| Oracle® Communications EAGLE SIGTRAN User's Guide Release 46.6 E97352 Revision 1 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
| Oracle® Communications EAGLE SIGTRAN User's Guide Release 46.6 E97352 Revision 1 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
EAGLE can be deployed with completely redundant IP network paths, each of which must be capable of sustaining the worst-case traffic load. Either of these two methods can be applied, depending on the application used:
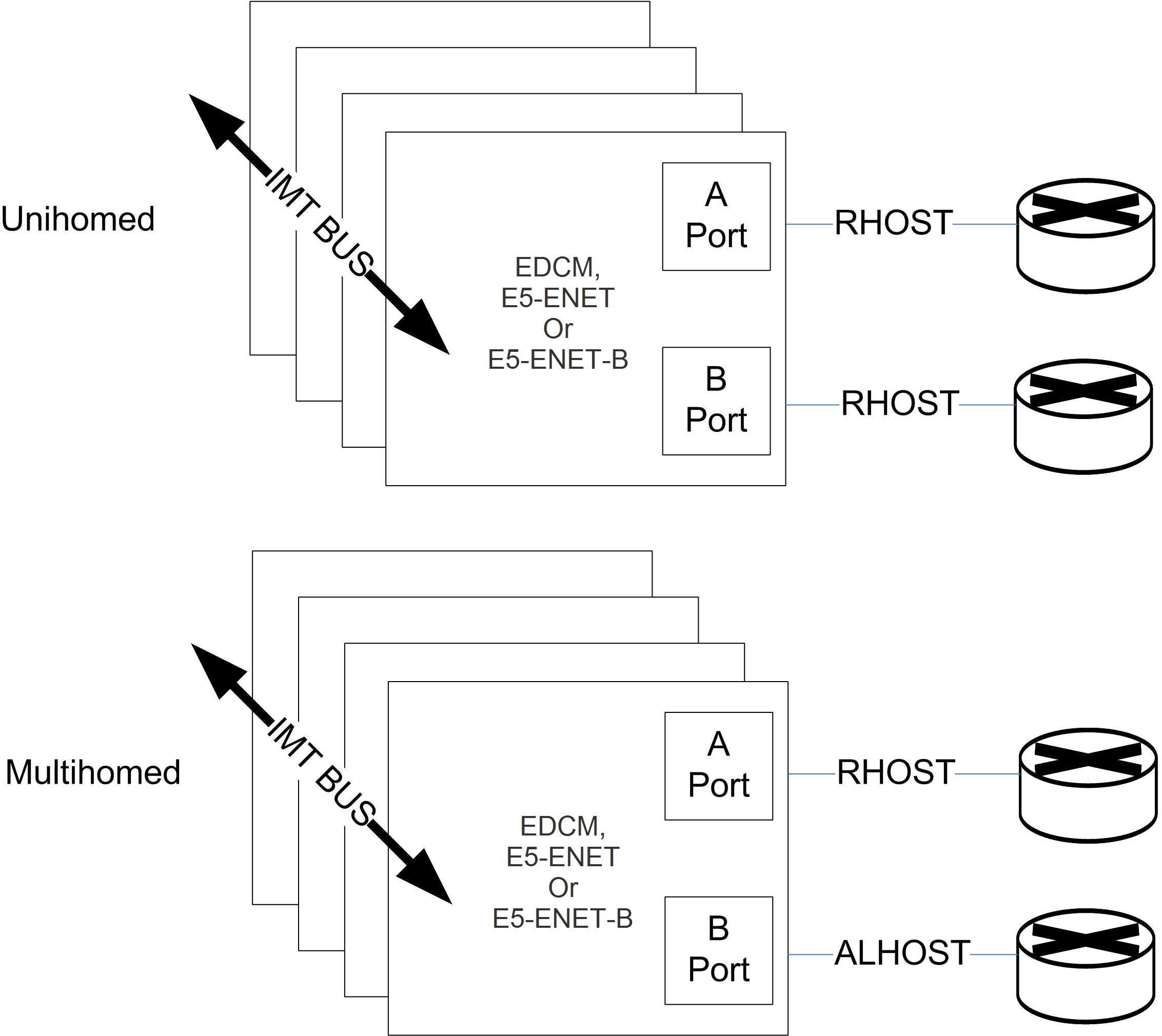
Unihoming
For unihoming, a set of IPLIMx or IPSG cards, which are configured for worst-case traffic load, hosts one signaling link per linkset. Each signaling link is assigned to a unihomed SCTP association, where half of the associations are assigned to one independent IP network path, and the other half are assigned to another independent IP network path. Each network path must have dedicated bandwidthsufficient to sustain the worst-case traffic load.
Multihoming
For multihoming, a set of IPLIMx or IPSG cards, which are configured for worst-case traffic load, is hosting one signaling link per linkset. Each signaling link is assigned to a multihomed SCTP association, which is mapped to an IP network having at least two completely redundant paths. Each network path must have dedicated bandwidth sufficient to sustain the worst-case traffic load.
Multihoming is very important for M3UA and SUA connections because it is the only means of lossless handover in the event of a path failure.
Multihoming provides network-level resilience for SCTP associations by providing information on alternate paths to a signaling end point for a single association.
SCTP multihoming supports only communication between two end points, of which one or both are assigned with multiple IP addresses on possibly multiple network interfaces. Each IPx card maintains a single static IP route table, utilized by both Ethernet interfaces or ports. By checking the destination address in this IP route table, the router determines the port from which the message is transmitted by the IPx card.
This means that it is not possible to have a route to a single destination from both ports of an IP card – it must be one port or the other. SCTP multihoming does not support communication ends that contain multiple end points (i.e., clustered end points) that can switch over to an alternate end point in case of failure of the original end point.
Figure 5-5 Unihoming versus multihoming
Multi-homing can be used for M2PA links if the M2PA linkset has only one link.
If the M2PA linkset has more than one link, then the value of the M2PA Timer T7 should be lower than RMIN * RTIMES in order for the MTP3 level to trigger a Change Over procedure for MTP3 links.
Note:
RMIN*RTIMES is the minimum time required for an association to restart due to the RTIMES retransmission (via the primary and alternate path in round robin fashion) for an association without receiving any SACK. If the association is closed before the T7 expiration, then the buffer is cleared before the Change Over procedure is triggered by the MTP3 level.