6. Planned Outage Support Server
6.1 Introduction
Planned Outage Support Server (POSS) is the data replica of the host server and facilitates the channels to support the database server without any downtime during the planned outages.
When POSS is active:
- EOD will not run
- Non-Channel Interface has to be switched off.
- ELCM enterprise has to be switched off.
- Messaging and notification cannot be done.
A new server state XML is created for which the path is decided based on the entry in the properties file. The XML contains a parameter <SERVERSTATE> which can have any of the following values:
- A – Available
- S – Sleep
- U – Unavailable
- R - Replay
Gateway EJB takes the request information from the SSB when the full session bean retains the information.
This chapter contains the following sections:
6.2 Handling Planned Outages
This section contains the following topics:
- Section 6.2.1, "Host Up"
- Section 6.2.2, "Outage Start"
- Section 6.2.3, "Host Down and POSS Up:"
- Section 6.2.4, "Host Up, Start Replay from POSS:"
- Section 6.2.5, "ELCM Impact"
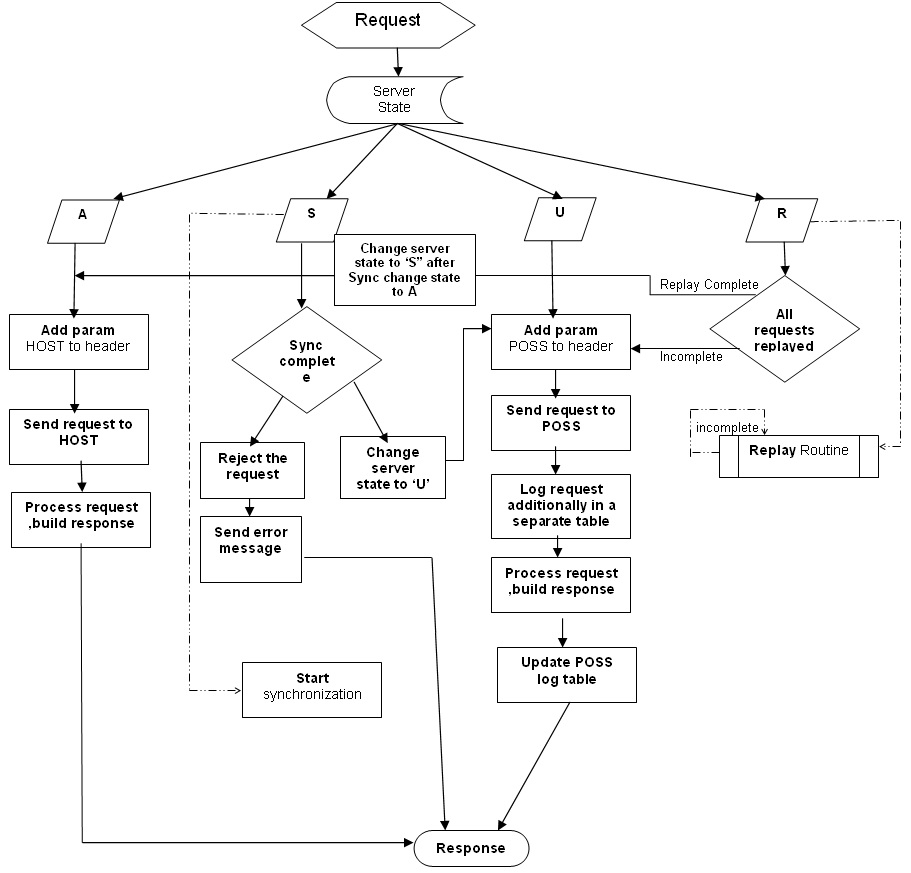
6.2.1 Host Up
When the request comes from the channel, it reaches the Gateway EJB or MDB and the bean check for the state of server. If the server state is ‘A’ (Available), the bean picks up the JNDI host server details from the properties file and add a parameter to the xml which implies that the request is being served at the host.
Then the request is processed at the back end and the response from the back end reaches the bean and then to the endpoint.
6.2.2 Outage Start
Using the restore point, the request data is synchronized from host server to POSS. Before the planned outage, the server state has to be changed into ‘S’ (Sleep) from ‘A’ to indicate that the server is down as soon as the synchronization starts.
During synchronization, if any new request comes to the bean, the gateway layer rejects the request and a XML error message is generated. Once the synchronization is completed, the server state is changed into ‘U’ (Unavailable) which indicates the bean that the host server is down and from then on any request that comes is processed at POSS.
6.2.3 Host Down and POSS Up:
When the host is down and POSS is up, the server state is ‘U’. During this time, all the requests that reach the bean is served at POSS. The bean picks up the JNDI details of POSS from the properties file, establishes a connection, and sends the request which is logged into a table at the backend.
The log table have details which indicates if:
- the response has been built successfully
- the request has to be replayed at the host during replay
- any error has occurred and oracle SCN
The response is sent back to the bean which will send the response to the end point.
6.2.4 Host Up, Start Replay from POSS:
Once the host is up, a ‘REPLAY ROUTINE’ (which is a java routine) is carried out which consists of the following steps:
- The server state is changed from ‘U’ to ‘R’ (Replay mode).
- The replay routine get the requests from the log table at POSS for which response building has been completed and these are replayed to the host.
- The replay routine logs all message logs and places the message onto Oracle AQ on the Host database.
- Multiple processes, equal to the number of locks defined, start the request processing based on SCN.
- Each process replays the requests on to the host by calling a procedure in the service router.
- Once a record is replayed, the thread updates the log table indicating that the replay of this record is complete.
When the server state is ‘R’ and any new request comes to the bean, it executes a DAO to check for records in POSS that need to be replayed to the host. If any such record is found, the new request is sent to POSS else the server state is changed from ‘R’ to ‘A’.
When the server state is ‘R’ the bean also slows down the processing of new requests to ensure there is a switch over back to host.
The following chart depicts a clear picture of request information that pass on to the various stages that are discussed.
6.2.5 ELCM Impact
When the request comes, two ELCM gateways are deployed pointing towards the Host and the POSS. The external interface at ELCM is switched off and the transactions which are initiated through FLEXCUBE are serviced.
6.3 Services Supported during Outage
Oracle FLEXCUBE ELCM supports following services during outage.
- COCategoryTypeService
- COExposureTypeService
- COHaircutTypeService
- COProductTypeService
- ELCMBatchService
- ELCollCategoryService
- ELCollateralService
- ELCollteralService
- ELCollteralTypeService
- ELCovenantService
- ELCreditAgencyService
- ELCreditScoreService
- ELCustLiabService
- ELCustomerLiabService
- ELExposureBlockService
- ELExposureService
- ELFacilityBlockService
- ELFacilityService
- ELFileProcessService
- ELInsuranceCompanyService
- ELInsuranceTypeService
- ELIssuerService
- ELLiabilityService
- ELPoolService
- ELSectorIndustryService
- ELSecuritiesService
- ELSecurityService
For more information about operations performed by each service, refer to Gateway Web Services.