| Oracle Agile Engineering Data Management Architecture Guide Release e6.2.1.0 E69173-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
| Oracle Agile Engineering Data Management Architecture Guide Release e6.2.1.0 E69173-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
In general, the EDM server components can reside on the same server where the EDM server processes are executed (recommended for Business Services), or can reside on any other computer in the network (especially for the File Management Service).
Due to this additional separation of server components and services, Agile e6 features a distributed architecture.
The entire communication is based on TCP/IP. Only unprivileged ports (higher 1024) are used. Once a TCP/IP connection is established, the port will not be changed dynamically.
The Business Services run on top of WebLogic application server and provide the following capabilities:
Permission Manager
The permission manager is responsible to manage all user role assignments and the resulting permissions. It provides user authentication and authorization checks for both the Agile e6 core server and other components of the business services.
An optional caching mechanism allows having fast access to data like user jobs and roles.
Workflow
The workflow engine is used to execute activity-based business workflows.
Product Configurator
The configurator engine, responsible for calculating valid product configuration based on logical rules.
Files are stored on any server in the network under control of the File Management Service (FMS). The File Management Service manages documents (referred to as "Files") in vaults, thus implementing the "check-in" and "check-out" functionality provided by the Document Management System in Agile e6.
The File Management Service consists of an FMS Client and an FMS Server. An FMS client communicates with the corresponding FMS server to check-in and check-out files.
Detailed descriptions about the access from the different clients can be found further on in this document in the respective client communication chapters.
Java Client
The FMS Client is embedded and is not required to be installed separately.
Web Client
The FMS Client is executed on the Web Server and does not require any installation on the front end.
The FMS Server is installed on one or more server computers. Each FMS Server can manage one or more vaults.
If the FMS Server is installed on a Windows platform, this server must be NTFS based. FAT does not work.
The vaults managed by an FMS Server have to be created on local hard discs of the computer where the corresponding FMS Server is running, or on a SAN. The SAN has to be configured in a way that IO from the file and the database server are separated IO channel).
The FMS Client communicates with the Agile e6 application server process using sockets.
The FMS Server and the FMS Client communicate with Remote Procedure Calls (RPC) and sockets. The FMS Server does not communicate directly with the EDM server process.
In a very simple configuration, there is only one FMS Server with a single vault (e.g. when Agile e6 is installed on a single work group server or on a laptop).
For large installations of Agile e6, there may be FMS Servers running on several computers, each FMS Server managing multiple vaults.
Installations with remote users that connect to an EDM Server through a Wide Area Network (WAN), e.g. an external office that is connected to the headquarters, would usually be limited when accessing files by a small network bandwidth. To improve performance in such a configuration, an FMS Server and one or more vaults can also be installed at the remote location (even though the EDM Server and the database are running at the headquarters). Files can be checked-in and checked-out into these vaults by any FMS Client that is able to communicate with this FMS Server.
The Distributed File Management (DFM) module controls the transfer and replication of document files between several distributed sites. Redundant storage of files is the basic working principle of this module. The aim of this data redundancy is to reduce network transfers in conjunction with the use of local vaults for file check-in and check-out processes. These measures can result in a significant reduction of transfer volume costs and increase the overall network performance. Files stored at distributed sites can be accessed at all times.
The Distributed File Management (DFM) module provides two methods for the replication of data:
Data can be replicated by means of scheduled batch processes that are run automatically in regular intervals.
Alternatively, specific files can be replicated online through user interaction.
The main advantage of automatic data replication is that file transfers can be initiated at off-peak times (e.g. at night), when the additional network traffic does not affect the overall network performance.
In an internet environment it is necessary to provide a file storage access via HTTP/HTTPS. The Web Fileservices are providing a scalable access to the file vaults which are managed by the Core File Server.
Prerequisites:
Required hardware
All supported platforms for EDM
Required Software
WebLogic Server, or TOMCAT for DFM locations
Required Knowhow
Administration of a WebLogic Server, or TOMCAT for DFM locations
|
Note: For further information about how to enable secure socket layer support in WebLogic/TOMCAT, see the respective WebLogic/TOMCAT documentation. |
The following graphic shows the communication lines when using Web Fileservice.
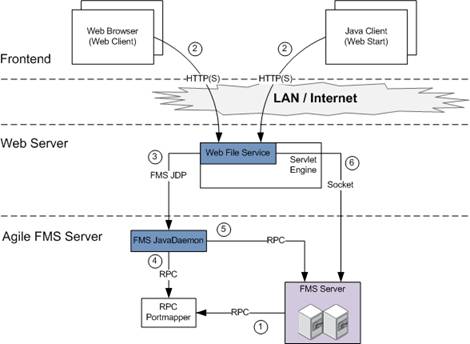
The FMS Server (File Server) registers itself by the RPC Portmapper.
An EDM Client (Web Client or Java Client) contacts the Web Fileservice to check-in or check-out a file.
The Web Fileservices uses the configured FMS Java Daemon to get the transfer socket to the FMS Server.
The FMS Java Daemon requests the connect information for the FMS Server from the RPC Portmapper.
The FMS Java Daemon contacts the FMS Server and requests a transfer socket to upload or download the file.
The Web Fileservice uses the transfer socket to upload or download the file.
The following table shows the connections used. For more information, refer to the Administration Guide for Agile e6.2.1.0.
| Module | Port Configurable | Description |
|---|---|---|
| FMS | yes | HTTP(S) access to the Web Fileservice (2) |
| FMS | yes | FMS Java Daemon with the FMS Java Daemon Protocol (3) |
| FMS | no | RPC Portmapper (1), (4), (5) |
| FMS | no | FMS communication socket for file transfer (6) |
The purpose of the FMS Java Daemon is to get rid of the necessity to deal with native libraries in WebLogic context when using native FMS.
The Java Daemon is contacted by the Java Client in order to connect to the Agile EDM server process. Java Daemon initiates the startup of the Agile EDM server process and routes the connect parameters to the Java Client.
In addition, it is Java Daemon's responsibility to shut down server processes if the Java Client is closed by user. Therefore, the Java Daemon checks on a regular basis, if the Java Client is still alive. If the Java Client is no longer alive, it will shut down the corresponding server process.
In order to allow Java Client to connect via HTTPS, it is necessary to translate the native RPC calls normally sent between Java Client and Agile EDM Server. PLM-API Proxy provides the gateway to translate HTTP calls into RPC calls and vice versa.
|
Note: We recommend using the AutoVue Server as a separate server.The Agile e6 AutoVue Integration simplifies the loading and viewing of Enterprise Documents such as CAD, PDF, Office documents, etc., within the Agile e6 system. |
|
Note: Only applies to the Java Client. |
The advantage of installing Agile e6 Autovue Integration is that you do not require any corresponding authoring system to be installed on a the machine.
The enterprise documents can be edited in the Viewer, thus creating and attaching different types of a markup file (e.g. text, note, or attachment). Also, the Agile e6 AutoVue Integration supports the feature to add a header/footer and watermark during printing or to show a permanent watermark in viewing mode.
The View Server deployment contains the AutoVue Server, AutoVue Proxy, and the VueLink integration. The VueLink integration provides the metadata and the files to the AutoVue server.
The Java Client includes the Agile e6 AutoVue Integration plugin, which downloads the AutoVue Viewer from the View Server Deployment, and shows the AutoVue Viewer inner frame or outer frame on the client machine.
The following graphic shows the communication between the involved components.
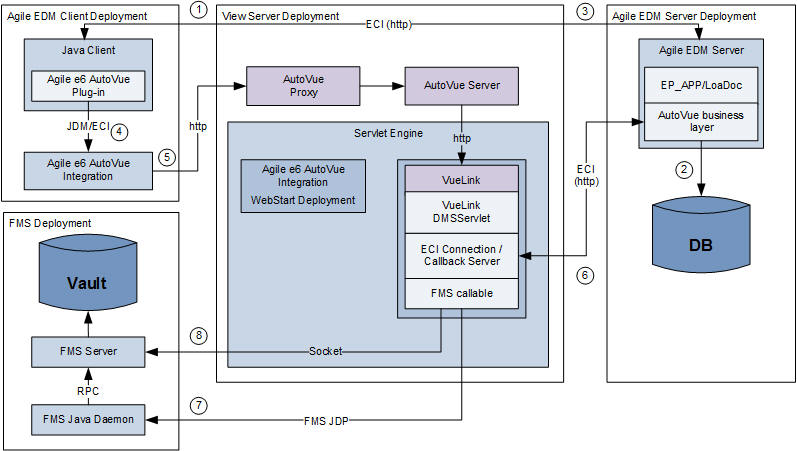
The user requests to view/markup a document.
The business logic determines the view which must be used to view the document. In this case, the Agile e6 AutoVue Integration should be used and the system stores the information to view the document into the database.
The EDM Server calls a client callback to view the file with the AutoVue viewer.
The Agile e6 AutoVue Integration plug-in starts the AutoVue viewer (once per session) from the local installation or via WebStart from the AutoVue deployment.
The Agile e6 AutoVue Integration plug-in calls the AutoVue viewer to load the document and the AutoVue viewer contacts the AutoVue server to request the viewing data for the document to view. The AutoVue viewer can use HTTP or a plain socket to contact the AutoVue server.
The VueLink DMS servlet connects to the same EDM server instance which is used by the Java Client and retrieves the data to view the document.
If the AutoVue server does not have the files already cached, the VueLink DMS servlet uses the FMS Java Daemon to contact the FMS server.
The file transfer is done through a direct socket connection.
The following table shows the connections used. For more information, refer to the Administration Guide for Agile e6.2.1.0.
| Module | Port Configurable | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ECI | yes | EDM Java Daemon |
| ECI | yes | ECI communication socket |
| FMS | yes | FMS Java Daemon |
| FMS | no | RPC Portmapper |
| FMS | no | FMS communication socket, the port range depends on the max. number of concurrent users |
| AutoVue | yes | HTTP communication between the AutoVue viewer and the AutoVue Proxy |
| AutoVue | yes | Socket communication between the AutoVue Proxy and the AutoVue Server |
| AutoVue | yes | HTTP communication between the AutoVue Server and the VueLink DMS Servlet |
| AutoVue | yes | HTTP download of the AutoVue viewer |
The Batch Client is a special version of the Java Client without any UI. The Batch Client supports client side callables which are used by the EDM Server to start client side activities like the startup of an external program, or the FMS Client to check-in / check-out files from the File Server. The standard features to exchange files with the EDM Server are also supported.
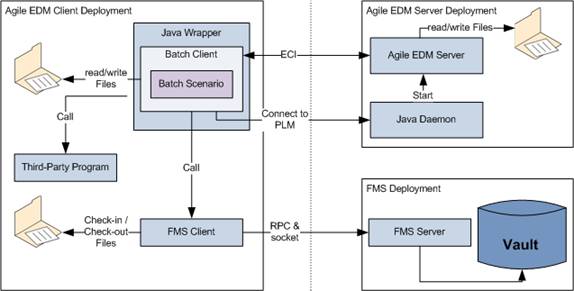
In "old" batch designs, that loop is implemented in LogiView. Sometimes there are external programs used to implement the sleep functionality to wait for a new batch job.
That batch job loop has to be moved into the batch control scenario on client side for some reasons.
The Batch Client provides the "sleep" functionality to wait for a new batch job.
The Batch Client communicates via ECI with the EDM Server, and to keep the connection open, it checks for a new batch job.
The following table shows the connections used. For more information refer to the Administration Guide for Agile e6.2.1.0.
| Module | Port Configurable | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ECI | yes | EDM Java Daemon |
| ECI | yes | ECI communication socket |
| FMS | yes | FMS Java Daemon |
| FMS | no | RPC Portmapper |
| FMS | no | FMS communication socket, the port range depends on the max. number of concurrent users |
The EDM Server is started by the Java Daemon and the Java Daemon communicates with the EDM Server for controlling purposes.
|
Note: If the EDM Server is in a LogiView loop, the communication with the Java Daemon is not possible. |
The Batch Client uses the Java Wrapper like the Java Daemon to support being installed as a service.
Many companies are using an LDAP server (Oracle Internet Directory, OpenLDAP, Microsoft Active Directory, or any other LDAPv3 server) to manage their users.
The LDAP integration allows authenticating Agile EDM users with their credentials from the LDAP server. The integration supports name mapping and multi domains.
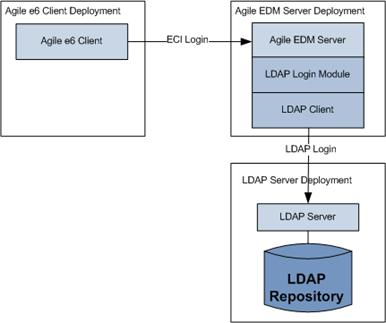
The Agile e6 Client sends a login request to the Agile EDM Server. The user uses the Agile e6 user account with the LDAP user account password.
The Agile EDM Server maps the Agile e6 user name to the LDAP user name and contacts the configured LDAP server to execute the login request.
It is possible to configure more than one LDAP server. In the user configuration, the user account can be linked to a dedicated LDAP server and/or BaseDN.
The following table shows the connections used. For more information, refer to the Security Guide for Agile e6.2.1.0.
| Module | Port Configurable | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ECI | yes | ECI communication socket |
| LDAP | yes | Connection to the LDAP repository |