About Virtual Machines and Oracle Database Appliance Virtualized Platforms
Oracle Database Appliance Virtualized Platform is designed to run and deploy virtual machines to manage system resources.
Configure virtual machines on Oracle Database Appliance Virtualized Platform to manage your application use of shared repository resources, such as the CPU pool, memory, and other shared resources.
Virtual Machine Templates
Virtual machines can be created from a template or assembly containing preconfigured virtual machines. The creation of a virtual machine from a template is based on cloning: the template is imported as an archive, unpacked, and stored as a virtual machine configuration file with disk images. These disk images are cloned to create a new instance in the form of a virtual machine. In the same way, an existing virtual machine can be cloned to create a new virtual machine, or cloned to create a new template.
Virtual Machine Assemblies
Virtual machine assemblies are often described as a template of a group of virtual machines, or a collection of virtual machine templates. An assembly can contain a single virtual machine or a collection of virtual machine templates.
Domains, Guests and Virtual Machines
The terms domain, guest, and virtual machine are often used interchangeably, but they have subtle differences. A domain is a configurable set of resources, including memory, virtual CPUs, network devices, and disk devices, in which virtual machines run. A guest is a virtualized operating system running within a domain. Multiple guests can run on the same instance of Oracle Database Appliance Virtualized Platform, each within its own domain. A virtual machine is granted virtual resources, and can be started, stopped, and restarted independently.
Virtual Disks
In addition to virtual machines, you can create virtual disks in shared repositories. Virtual disks provide additional storage options for virtual machines by enabling you to attach additional block storage to your virtual machines. Similarly, you can detach the storage if you no longer need the additional space. You can use virtual disks to expand existing file system storage inside the virtual machine by extending the storage volume onto a virtual disk, or by creating a new file system on a virtual disk. Your virtual disks can also share multiple virtual machines running on the same shared repository.
Shared Repositories
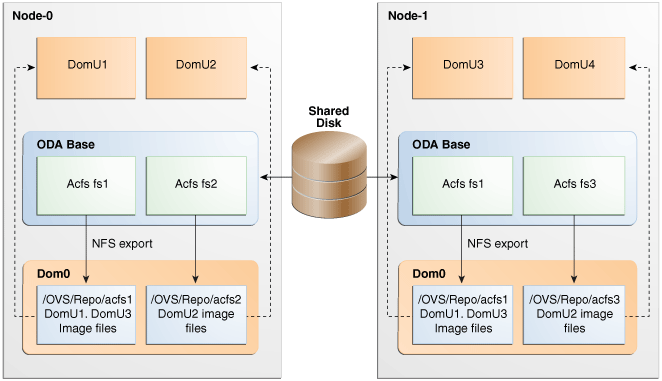
A shared repositoryis a central location for storing resources that are essential to creating and managing virtual machines. These resources include virtual machine templates and assemblies, ISO files (virtual DVD images), virtual machine configuration files, and virtual disks. Shared repositories are configured on an Oracle Automatic Storage Management Cluster File System (Oracle ACFS) and then presented to the Oracle Database Appliance nodes that need access to those resources. Oracle Database Appliance Virtualized Platform uses shared repositories to optimize available disk space usage in the environment, and for easy reallocation of virtual machines if a physical server fails. The virtual machine files can be stored on shared disks, providing shared storage for the virtual machines. Additionally, you can configure CPU pools and a resizeable Oracle Database domain (ODA_BASE) to ensure that the virtual machines do not consume cycles from each other or from your assigned database CPU cores.
-
The shared disks on Oracle Database Appliance Virtualized Platform are connected directly to ODA_BASE.
-
ODA_BASE contains three shared repositories named fs1, fs2, and fs3.
-
Each shared repository is an Oracle ACFS in ODA_BASE created on top of the Oracle Automatic Storage Management (Oracle ASM) disk group (DATA or RECO) chosen by the user when creating the shared repository.
-
The process that creates a shared repository also performs a network file system (NFS) export of the shared repository to the respective Dom0 by using the private network.
-
The export enables shared storage for the virtual machine files.
Figure 3-2 Architecture Overview of Oracle Database Appliance Virtualized Platform Shared Repositories
Description of "Figure 3-2 Architecture Overview of Oracle Database Appliance Virtualized Platform Shared Repositories"
With the configuration shown in the illustration, you can:
-
Create multiple repositories.
-
Mount these repositories either on the nodes where the virtual machine needs to run (such as fs2 and fs3 in the illustration), or on both the nodes (such as fs1 in the illustration).
-
Create one or more virtual machines or virtual machine templates on the shared repositories.
-
Use OAKCLI commands to create and manage shared repositories, virtual disks, and their virtual machines, and the underlying architecture shown in the illustration.