4 XCMD XAPI Server Operator Commands
This chapter describes XAPI server operator commands supported by XCMD. These commands enable an operator or administrator to monitor the ACSLS XAPI component. Supported commands include:
Issue these commands from the ACSLS user_proc using the XCMD command. See "XCMD Command Conventions" for more information.
See "Syntax Conventions" for conventions used in the syntax flow diagrams included in the following command sections.
LOG
The following section describes the LOG command.
Description
The LOG command changes or lists the current XAPI server log settings.
Note:
The log file name and location are set by ACSLS environmental variables and default to file namevlog.file in the XAPI_WORK_PATH directory.Parameters
As shown in Figure 4-1, the LOG command includes the following parameters:
- LIst
-
optionally, specifies that the current log setting is displayed. The default if no command parameters are specified is
LIst. - log_setting
-
optionally, indicates the desired log setting specified as a series of '0' and '1' characters.
-
0signifies that the desired positional log setting should beOFFor disabled. -
1signifies that the desired positional log setting should beONor enabled.
The value specified completely replaces, and is not merged with the current log setting. The positional log settings are as follows:
-
1- Log error messages to the ACSLS XAPI component log. -
01- Log messages to log file. -
001- Log input transaction errors to the log file. -
0001- Log all XML recv() packets to the log file. -
00001- Log all XML send() packets to the log file. -
000001- Log local commands and responses to the log file.
XAPI
LOGmessages will be saved in the$ACS_HOME/log/xapi/vlog.file.Note:
TheLOGcommand enables you to set and display more positions of 0's and 1's (16) than are currently defined asLOGsettings above; this allows for future expansion and any extraneous 0 or 1LOGsetting are simply ignored. -
- OFF
-
optionally, specifies that logging should be disabled. This is equivalent to
LOG 0.
LIST
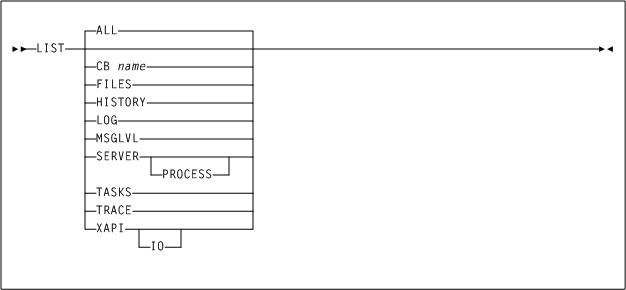
The following section describes the LIST command.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 4-2, the LIST command includes the following parameters:
- ALL
-
optionally, displays all XAPI server status and settings. This is the default if you issue the
LISTcommand with no parameters. - CB name
-
Specifies that the named control block is displayed in character, and character hexadecimal format. Use only at the direction of Oracle support.
Specify one of the following control blocks for
name:-
HTTPCVT -
HTTPGBL -
HTTPREQ-nnn -
HTTPAPI-nnn
For
LIST CB HTTPREQandLIST CB HTTPAPI, an index between 0 and 999 must be specified. Additionally, the index must be delimited from the control block name by a single dash ("-") with no intervening spaces. For example:LIST HTTPREQ-0or
LIST HTTPAPI-900 -
- FILES
-
optionally, specifies that the full path name of XAPI server control, log, and trace files is displayed.
- HISTORY
-
optionally, specifies that the XAPI transaction count history is displayed for the past 24 hours.
- LOG
-
optionally, specifies that the current XAPI server log setting is displayed. This is equivalent to issuing a
LOGcommand with no parameters. - MSGLVL
-
optionally, specifies that the current XAPI server message level setting is displayed. This is equivalent to issuing
MSGLVLcommand with no parameters. - SERVER
-
optionally, specifies that the current XAPI server and UNIX versions, relevant parameters and environment variables, and shared segment and message queues are displayed.
You can optionally include the
PROCESSkeyword to request that all active XAPI server process ids, thread and open file counts, CPU and memory usage are also displayed. - PROCESS
-
When specified with
SERVER, thePROCESSkeyword requests that all active XAPI server process ids, thread and open file counts, CPU and memory usage are displayed as well. - TASKS
-
optionally, specifies that the current XAPI server system and work tasks are displayed
- TRACE
-
optionally, specifies that the current XAPI server trace setting is displayed. This is equivalent to issuing a
TRACEcommand with no parameters - XAPI
-
optionally, specifies that the current XAPI server listener port, and IP address are displayed.
You can optionally include the
IOkeyword to request that all XAPI server listener statistics are also displayed.
MSGLVL
The following section describes the MSGLVL command.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 4-3, the MSGLVL command includes the following parameters:
- LIst
-
Specifies that the current
MSGLVLsetting is displayed. The default if no command parameters are specified is LIst. - level
-
specifies the desired
MSGLVLsetting. The higher the level, the more verbose the XAPI server messaging. Message levels are cumulative;MSGLVL 8produces all messages up to and includingMSGLVL 8(that is,MSGLVL 0through8are produced). Message levels are generalized as follows:-
0 - Normal startup, shutdown, and error messages; these messages cannot be suppressed.
-
4 - Serious warning messages.
-
8 - Minor warning messages.
-
12 - Startup parameter and option messages.
-
16 - Additional startup and shutdown messages.
-
20 - Additional diagnostic level 20 messages.
-
24 - Additional diagnostic level 24 messages.
-
28 - Additional task startup and shutdown messages.
-
- OFF
-
Specifies that all verbose messages should be disabled. This is equivalent to
MSGLVL 0.
TRACE
The following section describes the TRACE command.
Description
The TRACE command changes or lists the XAPI server trace settings.
Note:
-
The trace file name and location are set by ACSLS environmental variables and default to file name
vtrace.filein theDV_TAG_XAPI_WORK_PATHvariable. -
Tracing can have significant impact on system performance. Only set tracing ON at the request of Oracle StorageTek support.
-
The
TRACEcommand enables you to set and display more positions of 0's and 1's (16) than are currently defined asTRACEsettings above; this allows for future expansion and any extraneous 0 or 1TRACEsetting is simply ignored.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 4-4, the TRACE command includes the following parameters:
- LIst
-
optionally, specifies that the current trace setting is displayed. The default if no command parameters are specified is
LIst. - trace_setting
-
optionally, indicates the desired trace setting specified as a series of '0' and '1' characters. 0 signifies that the desired positional trace setting should be
OFFor disabled, while 1 signifies that the desired positional trace setting should beONor enabled. The value specified completely replaces, and is not merged with the current trace setting. The positional trace settings are as follows:-
1- Trace errors to the trace file. -
01- Trace TCP/IP functions and events to the trace file. -
001- Trace PGMI or ACSAPI functions and events to the trace file. -
0001- Trace otherwise unclassified XAPI server events to the trace file. -
00001- Trace malloc() and free() events to the trace file. -
000001- Trace XML parser events to the trace file. -
0000001- Trace command server process events to the trace file. -
00000001- Trace monitor process events to the trace file. -
000000001- Trace CSV functions and events to the trace file.
-
- OFF
-
optionally, Specifies that tracing is disabled. This is equivalent to
TRACE 0.