6 ELS Facilities for VSM console
This chapter describes the following ELS-related topics that affect VSM console commands, operations, and usage.
Using an MVS Client with the VSM Console
This section describes how to use Oracle's StorageTek Storage Management Component (SMC) as an MVS client connected to the VSM console.
Overview
oVTCS on a VSM console server requires the following:
-
VSM 6 or VSM 7 as the VTSS
-
SMC 7.3 or higher (with the XAPI support), serving as an MVS client to VSM console.
-
ACSLS 8.4 on a VSM console server (not required in a VSM console configuration processing VTVs only, or if the ACSLS is replaced by VLE(s) for multi-volume cartridge (MVC) support)
Figure 6-1 shows the MVS Client/VSM console server data flow. In this example, VSM console is configured with both ACSLS and oVTCS LDOMs to support both native tapes in an SL library and VTVs in a VSM 6.
As shown in Figure 6-1:
-
XAPI protocol over TCP/IP is used for the following paths:
-
Control path from SMC to ACSLS on the VSM console (path 1).
-
Control path from the SMC on MVS to oVTCS on the VSM console (path 2).
-
Control path from oVTCS to ACSLS with XAPI support (path 3).
-
-
HLI protocol over TCP/IP is used for the control path from ACSLS on the VSM console to the SL library (path 4).
-
ECAM-T protocol over TCP/IP is used for the control path from the oVTCS software on the VSM console to the VTSS (path 5).
-
FICON is used for the following paths:
-
Data Path from MVS to the real tape drives in an SL library (path 6).
-
Data path from MVS to the VTDs in the VTSS (path 7).
-
Data path from the VTDs on the VTSS to the RTDS in the SL library (path 8).
-
As shown in Figure 6-1, the SMC client to VSM console software control path works as follows:
-
An MVS job sends a tape request to MVS tape allocation and mount or dismount services.
-
The SMC client receives the tape request from MVS tape services.
-
The SMC client, using XAPI protocol over TCP/IP, sends the following:
-
Virtual tape requests to oVTCS on a VSM console server.
-
Real tape requests to ACSLS with XAPI on a VSM console server.
-
Note:
-
If all tape drives in the SL library are oVTCS RTDs, and all tape cartridges in the SL library are oVTCS MVCs, then the SMC client does not require access to the SL library. In this scenario, a control path from the SMC Client to ACSLS with XAPI support (path 1), and data path from MVS to the Tape Drives in the SL Library (path 6) are eliminated. See "Connecting SMC to ACSLS on the VSM console Server".
-
If oVTCS is configured for VTVs only, then there are no oVTCS RTDs and no oVTCS MVCs. In this scenario, there is no SL library, and ACSLS with XAPI Support is not required.
-
If all oVTCS MVCs are on VLEs, then ASCLS with XAPI Support is not required.
-
If you also have a HSC and VTCS on MVS connected to a separate VTSS that configured as the Cross Tape Replication target from oVTCS on the VSM console, then additional data paths and control paths are required.
Connecting SMC to the VSM Console Server Applications
The following sections describe how to enable the SMC client to connect to the oVTCS and ACSLS applications on the VSM console server. This is dependent on your configuration. See "Overview".
Connecting SMC to oVTCS on the VSM console Server
You must perform the following steps to configure the XAPI control path from the SMC client to oVTCS on the VSM console. This is path 2 in Figure 6-1.
-
In your SMC client's SMCCMDS or SMCPARMS data set, include SMC
TAPEPlexandSERVercommands to define the oVTCS on the VSM console server as a TapePlex and define the TCP/IP control path between the SMC client and the oVTCS LDOM on the VSM console server.For example:
TAPEPLEX NAME(VTSP31) ENABLE SERVER NAME(VTSP31S) ENABLE TAPEPLEX(VTSP31) + HOST (VTSP31.yourhost.com) PORT(7070)This example includes the following:
-
An SMC
TAPEPlexcommand that defines an oVTCS TapePlex,VTSP31, on the VSM console server. -
An SMC
SERVercommand that defines a TCP/IP control path to the VSM console, where:-
The TapePlex name (
VTSP3) matches the name specified on theTAPEPlexstatement. -
The VSM console server name is
VTSP3S. -
The VSM console host name address is
VTSP31.yourhost.com. TheHOSTparameter may be replaced by specifying theIPADDRESSparameter instead. -
The server
PORTparameter value is7070. This value must match the listener port configured for oVTCS on the VSM console (the default value of the oVTCS listener port7070).
-
Refer to the ELS publication Configuring and Managing SMC for information about the SMCCMDS and SMCPARMS data sets, and the ELS Command, Control Statement, and Utility Reference for information about the SMC
TAPEPlexandSERVercommands. -
-
Configure MVC and virtual volumes.
Create an oVTCS parameter file to define MVC and virtual volumes and pools and create Management and Storage Classes to route data to VSM 6 or VSM 7 and/or tape drives on a SL Library. Using the
SMCUUUIutility, specify the oVTCSMGMTDEFcommand to load this parameter file. See "Loading the oVTCS Policy Parameter File Using the SMCUUUI Utility".
Connecting SMC to ACSLS on the VSM console Server
The following describes how to configure the XAPI control path from the SMC client to ACSLS with XAPI support on VSM console. This is path 1 in Figure 6-1.
This procedure may not be required depending upon the how the SL library is configured:
-
If your SL library includes non-RTD tape drives, and non-MVC tape cartridges accessible to MVS, then you must configure the XAPI control path from the SMC to ACSLS as documented below.
-
If all tape drives in the SL library are RTDs, and all of the tape cartridges in the SL library are MVCs, then the SMC client does not require access to the SL library. In this scenario, you are not required to configure the XAPI control path from the SMC client to ACSLS on the VSM console.
To connect SMC to ACSLS:
In your SMC client's SMCCMDS or SMCPARMS data set, include SMC TAPEPlex and SERVer commands to define the ACSLS on the VSM console server as a TapePlex and define the TCP/IP control path between the SMC client and the ACSLS LDOM on the VSM console server.
For example:
TAPEPLEX NAME(ACSLSLIB) ENABLE
SERVER NAME(ACSLSSRV) ENABLE TAPEPLEX(ACSLSLIB) +
HOST (myhost.hostname.com) PORT(50020)
This example includes the following:
-
An SMC
TAPEPlexcommand, which defines an ACSLS TapePlex,ACSLIB, on the VSM console server. -
An SMC
SERVercommand that defines a TCP/IP control path to the VSM console, where:-
The TapePlex name (
ACSLSLIB) matches the name specified on theTAPEPlexstatement. -
The VSM console server name is
ACSLSSRV. -
The VSM console host name address is
myhost.hostname.com. TheHOSTparameter may be replaced by specifying theIPADDRESSparameter instead. -
The server
PORTparameter value is50020. This value must match the listener port configured for ACSLS on the VSM console (the default value of the ACSLS listener port is50020).
-
Refer to the ELS publication Configuring and Managing SMC for information about the SMCCMDS and SMCPARMS data sets, and the ELS Command, Control Statement, and Utility Reference for information about the SMC TAPEPlex and SERVer commands.
Running the oVTCS CDS Database Server
The oVTCS CDS database server component proxy enables a client oVTCS running on the VSM console server to act as a local z/OS VTCS so that it can access the z/OS-resident CDS database.
The oVTCS client must have its own "host slot" within the CDS to send and receive broadcast messages, hold locks, and so forth. This requirement imposes the following limitations on executing the oVTCS CDS database server:
-
The oVTCS CDS database server cannot execute on a z/OS host that has VTCS executing or that may have VTCS executing. The HSC subsystem must be started with the NOVTCS startup parameter specified in the EXEC statement.
-
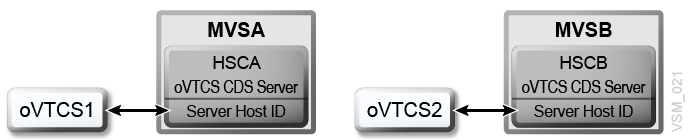
The oVTCS CDS database server is restricted to communicating with a single oVTCS client; there is a 1-to-1 relationship between client and server. For example, if there are two oVTCS appliances, they each require their own HSC host. As a result, there are two instances of HSC each executing their own oVTCS CDS database server as shown in Figure 6-2:
The "Server Host ID" boxes in Figure 6-2 represent the server on which the
DBSERVercommand is issued (see "DBSERVer command"). It is also the host that supplies the proxy host ID for the oVTCS client CDS. Thus, oVTCS1 is host ID MVSA and oVTCS2 is host ID MVSB. Note that MVSA and MVSB may share the same CDS, but they must have separate host IDs. -
The oVTCS CDS database server requires HSC database services be active. Therefore, the oVTCS CDS database server cannot be started before the HSC has reached BASE service level.
-
You can include the
DBSERVer STARTcommand in the HSC startup parameter file, or you can issue it as an HSC operator command. It is not a UUI/XAPI enabled command. -
The oVTCS CDS database server requires its own TCP/IP port assignment for its socket listener. The port number is specified on the
DBSERVer STARTcommand. If you execute the SMC HTTP server on the same host as the oVTCS CDS database server, you must specify different port numbers. -
If requested by Oracle StorageTek Software support, use GTF and the TRace VTcs command to enable tracing of the oVTCS CDS database server on z/OS.
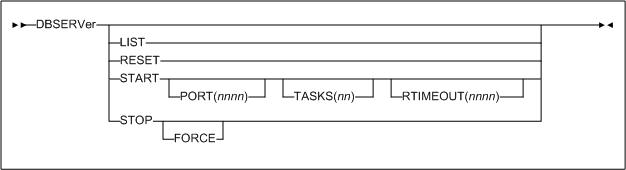
DBSERVer command
Interfaces:
-
console or utility only
-
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC required. VTCS must not be active.
Description
The DBSERVer command starts or stops the oVTCS CDS database server. The oVTCS CDS database server services CDS database I/O requests from an oVTCS client.
Note:
You can only start an oVTCS CDS database server in an HSC subsystem with no executing VTCS component.Parameters
- LIST
-
optionally, list the settings and status of the oVTCS CDS database server.
- RESET
-
optionally, force a reset of the oVTCS CDS database server which closes the accepted socket, clear any pending work, and listen again for the oVTCS client to re-connect.
- START
-
optionally, start the oVTCS CDS database server.
- PORT(nnnn)
-
optionally, specifies the socket listener port,
nnnn. If you do not specifyPORT(nnnn), the default is 8081. - TASKS(nn)
-
optionally, specifies the maximum number of tasks for asynchronous CDS reads. Allowable values are 1-10. If you do not specify
TASKS(nn), the default is 4. - RTIMEOUT(nnnn)
-
optionally, specifies the reserve timeout in seconds,
nnnn. Allowable values are 1-3600. If you do not specifyRTIMEOUT(nnnn), the default is 180.
- STOP
-
optionally, stop the oVTCS CDS database server.
- FORCE
-
optionally, force termination even when the oVTCS CDS database server has not terminated successfully.
oVTCS CDS Database Server and DBSERVer command Messages
Cannot start the oVTCS CDS server; CCCCCCCC
Explanation: The DBSERVER command specified the START option but the oVTCS CDS database server could not be started for the reason stated.
System Action: The command is rejected.
User Response: Correct the condition and resubmit the DBSERVER command.
oVTCS CDS database server started on PORT=NNNN
Explanation: The DBSERVER command specified the START option and was successfully started listening on the specified PORT number.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.
Timeout waiting for oVTCS CDS database server startup
Explanation: The DBSERVER command specified the START option and but the oVTCS CDS database server did not successfully start within the allotted timeout period.
System Action: None.
User Response: Check the console for messages indicating the reason for the startup failure.
Cannot {LIST|RESET|STOP} the oVTCS CDS server; not currently active
Explanation: The DBSERVER command specified the LIST or STOP option but the oVTCS CDS database is not currently active.
System Action: The command is rejected.
User Response: None.
Timeout waiting for oVTCS server CCCCCCCC termination
Explanation: The DBSERVER command specified the STOP option but the indicated oVTCS CDS database server component did successfully terminate within the allotted timeout period.
System Action: None.
User Response: Check the console for messages indicating the reason for the termination failure. If the problem persists, use the DBSERVER STOP FORCE option.
oVTCS CDS database server termination complete
Explanation: The DBSERVER command specified the STOP option and was successfully terminated.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.
oVTCS server TCP/IP error; func=CCCCCCCC, errno=NN
{TERMINATING|RESETTING|RETRYING|CONTINUING}
Explanation: The oVTCS CDS database server encountered a TCP/IP error during its processing.
System Action: Depending upon the action specified, the oVTCS CDS database server will terminate, reset itself, retry the operation, or simply ignore the error and continue.
User Response: If the problem persists, then check the MVS system log for TCP/IP stack issues.
oVTCS server transaction error; CCCCCCCC
Explanation: The oVTCS CDS database server encountered an error processing an oVTCS transaction or response.
System Action: Communication with the oVTCS client is reset.
User Response: If the problem persists, then contact StorageTek Software Support.
oVTCS protocol failure: CCCCCCCC
Explanation: The oVTCS CDS database server detected a serious error communicating with the oVTCS client or processing an oVTCS request. This unexpected error or breach in protocol has affected the oVTCS server integrity.
System Action: Communication with the oVTCS client is reset.
User Response: If the problem persists, contact StorageTek Software Support.
oVTCS client has held the CDS reserve for NNN seconds
Explanation: The oVTCS CDS database server detected a long database reserve initiated by the oVTCS client. This is abnormal and exceeds expected CDS reserve duration.
System Action: The CDS reserve is released and communication with the oVTCS client is reset.
User Response: Check log files for the oVTCS client and HSC. If the problem persists, contact StorageTek Software Support.
oVTCS CDS server cannot continue; CCCCCCCC
Explanation: The oVTCS CDS database server encountered a serious error and cannot continue.
System Action: The oVTCS CDS database server terminates.
User Response: Issue the DBSERVER START command with the appropriate parameters to re-start the oVTCS CDS database server, and contact StorageTek Software Support.
oVTCS CDS server reset complete; awaiting new connection
Explanation: The oVTCS CDS database server stopped and then restarted itself in response to an unexpected event or operator DBSERVER RESET command.
System Action: The existing oVTCS client connection is closed and the connection process restarted. The oVTCS server is now ready for the oVTCS client to reconnect.
User Response: Check to MVS or HSC logs for the root cause of the reset event.
oVTCS client connection accepted from CCCCCCCC
Explanation: The oVTCS CDS database server accepted a new socket connection from IP address CCCCCCCC.
System Action: The oVTCS CDS database server is now ready to process requests from the specified client.
User Response: None.
oVTCS Server status:
oVTCS Server started: DD/MM HH:MM:SS
Socket listener port: NNNNN
CDS reserve time in seconds: NNNN
CDS asynchronous read tasks: NN
Data trace length in bytes: NNNNN
Number of input messages: NNN,NNN,NNN
Number of output messages: NNN,NNN,NNN
Number of input bytes NNN,NNN,NNN{K|M}
Number of output bytes: NNN,NNN,NNN{K|M}
Number of process resets: NNN,NNN,NNN
Client connected MM/DD HH:MM:SS from NN.NN.NN.NN
Explanation: The DBSERVER command specified the LIST option.
System Action: The oVTCS CDS database server settings and status are displayed.
User Response: None.
Starting/Stopping the VSM console Message Processor
The SMC VMSG command starts or stops the SMC oVTCS message processor.
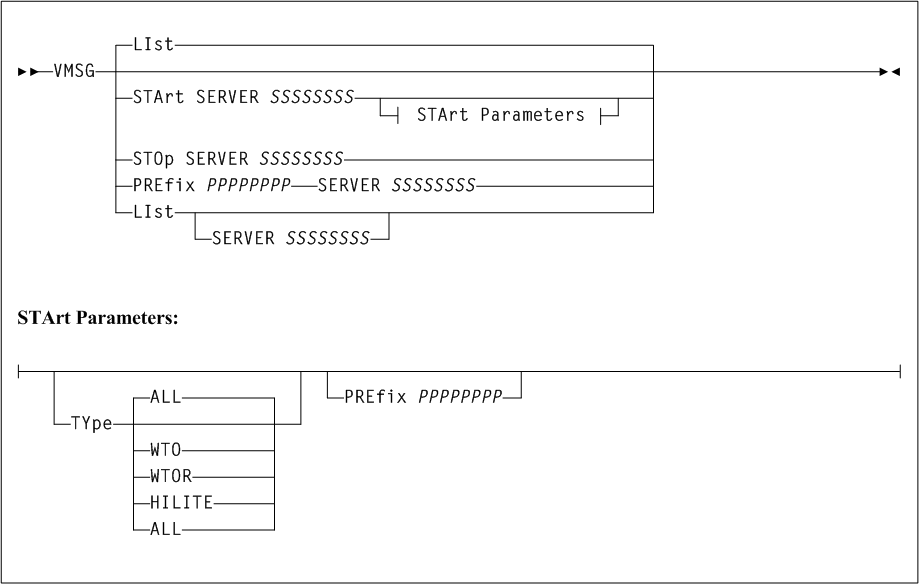
VMSG command
Interfaces:
-
Console, utility, SMCCMDS data set, SMCPARMS data set
-
UUI Support: Yes (no XML/CSV output)
Subsystem Requirements:
Active SMC required.
Description
The SMC VMSG command is used to start and stop the Virtual Storage Manager console (VSMc) message processor client. The VMSG message processor client allows the local SMC subsystem to receive and reply to messages issued by the remote VSM consoleserver.
Parameters
- LIst
-
optionally, displays
VMSGtask status information.- SERVER SSSSSSSS
-
optionally, lists only the VMSG processor for the named server. If specified, then the named server must have been previously defined by an SMC
SERVercommand.LIstis the default when theSTArt,STOp, orPREfixkeywords are not specified.
- START
-
optionally, starts a VMSG message processor client.
- SERVER SSSSSSSS
-
specifies the server name for the VMSG processor. The server name is required and must have been previously defined by an SMC
SERVercommand.
- TYPE (type-list)
-
optionally, defines a type-list containing one or more type(s) of messages that are received by the
VMSGclient.Specify one or more of the following in the type-list, using a comma to separate values:
- ALL
-
Receive all messages. If
ALLis specified, it cannot be specified with any other message types. This is the default. - HILITE
-
Receive highlighted WTO messages.
- WTO
-
Receive non-highlighted WT0 messages.
- WTOR
-
Receive messages that require a reply.
- PREfix PPPPPPPP
-
optionally, specifies the message prefix identifier that will identify messages from this VSM console server in the SMC subsystem log. If not specified, then the specified
servername is used as the message prefix. The prefix can be a maximum of 8 characters in length and can contain any combination of the following:-
A-Z
-
0-9
-
@#$,.()+-=<|!;%>?:
-
- STOP
-
optionally, stops a VMSG message processor client.
- SERVER SSSSSSSS
-
specifies the server name for the
VMSGprocessor. The server name is required and must have been previously defined by an SMCSERVercommand.
- PREfix PPPPPPPP
-
optionally, specifies the message prefix identifier that will identify messages from this VSM console server in the SMC subsystem log. If not specified, then the specified server name is used as the message prefix. The prefix can be a maximum of 8 characters in length and can contain any combination of the following:
-
A-Z
-
0-9
-
@#$,.()+-=<|!;%>?:
- SERVER SSSSSSSS
-
specifies the server name for the VMSG processor. The server name is required and must have been previously defined by an SMC
SERVercommand.
-
VMSG Messages
CCCCCCCC command parameter=PPPPPPPP value=VVVVVVVV is invalid; RRRRRRRRRR
Level: 0
Explanation: An invalid value VVVVVVVV was specified for the parameter PPPPPPPP of the CCCCCCCC command. The value was invalid because of the command context.
System Action: None.
User Response: Correct the parameter value and resubmit the command.
VMSG task for server SSSSSSSS [START|STOP|message prefix updated]
Level: 0
Explanation: VMSG task for server SSSSSSSS was either STARTED, STOPPED, or the message prefix was updated.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.
VMSG server SSSSSSSS exception reason: RRR...RRR
Level: 4
Explanation: The VMSG task for server SSSSSSS encountered an exception while processing the request.
System Action: The VMSG request is retried.
User Response: Investigate the cause of the error. If necessary, stop and restart the VMSG task associated with the server.
PPPPPPPP SSS...SSS
Level: 0
Explanation: This message is received in response to a VMSG task. The PPPPPPPP is the specified message prefix or the server name, if the message prefix is not specified.
System Action: None.
User Response: See the associated product for specific messages.
VMSG TASK STATUS:
TAPEPLEX=CCCCCCCC SERVER=CCCCCCCC
Prefix=PPPPPPPP Msg types=MMM...MMM
Status: SSSSSSSS
Started: mon dd hh:mm:ss
Last msg: mon dd hh:mm:ss
WTOs=NNNNNN WTORs=NNNNNN DOMs=NNNNNN
Level: 0
Explanation: An SMC VMSG LIst command was issued. The SMC0304 multiline message lists the status of each VMSG task.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.
Off-loading VSM console SMF Records
The SMC SMCUSMF utility enables you to offload SMF records from a VSM console server. The SMF records are placed in a z/OS data set with the following DCB attributes:
-
recfm - VB
-
lrecl - 27990
-
blksize - 27994
Refer to the ELS publication ELS Programming Reference for information about these HSC/VTCS SMF records.
Parameters
The following SMCUSMF utility parameters may be specified for pgmparms in the sample JCL:
- NOHDR
-
optionally, specifies that the
STDOUTreport headings and pagination carriage control are not produced. - LINECNT(nn)
-
optionally, specifies
STDOUTreport pagination line count setting.- nn
-
the number of lines per page. Valid values are 10-99.
- SERVer(ssss)
-
specifies the name of the VSM console SERVER from which SMF records are to offloaded. The specified SERVER must be the ACTIVE server for the VSM console TapePlex.
SERVeris a required parameter.- ssss
-
the server name.
- BEGIN(
begin-date:begin-time) -
specifies the beginning of the period of SMF record creation. This is the server date and time.
- begin-date
-
the starting date, expressed in
yyyymmddformat.- yyyymmdd
-
the beginning date.
- TODAY
-
specifies TODAY as the beginning date.
- YESTERDAY
-
specifies YESTERDAY as the beginning date.
- begin-time
-
the starting time-of-day (24-hour value, expressed in
hhmmssformat. The allowable range for begin-time is 000000 to 235959. The default value is 000000.
- END(end-date:end-time)
-
optionally, specifies the end of the period of SMF record creation. This is the server date and time.
- end-date
-
the ending date, expressed in
yyyymmddformat.- yyyymmdd
-
the ending date.
- TODAY
-
specifies TODAY as the ending date.
- YESTERDAY
-
specifies YESTERDAY as the ending date.
- end-time
-
the ending time-of-day (24-hour value, expressed in
hhmmssformat. The allowable range for the end-time parameter is 000000 to 235959. The default value is 235959.
- SMFTYPE(nnn)
-
optionally, specifies the SMF record type for the output records.
- nnn
-
the SMF record type. Valid values are 128 to 255. The default is 255.
Required Data Set Definition (DD) Statements
The following DD statements are required:
- STDOUT
-
The
SMCUSMFutility reports final completion code and any error messages in theSTDOUTdata set. - SMCSMF
-
The
SMCUSMFutility places SMF records in theSMCSMFdata set. This is a variable blocked file. The DCB attributes must be:DCB=(RECFM=VB,LRECL=27990,BLKSIZE=27994)
SMCUSMF Usage
If the VSM console TapePlex is defined with two SERVERS and each server has functioned as the active server for that TapePlex since the last run of SMCUSMF, you must run the following procedure to collect all SMF records from both servers.
With SERVER1 active and SERVER2 inactive:
-
Run
SMCUSMFwithSERVER(SERVER1). -
Disable SERVER1:
SERVER NAME(SERVER1) DISABLEThis command makes SERVER2 active.
-
Run
SMCUSMFwithSERVER(SERVER2). -
Re-enable SERVER1:
SERVER NAME(SERVER1) ENABLE
SERVER2 remains active but SERVER1 is eligible to become the active server if SERVER2 becomes inaccessible. To make SERVER1 the active server once again (if desired), disable SERVER2 and then enable it once SERVER1 has become the active server for the TapePlex.
SMC Messages
The following describes messages issued by SMC. These messages are identified by the "SMC" prefix.
Copyright (c) YYYY, YYYY, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server has been started.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.
Communication server initialization starting
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server startup has commenced.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.
Communication server initialization complete
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server startup has completed.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.
Communication server release=N.N.N active on host=HHHHHHHH, port=NNNN, TapePlex=PPPPPPPP
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server status message lists the release, host name, listening port number, and TapePlex name. The status message is displayed at startup and once each day after midnight.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.
Error allocating shared memory segment, key=XXXXXXXX, errno=NN (CCCC...CCCC); { server terminating | RESET specified, continuing | EXCL not specified, continuing}
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server encountered the indicated error while attempting to define a required shared memory segment during XAPI communications server startup.
System Action: Depending upon the XAPI communications server startup option(s), the shared memory segment may be required as exclusive or shared. If the exclusive option was specified (EXCL), the server will terminate. Otherwise, the XAPI communications server will continue startup by sharing (i.e. resetting) the indicated shared memory segment.
User Response: When EXCL is specified, it prevents the startup of a duplicate XAPI communications server when one is already active. If you are certain that the XAPI communications is not already started then you may specify the RESET startup option. Alternatively, you may use UNIX facilities to remove the existing IPC shared memory segment.
Error attaching shared memory segment, id=XXXXXXXX, errno=NN (CCCC...CCCC); SSSSSSSS terminating
Level: 0
Explanation: An XAPI communications server task encountered the indicated error while attempting to attach a required shared memory segment during XAPI communications execution.
System Action: The indicated XAPI communications server service, SSSSSSSS, terminates.
User Response: Use UNIX services to determine the status of the IPC shared memory segment. If the shared memory segment has been inadvertently removed, then a restart of the XAPI communications server is required.
Error initializing CCCCCCCC semaphore, errno=NN (CCCC...CCCC); server terminating
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server encountered the indicated error while attempting to initialize a required semaphore during XAPI communications server startup.
System Action: XAPI communications server startup is terminated.
User Response: Use the indicated errno and reason to determine why the semaphore could not be initialized.
Error in EEEEEEEE variable; using { default | truncated } value=VVVV...VVVV
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server encountered an error obtaining the indicated environment variable, EEEEEEEE.
System Action: The default or truncated value, VVVV...VVVV, will be used for the indicated environment variable, EEEEEEEE.
User Response: Use UNIX services to determine the value of the indicated environment variable, EEEEEEEE.
Error writing WTO mque id=QQQQ...QQQQ errno=NN (CCCC....CCCC) trying printf
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server encountered the indicated error while attempting to queue a message for output by the VSMc WTO message service.
System Action: The XAPI communications server will write the message to stdout instead.
User Response: Use UNIX services to determine the status of the indicated IPC message queue, QQQQ...QQQQ.
Error msgsnd diag message queue=QQQQ...QQQQ errno=NN (CCCC...CCCC); { log service | trace service} disabled trying printf
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server encountered the indicated error while attempting to queue a diagnostic log or trace record for output to the XAPI communications server log and trace service.
System Action: The XAPI communications server log service or trace service will be disabled.
User Response: Use UNIX services to determine the status of the indicated IPC message queue, QQQQ...QQQQ.
Error { creating | opening | reading | writing | retrying } file=FFFF...FFFF errno=NN (CCCC...CCCC); SSSSSSSS terminating
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server encountered the indicated error processing file, FFFF...FFFF.
System Action: The indicated XAPI communications server service, SSSSSSSS, is terminated.
User Response: Use the indicated errno and reason to determine why the file operation failed.
{ log | trace } file at NNNNN bytes
Level: 8
Explanation: The XAPI communications server has written the indicated number of bytes to the log or trace file.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.
Unknown message type=NNNN on diag message queue=QQQQ...QQQQ; message ignored
Level: 04
Explanation: The XAPI communications server diagnostic service has encountered an unknown message type, NNNN, in its queue, QQQQ...QQQQ.
System Action: The unknown message is ignored.
User Response: If the problem persists contact StorageTek Software Support.
Communication server termination starting
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server termination has commenced.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.
Communication server terminating { work | service } process PPPPPPPP=NNNNN
Level: 0
Explanation: During XAPI communications server termination, the indicated process PPPPPPPP (pid=NNNNN) did not terminate itself as requested.
System Action: The indicated process is killed and termination continues.
User Response: None.
Communication server termination complete
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server has completed its termination process.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.
ftok errno=NN (CCCC...CCCC} for { WTO message queue | diagnostic message queue | HTTPCVT } from path=FFFF...FFFF; server terminating
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server encountered the indicated ftok error for the file path, FFFF...FFFF.
System Action: XAPI communications server startup is terminated.
User Response: Use the indicated errno and reason to determine why the ftok operation failed.
Internal error; file=SSSS...SSSS[NNNN], function=FFFFFFFF, RRRR...RRRR {errno=NN (CCCC...CCCC) }
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server encountered an internal error in source file SSSS...SSSS at line NNNN in function FFFFFFFF. The reason RRRR...RRRR and possible errno are also displayed.
System Action: The current operation is terminated.
User Response: Contact StorageTek Software Support.
Error starting work process smcvcvt; no free HTTPREQ
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server received a new transaction request, but the request could not be processed because the server is at its task limit.
System Action: The new transaction request is rejected.
User Response: Distribute the work load among multiple XAPI communication servers.
Abnormal termination; process=NNNNN, signal=NN (CCCC...CCCC)
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server process nnnn was terminated with the unexpected signal NN.
System Action: The current request is terminated.
User Response: Gather the diagnostics indicated in the SMC9020 and SMC9021 messages and contact StorageTek Software Support.
NNN stack trace entries returned for process=NNNNN
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server process NNNNN was terminated.
System Action: NNN backtrace entries were available for process NNNNN and are listed.
User Response: Gather the diagnostics indicated in the SMC9020 and SMC9021 messages and contact StorageTek Software Support.
Core dump { generated to file: FFFF...FFFF |
requested but could not be written |
requested but could not be renamed |
request failed, errno=NN (CCCC...CCCC) }
Level: 0
Explanation: An XAPI communications server process was terminated.
System Action: The XAPI communications server requested a core dump image. The core dump image result is displayed.
User Response: Gather the diagnostics indicated in the SMC9020 and SMC9021 messages and contact StorageTek Software Support.
CCCCCCCC command received
Level: 8
Explanation: The CCCCCCCC operator command was received by the XAPI communications server.
System Action: CCCCCCCC command processing continues.
User Response: None.
CCCCCCCC command RC=NN
Level: 8
Explanation: The CCCCCCCC operator command was processed by the XAPI communications server and completed with return code NN.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.
CCCCCCCC is an invalid command
Level: 0
Explanation: The CCCCCCCC operator command was input to the XAPI communications server but CCCCCCCC is not a valid command verb.
System Action: The command is rejected.
User Response: Correct and re-enter the command.
CCCCCCCC command requires a value
Level: 0
Explanation: The cccccccc operator command was input to the XAPI communications server without a value but the CCCCCCCC command requires a value.
System Action: The command is rejected.
User Response: Correct and re-enter the command.
VVVVVVVV is an invalid value for the CCCCCCCC command
Level: 0
Explanation: The CCCCCCC operator command was input to the XAPI communications server with invalid value VVVVVVVV.
System Action: The command is rejected.
User Response: Correct and re-enter the command.
KKKKKKKK=VVVVVVVV
Level: 0
Explanation: An operator command was input to the XAPI communications server that resulted in a list of values being displayed. Keyword or command KKKKKKKK has value VVVVVVVV.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.
Startup parameter PPPPPPPP successfully processed
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server executable was initiated with command line option PPPPPPPP which was successfully processed at startup.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.
Startup parameter PPPPPPPP { is invalid | requires a value | contains an invalid value}
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server executable was initiated with command line option PPPPPPPP which was not successfully processed at startup for the indicated reason.
System Action: The command line option PPPPPPPP is rejected but startup continues.
User Response: Correct the command line option(s).
Startup parameter PPPPPPPP is mutually exclusive with XXXXXXXX
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server executable was initiated with command line options PPPPPPPP and XXXXXXXX, but PPPPPPPP and XXXXXXXX cannot be specified together.
System Action: The command line option PPPPPPPP is accepted, command line option XXXXXXXX is rejected, but startup continues.
User Response: Correct the command line option(s).
Line parse error={ mismatched or invalid quotes detected |
mismatched or invalid parenthesis detected |
maximum token number exceeded | parameter truncated }
Level: 0
Explanation: An operator command was input to the XAPI communications server but the command line could not be processed because of the indicated parse error.
System Action: The command is rejected.
User Response: Correct and re-enter the command.
XAPI PORT=NNNNN IPADDRESS=NNN.NNN.NNN.NNN HOST=HHHH...HHHH
MAXCLIENTS=NNN XSECURITY={ ON | OFF }
Total: I/Os=NNNNNN bytes=NNNNNN accepts=NNNNNN intervals=NNNNNN
Total: processed input reqs=NNNNNN rejects=NNNNNN
Last: I/Os=NNNNNN bytes=NNNNNN accepts=NNNNNN
High: I/Os=NNNNNN bytes=NNNNNN accepts=NNNNNN tasks=NNNNNN
Avg: I/Os=NNNNNN bytes=NNNNNN accepts=NNNNNN
Total: errs=NNNNNN retries=NNNNNN
Total: maxclient errs=NNNNNN other errs=NNNNNN xsec errs=NNNNNN
Level: 0
Explanation: An XAPI communications server XAPI LIST I/O command was received. The current XAPI settings are displayed along with I/O and error statistics.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.
Current tasks:
Name Pid Tid Count Last Time Status
smcvmai NNNNN XXXXXXXX NNNNNN MM/DD HH:MM:SS SSSS...SSSS
smcvwts NNNNN XXXXXXXX NNNNNN MM/DD HH:MM:SS SSSS...SSSS
smcvdts NNNNN XXXXXXXX NNNNNN MM/DD HH:MM:SS SSSS...SSSS
smcvops NNNNN XXXXXXXX NNNNNN MM/DD HH:MM:SS SSSS...SSSS
smcvmon NNNNN XXXXXXXX NNNNNN MM/DD HH:MM:SS SSSS...SSSS
smcvlis NNNNN XXXXXXXX NNNNNN MM/DD HH:MM:SS SSSS...SSSS
smcvwrk-NNNN NNNNN XXXXXXXX NNNNNN MM/DD HH:MM:SS SSSS...SSSS
Level: 0
Explanation: An XAPI communications server XAPI LIST TASKS command was received. The current XAPI communications server system and work tasks are displayed along with their execution counts, and status. Multiple smcvwrk-NNNN work tasks may be listed depending upon work load and process hi-water.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.
process reuse required for cmd server; retrying
Level: 0
Explanation: An operator command was input to the XAPI communications server but there are no free tasks available to process the request.
System Action: The XAPI communications server tries to find an available reusable task to process the request.
User Response: None.
task recovery failed for cmd server; now in single user mode
Level: 0
Explanation: An operator command was input to the XAPI communications server but there are no free tasks, and no available reusable tasks available to process the request.
System Action: The XAPI communications server operator command service now processes the request in single task mode.
User Response: None.
{ Thread XXXXXXXX | Process NNNNN } active at termination
Level: 0
Explanation: During XAPI communications server termination, the indicated thread or process was active at termination after the initial XAPI communications server termination signal.
System Action: The indicated process is killed and termination continues.
User Response: None.
Server status:Server name=CCCC release=N.N.N version=CCCC started on MM/DD ...
TapePlex=CCCCCCCC type={ ACSLS | oVTCS }
RLIMITM=NNN RLIMITS=NNN RLIMITW=NNN
Task mode=MMMM (CCCC...CCCC) signal handling={ VTCS | SMCV }
Work task={ PERMWORK | TERMWORK } (CCCC...CCCC)
System name=SSSS release=NN machine=MMMM ({ little | big } endian)
System version=CCCC...CCCC
rlimit_stack=NNN rlimit_data=NNN rlimit_as=NNN rlimit_nproc=NNN
...more rlimit values
SSCVT shared segment key=XXXXXXXX id=NNNNNN size=NNNN
CVT shared segment key=XXXXXXXX id=NNNNNN size=NNNN
WTO message queue key=XXXXXXXX id=NNNNNN
DIAG message queue key=XXXXXXXX id=NNNNNN
Level: 0
Explanation: An XAPI communications server XAPI LIST SERVER command was received. The current XAPI communications server settings and environment are displayed along its IPC resources.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.
control block name:XXXXXXXX +0000| XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXX|CCCC...CCCC|
XXXXXXXX +0010| XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXX |CCCC...CCCC|
...
Level: 0
Explanation: An XAPI communications server XAPI LIST CB command was received. The specified control block is listed in character hexadecimal in 16 byte increments.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.
malloc() failure, bytes=NNNN, request=CCCC...CCCC;
{ transaction lost | csv output lost | XML parse failure |
HTTP metadata lost | work task terminated | request terminated }
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server attempted to malloc NNNN bytes for request or control block CCCC...CCCC but storage was not available.
System Action: The transaction or request is terminated.
User Response: Use appropriate Unix commands to determine memory usage and contact StorageTek Software Support.
ACSLS cp_proc_int failure=NNNN; work task terminated
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server attempted to invoke the ACSLS
cl_proc_init RPC service during process initiation, but the request failed with the indicated return code.
System Action: The transaction or request is terminated.
User Response: Ensure that ACSLS is active.
Communication error: { TCP/IP cccc failure ( reqId=XXXXXXXX ... ) |
Unsuccessful login from CCCC...CCCC port=NNNNN |
TCP/IP bind failure; port=NNNNN, socket=NN, CCCC...CCCC; retrying |
TCP/IP accept failure; port=NNNNN, socket=NN, CCCC...CCCC |
requests=NNN exceeds MAXCLIENTS=NNN;
rejected connection from CCCC...CCCC |
free HTTPREQ error; rejected connection from CCCC...CCCC |
work task start error; rejected connection from CCCC...CCCC |
AF_UNIX accept failure; socket=NN, file=CCCC...CCCC; errno=NN |
XML parse failure; reqId=XXXXXXXX |
work task start error; retrying |
XAPI work task limit exceeded |
command listener attach failure; start work task error }
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server received a request but the indicated communication error caused the request to be rejected. Most of the indicated errors are transient errors caused by internal or external resource constraints. In most cases the client will retry the rejected request.
System Action: The transaction or request is rejected.
User Response: None.
Invalid format for the CCCCCCCC command
Level: 0
Explanation: The CCCCCCCC operator command was input to the XAPI communications server but the command contained too many or too few tokens to be a valid command.
System Action: The command is rejected.
User Response: Correct and re-enter the command.
IPC error: { socketpair failure=NN-NN; errno=NN (CCCC...CCCC) |
sem_init failure; errno=NN (CCCC...CCCC), HTTPTASK=NNNN |
sem_wait failure; errno=NN (CCCC...CCCC), HTTPTASK=NNNN |
sem_timedwait failure; errno=NN (CCCC...CCCC), HTTPTASK=NNNN |
sem_post failure; errno=NN (CCCC...CCCC), HTTPTASK=NNNN }
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server received a request but the indicated IPC error caused the request to be rejected.
System Action: The transaction or request is terminated.
User Response: Contact StorageTek Software Support.
Invalid HOSTNAME specified; header=HHHHHHHH, actual=AAAAAAAA
Level: 8
Explanation: The XAPI communications server received a request but the host name specified in the XAPI request header, HHHHHHHH, does not match the actual gethostbyaddr() host name, AAAAAAAA.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.
Request id=XXXX pid=NNNN (CCCC...CCCC) cancelled;
RC=NNNN reason=NNNN
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server received the CCCC...CCCC request but the request was terminated within the VSMc PGMI processor with the indicated return and reason codes.
System Action: The request is terminated.
User Response: Check the VSMc logs for the cause of the failure.
XAPI server not active
Level: 0
Explanation: An XCMD command was input to the ACSLS cmd_proc executable, but the XAPI server was not active to receive the command.
System Action: The request is rejected.
User Response: Start the ACSLS XAPI server.
Startup file=CCCC...CCCC does not exist
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server was started, but the indicated file containing startup and initialization commands does not exist.
System Action: XAPI communications startup continues.
User Response: Move your startup file to the indicated path.
CCCCCCCC command { not allowed from operator |
not allowed from file | not allowed from XCMD |
not allowed from VSM }
Level: 0
Explanation: The CCCCCCCC operator command was input to the XAPI communications server but the command is not allowed from the indicated command origin.
System Action: The command is rejected.
User Response: Re-enter the command from an allowed origin.
{ XCLIENT | XUDB } record { for IPADDRESS nnn.nnn.nnn added |
for IPADDRESS nnn.nnn.nnn updated |
(suppressed) updated |
(suppressed) updated in VSMc |
(suppressed) added |
(suppressed) added in VSMc |
(suppressed) exists; updated in VSMc |
(suppressed) add error; RC=nn, reason=cccc...cccc |
(suppressed) deleted |
(suppressed) deleted from VSMc }
Level: 0
Explanation: An XCLIENT or XUDB operator command was input to the XAPI communications server.
System Action: The XCLIENT or XUDB record is updated, added, or deleted in the XAPI communications server shared memory, or VSMc tables as indicated. The XUDB user information is listed as (suppressed) in the XAPI communications server log.
User Response: None.
No { XCLIENT | XUDB } records to list
Level: 0
Explanation: An XCLIENT LIST or XUDB LIST operator command was input to the XAPI communications server but there are no records of the specified type to list.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.
{ no matching | matching } XUDB record
{ found for update | found for delete | already exists }
Level: 0
Explanation: An XUDB ADD, UPDATE, or DELETE operator command was input to the XAPI communications server but the record already exists (for ADD), or does not exist (for UPDATE or DELETE).
System Action: None.
User Response: Correct and re-enter the command.
{ No XUDB(s) defined; user(s) defined in VSMc |
No XCLIENT(s) defined; XAPI server using VSMc definitions |
No XUDB(s) or XCLIENT(s) defined; XAPI server will reject
all requests }
Level: 0
Explanation: An XUDB DELETE operator command was input to the XAPI communications server with the result that XAPI security user ids are no longer defined.
System Action: In the absence of other application security, such as from VSMc, all incoming requests may be rejected.
User Response: Validate that either XAPI communications server XSECURITY is OFF, or appropriate user(s) are defined in VSMc.
Communication server terminating; invalid startup parameters
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server was started with invalid command line options.
System Action: XAPI communications server startup is terminated.
User Response: Correct the command line options and restart.
Startup file=CCCC...CCCC processing starting
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server was started and the file of startup and initialization commands, CCCC...CCCC, has been opened for processing.
System Action: XAPI communications server startup continues.
User Response: None.
Startup file=CCCC...CCCC processing complete; RC=NN
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server was started and the file of startup and initialization commands, CCCC...CCCC, has been processed. The indicated return code is the highest return code for all command(s) processed in the file.
System Action: XAPI communications server startup continues.
User Response: None.
Invalid keyword KKKKKKKK for the CCCCCCCC command
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server encountered a command, CCCCCCCC, that specified invalid keyword KKKKKKKK.
System Action: The command is rejected.
User Response: Correct and re-enter the command.
Invalid value VVVVVVVV for keyword or tag KKKKKKKK of the CCCCCCCC command
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server encountered a command, CCCCCCCC, that specified keyword KKKKKKKK with an invalid value VVVVVVVV.
System Action: The command is rejected.
User Response: Correct and re-enter the command.
Keyword or tag KKKKKKKK of the CCCCCCCC command requires a value
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server encountered a command, CCCCCCCC, that specified keyword KKKKKKKK without a required value.
System Action: The command is rejected.
User Response: Correct and re-enter the command.
Unexpected format for positional parameter in command CCCCCCCC
Level: 0
Explanation: The positional parameter of command CCCCCCCC is not correctly formatted.
System Action: The command is rejected.
User Response: Correct and re-enter the command.
Duplicate keyword or tag KKKKKKKK specified for the CCCCCCCC command
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server encountered a command, CCCCCCCC, that specified keyword KKKKKKKK multiple times.
System Action: The command is rejected.
User Response: Correct and re-enter the command.
Keyword or tag KKKKKKKK of the CCCCCCCC command is mutually exclusive with keyword or tag XXXXXXXX command
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server encountered a command, CCCCCCCC, that specified multiple keywords, two of which (KKKKKKKK and XXXXXXXX) are mutually exclusive.
System Action: The command is rejected.
User Response: Correct and re-enter the command.
Keyword or tag KKKKKKKK of the CCCCCCCC command requires keyword or tag RRRRRRRR command
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server encountered a command, CCCCCCCC, that specified keyword KKKKKKKK, but not the required co-requisite keyword RRRRRRRR.
System Action: The command is rejected.
User Response: Correct and re-enter the command.
Keyword or tag KKKKKKKK of the CCCCCCCC command is required command
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server encountered a command, CCCCCCCC, that did not specify the required keyword KKKKKKKK.
System Action: The command is rejected.
User Response: Correct and re-enter the command.
Invalid range VVVV...VVVV for keyword KKKKKKKK of the CCCCCCCC command
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server encountered a command, CCCCCCCC, that specified a range value VVVV...VVVV for keyword KKKKKKKK. However the range value is invalid either because the left value is higher than the right value, or the left and right values have different formats.
System Action: The command is rejected.
User Response: Correct and re-enter the command.
Unrecognized XML tag=TTTTTTTT for the CCCCCCCC command
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server encountered a input request in XML format containing a tag, TTTTTTTT, that is not recognized as valid for the CCCCCCCC command. This message can be caused when the current software level does not support a tag that was valid in an earlier level, or has not been upgraded to support a new tag.
System Action: The individual parameter is ignored, but command processing continues.
User Response: Verify that the command is correctly specified.
Value=VVVVVVVV is invalid type for keyword or tag=KKKKKKKK in command=CCCCCCCC
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server encountered a command, CCCCCCCC, that specified an invalid value type for keyword KKKKKKKK.
System Action: The command is rejected.
User Response: Correct and re-enter the command.
Keyword or tag=KKKKKKKK may not have a value in command=CCCCCCCC
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server encountered a command, CCCCCCCC, that contained a value for a keyword or XML tag that does not allow a value.
System Action: The command is rejected.
User Response: Correct and re-enter the command.
Length of value=VVVV...VVVV is invalid for keyword or tag=KKKKKKKK in command=CCCCCCCC
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server encountered a command, CCCCCCCC, that contained a keyword value VVVV...VVVV that was too long.
System Action: The command is rejected.
User Response: Correct and re-enter the command.
Error parsing XML values for XML tag=TTTTTTTT in command=CCCCCCCC; RC=NNNN
Level: 0
Explanation: The XAPI communications server encountered an XML format command that contained a value or parse error related to the listed tag. The parse return code is included in the message for diagnostics.
System Action: The command is rejected.
User Response: Correct and re-enter the command.
Error: EEEE...EEEE; AAAA...AAAA
Level: 0
Explanation: During XAPI communications server processing, the EEEE...EEEE error occurred.
System Action: The EEEE...EEEE error caused the system to take the resulting action, AAAA...AAAA.
User Response: Contact StorageTek Software Support.
CCCC...CCCC
Level: 12
Explanation: The XAPI communications server has issued a diagnostic message.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.
Error: EEEE...EEEE; AAAA...AAAA
Level: 12
Explanation: The XAPI communications server has issued a diagnostic message.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.
oVTCS Messages
The following describes messages issued by oVTCS.
Unexpected exception thrown: RRRRRRRRR
Explanation: A software error has been detected and this has caused an exception to be raised. The reason RRRRRRRRR gives details of the error that occurred.
System Action: If necessary, a dump of the process will be taken. Attempts will also be made to recover the failing task or thread.
User Response: Because the error is unexpected, it is possible that any recovery action may not be successful. Therefore check the system and if necessary restart the process that suffered the failure. Refer the problem to StorageTek Software Support.
PPPPPPPP/NNNN: Uncaught exception terminating thread
Explanation: A software error has been detected in process the PPPPPPPP with an Id of NNNN and this has caused an exception to be raised. There is no recovery routine active to recover from the error.
System Action: The effected task or thread will be terminated. Typically no additional recovery actions will be performed.
User Response: More than likely, the effected process will need to be restarted. Check for additional messages that might also be a trigger for this error message. Refer the problem to StorageTek Software Support.
PPPPPPPP/NNNN: Abnormal thread termination: RRRRRRRRR
Explanation: A software thread has decided to terminate unexpectedly within process PPPPPPPP with an Id of NNNN. The reason RRRRRRRRR gives details of the triggering error.
System Action: The effected task or thread will be terminated. A dump may also be taken. Typically no additional recovery actions will be performed.
User Response: More than likely, the effected process will need to be restarted. Check for additional messages that might also be a trigger for this error message. Refer the problem to StorageTek Software Support.
PPPPPPPP/NNNN: Call to terminate()
Explanation: A software error has occurred that means that the run-time environment for the process PPPPPPPP with an Id of NNNN has decided that it cannot continue.
System Action: The effected process will be terminated. A dump may also be taken. Depending upon circumstances, the system may restart the failed process.
User Response: Check that the failing process restarted. If not then perform a manual stop and start of the process. Check for additional messages that might also be a trigger for this error message. Refer the problem to StorageTek Software Support.
PPPPPPPP/NNNN: Unexpected exception called
Explanation: A software error has been detected in process PPPPPPPP with an Id of NNNN and this has caused an exception to be raised. There is no recovery routine active to recover from the error.
System Action: The effected task or thread will be terminated. Typically no additional recovery actions will be performed.
User Response: More than likely, the effected process will need to be restarted. Check for additional messages that might also be a trigger for this error message. Refer the problem to StorageTek Software Support.
PPPPPPPP/NNNN: Call to terminate()
Explanation: A software error has occurred that means that the run-time environment for the process PPPPPPPP with an Id of NNNN has decided that it cannot continue.
System Action: The effected process will be terminated. A dump may also be taken. Depending upon circumstances, the system may restart the failed process.
User Response: Check that the failing process restarted. If not then perform a manual stop and start of the process. Check for additional messages that might also be a trigger for this error message. Refer the problem to StorageTek Software Support.
Cannot create TCP/IP socket: RRRRRRRRR
Explanation: An attempt was made to create a socket for TCP/IP communications. This failed with the error code RRRRRRRRR.
System Action: The function attempting to create the socket will fail.
User Response: This maybe a network or a server resource problem. Additional messages produced around the same time should also give an indication of what function is effected.
Cannot bind to port NNNN: RRRRRRRRR
Explanation: An attempt was made to bind to port NNNN for TCP/IP communications. This failed with the error code RRRRRRRRR. If this reason is 'address already in use', then it probably means that a server component has not completed termination before the replacement was started.
System Action: The function attempting to bind to the port will fail.
User Response: This maybe a network or a server resource problem. Additional messages produced around the same time should also give an indication of what function is effected.
Listen on port NNNN failed: RRRRRRRRR
Explanation: An attempt was made to listen for connections to port NNNN for TCP/IP communications. This failed with the error code RRRRRRRRR.
System Action: The function attempting to listen to the port will fail.
User Response: This maybe a network or a server resource problem. Additional messages produced around the same time should also give an indication of what function is effected.
Cannot create AF_UNIX socket: RRRRRRRRR
Explanation: An attempt was made to create a socket for internal communications as a server. This failed with the error code RRRRRRRRR.
System Action: The function attempting to create the socket will fail.
User Response: This is probably a server resource problem. Additional messages produced around the same time should also give an indication of what function is effected.
Cannot bind to file FFFFFFFF: RRRRRRRRR
Explanation: An attempt was made to bind to file FFFFFFFF for internal communications. This failed with the error code RRRRRRRRR. If this reason is 'address already in use', then it probably means that a server component has not completed termination before the replacement was started.
System Action: The function attempting to bind to the file will fail.
User Response: This is probably a server resource problem. Additional messages produced around the same time should also give an indication of what function is effected.
Listen on file FFFFFFFF failed: RRRRRRRRR
Explanation: An attempt was made to listen for connections to file FFFFFFFF for internal communications. This failed with the error code RRRRRRRRR.
System Action: The function attempting to bind to the file will fail.
User Response: This is probably a server resource problem. Additional messages produced around the same time should also give an indication of what function is effected.
Failed lookup of HHHHHHHH:PPPP: RRRRRRRR
Explanation: An attempt was made to resolve the network address of HHHHHHHH and port PPPP and this failed with the error code RRRRRRRRR.
System Action: The function attempting to resolve the address will fail.
User Response: Check that HHHHHHHH is either a valid IPv4 address, IPv6 address or DNS address. Short form DNS addresses are only valid if it can be converted to a full address by using one of the DNS search suffixes. Additional messages produced around the same time should also give an indication of what function is effected.
Failed connect to HHHHHHHH:PPPP: RRRRRRRR
Explanation: An attempt was made to connect to the network address HHHHHHHH and port PPPP and this failed with the error code RRRRRRRRR. If this reason is 'connection refused', then it probably means that a server component is not running. If this reason is 'no route to host' or 'connection timed out', then it is probably some kind of network problem.
System Action: The function attempting to connect to the address will fail.
User Response: Check that the system HHHHHHHH is up. Then check that the network route to system is correct and functional. If the target system is on another sub-net, then the default router must be configured correctly. Additional messages produced around the same time should also give an indication of what function is effected.
Cannot create AF_UNIX socket
Explanation: An attempt was made to create a socket for internal communications as a client.
System Action: The function attempting to create the socket will fail.
User Response: This is probably a server resource problem. Additional messages produced around the same time should also give an indication of what function is effected.
Failed connect to FFFFFFFF: RRRRRRRR
Explanation: An attempt was made to connect to file FFFFFFFF for internal communication and this failed with the error code RRRRRRRRR. If this reason is 'connection refused', then it probably means that a server component is not running.
System Action: The function attempting to connect to the address will fail.
User Response: Check that the service that should connected to file FFFFFFFF is up. Additional messages produced around the same time should also give an indication of what function is effected.
Accept on port NNNN failed: RRRRRRRR
Explanation: An attempt was made to accept a connection on port NNNN and this failed with the error code RRRRRRRRR.
System Action: The function attempting to accept the connection will fail. Typically this will cause an additional failure within the server component attempting the connection.
User Response: Additional messages produced around the same time should also give an indication of what function is effected.
Connection from SSSSSSSS
Explanation: A server has received a TCP/IP connection request from the system SSSSSSSS.
System Action: Depending upon the nature of the connection, processing will proceed within the server component.
User Response: This is informational only.
PPPPPPPP: PGMI server running
Explanation: The process PPPPPPPP has started an instance of the server component for handling command execution.
System Action: Processing of commands now commences.
User Response: None.
Process PPPP trace state is SSSS
Explanation: The tracing state of process PPPP has now changed to SSSS.
System Action: If 'Off', then tracing has been disabled. If 'On', then the file to which tracing is now being done is reported.
User Response: None.
PPPPPPPP/NNNN: Normal shutdown complete
Explanation: The process PPPPPPPP with an Id of NNNN has shut down as a result of a service level change.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.
Dump written to FFFFFFFF
Explanation: A software error has occurred and a dump of the failing process has been written to file FFFFFFFF.
System Action: If possible, recovery routines will be invoked. Depending upon the nature and reason for the error, the recovery may or may not be successful.
User Response: Additional messages produced around the same time should also give an indication of what function is effected. Refer the problem to StorageTek Software Support.
Response to message NNNN was RRRRRRRR
Explanation: The REPLY command has been used against the outstanding message with the Id of NNNNN. The response text was RRRRRRRR.
System Action: The function awaiting the response to the message will be woken up and passed the relevant text.
User Response: None.
Message NNNN has been deleted
Explanation: The outstanding message with the Id of NNNNN has been deleted by the system.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.
Manual dump of process PPPP initiated: TTTTTTTT
Explanation: A manual dump of process PPPP has been initiated via a command. The reason for the dump was given as TTTTTTTT.
System Action: After the dump has been taken, processing should continue.
User Response: Assuming this is at the request of StorageTek Software Support, use the DIAGS command or the GUI to add the generated dump to the relevant support bundle.
Security failure on CCCCCCCC command matching rule on line LLLL RRRRRRRR
Explanation: A user attempted to execute CCCCCCCC command when matching the PERMIT/ALLOW rule on line LLLL. RRRRRRRR is additional resources that maybe triggering the failure.
System Action: Execution of the command will be rejected.
User Response: Contact your system administrator and get them to review the PERMIT/ALLOW rules for your User Id.
Security warning on CCCCCCCC command matching rule on line LLLL RRRRRRRR
Explanation: A user attempted to execute CCCCCCCC command when matching the PERMIT/ALLOW rule on line LLLL. RRRRRRRR is additional resources that maybe triggering the failure. The matching rule is currently set to just issue a warning.
System Action: Execution of the command continues.
User Response: Contact your system administrator and get them to review the PERMIT/ALLOW rules for your User Id.
Process PPPPPPPP/NNNN received termination request
Explanation: The process PPPPPPPP with an Id of NNNN has received a request to shut down as a result of a service level change.
System Action: Any work the process is performing will be quiesced before the shut down request is honoured. Typically from this point, new requests will be rejected.
User Response: None.
PPPPPPPP/NNNN: Communication failure writing TTTTTTTT to logger: RRRRRRRR
Explanation: An internal communications error has occurred when process PPPPPPPP with an Id of NNNN tried to send a message of type TTTTTTTT to the logger process. The reason for the failure is RRRRRRRR. The most likely reason for this problem, is the logger process failing.
System Action: The process PPPPPPPP will reset the connection and attempt to reconnect to the logger process. If the process is not available, then it will retry until the process becomes available. Some messages may have been lost as a result of this failure.
User Response: Check for additional messages that might also be a trigger for this error message.
Command CCCCCCCC: Internal Comms error: RRRRRRRR
Explanation: When executing the command CCCCCCCC, an internal communication failure with the reason RRRRRRRR occurred. This failure could have a number of reasons that are perfectly normal. A typical reason is a external command being cancelled or a service level change whilst a command is executing.
System Action: Depending upon the timing, the command CCCCCCCC may or may not continue executing.
User Response: Check for additional messages that might also be a trigger for this error message. Also review what any client systems were doing at the time.
Connection NNNNNNNN authorisation failure: RRRRRRRR
Explanation: When authorizing a client over a TCP/IP connection using the name NNNNNNNN, there was a failure with the reason RRRRRRRR. The previous SLS8017 message will give the network address of the client.
System Action: The connection request will be aborted after a short period of time.
User Response: Check the configuration and setup of the client. Also review what any client systems were doing at the time.
PPPPPPPP/NNNN: Communication failure to CDS proxy: RRRRRRRR
Explanation: The process PPPPPPPP with an Id of NNNN suffered an internal communication failure with the CDS proxy process. This can only occur in shared CDS mode where the CDS manages the connections to the ELS host.
System Action: This will typically cause follow-on errors as communications from the process to the CDS have been compromised and I/Os may have been lost.
User Response: Check the connection to the ELS host from the 'dbserv' process and confirm that the process is running. It maybe necessary to reset things by dropping and raising the service level.
Connected to CDS server SSSSSSSS
Explanation: The CDS proxy process has established a connection with the ELS system with then network address of SSSSSSSS.
System Action: Access to the CDS is now permitted and processing will continue.
User Response: None.
Communication failure to CDS server: RRRRRRRR
Explanation: The CDS proxy process has suffered a communications failure talking to the ELS host with a reason of RRRRRRRR.
System Action: This will typically cause follow-on errors as communications from other processes to the CDS have been compromised and I/Os may have been lost.
User Response: Check the connection to the ELS host from the 'dbserv' process and confirm that the process is running. Also check that the ELS host is running and that the DBSERVER command has been correctly issued. It maybe necessary to reset things by dropping and raising the service level.
Trying to reconnect to CDS server SSSSSSSS
Explanation: The CDS proxy process is trying to reconnect to the ELS host SSSSSSSS.
System Action: This will be done indefinitely until the connection has been established. Until this point, some functions that will require access to the CDS will fail and others will hang.
User Response: Check that the ELS host is running and that the DBSERVER command has been correctly issued.
Communication failure to CDS client: RRRRRRRR
Explanation: The CDS proxy process has detected that one of its client processes has dropped an internal connection for the reason RRRRRRRR.
System Action: Processing continues and the client's I/O requests will be dropped.
User Response: Check the other processes for error messages that may give an indication as to the source of the problem.
CDS version: VVVVVV Primary DSN: DDDDDDDD
Explanation: The CDS proxy has successfully connected to the ELS system that is serving up the CDS. The version of ELS is VVVVVV and the primary CDS is DDDDDDDDDD
System Action: Processing continues.
User Response: None.
Cannot create shared memory segment
Explanation: The process was unable to create the shared memory segment that is used for communication between processes.
System Action: The process will abort its start-up and take a dump.
User Response: Check the other processes for error messages that may give an indication as to the source of the problem. Try rebooting the LDOM.
Cannot attach shared memory segment
Explanation: The process was unable to attach to the shared memory segment that is used for communication between processes. It is possibly incompatible.
System Action: The process will abort its start-up and take a dump.
User Response: Check the other processes for error messages that may give an indication as to the source of the problem. Try rebooting the LDOM.
Local configuration change to host NNNN with name SSSSSSSS
Explanation: The local configuration has been updated and the system has been allocated an Id of NNNN and a name of SSSSSSSS.
System Action: Processing continues.
User Response: None.
Configuration connection from NNNN as host SSSSSSSS
Explanation: A cluster connection has been received from the system with an Id of NNNN and a name of SSSSSSSS.
System Action: Processing continues. This includes ensuring that both systems have correc6t configuration information.
User Response: None.
Configuration connection to NNNN as host SSSSSSSS using AAAAAAAA
Explanation: A cluster connection is been attempted to the system with an Id of NNNN and a name of SSSSSSSS using the network address AAAAAAAA.
System Action: Processing continues. This includes ensuring that both systems have correc6t configuration information.
User Response: None.
Configuration sent to NNNN as host SSSSSSSS
Explanation: This system has deduced that it has a more current configuration than the system with the Id of NNNN and the name of SSSSSSSS. It is therefore uploading the changed configuration to this target in order to bring both systems into line.
System Action: Processing continues. Once the configuration update has been received, notifications will be sent to the various processes to cause them to read in the update.
User Response: None.
Configuration received from NNNN as host SSSSSSSS
Explanation: This system with the Id of NNNN and the name of SSSSSSSS has deduced that it has a more current configuration than this system. It is therefore downloading the changed configuration to this system in order to bring both systems into line.
System Action: Processing continues. Once the configuration update has been received, notifications will be sent to the various processes to cause them to read in the update.
User Response: None.
Configuration connection to # NNNN as host SSSSSSSS terminated: RRRRRRRR
Explanation: The cluster connection to the system with the Id of NNNN and the name of SSSSSSSS has terminated for the reason of RRRRRRRR.
System Action: Processing continues. Depending upon the reason for the termination, other error messages maybe posted.
User Response: If this is not an expected condition, then check for error messages that may give an indication as to the source of the problem.
PPPPPPPP/NNNN: SQL error: EEEEEEEE Return Code: RRRR
Explanation: The process PPPPPPPP with an Id of NNNN has suffered an internal SQL of EEEEEEEE when accessing the CDS. The return code from the operation was RRRR.
System Action: This will typically cause follow-on errors as access to the CDS will have been compromised and I/Os may have been lost. Depending upon the nature of the error, some retries maybe attempted before giving up. on the operation.
User Response: Check the other processes for error messages that may give an indication as to the source of the problem. It maybe necessary to reset things by dropping and raising the service level. In a clustering environment where there are two systems, errors can be posted if communications to the primary system is lost.
CDS unavailable: RRRRRRRR
Explanation: The current operation was unable to complete because the CDS is unavailable because of the reason RRRRRRRR.
System Action: The function attempting to access the CDS will fail.
User Response: Check the connection to the ELS host from the 'dbserv' process and confirm that the process is running. It may be necessary to reset things by dropping and raising the service level.
DS access error: RRRRRRRR
Explanation: The current operation was unable to complete because the CDS access returned the error with a reason of RRRRRRRR.
System Action: The function attempting to access the CDS will fail.
User Response: Check for additional messages that might also be a trigger for this error message.
PPPPPPPP: Parameter change detected
Explanation: The process PPPPPPPP has been notified of a change to the main parameter file,
System Action: The process will read and process the updated parameter file.
User Response: This is informational only.
Restart of process PPPPPPPP detected
Explanation: The process PPPPPPPP has been restarted after previously suffering an uncontrolled termination.
System Action: Processing continues.
User Response: None.
Received=RRRR/rrrrrrrr, Sent=SSSS/ssssssss, Duplicate reads=DDDD, Cache reads=CCCC
Explanation: This reports the statistics for accessing the CDS via an ELS host and is normally issued when the 'dbserv' process is shut down.
The RRRR/rrrrrrrr value is the number of messages received from the ELS host and the number of bytes transferred.
The SSSS/ssssssss value is the number of messages sent to the ELS host and the number of bytes transferred.
The DDDD value is the number of read requests to the ELS host that were suppressed because the same request was already in-flight.
The CCCC value is the number of read requests to the ELS host that could be satisfied from a client side cache.
System Action: Processing continues.
User Response: None.
Number of CDS I/O operations=IIII, Response time=TTTTTTT
Explanation: This reports the statistics for accessing the CDS via an ELS host and is normally issued by each process when it stops doing I/O to the CDS. The IIII value is the number of CDS I/O operations performed. The TTTTTTTT value is the average response time of the CDS I/O requests. At times this may appear lower than expected because some requests are services from a cache or because the request is a duplicate of an existing request.
System Action: Processing continues.
User Response: None.
Configuration connection from NNNN as host SSSSSSSS rejected
Explanation: This system with the Id of NNNN and the name of SSSSSSSS attempted to connect to this system in order to form part of a cluster. This was rejected because the system is not deemed to be part of the cluster.
System Action: Processing continues on this system. On the system attempting to connect, it should drop into a failed state and refuse to start. This is to avoid a split-brain scenario with the CDS.
User Response: Investigate the history of the two systems. Check for additional messages that might also be a trigger for this error message.
When attempting to recover from this situation it is important that a full picture of the state and history is obtained. If this is not done, then it is easy to make the wrong decision and destroy the CDS contents.
Allowing MySQL to start: RRRRRRRR
Explanation: The cluster control process has deemed that it is OK to permit access to the SQL based CDS. The reason for the decision is given as RRRRRRRR.
System Action: Processing continues and the internal SQL database is started up.
User Response: None.
Configuration shutdown - Possible split-brain condition
Explanation: The cluster control process has detected a condition whereby continuing to start could result in a split-brain condition.
System Action: The clustering process shuts down and this will in turn shut down all other dependent process. Access to the internal SQL CDS is disabled.
User Response: Investigate the history of the systems. Check for additional messages that might also be a trigger for this error message upon this and any other systems.
When attempting to recover from this situation it is important that a full picture of the state and history is obtained. If this is not done, then it is easy to make the wrong decision and destroy the CDS contents.
Cluster connection to NNNN down. In single server mode
Explanation: The connection from the cluster control process to the host with the Id of NNNN can either not be established or has failed.
System Action: Processing continues. This does mean that the CDS is only running with a single copy active and that any subsequent failure could be fatal.
Depending upon the reason for the connection loss, there maybe transient errors reported.
User Response: Investigate the history of the systems. Check for additional messages that might also be a trigger for this error message upon this and any other systems.
Database state compromised - Check service levels
Explanation: A check of the internal SQL database state has indicated that not all of the required parts are functional.
System Action: Processing continues. This does mean that the CDS is only running with a single copy active and that any subsequent failure could be fatal.
User Response: Investigate the history of the systems. Check for additional messages that might also be a trigger for this error message upon this and any other systems.
Check that the service levels are correct upon each member of the cluster and adjust if necessary.
Process PPPPPPPP/NNNN running
Explanation: The process PPPPPPPP with an Id of NNNN has started executing.
System Action: None.
User Response: None.