10 VSM Extended Storage Feature
The VSM Extended Storage feature (ExS) is a VTCS software enhancement that allows the VTSS to access and utilize storage external to the VTSS.
With this feature, a VSM 6 or VSM 7 system can migrate and recall VTVs to storage targets ”extended” beyond the typical Oracle StorageTek targets (for example, tape libraries, tape drives, and Virtual Library Extension).
ExS is included in the base VSM 6 or VSM 7 microcode and is configured by Oracle Services personnel as part of the VSM configuration.
ExS supports targets that utilize the OpenStack Swift (object storage) protocol and those that support network attached storage (NAS). These include:
-
Oracle Object Storage Classic (OCC)
-
Oracle Archive Storage Classic (OCC)
-
Any private cloud that supports the OpenStack Swift protocol
-
Oracle ZS5-2 or ZS5-4 configured as a Swift target
-
Oracle ZS5-2 or ZS5-4 configured as an NSF target
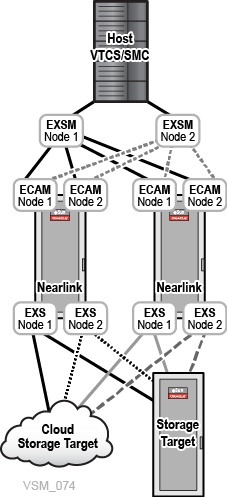
The following figure illustrates a VSM 7 environment using VSM Extended Storage for cloud attach:
As shown in Figure 10-1, ExS software is distributed across multiple VSM nodes, and communicates as follows:
-
VTCS or oVTCS resides on the customer network and communicates with all Extended Storage Manager (EXSM) instances using the UUI protocol to NET0 on all VTSS nodes.
-
All EXSM instances communicate with all ECAM/IP instances on all VTSS nodes through NET0.
-
All EXS instances communicate with all Extended Storage targets through the VTSS REP ports.
ExS software is maintained as part of the VTSS code. ExS reconfiguration requires a disruptive outage of the VTSS in order to initiate changes.
Oracle Cloud Options
VSM 7 Extended Storage supports three Oracle Cloud options:
-
Oracle Cloud Object Storage Classic
-
Oracle Cloud Archive Storage Classic
-
Encryption within Oracle Cloud
For each option, the Oracle CSE must retrieve the customer's Oracle Cloud account information to create and configure your initial connection between VSM Extended Storage and Oracle Cloud. Account information includes the following:
-
Account Name
-
User Name
-
User Password
-
Authentication URL
For information about how to get started with the Oracle Cloud:
http://docs.oracle.com/cloud/latest/trial_paid_subscriptions/CSGSG/toc.htm
For more information about the Oracle Cloud subscription:
http://docs.oracle.com/en/cloud/iaas/storage-cloud/index.html
For up-to-date Cloud information:
http://docs.oracle.com/cloud/latest/
Oracle Storage Cloud Service – Object Storage
Storing data in the Oracle Cloud is much like storing data in a VLE local disk pool. The following steps outline what is needed to configure VSM Extended Storage for storing a virtual tape volume (VTV) in Oracle Cloud.
MVC ranges are determined by the customer. They are used to configure VTCS host software and provided to the Oracle support team for configuration of the VSM Extended Storage feature.
If the VSM ExS will store VTV data in the Oracle Cloud, you must define and configure the vMVC pool range for VSM ExS Oracle Cloud Storage.
The performance of VSM ExS to cloud data transfer performance is subject to IP bandwidth and delay as well as Oracle Cloud performance capabilities.
Oracle Storage Cloud Service – Archive Storage
Storing data in the Oracle Cloud is much like storing data locally, though there are some exceptions regarding a recall of data stored in the Cloud Archive.
The steps for setting up the VLE for using the Oracle Storage Cloud Service – Archive Storage is similar to the steps for Oracle Cloud.
MVC ranges are determined by the customer. They are used to configure VTCS host software and given to the Oracle support team for configuration of VSM Extended Storage. The customer must provide up to two vMVC ranges when using Cloud Archive:
-
A vMVC range for VSM ExS Storage Cloud
-
A vMVC range for VSM ExS Cloud Archive Storage
When creating vMVCs on the ExS, the Oracle support person selects an ’archive' flag for vMVCs that will use Cloud Archive. This is what triggers the ’archive' functionality within the Oracle Cloud. Once VMVC definitions are configured, VTV Migrate, Recall, and Copy operations are possible for both vMVC ranges, however there are exceptions for the Cloud Archive range of vMVCs.
Migrate
VTV migrate operations perform the same for VTVs migrated to VLE local disk pool or VTVs migrated to the Oracle Cloud Service. Once a VTV is migrated to Oracle Cloud Object Storage, it automatically moves to Oracle Cloud Archive Storage.
Restore and Recall
Once a migrated VTV is moved to Oracle Cloud Archive Storage, you must manually restore the VTV before it can be recalled by ExS. This involves moving the VTV from Oracle Cloud Archive Storage back to Oracle Cloud Object Storage.
Use a RESTORE_VTV request to manually restore a VTV from Oracle Cloud Archive Storage. Use a Route command to issue this request for the appropriate ExS storage manager.
Use and of the following methods to process the RESTORE_VTV request:
-
Issue the SMC
Routecommand from an MVS console.F ELS73SMC, ROUTE DVTGRD13 RESTORE_VTV VOLUME=5B1307 VTV=CV1234
-
Issue the SMC
Routecommand from theSMCUUUIutility. Include theRoutecommand in theUUIINdata set. Refer to the ELS command, Control Statement, and Utility Reference for more information. -
Issue the SMC
Routecommand from the VSM GUI.ROUTE DVTGRD13 RESTORE_VTV VOLUME=5B1307 VTV=CV1234
Displaying Progress
Issue a QUERY_RESTORE request to display progress for the VTVs that are in the restore process. For example:
ROUTE DVTGRD13 QUERY_RESTORE VOLUME=5B1307 VTV=CV1234
Progress is displayed. For example:
Restore initiated via SMCUUI Interface:
-
Archived -
In Progress -
Complete - Restored -
Complete - Not Archive
Once a Complete response is received, the VTV can be recalled normally.
Note:
Once a VTV is restored, it will remain in Oracle Storage Cloud Service – Object Storage for 24 hours; then it will return to Archive state. Oracle service level agreement (SLA) to restore a VTV is 4 hours. MultipleRESTORE_VTV commands can be initiated at the same time.Oracle Cloud Encryption
Encryption, if VTV data is stored in the Oracle Cloud, is offered for both Archive and non-Archive Cloud offerings.
Encryption is controlled at the vMVC boundary, that is, if a vMVC is created with the Encryption flag set, all of the VTVs in that vMVC will be encrypted. Migrate and recall operations for encrypted VTVs behave exactly the same for each of the respective Clouds (Archive and non-archive) as described above. The only behavior difference is a performance decrease of 10% for encrypted VTVs. The steps for setting up the VSM Extended Storage for Oracle Cloud Encryption are very similar to steps above for Oracle Cloud and Oracle Cloud Archive.
MVC ranges are determined by the customer. They are used to configure VTCS host software and given to the Oracle support team for configuration of VSM Extended Storage. The customer must provide up to two vMVC ranges when using Cloud with Encryption:
-
A vMVC range for VSM ExS Storage Cloud
-
A vMVC range for VSM ExS Cloud Archive Storage (with or without Encryption)
When creating vMVCs on ExS, an Oracle support person sets an encryption flag for any vMVCs that will contain encrypted VTVs. Other than the performance there is no difference in the way VTV data is stored (Migrate) and retrieved (Recall) from an ExS or host perspective.
Visit the Oracle Cloud website for information pertaining to the Encryption feature as it is handled within the Oracle Cloud.
Configuring VTCS or oVTCS for Extended Storage
VTCS and oVTCS applications recognize the ExS system as a Storage Manager, similar to a standard VLE system. Therefore, configuration is the same as for VLE 1.5.3 Cloud storage.
Refer to the VLE publication Configuring Host Software for VLE Guide for more information.
Updating ELS PARMLIB
To define the Extended Storage Manager name and define RTDs in VTCS or oVTCS:
-
Define the Extended Storage Manager name.
Use the VTCS
CONFIg TAPEPlex STORMNGRstatement to define the Extended Storage Manager name.For example:
TAPEPLEX THISPLEX(tapeplex_name) STORMNGR(exs_name)
Refer to the your Oracle StorageTek Enterprise Library Software (ELS) publications for more information about these commands.
-
Define RTD(s) to the ExS STORMNGR.
Use the VTCS
CONFIg RTDpathstatement to define the path to the ExS STORMNGR, using only theSTORMNGRandIPIFparameters.RTD NAME=EXSRTDxx STORMNGR=exs_name IPIF=nn:nn
Refer to the your Oracle StorageTek Enterprise Library Software (ELS) publications for more information about these commands.
Updating SMC PARMLIB
To define the ExS STORMNGR and SERVER in SMC:
-
Define and enable the ExS STORMNGR.
Use the SMC
STORMNGRcommand to define and enable the ExS storage manager to SMC.STORMNGR NAME(exs_name) ENABLEThe
ENAblekeyword enables the specified ExS Storage Manager. This is the default when a new ExS Storage Manager is added.Refer to the your Oracle StorageTek Enterprise Library Software (ELS) publications for more information about these commands.
-
Define the ExS SERVER.
Use the SMC
SERVercommand to define a named path for the ExS Storage Manager.For example:
SERVER NAME(server_name) STORMNGR(exs_name) IP(vtssnet0ipaddress) PORT(60000)
Before a
SERVeris defined, the ExS Storage Manager that it references must be defined using aSTORMNGRcommand. The ExS Storage Manager name associated with aSERVercannot be changed.Refer to the your Oracle StorageTek Enterprise Library Software (ELS) publications for more information about these commands.
Defining POOLPARM MVCs and VOLPARM VOLSERs
To define MVC pools:
-
Code
POOLPARMorVOLPARMstatements to define the MVC pools.POOLPARM NAME(LEPOOL1) TYPE(MVC) VOLPARM VOLSER(A00000-A00099)
-
Use the
SET VOLPARMcommand to validate thePOOLPARMorVOLPARMstatements without loading them.SET VOLPARM APPLY(NO)
-
Use the
SET VOLPARMcommand to load thePOOLPARMorVOLPARMstatements.SET VOLPARM APPLY(YES)
Refer to the your Oracle StorageTek Enterprise Library Software (ELS) publications for more information about these commands.