Portlets - Addressing Mixed Content - CHROME
Issue *
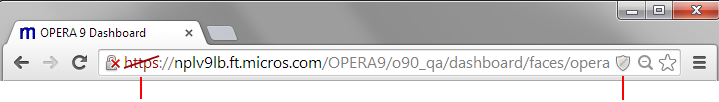
Websites that ask for sensitive information, such as usernames and passwords, often use secure connections to transmit content to and from the computer you're using. If you're visiting a site via a secure connection, Google Chrome will verify that the content on the web page has been transmitted safely. If it detects certain types of content on the page coming from insecure channels, it can automatically prevent the content from loading and you'll see a shield icon ![]() appearing in the address bar. By blocking the content and possible security gaps, Chrome protects your information on the page from falling into the wrong hands.
appearing in the address bar. By blocking the content and possible security gaps, Chrome protects your information on the page from falling into the wrong hands.
As a result, parts of the
page may not display when Chrome blocks the insecure content.
To enable the insecure content
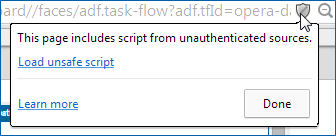
Although not recommended, you can choose to override the alert for the page by selecting Load unsafe script. Chrome will refresh the page and load its content, including any insecure content. The URL in the address bar will show ![]() to indicate that the page is not fully secure.
to indicate that the page is not fully secure.
Advanced tips
You can choose to block certain types of web content, such as JavaScript and images, for all sites by visiting your Settings page. See more information on adjusting your web content settings.
Although not recommended, you can also use the command line flag --allow-running-insecure-content to prevent Chrome from checking for insecure content. Instructions on how to add a command line flag can be found on the Chromium site (English only).
|
* Excerpts from "This page has insecure content."Retrieved 6 May 2014.
† screenshots in these examples are taken from Chrome Version 34.0.1847.131 m
|