| Oracle® Retail Integration Bus Implementation Guide Release 13.0.2 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
The Oracle Retail Integration Bus (RIB) is a fully distributed integration infrastructure that uses Message Oriented Middleware (MOM) to integrate applications. RIB enables various Oracle Retail applications to integrate in an asynchronous and near real time fashion. RIB provides additional value added business and infrastructure services to the Oracle Retail applications in addition to providing integration connectivity.
Each of the Oracle Retail Applications has their own implementation and deployment strategies and approaches, as well as individual integration touch points defined. The implementation of the RIB has to take into account the overall Oracle Retail application enterprise deployment architecture and try to fit into the model seamlessly.
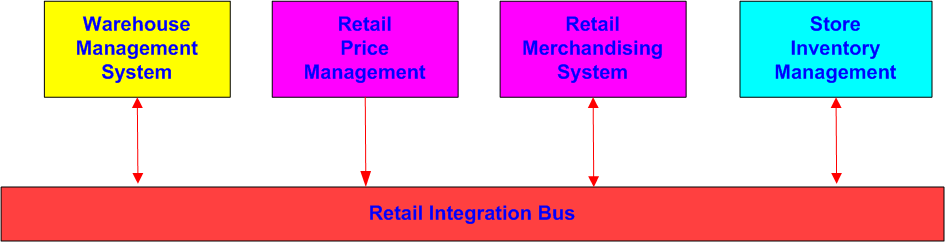
The RIB acts as a shared communication layer for connecting various Oracle Retail applications and external applications throughout an enterprise computing infrastructure. It supplements the core asynchronous messaging backbone with additional application functionality such as intelligent transformation, routing and error handling.
Communication across the RIB is via xml messages (payloads). These payloads describe the retail business objects (such as items, purchase orders, suppliers, and so on) in a standard way and are governed by RIB on behalf of the Oracle Retail applications.
The RIB architecture is based on standard Java EE components and the Java Message Service (JMS). JMS is an integral part of the Java EE (Java Enterprise Edition) Technology stack. This is very different from the previous RIB releases that were based on a centralized model implemented using eGate proprietary components.
The integration solution provided by RIB system is made up of multiple Java EE RIB applications (rib-<app>.ear) that are autonomous in their execution behavior, and are deployed in a fully distributed topology. Even though they (rib-<app>.ear) are distributed and autonomous they communicate and coordinate messages with each other and works to provide the final asynchronous integration solution that the enterprise expects. The issues and considerations needed to properly deploy and configure it within an enterprise are the subject of this guide.