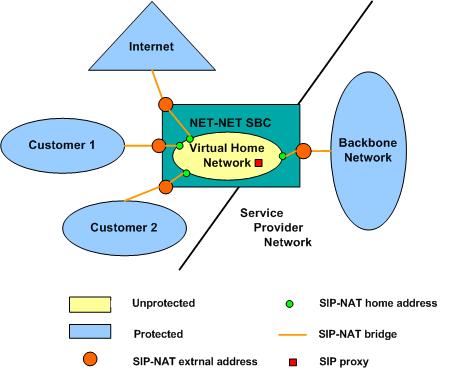
About SIP NAT Bridging
Each SIP NAT has a presence in two realms, trusted and untrusted. The SIP NAT bridge is the conduit for packages in and out of the home realm. It creates a bridge between realms by providing address translations; removing all references to the original IP addressing from the packets sent to the destination network.
With the SIP NAT bridge, an untrusted (or public) home network can reside within the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller, while the other entities (the backbone network, the Internet, or customer networks) are all trusted (or private). One of the primary functions of the SIP NAT bridge is to protect networks from one another so that address bases can remain hidden. Using a SIP NAT bridge, no one network has direct access to the data of other networks.
Establishing a SIP NAT bridge lets you route every SIP Request message through the backbone. Without using this functionality, it would appear as though all messages/sessions were coming from the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller’s SIP proxy (the SIP server that receives SIP requests and forwards them on behalf of the requestor).
The following diagram illustrates this unprotected (or public) and protected (or private) division.