MSC Server-Assisted Mid-Call Feature Supported by CSS AS
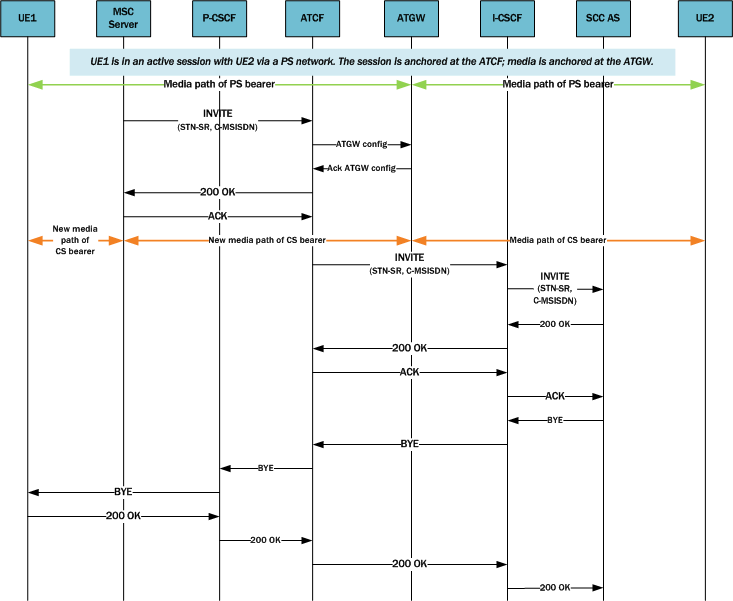
The following scenario assumes an active session between UA1 and UA2, and that UA1 attaches to the CS domain. It is also assumed that the CS-MGW supports the codecs used for LTE voice calls, minimizing the likelihood that the ATCF will need to instruct the ATGW to insert codecs.
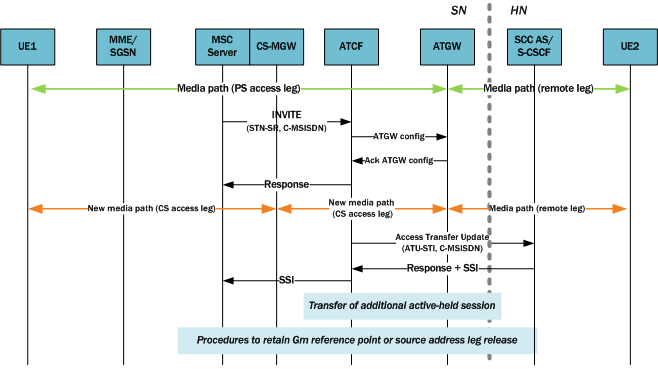
Upon receiving the Access Transfer message, the ATCF identifies the correct anchored session and proceeds with the transfer of the most recently active session. Using a Configure ATGW message, the ATCF replaces the existing PS access leg media path information with new CS access leg media path information for the ATGW. However, the ATCF might instruct the ATGW to continue using the local port of the PS access leg media path. Once the ATGW acknowledges the ATCF’s Configure message, the ATCF sends the MSC server an Access Transfer response and the media path is moved to the CS when receiving SDP information.
Voice break interruption starts either when media moves to the CS MGW (controlled by the MSC server enhanced for SRVCC) or when the UE relocates to the target—whichever comes first. When the UE tunes to the target or media switches to the CS MGW (whichever is last), the voice break interruption ends. The assumption is that media is switched to the CS MGW during the time to UE tunes to the target.
After receiving the Access Transfer message, the ATCF re-establishes communication with the SCC AS and updates the SCC AS. When the MSC server supports the mid-call feature, the ATCF also communicates this fact to the SCC AS. The ATU message initiates a new dialog between the ATCF and SCC AS, a dialog the SCC AS associates with the old dialog using the C-MSISDN. This new dialog is necessary because it replaces the old dialog set up over PS access, thereby assuring that if the PS user registration expires the new home leg will not be released or even affected.
The following shows a sample INVITE request the ATCF sends to the S-CSCF. Note the following:
- The Request-URI header contains the ATU-STI, as routed to the SCC AS.
- The Target dialog header specifies the existing dialog is associated with this request.
- The P-Asserted-Identity header reflects the C-MSISDN of the UE being served.
- The From header reflects the C-MSISDN of the serving UE.
- The SDP reflects the media information at the ATGW.
INVITE sip:AUT-STI1@sccas.home1.net SIP/2.0 Via: SIP/2.0/UDP msc1.visit1.net;branch=z9hG4bk731b87 Max-Forwards: 70 P-Asserted-Identity: <tel:+1-237-555-2222> P-Charging-Vector: icid-value="AyretyU0dm+602IrT5tAFrbHLso=023551024";orig-ioi=visit1.net Privacy: none From: <tel:+1-237-555-9999>;tag=171828 To: <tel: +1-237-555-4444> Call-ID: cb03a0s09a2sdfg1kj490334 Cseq: 127 INVITE Supported: 100re1, precondition, gruu Target-Dialog: me03a0s09a2sdfgjk1491777; to-tag=774321; from-tag=64727891 Accept-Contact: *;+g.3gpp.icsi-ref="urn%3Aurn-7%3gpp-service.ims.icsi.mmtel" P-Asserted-Service: urn:urn-7:3gpp-service.ims.icsi.mmtel Contact: <sip:msc1.home1.net;gr=urn:uuid:f81d4fae-7dec-11d0-a765-00a0c91e6bf6>;+g.3gpp.icsi-ref="urn%3Aurn-7%3gpp-service.ims.icsi.mmtel" Allow: INVITE, ACK, CANCEL, BYE, PRACK, UPDATE, REFER Content-Type: application/sdp Content-Length: (...) v=0 o=- 2987933615 2987933615 IN IP6 5555::aaa:bbb:ccc:ggg s= c=IN IP6 5555::aaa:bbb:ccc:ggg t=0 0 m=audio 3456 RTP/AVP 97 96 a=tcap:1 RTP/AVPF a=pcfg:1 t=1 b=AS:25.4 a=curr:qos local sendrecv a=curr:qos remote none a=des:qos mandatory local sendrecv a=des:qos none remote sendrecv a=rtpmap:97 AMR a=fmtp:97 mode-set=0,2,5,7; mode-change-period=2 a=rtpmap:96 telephone-event a=maxptime:20
The SCC AS sends the ATCF a confirmation, including the session state information (SSI) if the SCC AS and the MSC server support the mid-call feature. The MSC server receives the SSI from the ATCF; the access leg for the control has moved to the CS access. When MSC server receives SSI for more multiple active or inactive speech sessions, it initiates transfer directed at the SSC AS for the additional sessions.
The following diagram shows a call session in the active phase for MSC server assisted midcall feature when supported by the SCC AS.