is a common requirement. When a client requests a service, it should make no difference if the service runs on a single server or across several servers. The clustering abstraction provides you with a clear route to improve the performance and scalability of your applications, although there is an increase in the administration of hardware and network resources.
WebLogic clustering offers three important benefits:
· Scalability: A solution that allows you to create additional capacity by introducing more servers to the cluster, thereby reducing the load on existing servers.
· Load Balancing: The ability to distribute requests across all members of the cluster, according to the workload on each server.
· High Availability: A mix of features that ensure applications and services are available even if a server or machine fails. Clients can continue to work with little or no disruption in a high availability environment. WebLogic server achieves high availability using a combination of features like replication and failover.
The following types of clustering are available:
· Vertical Clustering: The servers that are members of a cluster can be located on the same host computer and node.
· Horizontal Clustering: The servers that are members of a cluster can be located on different host computers and nodes.
Figure 1: Clustered Environment

To configure OFS AAI in a clustered environment, follow these steps:
1. Create a WebLogic Domain.
You can create WebLogic domains either by configuring all the machines/ servers at the time of domain creation or create a WebLogic domain and configure only for Admin Server. All the wanted resources will be configured from the Admin Console.
2. Execute the script to create a domain.
<Web_logic_Instalation_path> /wlserver_10.3/common/bin/config.sh
3. Log in to Admin Console.
4. Navigate to Environment and then Servers.
The Summary of Servers window is displayed.
Figure 2: Summary of Servers Window
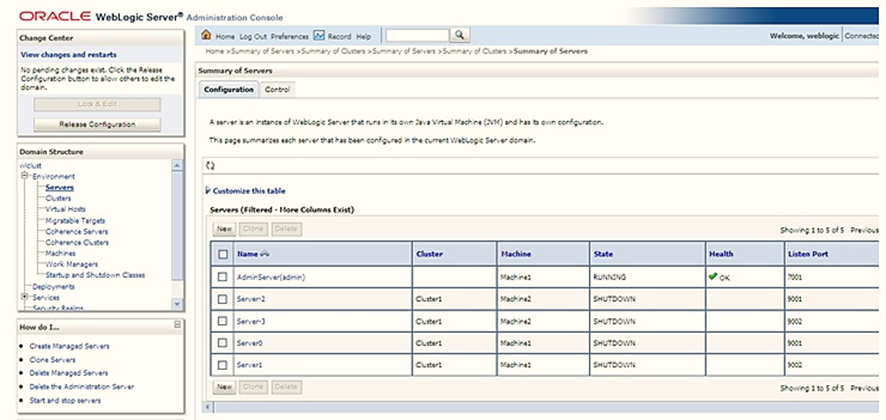
5. Click New to create a server.
6. Enter the details mentioned in the following table:
Fields |
Description |
|---|---|
Server Name |
Enter the server name. |
Server Listen Address |
Enter the listen address. |
Server Listen Port |
Enter the listen port. |
7. Create the number of Servers which should be a part of the cluster.
8. Navigate to Server < Protocol and Enable Tunneling for all the servers which are going to be the part of the cluster.
9. Navigate to Environment and then Clusters.
10. Click New to create a cluster.
The Create a New Cluster window is displayed.
Figure 3: Create a New Cluster

11. Enter the following details.
Fields |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Enter the name of the cluster |
Message Mode |
When creating a new cluster, it is recommended that you use unicast for messaging within a cluster. For backward compatibility with previous versions, WebLogic Server you must use multicast for communications between clusters |
12. Open the created Cluster in editable mode and specify the following details.
Fields |
Description |
|---|---|
Default Load Algorithm |
As there are so many load algorithms the default web logic offers, select the one as per your requirement. Visit the following link for more understanding. http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E11035_01/wls100/cluster/load_balancin g.html. |
Cluster Address |
All servers, which are required to be a part of the Cluster machine, should be mentioned here with a comma-separator. For example: <IP_addresss1>:<Port1>,-<IP_addresss2>:<Port2>,-<IP_addresss3>:<P ort3> Make sure to enable Web Logic Plug-In Enabled as it is required to access the app from Apache proxy. |
13. Navigate to Servers Tab all the servers which need to be part of the cluster.
This step is required to Cluster to identify all servers which are the part of Cluster.
Figure 4: Settings for Cluster

14. Navigate to Environment and then to Machines.
This step is required for configuring the Node manager for the cluster.
15. Click New to create a new machine.
Figure 5: Create a New Machine

16. Enter the details in the following table.
Fields |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Enter the machine name. |
Machine OS |
Enter the Machine OS. |
17. Open machine in Edit mode.
18. Navigate to the Servers tab.
19. Add all created Servers on this screen that you want to bind with a machine (Node manager).
20. The monitoring tab will show the current status of the node manager.
21. If node manager status is inactive you can restart nodemanager from the command prompt.
<Web_Logic_bin_Dir>/startNodeManager.sh
NOTE:
Importance of Node Manager: The Managed Servers in a production Web Logic Server environment are often distributed across multiple machines. If you run Node Manager on a machine that hosts Managed Servers, you can start and stop the Managed Servers remotely using the Administration Console or from the command line. Node Manager can also automatically restart a Managed Server after an unexpected failure.
Refer to the following link for more information http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E13222_01/wls/docs90/server_start/nodemgr.html.
22. Navigate to Environment and then click the Deployment tab.
The Install Application Assistant window is displayed.
Figure 6: Install Application Assistant
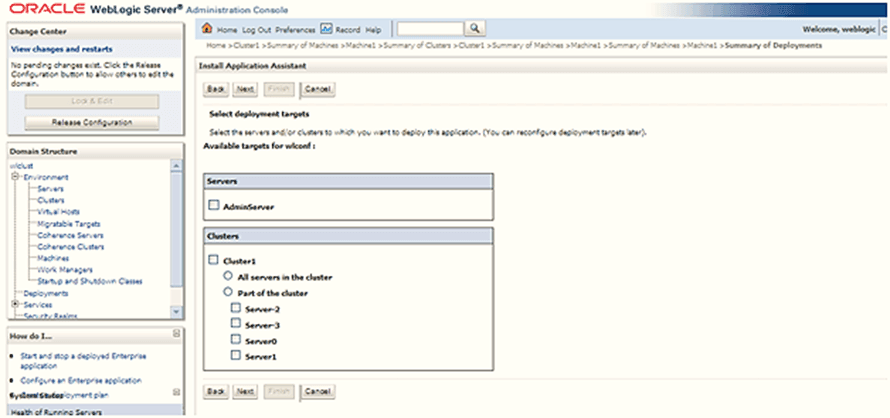
23. Select deployment targets as Cluster was created earlier.
To configure changes in the Node Manager, follow these steps:
1. Change the node manager type to SSL/Plain based on the requirement.
2. Navigate to <Web_logic_Instalation_path>/common/node manager directory
3. Open configuration file nodemanager.properties and do the following changes to the node manager to work properly.
§ Set SecureListener to true/false based on the section in machine configuration.
§ Set StartScriptEnabled to true.
§ Paste the following lines
LISTEN_PORT=5556 export LISTEN_PORT
LISTEN_ADDRESS=<Machine IP address> export LISTEN_ADDRESS
DISPLAY=:1.0
export DISPLAY
4. Start Node manager from the path
<Web_logic_Instalation_path>/server/bin/startNodeManager.sh
NOTE
All servers in a cluster should be part of the same WebLogic Domain.
Figure 7: Node Manager

To configure the Apache proxy plugin for WebLogic, follow these steps:
1. Download Apache Web server version 2.0 or later.
2. Copy the mod_wl_20.so file from the BEA_HOME\server\plugin\win\32 directory to the APACHE_HOME\modules directory.
3. Open the httpd.conf file from the APACHE_HOME\conf directory, and add the following at the end of this file:
LoadModule weblogic_module modules\mod_wl_20.so. LoadModule rewrite_module modules/mod_rewrite.so LoadModule ssl_module modules/mod_ssl.so.
b- <IfModule mod_weblogic.c> WebLogicCluster node1:node1_port,node2:node2_port DebugConfigInfo ON
MatchExpression *.jsp MatchExpression *.xyz
</IfModule>
<IfModule mod_ssl.c> Include conf/ssl.conf
</IfModule>
<Location /HTTPClnt> SetHandler weblogic-handler
</Location>
<Location /iiop> SetHandler weblogic-handler
</Location>
<Location /<name of EAR file of deployed application> > SetHandler weblogic-handler
DebugConfigInfo ON PathTrim /weblogic
</Location>
4. Restart Apache.
NOTE
Refer to the following link for more information http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E14049_01/doc.9101/e14047/apacheproxy.htm.
5. For registering the node manager present in a different host(HOST A) with the admin present in a different host(HOST B). The admin server requires the nodemanager to communicate with the managed servers to do the following process.
NOTE
This step is required only for horizontal clustering.
Let say admin is present in HOST A and Node manager is present in HOST B.
Log in to the HOST B box and execute the following commands.
1----<Java_path> -cp <Web_logic_lib_path>/ weblogic.jar weblogic.WLST
EX-/home/weblogic/jdk1.6.0_17/bin/java -cp /oracle/weblogic/Oracle/Middle- ware/wlserver_10.3/server/lib/weblogic.jar weblogic.WLST
2----connect(weblogic_user_id_HOST A,'Web_logic_password_HOST A','t3://<Admin_console_ip_HOST A>:<Admin_console_port Host A>')
EX-connect('weblogic','weblogic123','t3://10.184.108.86:7001') 3---wls:/weblogic/serverConfig>nmEnroll( ‘<Web_logic_Domain_path_Host A>’, ‘<Web_logic_Node_manager_path_Host A>’
Ex-wls:/weblogic/serverConfig>nmEnroll( '/oracle/weblogic/Oracle/Middleware/user_projects/domains/wlclust', '/oracle/weblogic/Oracle/Middleware/wlserver_10.3/common/nodemanager')
NOTE
Refer to the following link for more information http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E13222_01/wls/docs81/admin_ref/cli.html.
Figure 8: WebLogic Server Domain

NOTE
The path where WebLogic is installed should be the same for different machines. Across a cluster (valid for horizontal clustering), else clustering will not work properly. The installer creates the web logic path on the machines. This path should be identical to the other machine. Else Servers will not run properly so as machines.
To create a domain in Host B from Host A, follow these steps:
1. By the pack command create the <Domain_Name>.jar from HOST A machine and unpacked it in HOST B.
2. Include the following in PATH variable in .profile
export PATH=/BEA_HOME /common/bin:$PATH
3. Run the following command in HOST A
pack.sh -managed=true -domain=<User_Project_Dir> /domains/<Domain_Name> -tem- plate=<User_Project_Dir> /domains /<Domain_Name>.jar -template_name="<Domain_name>"
Ex-pack.sh -managed=true -domain=/home/isve/ofsaa/INSTLD/Oracle/Middle- ware/user_projects/domains/ror732 -template=/home/isve/ofsaa/INSTLD/Oracle/Middle- ware/user_projects/domains/ror732.jar -template_name="ror732"
<Domain_Name>.jar will be created, move the file to User_Project_Dir> /domains location in HOST B.
4. Run the following command in HOST B
unpack.sh -template=<User_Project_Dir>/domains /<Domain_Name>.jar
-domain=<User_Project_Dir>/domains/<Domain_Name>
Ex-unpack.sh -template=/home/isve/ofsaa/INSTLD/Oracle/Middleware/ror732.jar
-domain=/home/isve/ofsaa/INSTLD/Oracle/Middleware/user_projects/domains/ror732
NOTE
Ensure that the /tmp Directory in the <persistent-store-dir>/tmp</persistent-store-dir> Tag is created in a location that is accessible to all the nodes of a Clustered WebLogic Environment.
To replicate sessions between servers, follow these steps:
1. For session replication, include weblogic.xml in EAR creation.
2. Put the weblogic.xml file in the <Path_of_Server> /webroot/WEB-INF directory and build the EAR. The same EAR should be used for session replication. This file consists of the session-descriptor which is used for replicating the session.
3. There is several type of session replication in weblogic. Refer the following. http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E12840_01/wls/docs103/webapp/sessions.html.
Sample file is shown in the following:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<weblogic-web-app xmlns="http://www.bea.com/ns/weblogic/90">
<session-descriptor>
<persistent-store-type>file</persistent-store-type>
<persistent-store-dir>/tmp</persistent-store-dir>
<sharing-enabled>true</sharing-enabled>
<timeout-secs>3600</timeout-secs>
<invalidation-interval-secs>60</invalidation-interval-secs>
<cookie-name>MYSESSIONCOOKIE</cookie-name>
<id-length>12</id-length>
<encode-session-id-in-query-params>true</encode-session-id-in-query-params>
<cookie-max-age-secs>-1</cookie-max-age-secs>
<cookie-http-only>true</cookie-http-only>
<url-rewriting-enabled>true</url-rewriting-enabled>
</session-descriptor>
</weblogic-web-app>
4. Rename the file to weblogic.xml before placing in the -<Path_of_Server> /webroot/WEB-INF directory.
5. Delete the following entry from the web.xml file before creating the .ear file as there is no servlet mapping for the same.
1--<!-- ofs summary -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>context</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.ofs.reveleus.common.summary.common.ContextDocLoader</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
2--Change the FIC_PHYSICAL_HOME_LOC and FIC_HOME value in web.xml file to a path and give read access.
6. Copy the /webroot/conf directory to the path of the server.