| Oracle® Communications EAGLE SIGTRAN User's Guide Release 46.6 E97352 Revision 1 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
| Oracle® Communications EAGLE SIGTRAN User's Guide Release 46.6 E97352 Revision 1 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
This section provides a basic overview of the steps involved to provision the IPGWx application for M3UA. For detailed procedures, see Database Administration - IP7 User's Guide of your current EAGLE documentation suite.
enable-ctrl-feat).rept-stat-iptps).ent-card).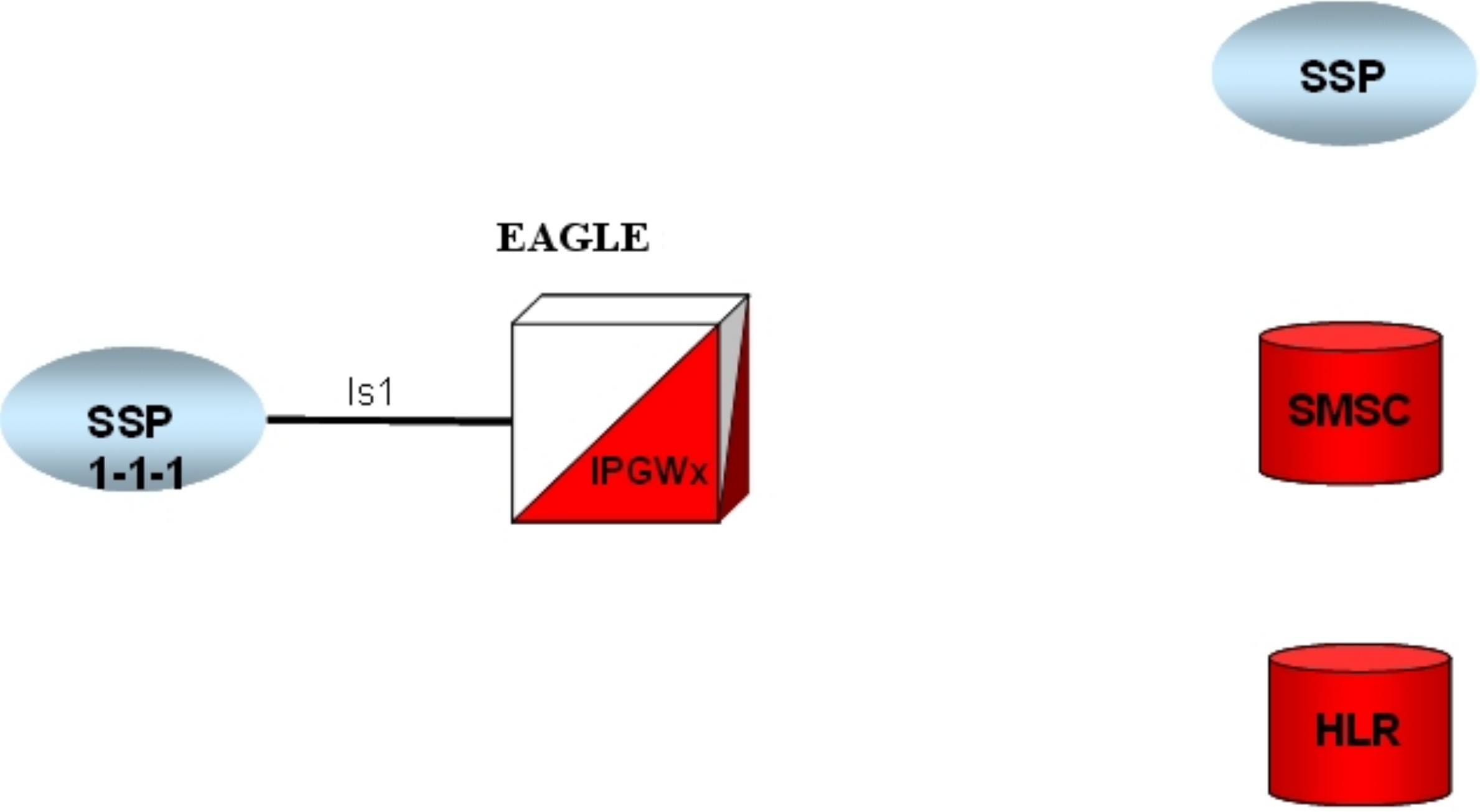
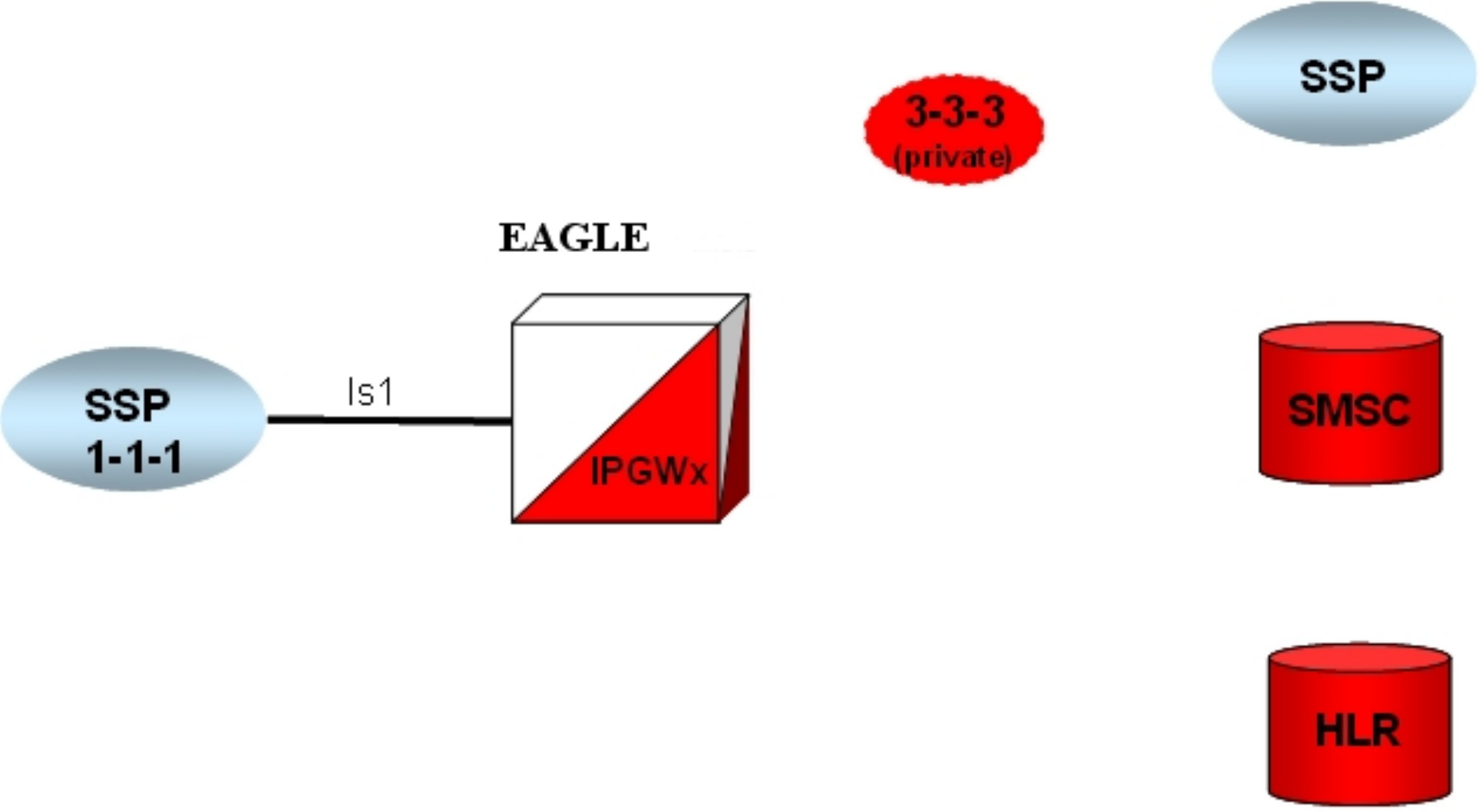
ent-dstn).To create a virtual IPGWx SS7 link, first create an SS7 linkset and an Adjacent Point Code (APC).
The adjacent node functionality for an IPGWx linkset is performed by the IPGWx software to provide SS7-to-IP interworking. For this reason, IPGWx APCs are referred to as “adjacent” point codes. Syntaxes that are normally not allowed for point codes, such as 0-0-1, are allowed for virtual adjacent point codes to minimize depletion of point code space. In addition, beginning with EAGLE 34.0, private point codes can be utilized (and are recommended by Oracle Communications) for IPGWx APCs. Private point codes are used for internal routing within the EAGLE and are not known outside of the EAGLE. By making APCs private, it is possible to have a point code value indicated as private and still have the same point code value (as not private) available for network configuration.
ent-ls).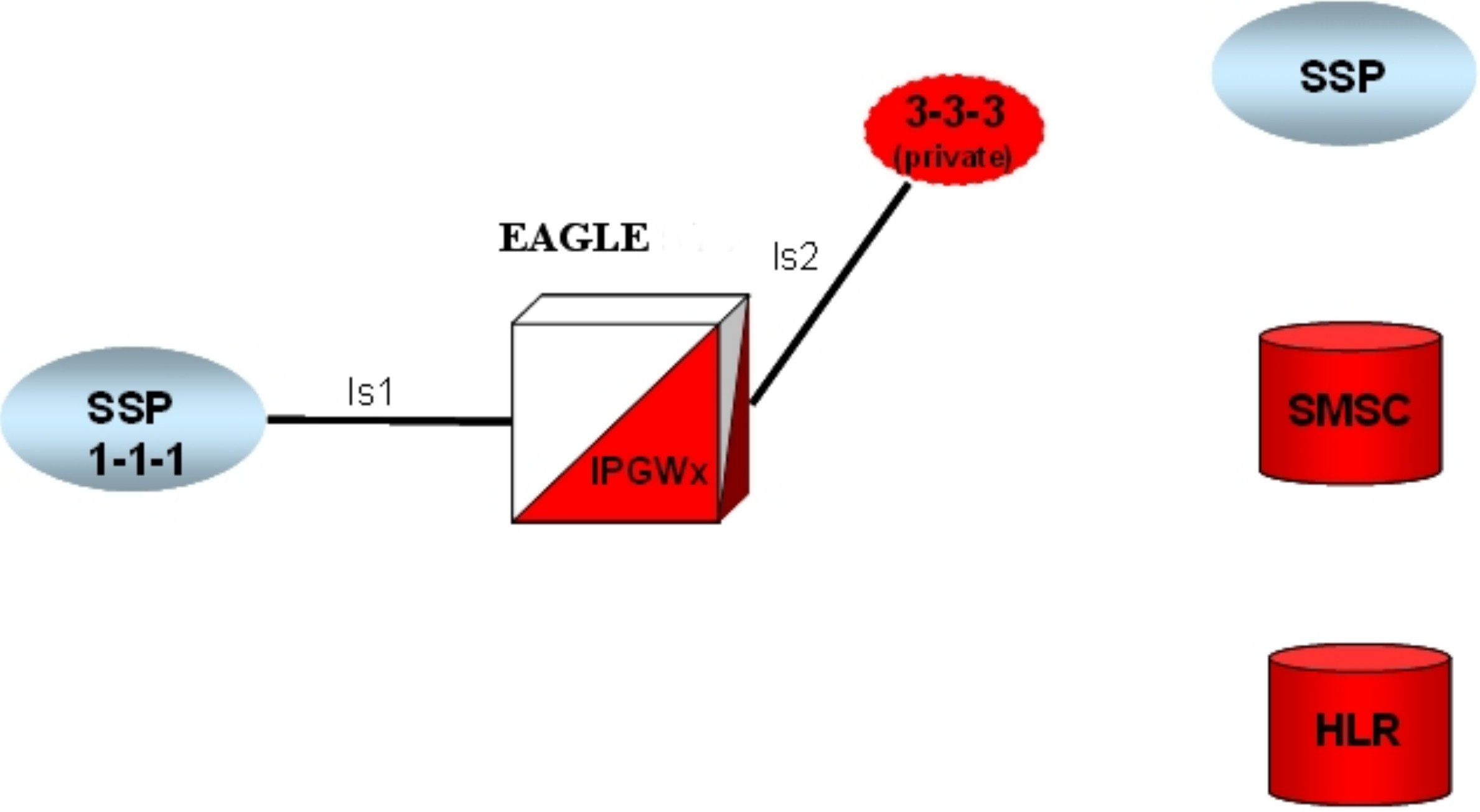
ent-slk).ent-dstn).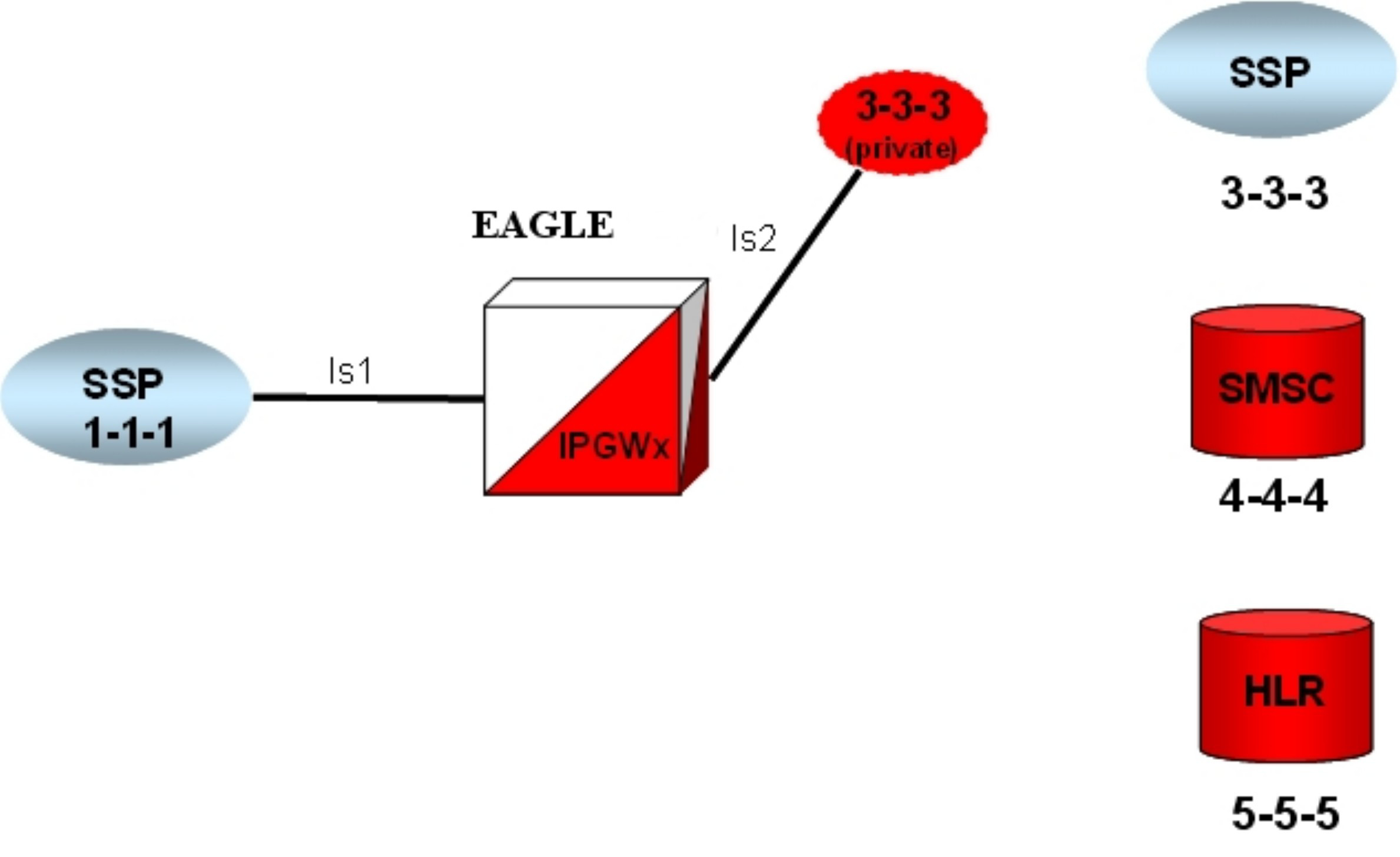
ent-rte).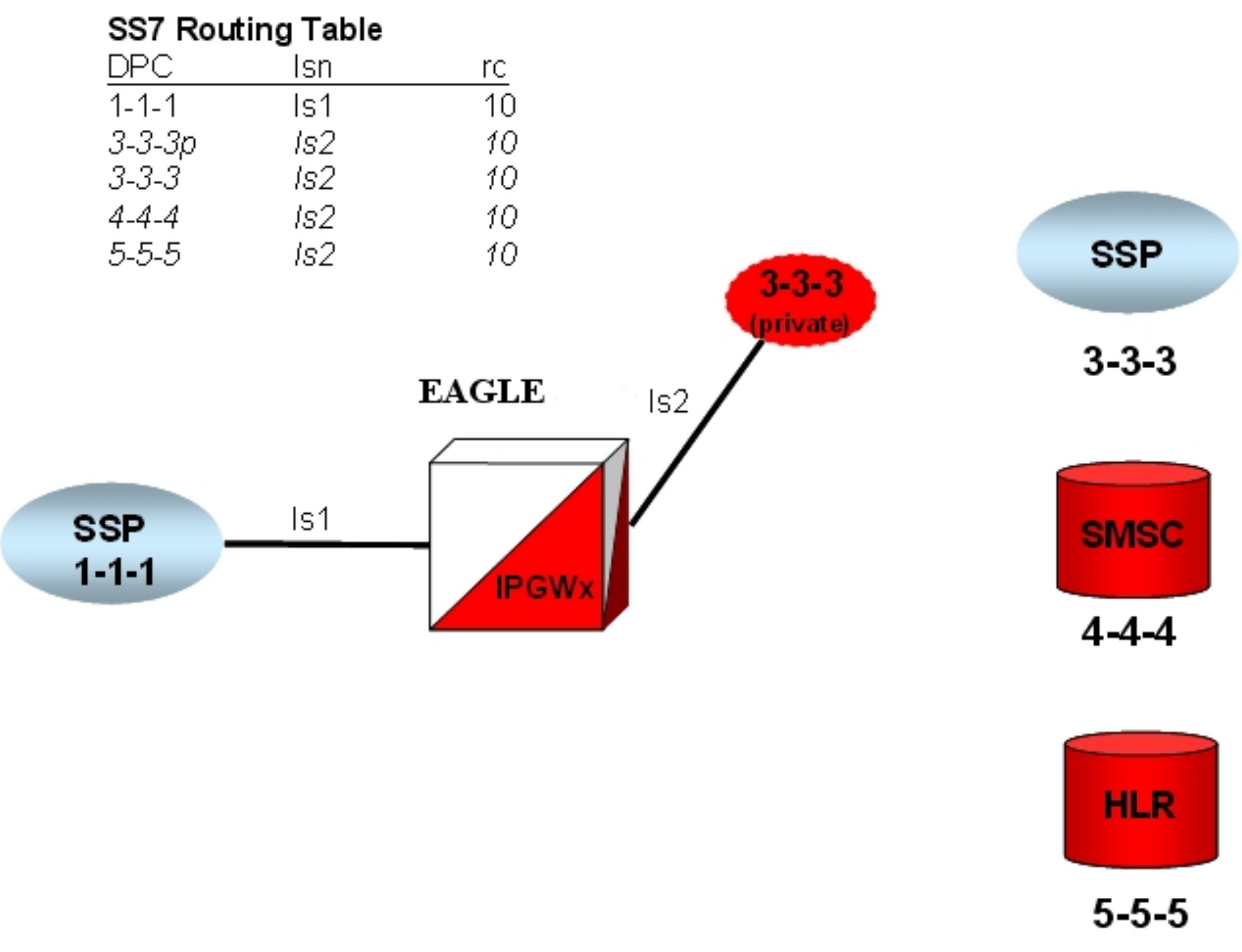
chg-ip-lnk).entip- host).chg-ip-card).ent-assoc).chg-ip-lnk).ent-assoc)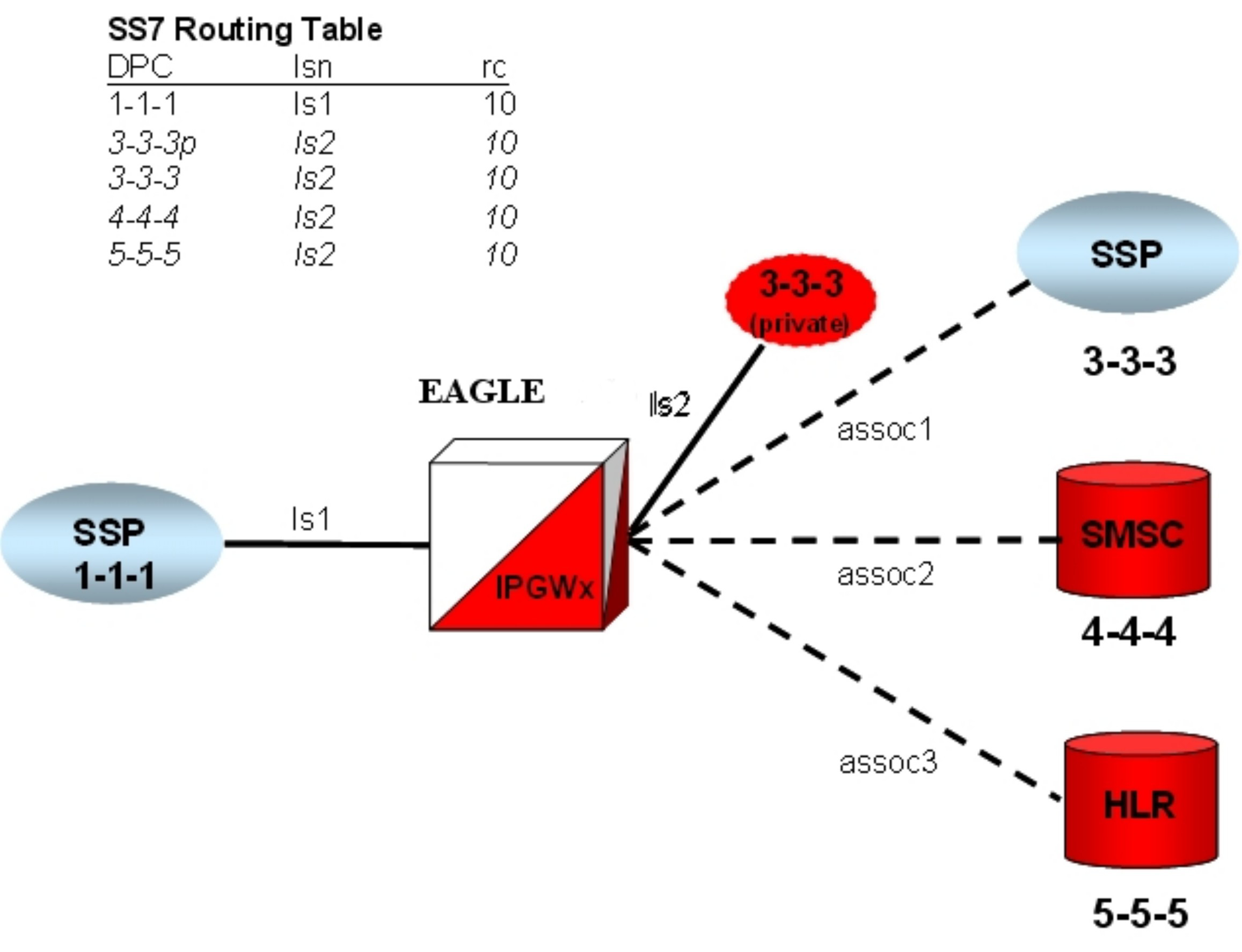
Multihomed end points are SCTP associations configured with both the LHOST and ALHOST parameters specified. In this case, the LHOST represents an IP address corresponding to one of the network interfaces (A or B) of the IP application card, while the ALHOST represents an IP address corresponding to the other network interface of the same IP application card.
This command includes the rmin and rmax parameters.
ent-assoc).ent-as).An Application Server is a logical entity serving a specific routing key or set of routing keys. The first ent-as command entered creates the Application Server, and subsequent ent-as commands add additional associations to the existing Application Server.
ent-na).alw-card).act-slk).