You can log into the LSMS active server or into a specific server from any terminal that has a Secure Shell (ssh) client installed.
You must have a user ID and password before you can log in to LSMS.
- From a command-line prompt on a Windows-based or Linux-based terminal, enter the following command to start a secure shell session with the LSMS server:
ssh -X <username>@<server_IP_address>For <username> and <server_IP_address>, specify values shown in Table 1 that are appropriate to the procedure you are performing:
Parameters Used in Accessing Server Command Line Parameter
Value
<username>
Use one of the following:
- lsmsmgr to access the lsmsmgr text interface for configuration, diagnostics, and other maintenance functions
- syscheck to run the syscheck command with no options, which returns overall health checks and then exits the login session (for more information about the syscheck command, see syscheck)
- Other user names, as directed by a procedure
<server_IP_address>
Use one of the following:
- Virtual IP address (VIP) to access the LSMS Web GUI
- IP address of the specific server, when directed by a procedure to access a particular server
- When prompted, enter the password associated with the user name.
- You can now continue with any of the following functions:
- If you entered lsmsmgr as the username, the lsmsmgr text interface displays. You can use any of the lsmsmgr functions.lsmsmgr Text Interface Main Menu
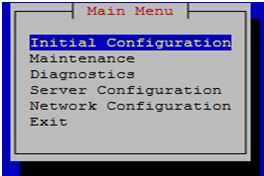 Note: Selections in the lsmsmgr text interface are made by either using the Up and Down Arrow keys on your keyboard or typing the first letter of any menu item to change which menu item is highlighted. When the desired menu item is highlighted, press the Enter key.
Note: Selections in the lsmsmgr text interface are made by either using the Up and Down Arrow keys on your keyboard or typing the first letter of any menu item to change which menu item is highlighted. When the desired menu item is highlighted, press the Enter key.In this manual, menu selections are indicated as a series; for example, select Maintenance > Start Node indicates that you should highlight the Maintenance item on the main menu, press Enter, then highlight the Start Node item on the next menu, and press Enter.
- If you entered syscheck as the username, the command line window displays the System Health Check output. For more information about syscheck, see syscheck.
- If you entered any other username the command line prompt displays a prompt that shows the username and host name, similar to the following example (in this example, the user logged in as the lsmsadm user to the server whose host name is lsmspri):
[lsmsadm@lsmspri lsmsadm] $
Note: In this manual, the prompt will be indicated simply by $.LSMS commands can be entered at this prompt. If you need to start an LSMS GUI session, see Starting an LSMS GUI Session.
- If you entered lsmsmgr as the username, the lsmsmgr text interface displays. You can use any of the lsmsmgr functions.