| Oracle® Retail Integration Bus Service-Oriented Architecture Enabler Tool Guide Release 14.0 E49440-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
| Oracle® Retail Integration Bus Service-Oriented Architecture Enabler Tool Guide Release 14.0 E49440-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
The purpose of the Retail Service-Oriented Architecture Enabler (RSE) tool is to provide a standard, consistent way to develop Web services for PL/SQL and Java EE applications. Because it allows them to expose their business logic, the focus of development can be on the business logic code, not on the Web service infrastructure.
The RSE tool creates Web service provider end-points, consumer clients for Web service providers, and templates for interfacing with PL/SQL APIs and Java EE APIs.
The tool also produces design time and run time artifacts. It works in conjunction with another RTG tool, the Retail Functional Artifact Generator.
The following is a list of the essential features of the RSE tool:
The RSE tool is standards based.
The RSE tool supports SOAP and RESTful based web services.
SOAP based web services:
All services are generated in a consistent and standard manner.
All services are SOAP/HTTP based.
All services comply with the JAX-WS specification.
All services are WS-Addressing enabled.
WS-Security can be plugged into these Web services without any code change.
All Web services are Document Literal Wrapped.
Generated services are capable of using SOAP headers.
RESTful based web services:
REST is an architectural style, not a standard.
The services comply with the JAX-RS specification.
The services support all HTTP methods.
WS-Security can be plugged into these Web services without any code change.
The RSE tool generates technology-specific API templates for PL/SQL APIs and Java EE.
It supports PL/SQL as a Web service provider.
PL/SQL code can directly call any third party SOAP/HTTP based Web services.
It supports java code as a Web service provider.
It supports java code as a Web service consumer.
Generation by the RSE tool is controlled by a single Service Definition Library XML file.
By creating Web services from the high level abstraction in the Service Definition Library, top down Web services development is supported.
All service operation inputs and outputs are validated against the XML schema.
There is a single source of truth for all service and domain object documentation.
The same documentation is propagated to static WSDL, Java/PLSQL API code, UDDI published content, and live WSDL.
The Service Definition Library XML file is a service-oriented architecture governance asset.
The generated services deploy in any Java EE 5 with JDK 7 compliant application server, with certification on Oracle WebLogic Server. (Services are deployable to a clustered Java EE application server.)
The generated services are callable as SOAP based Web services over SOAP/HTTP, local EJB calls, remote EJB calls, or POJO services.
All services support Web service versioning strategy.
All generated Web services are forward and backward compatible.
For every Web service, a static WSDL is generated. (The generated static WSDL pulls in all of the Business Object (BO) and Web service level documentation.)
All deployed services can be published to any standard UDDI registry.
UDDI publishing has been tested with both WebLogicServer and Oracle Service Repository (OSR).
Every generated <appname>-service.ear contains an Infrastructure Management Service that can "talk to" the UDDI registry and publish all the services available within the .ear to the registry.
Services can take advantage of Oracle Database Real Application Cluster (RAC).
The RSE tool has the following built-in functionality:
Every service generated has a ping operation to test for network connectivity.
A Service Operation Context is passed to both Java EE and PL/SQL service provider API implementation code.
The Web service consumer generated has client side asynchronous service invocation capability.
User-defined Web service Faults are automatically generated and handled by the infrastructure at runtime. The definitions are made in the Service Definition Library XML file.
All Web service operations are transactional. A SOAP Fault response automatically rolls back the service operations transaction. A success response automatically commits the service operations transaction.
Web service consumers do not participate in the Web service provider side transaction. There is no transaction context propagation from client to server.
Service-oriented architecture (SOA) is a strategy for constructing business-focused software systems from loosely coupled, interoperable building blocks (called Services) that can be combined and reused quickly, within and between enterprises, to meet business needs (as described in Oracle Fusion Reference Architecture, SOA Foundation Release 1.0).
Service Infrastructure products focus on enabling SOA projects, rather than developing new business function, or providing for other business driven needs. The goal of Service Infrastructure is to enable delivery teams to deliver SOA projects faster, and to make the overall SOA undertaking much more manageable.
The Retail Service-Oriented Architecture Enabler Tool (RSE) is designed and developed to support the creation of Web services by allowing a high level abstraction, higher than the WSDL, and tailored to the business analyst/functional analyst. The Business Analyst can easily understand, define, and design without knowing the intricacies of WSDLs and the technical details of the implementation. This approach is also called top-down Web services development.
A service can be described as a way of packaging reusable software building blocks to provide functionality to users and to other services. A service is an independent, self-sufficient, functional unit of work that is discoverable, manageable, and measurable, has the ability to be versioned, and offers functionality that is required by a set of users or consumers.
A logical definition of a service has three components:
Contract: A description of what the service provides (and its constraints).
Interface: The means by which the service is invoked.
Implementation: The deployed code and configuration of infrastructure.
It is important to understand the position and role of the RSE tool within the broader context of service-oriented architecture and development. It is beyond the scope of this document to cover the range of SOA approaches and methodologies, but it is necessary to cover some aspects to place the tool in the appropriate context.
Oracle has developed and published the Oracle Fusion Reference Architecture (OFRA) for building and integrating enterprise-class solutions, part of the IT Strategies from Oracle collection.
The Oracle Fusion Architecture Framework is a collection of assets designed to provide guidance on building solutions for the Oracle Fusion solution environment, which includes the Oracle Fusion Reference Architecture (OFRA). The following diagrams and definitions are from OFRA documentation.
|
Note: See Oracle Practitioner Guide Software Engineering in an SOA Environment Release 1.0 E14486-01. |
The service analysis phase of the Oracle Service Engineering Framework consists of three main sets of engineering practices: SOA Requirements Management, Service Identification & Discovery, and Service Release Planning.
As with traditional software engineering, service engineering also begins with requirements and analysis, as illustrated below:
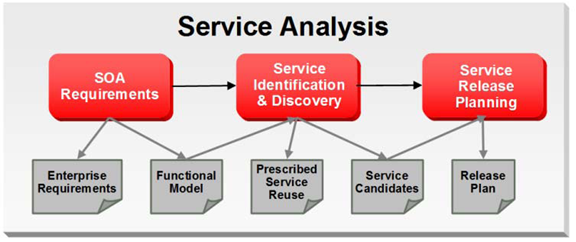
After Service Analysis, the next phase is Service Delivery, which includes the core delivery engineering activities. In this phase, a service candidate is molded into one or more services. Service candidates entering this phase have been justified for realization and scheduled for release.
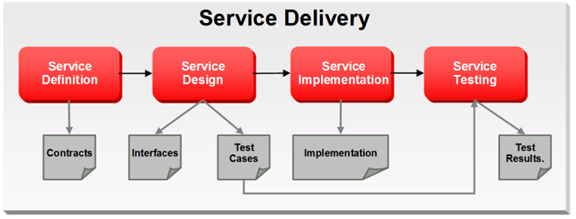
Service Delivery begins with Service Definition, which primarily determines service boundaries as well as the construction of the service contract.
Service Design then acts upon the Service contracts to develop the Services' interfaces. The process of defining a Service interface is much more involved than simply coming up with the input and output for the Service. Service design analyzes the contract from the consumer's perspective, and is influenced by factors such as scope (enterprise, LOB, application, and so on), message exchange patterns (MEPs) as well as non-functional requirements such as expected volume, and response time requirements (specified in the contract).
Service Implementation ensures that all aspects of the service contracts are implemented and upheld through the delivery of business logic as well as the deployment to Service Infrastructure. The implementation must faithfully realize the Service Contract and interface which are defined through Service definition and design.
|
Note: See: Oracle Fusion Reference Architecture, Overview. Release 1.0 E14482-01 |
The Retail Service-Oriented Architecture Enabler (RSE) is a Service Infrastructure tool developed by Oracle Retail to enable the adoption of service-oriented architecture (SOA) and avoid some of the typical pitfalls of many SOA projects. It addresses many common issues, such as versioning, contract design, security, consistency, reuse, documentation, governance, compliance, and customization. It does this by enforcing SOA Best Practices and patterns that are proven and time tested by various SOA pioneers.
The tool provides the capability for business analysts and developers to define the correct service contract. It provides ease-of-use and a level of abstraction such that the domain experts or subject matter experts are not required to understand code to design services. The SOA developers can be completely focused on implementing the business logic code behind the service and do not have to worry about SOA infrastructure issues such as versioning and customization.
The Retail Service-Oriented Architecture Enabler Tool fits within the Service Delivery phases. The appropriate use of the tool is after the service analysis phases and the development team is ready for service definition and design. The RSE tool outputs can then be used in the Service Implementation.
RSE is designed to support this type of approach, which is also called top-down Web services development.
The Oracle Retail SOA Enabler tool has dependencies on Oracle Retail application installations. This section covers these requirements.
| Supported On | Version Supported |
|---|---|
| Application Server OS | OS certified with Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g Release1 (11.1.1.6). Options are:
|
| Application Server | Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g Release 1 (11.1.1.6)
Components:
|