An interpreter reads and executes the instructions written in a programming or scripting language without compiling the high-level language code into a machine language program.
Topics:
· Creating a New Interpreter Variant
To access interpreters, follow these steps:
1. Click the Navigation Menu ![]() on the upper-left corner on the FCC Studio landing page.
on the upper-left corner on the FCC Studio landing page.
The menu items are listed.
2. Click Interpreters.
The Interpreters page is displayed.

3. Click the interpreter that you want to access from the list displayed on the LHS.
The default interpreter variant configured is displayed on the RHS.
4. Modify the required values.
5. Click Update.
The modified values are updated in the interpreter.
In FCC Studio, you can either use a default interpreter variant or create a new variant for an interpreter. You can create more than one variant for an interpreter.
§ For a sample on creating a new interpreter variant, see Creating a New fcc-jdbc Interpreter Variant
§ To enable a second Spark/PySpark interpreter, see Enabling a Second Spark/PySpark Interpreter chapter in the OFS Crime and Compliance Studio Installation Guide (On-Premise).
To create a new fcc-jdbc interpreter variant, follow these steps:
1. Navigate to the Interpreters page.
2. Click the fcc-jdbc interpreter from the list displayed on the LHS.
The default interpreter variant is displayed on the RHS.
3. Click  Add to create a new variant for the selected interpreter:
Add to create a new variant for the selected interpreter:
The Create Interpreter Variant dialog box is displayed.
4. Enter the Name for the new interpreter variant.
5. Click Create.
A new variant is created with name, <Interpreter Type>.<Variant Name>.
6. Provide the new schema details such as the default.url, default.user, and default.password.
7. Click Update.
A new variant is created for the jdbc interpreter.
8. The Oracle Database schema that you have created must be granted with the same permissions that are granted to the BD or ECM atomic schema.
For more information, see the Prerequisite Environmental Settings section in the OFS Crime and Compliance Studio Installation Guide.
9. Run the following script after modifying the schema name with the newly created schema:
../OFS_FCCM_STUDIO/metaservice/model/SQLScripts/Atomic_Schema/FCC_JRSDCN_CONTEXT_ATOMIC.sql
../OFS_FCCM_STUDIO/metaservice/model/SQLScripts/Atomic_Schema/PKG_FCC_STUDIO_JURN_VPD.sql
../OFS_FCCM_STUDIO/metaservice/model/SQLScripts/Atomic_Schema/PKG_FCC_STUDIO_JURN_VPD_BODY_ATOMIC.sql
10. For using the new interpreter variant in the notebook paragraphs, use the following format:
%fcc-jdbc.newVariant
<Your SQL query>
11. Configure the required values for the properties.
12. Click Update.
A new variant is created for the JDBC interpreter.
The list of interpreters in FCC Studio are as follows:
· Configuring fcc-jdbc Interpreter Variant
· Linking Wallet Credentials to fcc-jdbc Interpreter
The configurations for the ofsaa-jdbc interpreter are given as follows:
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
pgx.baseUrl |
Enter the PGX URL in this field. This is the location where the data is pushed. For example: http://<HOSTNAME>:7007 |
|
default.url |
Enter the ofsaa jdbc URL in this field. For example: jdbc:mysql://localhost:5554/world NOTE: If you want to use the Oracle wallet credentials, you must enter the alias name in the following format: jdbc:oracle:thin:@<alias_name> |
|
zeppelin.jdbc.principal |
Enter the principal name to load from the keytab. |
|
default.driver |
Enter the default JDBC driver name. For example: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver |
|
default.completer.ttlInSeconds |
Enter the time to live sql completer in seconds. |
|
default.password |
Enter the default password. NOTE: This value can be null if you have entered the alias name in the default.url parameter for the fcc-jdbc interpreter. |
|
default.splitQueries |
This field indicates the presence of default split queries. Each query is executed apart and returns the result. Enter “true” or “false”. |
|
default.completer.schemaFilters |
Enter a comma-separated schema filters to get metadata for completions. |
|
ofsaa.sessionservice.url |
Enter the session service URL in this field. For example: http://<HOSTNAME>:7047/sessionservice Here, <HOSTNAME> refers to the server name or IP where fcc-Studio will be installed. |
|
default.user |
Enter the name of the default user in this field. For example: root |
|
zeppelin.jdbc.concurrent.max_connection |
Enter the number of maximum connections allowed. |
|
ofsaa.metaservice.url |
Enter the metaservice URL in this field. For example: http://<HOSTNAME>:7045/metaservice Here, <HOSTNAME> refers to the server name or IP where fcc-studio will be installed. |
|
common.max_count |
Enter the maximum number of SQL result to display. |
|
zeppelin.jdbc.auth.type |
Enter the default jdbc authentication type. |
|
zeppelin.jdbc.precode |
Enter the snippet of code that executes after the initialization of the interpreter. |
|
zeppelin.jdbc.concurrent.use |
Enter to enable or disable concurrent use of JDBC connections. Enter “true” or “false”. |
|
zeppelin.jdbc.keytab.location |
Enter the keytab file ocation. |
You can link the credentials (a wallet and a password) to fcc-jdbc interpreter variant to enable secure data access. This linking enables the fcc-jdbc interpreter to securely connect to the specified Oracle DB. For more information, see Managing Credentials.
To link the wallet credentials to fcc-jdbc interpreter, follow these steps:
1. Configure the following parameters in the ofsaa-jdbc interpreter as follows:
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
default.url |
If you want to use the Oracle wallet credentials, you must enter the alias name in the following format: jdbc:oracle:thin:@<alias_name> |
|
default.password |
This value can be null if you have entered the alias name in the default.url parameter for the fcc-jdbc interpreter. |
1.
2. Configure the other parameters in the ofsaa-jdbc interpreter as given in Configuring fcc-jdbc Interpreter Variant.
3. Link the wallet credentials to the fcc-jdbc interpreter variant. For more information, see Linking Credentials to Interpreter Variants
The configurations for the fcc-ore interpreter are given as follows:
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
ore.sid |
Enter the SID of DB server where the fcc-ore interpreter wants to connect. |
|
rendering.row.limit |
Indicates the number of rows to be shown in the fcc-ore interpreter output. For example: 1000 |
|
ore.conn_string |
Enter the DB connection URL with which the fcc-ore interpreter can make the connection to the schema. This field can be left blank. |
|
https_proxy |
Enter the Proxy server using which connection to the internet can be established. For example: www-proxy-hqdc.us.oracle.com:80 |
|
ore.type |
Enter the fcc-ore interpreter type as Oracle. |
|
ore.password |
Enter the schema password where the fcc-ore interpreter wants to connect. |
|
libpath |
Indicates the custom library path from where R packages will be installed via FCC Studio and will be added to R lib Path. Enter the path to be mentioned under the home directory where FCC Studio is installed. For example: If you want the packages to be available under /home/user/library, and FCC Studio is installed at /home/user/datastudio, then mention /library as the libpath. |
|
ore.host |
Enter the hostname of the DB server where the fcc-ore interpreter wants to connect. |
|
rserve.password |
Indicates the Rserve password. |
|
rendering.numeric.format |
Indicates the Number of digits to round off. For example: %.2f |
|
ore.service_name |
Enter the Service Name of DB server where the fcc-ore interpreter wants to connect. |
|
rserve.try.wrap |
Enter False. |
|
rserve.host |
Indicates the Rserve host. |
|
repo_cran |
Indicates the CRAN URL from where R libraries are downloaded to install R packages. For example: https://cran.r-project.org/ |
|
ofsaa.sessionservice.url |
Enter the session service URL in this field. For example: http://<HOSTNAME>:7047/sessionservice Here, <HOSTNAM> refers to the server name or IP where fcc-studio will be installed. |
|
ore.all |
Indicates all tables are synced to the fcc-ore interpreter. Enter the value as True. |
|
rserve.plain.qap.disabled |
Indicates whether plain QAP is disabled in the server or not. If disabled, the connection will always be attempted using SSL. For example: False |
|
ore.user |
Enter the schema name where the fcc-ore interpreter wants to connect. |
|
http_proxy |
Enter the Proxy server using which connection to the internet is established. This value is used to set the initial setting that makes the environment compatible to download the libraries available in R. For example: www-proxy-hqdc.us.oracle.com:80 |
|
rserve.port |
Indicates the Rserve port. |
|
rserve.secure.login |
Enter TRUE to enforce secure login. |
|
rendering.knitr.options |
Enter the Knitr output rendering option. For example: out.format = 'html', comment = NA, echo = FALSE, results = 'verbatim', message = F, warning = F, dpi = 300 |
|
rserve.user |
Indicates the Rserve username. |
|
ore.port |
Enter the port number of the DB server where the fcc-ore interpreter wants to connect. |
|
ofsaa.metaservice.url |
Enter the metaservice URL in this field. For example: http://<HOSTNAME>:7045/metaservice Here, <HOSTNAME> refers to the server name or IP where fcc-studio will be installed. |
|
rendering.include.row.name |
Indicates whether to include row names. For example: false |
|
rendering.knitr.image.width |
Indicates the image width specification for ore output. For example: 60 |
The configurations for the fcc-pyspark interpreter are given as follows:
|
Field |
Interpreter |
|---|---|
|
pgx.baseUrl |
Enter the pgx.baseUrl URL in this field. This is the location where the data is pushed. For example: http://##HOSTNAME##:7007 |
|
livy.spark.executor.instances |
Enter the number of executors to launch for the current session . |
|
livy.spark.dynamicAllocation.cachedExecutorIdleTimeout |
Enter the cached execution timeout in seconds. |
|
zeppelin.livy.url |
Enter the Livy URL in this field. Livy is an interface between Data Studio and Spark. For example: http://##HOSTNAME##:8998 |
|
zeppelin.livy.pull_status.interval.millis |
Enter the data pull interval in milliseconds. |
|
livy.spark.executor.memory |
Enter the amount of memory to use for the executor process. |
|
livy.spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled |
This field indicates whether Dynamic Allocation is enabled or not. Enter “true” or “false”. |
|
livy.spark.dynamicAllocation.minExecutors |
Enter the minimum number of required Dynamic Allocation executors. |
|
livy.spark.executor.cores |
Enter the number of executor cores to use for the driver process . |
|
zeppelin.livy.session.create_timeout |
Enter the Zeppelin session creation timeout in seconds. |
|
zeppelin.livy.spark.sql.maxResult |
Enter the maximum number of results that must be fetched. |
|
livy.spark.jars.packages |
Enter to add extra libraries to a livy interpreter. |
|
livy.spark.driver.cores |
Enter the number of driver cores to use for the driver process . |
|
zeppelin.livy.displayAppInfo |
This field indicates whether the application information must be displayed or not. Enter “true” or “false”. |
|
livy.spark.driver.memory |
Enter the amount of memory to use for the driver process. |
|
zeppelin.livy.principal |
Enter the principal name to load from the keytab. |
|
ofsaa.sessionservice.url |
Enter the session service URL in this field. For example: http://##HOSTNAME##:7047/sessionservice Here, ##HOSTNAME## refers to the server name or IP where fcc-studio will be installed. |
|
ofsaa.metaservice.url |
Enter the metaservice URL in this field. For example: http://##HOSTNAME##:7045/metaservice Here, ##HOSTNAME## refers to the server name or IP where fcc-studio will be installed. |
|
zeppelin.livy.keytab |
Enter the keytab location. |
|
livy.spark.dynamicAllocation.maxExecutors |
Enter the maximum number of required Dynamic Allocation executors. |
Topics:
· Configuring fcc-python Interpreter
· Changing Python Version in the fcc-python Interpreter
· Adding Python Packages to the fcc-python Interpreter
The configuration for the fcc-python interpreter is performed with the following fields:
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
zeppelin.python |
Enter the Python installed path. The value points to the default Python version set for the interpreter. NOTE: To use a different Python version, see Changing Python Version in the fcc-python Interpreter |
|
zeppelin.python.useIPython |
Set to True to use IPython, else set to False. |
|
zeppelin.python.maxResult |
Enter the maximum number of results that must be displayed. |
To use a different version of Python, follow these steps:
1. Navigate to the fcc-python Interpreter Settings page.
2. Perform one of the following:
§ Change the default Python version in the zeppelin.python parameter to the new version.
For example: python3.6
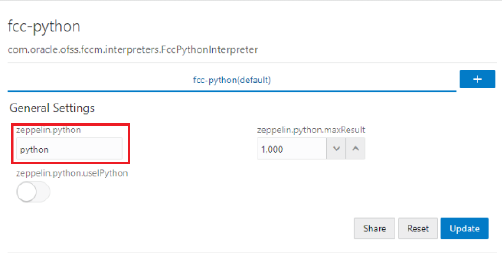
§ Create a new interpreter variant and configure the version in the zeppelin.python parameter. For information on creating a new interpreter variant, see Creating a New Interpreter Variant.
For example: To use Python 3.6, create a new fcc-python interpreter variant and enter the value as python3.6.
To add desired Python packages to the fcc-python interpreter, follow these steps:
· For FCC Studio installed on-premise:
To install additional Python libraries to the fcc-python interpreter, contact System Administrator to install the required additional Python libraries on the Processing Server (Studio Notebook Server). The newly added Python libraries must be accessible to the Linux user for FCC Studio
· For FCC Studio installed using Kubernetes:
To install additional Python libraries to the fcc-python interpreter, see Appendix - Modifying the Python Images for the Python Interpreter.
The configurations for the fcc-spark-scala interpreter are given as follows:
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
pgx.baseUrl |
Enter the pgx.baseUrl URL in this field. This is the location where the data is pushed. For example: http://<HOSTNAME>:7007 |
|
livy.spark.executor.instances |
Enter the number of executors to launch for the current session . |
|
livy.spark.dynamicAllocation.cachedExecutorIdleTimeout |
Enter the cached execution timeout in seconds. |
|
zeppelin.livy.url |
Enter the Livy URL in this field. Livy is an interface between Data Studio and Spark. For example: http://<HOSTNAME>:8998 |
|
zeppelin.livy.pull_status.interval.millis |
Enter the data pull interval in milliseconds. |
|
livy.spark.executor.memory |
Enter the amount of memory to use for the executor process. |
|
livy.spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled |
This field indicates whether Dynamic Allocation is enabled or not. Enter “true” or “false”. |
|
livy.spark.dynamicAllocation.minExecutors |
Enter the minimum number of required Dynamic Allocation executors. |
|
livy.spark.executor.cores |
Enter the number of executor cores to use for the driver process . |
|
zeppelin.livy.session.create_timeout |
Enter the Zeppelin session creation timeout in seconds. |
|
zeppelin.livy.spark.sql.maxResult |
Enter the maximum number of results that must be fetched. |
|
livy.spark.jars.packages |
Enter to add extra libraries to a livy interpreter. |
|
livy.spark.driver.cores |
Enter the number of driver cores to use for the driver process . |
|
zeppelin.livy.displayAppInfo |
This field indicates whether the application information must be displayed or not. Enter “true” or “false”. |
|
livy.spark.driver.memory |
Enter the amount of memory to use for the driver process. |
|
zeppelin.livy.principal |
Enter the principal name to load from the keytab. |
|
ofsaa.sessionservice.url |
Enter the session service URL in this field. For example: http://<HOSTNAME>:7047/sessionservice Here, <HOSTNAME> refers to the server name or IP where fcc-studio will be installed. |
|
ofsaa.metaservice.url |
Enter the metaservice URL in this field. For example: http://<HOSTNAME>:7045/metaservice Here, <HOSTNAME> refers to the server name or IP where fcc-studio will be installed. |
|
zeppelin.livy.keytab |
Enter the keytab location. |
|
livy.spark.dynamicAllocation.maxExecutors |
Enter the maximum number of required Dynamic Allocation executors. |
|
livy.spark.dynamicAllocation.initialExecutors |
Enter the initial Dynamic Allocation executors. |
The configurations for the fcc-spark-sql interpreter are given as follows:
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
pgx.baseUrl |
Enter the pgx.baseUrl URL in this field. This is the location where the data is pushed. For example: http://<HOSTNAME>:7007 |
|
livy.spark.executor.instances |
Enter the number of executors to launch for the current session . |
|
livy.spark.dynamicAllocation.cachedExecutorIdleTimeout |
Enter the cached execution timeout in seconds. |
|
zeppelin.livy.url |
Enter the Livy URL in this field. Livy is an interface between Data Studio and Spark. For example: http://<HOSTNAME>:8998 |
|
zeppelin.livy.pull_status.interval.millis |
Enter the data pull interval in milliseconds. |
|
livy.spark.executor.memory |
Enter the amount of memory to use for the executor process. |
|
livy.spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled |
This field indicates whether Dynamic Allocation is enabled or not. Enter “true” or “false”. |
|
livy.spark.dynamicAllocation.minExecutors |
Enter the minimum number of required Dynamic Allocation executors. |
|
livy.spark.executor.cores |
Enter the number of executor cores to use for the driver process . |
|
zeppelin.livy.session.create_timeout |
Enter the Zeppelin session creation timeout in seconds. |
|
zeppelin.livy.spark.sql.maxResult |
Enter the maximum number of results that must be fetched. |
|
zeppelin.livy.spark.sql.field.truncate |
Indicates to truncate field values longer than 20 characters or not. Enter "true" or "fasle". |
|
livy.spark.jars.packages |
Enter to add extra libraries to a livy interpreter. |
|
livy.spark.driver.cores |
Enter the number of driver cores to use for the driver process . |
|
zeppelin.livy.displayAppInfo |
This field indicates whether the application information must be displayed or not. Enter “true” or “false”. |
|
livy.spark.driver.memory |
Enter the amount of memory to use for the driver process. |
|
zeppelin.livy.principal |
Enter the principal name to lead from the keytab. |
|
ofsaa.sessionservice.url |
Enter the session service URL in this field. For example: http://<HOSTNAME>:7047/sessionservice Here, <HOSTNAME> refers to the server name or IP where fcc-studio will be installed. |
|
ofsaa.metaservice.url |
Enter the metaservice URL in this field. For example: http://<HOSTNAME>:7045/metaservice Here, <HOSTNAME> refers to the server name or IP where fcc-studio will be installed. |
|
zeppelin.livy.keytab |
Enter the keytab location. |
|
livy.spark.dynamicAllocation.maxExecutors |
Enter the maximum number of required Dynamic Allocation executors. |
Topics:
· Configuring jdbc Interpreter Variant
· Linking Wallet Credentials to jdbc Interpreter
The configurations for the jdbc interpreter are given as follows:
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
pgx.baseUrl |
Enter the pgx.baseUrl URL in this field. This is the location where the data is pushed. For example: http://<HOSTNAME>:7007 |
|
default.url |
Enter the jdbc URL in this field. NOTE: If you want to use the Oracle wallet credentials, you must enter the alias name in the following format: jdbc:oracle:thin:@<alias_name> |
|
zeppelin.jdbc.principal |
Enter the principal name to load from the keytab. |
|
default.driver |
Enter the default JDBC driver name. |
|
default.completer.ttlInSeconds |
Enter the time to live sql completer in seconds. |
|
default.password |
Enter the default password. NOTE: This value can be null if you have entered the alias name in the default.url parameter for the jdbc interpreter. |
|
default.splitQueries |
This field indicates the presence of default split queries. Enter “true” or “false”. |
|
default.completer.schemaFilters |
Enter comma-separated schema filters to get metadata for completions. |
|
ofsaa.sessionservice.url |
Enter the session service URL in this field. For example: http://<HOSTNAME>:7047/sessionservice Here, <HOSTNAME> refers to the server name or IP where fcc-studio will be installed. |
|
default.user |
Enter the name of the default user in this field. |
|
zeppelin.jdbc.concurrent.max_connection |
Enter the number of maximum connections allowed. |
|
ofsaa.metaservice.url |
Enter the metaservice URL in this field. For example: http://<HOSTNAME>:7045/metaservice Here, <HOSTNAME> refers to the server name or IP where fcc-studio will be installed. |
|
common.max_count |
Enter the maximum number of SQL result to display. |
|
zeppelin.jdbc.auth.type |
Enter the default jdbc authentication type. |
|
zeppelin.jdbc.precode |
Enter the snippet of code that executes after the initialization of the interpreter. |
|
zeppelin.jdbc.concurrent.use |
Enter to enable or disable concurrent use of JDBC connections. Enter “true” or “false”. |
|
zeppelin.jdbc.keytab.location |
Enter the keytab location. |
You can link the credentials (a wallet and a password) to jdbc interpreter variant to enable secure data access. This linking enables the jdbc interpreter to securely connect to the specified Oracle DB. For more information, see Managing Credentials.
To link the wallet credentials to jdbc interpreter, follow these steps:
1. Configure the following parameters in the jdbc interpreter as follows:
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
default.url |
If you want to use the Oracle wallet credentials, you must enter the alias name in the following format: jdbc:oracle:thin:@<alias_name> |
|
default.password |
This value can be null if you have entered the alias name in the default.url parameter for the jdbc interpreter. |
1.
2. Configure the other parameters in the jdbc interpreter as given in Configuring jdbc Interpreter Variant.
3. Link the wallet credentials to the jdbc interpreter variant. For more information, see Linking Credentials to Interpreter Variants.
The configurations for the md interpreter are given as follows:
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
markdown.parser.type |
Enter the markdown parser type. |
The configurations for the pgql interpreter are given as follows:
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
graphviz.formatter.class |
Indicates the class which implements the formatting of the visualization output. For example: oracle.datastudio.graphviz.formatter.DataStudioFormatter |
|
graphviz.driver.class |
The class which implements the PGQL driver. For example: oracle.pgx.graphviz.driver.PgxDriver |
|
base_url |
Enter the base URL of the PGX server in this field. For example: http://<HOSTNAME>:7007 |
|
zeppelin.interpreter.output.limit |
Indicates that the output message from interpreter exceeding the limit will be truncated. For example: 102,400 |
The configurations for the pgx-algorithm interpreter are given as follows:
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
graphviz.formatter.class |
Indicates the class which implements the formatting of the visualization output. For example: oracle.datastudio.graphviz.formatter.DataStudioFormatter |
|
graphviz.driver.class |
The class which implements the PGQL driver. For example: oracle.pgx.graphviz.driver.PgxDriver |
|
base_url |
Enter the base URL of the PGX server in this field. |
The configurations for the pgx-java interpreter are given as follows:
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
graphviz.formatter.class |
Indicates the class which implements the formatting of the visualization output. For example: oracle.datastudio.graphviz.formatter.DataStudioFormatter |
|
graphviz.driver.class |
The class which implements the PGQL driver. For example: oracle.pgx.graphviz.driver.PgxDriver |
|
base_url |
Enter the base URL of the PGX server in this field. |
|
zeppelin.interpreter.output.limit |
Indicates that the output message from interpreter exceeding the limit will be truncated. For example: 102,400 |
The configurations for the pgx-java interpreter are given as follows:
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
zeppelin.pyspark.python |
Indicates the Python binary executable to use for PySpark in both driver and workers. The default value is python. For example: python |
|
zeppelin.pyspark.useIPython |
Set to true to use IPython, else set to false. |
The configurations for the spark interpreter are given as follows:
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
pgx.baseUrl |
Enter the pgx.baseUrl URL in this field. This is the location where the data is pushed. For example: http://<HOSTNAME>:7007 |
|
spark.executor.memory |
Enter the amount of memory to use for the executor process. |
|
spark.master |
Enter the cluster manager to connect to. For example: local[*] |
|
spark.yarn.archive |
Enter the archive containing the required Spark jars for distribution to the YARN cache, to make Spark runtime jars accessible from the YARN side. |
|
spark.app.name |
Enter the name of the application. For example: Zeppelin |
|
zeppelin.spark.ui.hidden |
Set to true or false. |
|
zeppelin.spark.maxResult |
Enter the maximum number of results that must be fetched. |
|
spark.pyspark.python |
Enter the Python binary executable to use for PySpark in both driver and executors. For example: python |
|
zeppelin.spark.enableSupportedVersionCheck |
Set to true or false. |
|
args |
Enter the Spark command-line args. |
|
zeppelin.spark.useNew |
Set to true to use the new version of the SparkInterpreter. |
|
zeppelin.spark.useHiveContext |
Set to true to use HiveContext instead of SQLContext. |
|
zeppelin.spark.uiWebUrl |
This value overrides the Spark UI default URL. Note: The value must be a complete URL. |
|
zeppelin.spark.printREPLOutput |
Indicates to print the REPL output. |
|
spark.cores.max |
Enter the total number of cores to use. |