Assigning Objects
When you assign one object to another, you do not create a copy of the object, but only make a copy of the reference.
In the following example, &A1 and &A2 refer to the same object. The assignment of &A1 to &A2 does not allocate any database memory or copy any part of the original object. It makes &A2 refer to the same object to which &A1 refers.
Local Array of Number &A1, &A2;
&A1 = CreateArray(2, 4, 6, 8, 10);
&A2 = &A1;Image: Representation of two arrays
The following diagram shows how references of two arrays point to the same object.
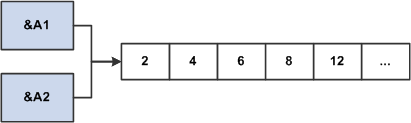
Image: Representation of two arrays with same content
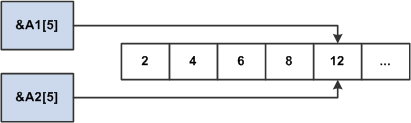
If the next statement
is &A2[5] = 12;, then &A1[5]
also equals 12, as shown in the following diagram:
The following example is not considered an object assignment:
Local number #
Local Array of Number &A1;
&A1 = CreateArray(2, 4, 6, 8, 10);
&NUM = &A1[3];&NUM is of data type Number, which is not an object type. If you later change the value of &NUM in the program, you will nott change the element in the array.