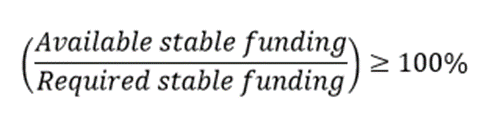
Net Stable Funding Ratio (NSFR) is one of the two minimum standards developed to promote funding and liquidity management in financial institutions. NSFR assesses the bank’s liquidity risks over a longer time horizon. Both the standards, complement each other, are aimed at providing a holistic picture of a bank’s funding risk profile, and aid in better liquidity risk management practices.
Topics:
· Overview
· Preconfigured USFED Regulatory NSFR Scenarios
NSFR is defined as the amount of available stable funding relative to the required stable funding. Available stable funding refers to the portion of capital and liabilities expected to be reliable over the horizon of 1 year. Required stable funding refers to the portion of assets and off-balance sheet exposures over the same horizon. The NSFR ratio is expected to be at least 100%.
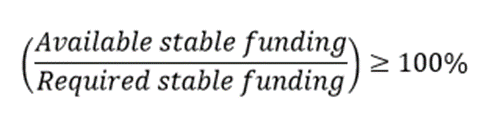
The NSFR ratio is expected to be at least 100%.
The Available Stable Funding (ASF) factor and Required Stable Funding (RSF) factor is applied through business assumptions and reflects through the execution of a Business as Usual (BaU) run in the application. The ASF and RSF factors are applied as weights at the account level with the Total ASF and Total RSF obtained by taking a sum of the all the weighted amounts. The ratio is then computed by the application as the (Total ASF amount)/(Total RSF amount). A set of pre-defined business assumptions for ASF and RSF as defined in the NSFR guidelines are prepackaged in the application. See Regulation Addressed through Business Assumptions for the complete list of pre-seeded ASF and RSF assumptions. The process flow is defined as follows:
Topics:
· Computing Available Amount of Stable Funding
· Computing Required Amount of Stable Funding
Maturity bucket of the instrument is one of the various dimensions used to allocate ASF and RSF factors. For NSFR computation, maturity bands are used to allocate the factors. The US FED NSFR band is pre-defined as per regulatory guidelines and has the following values:
· Less than 6 months
· Greater than or equal to 6 months but less than 1 year
· Greater than or equal to one year
· Open maturity
All accounts are categorized as one of the above bands depending on the maturity date. To categorize any product as open maturity, the Rule "LRM - Classification of Products as Open Maturity" must be edited and the product is included in the rule.
The available stable funding factor is a pre-determined weight ranging from 0% to 100% that is applied through business assumptions for the accounts falling under the dimensional combinations defined. The weights are guided by the NSFR standard. The available stable funding is taken as total of all the weighted amounts where an ASF factor is applied.
Foreign bank branches can account for the undrawn contractual committed facilities from its head office or other branches which are the same entity and are regional hubs as ASF up to 40% of the minimum ASF required to meet the minimum requirement of NSFR.
The formula to calculate the Available Amount of Stable Funding is:

An example of the application of the ASF factor is as follows:
Consider an assumption defined with the following dimensional combination and ASF factors, with the Based On the measure being Total Stable Balance:
Dimensional Combination |
ASF Factor |
||
|---|---|---|---|
Product |
Retail/Wholesale Indicator |
Residual Maturity Band |
|
Deposits |
R |
Less than or equal to six months |
95% |
Deposits |
R |
six months - one year |
95% |
Deposits |
R |
Greater than or equal to one year |
95% |
If there are five accounts with this dimensional combination, the resulting amounts after the assumption is applied with application of ASF factors is as follows.
Account |
Stable Balance |
ASF Weighted Amount |
|---|---|---|
A1 |
3400 |
3230 |
A2 |
3873 |
3679.35 |
A3 |
9000 |
8550 |
A4 |
1000 |
950 |
A5 |
100 |
95 |
NOTE:
LRRCUSFR application does not compute ASF items, such as: Tier 1 and Tier 2 capital, deferred tax liabilities, and minority interest. These items are downloaded from the OFS Basel application. By updating the latest Basel Run Skey as a setup parameter, the LRRCUSFR application picks up the respective standard accounting head balances and applies the respective ASF factors.
If OFS Basel is not installed, the following items must be provided as a download in the FCT_STANDARD_ACCT_HEAD table.
· Gross Tier 2 Capital
· Deferred Tax Liability related to Other Intangible Asset
· Deferred Tax Liability related to Goodwill
· Deferred Tax Liability related to MSR
· Deferred Tax Liability related to Deferred Tax Asset
· Deferred Tax Liability related to Defined Pension Fund Asset
· Net CET1 Capital post-Minority Interest Adjustment
· Net AT1 Capital post-Minority Interest Adjustment
· Total Minority Interest required for NSFR
The required stable funding factor is a pre-determined weight ranging from 0% to 100% which is applied through business assumptions for the accounts falling under the defined dimensional combinations. The weights are guided by the NSFR standard. The required stable funding is considered as sum of all the weighted amounts where an RSF factor is applied.
The required stable funding factor is a weight function and is applied similar to the ASF. The formula to calculate the Required Amount of Stable Funding is as follows:

Off balance sheet items are considered under the RSF factor and are given the appropriate factor as guided. Some combinations in line of credit have a pre-defined RSF factor as guided and available as pre-seeded assumptions. Other off balance sheet products such as Variable Rate Demand Notes (VRDN) and Adjustable Rate Notes (ARN) do not have pre-defined factors and are left to the discretion of the jurisdictions. For such products, the user can define assumptions and apply desired RSF factors as applicable.
Derivatives are handled through the application of both ASF and RSF factors as applicable. They can behave as either an asset or a liability, depending on the marked to market value. The application of factors on derivatives is done on the market value after subtracting the variation margin posted/received against the account. The computation is described below:
1. NSFR derivative liabilities = Derivative liabilities - (Total collateral posted as variation margin against the derivative liabilities)
2. NSFR derivative assets = Derivative assets - (Cash collateral received as variation margin against the derivative assets)
3. The factors are applied as follows:
§ ASF factor application
ASF amount for derivatives = 0% * Max ((NSFR derivative liabilities -NSFR derivative assets), 0)
§ RSF factor application
RSF amount for derivatives = 100% * Max ((NSFR derivative assets- NSFR derivative liabilities), 0)
Derivative liabilities are derivative accounts with market value as negative. Derivative assets are derivative accounts with market value as positive. Apart from the variation margin, the initial margin against derivative contracts is also treated with the appropriate factor.
Some covered companies do not require to maintain a 100% NSFR and can maintain a lower ratio. For such companies, the Rule LRM - Determining RSF Factor Percentage for the Modified NSFR, multiplies the RSF by the specified percentage in the Rule.
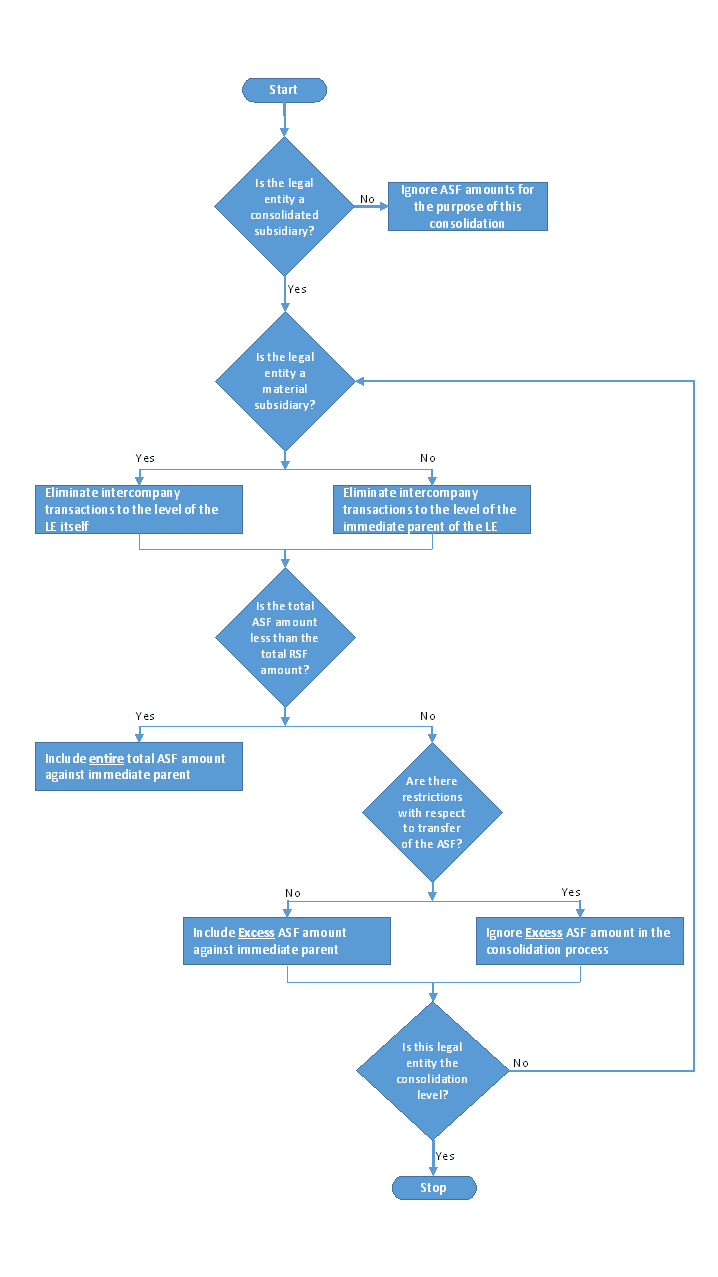
A consolidated NSFR is computed for a parent legal entity by considering transferability restrictions and material aspects of the legal entity. The process is as illustrated in the following flowchart.
Figure 39: NSFR Consolidation Process
The Net Stable Funding Ratio is calculated as follows:
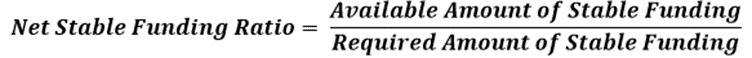
OFS LRRCUSFR supports out-of-the-box US FED NSFR assumptions according to US Federal Reserve guidelines.
The following table lists the Document Identifiers provided in the column Regulatory Reference of Regulations Addressed through Business Assumptions.
Regulation Reference Number |
Document Name |
Issued Date |
|---|---|---|
12 CFR Part 249 |
Net Stable Funding Ratio: Liquidity Risk Measurement Standards and Disclosure Requirements |
May 2016 |
NOTE:
This section gives only the contextual information about all the business assumptions. For more detailed information refer to OFS LRS application (UI).
The application supports multiple assumptions with preconfigured assumptions and scenarios based on regulator specified NSFR scenario parameters. The list of preconfigured business assumptions and the corresponding reference to the regulatory requirement that it addresses is provided in the following table:
Sl. No. |
Assumption Name |
Assumption Description |
Regulatory Requirement Addressed |
Regulatory Reference: Federal Reserve-12 CFR Part 249 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
[Fed]-Regulatory Capital Elements |
Common Equity Tier 1, Additional Tier 1, and Tier 2 capital prior to the application of capital adjustments or deductions. |
This assumption specifies factors for Tier 1 and Tier 2 capital, before the application of capital deductions and excluding the proportion of Tier 2 instruments with residual maturity of less than one year. |
Paragraph II-C-3(a) and K.104 |
2 |
[Fed]-Stable Retail Deposits |
Stable Retail deposits held directly at a covered company. |
This set of assumptions specifies factors for Retail Deposits based on whether it is brokered or not and if brokered-based on the type of brokered deposit such as Reciprocal, sweep and other deposits. |
Paragraph
II-C-3(b, c, and d) |
3 |
[Fed]-Less Stable Retail Deposits |
Less Stable Retail deposits held directly at a covered company. |
||
4 |
[Fed]-Reciprocal brokered deposits |
Fully insured and uninsured Reciprocal Brokered Deposits. |
||
5 |
[Fed]-Brokered Sweep Deposits |
All types of Brokered sweep deposits including insured and uninsured accounts, affiliated and unaffiliated broker accounts. |
||
6 |
[Fed]-Other Brokered Deposits |
Brokered deposits which are neither reciprocal nor sweep deposits. |
||
7 |
[Fed]-Retail non deposit funding |
Retail Funding which is not in the form of deposits. |
This assumption specifies the factors for all funding other than deposits from Retail customers. |
Paragraph II-C-3(e.) |
8 |
[Fed]-Non operational balances from non financial customers |
Non-operational funding received from wholesale customers who are not financial entities or consolidated entities of a financial entity and which matures within 6 months. |
This set of assumptions specifies the factors for deposits from wholesale customers based on operational deposit, type of wholesale counterparty, and secured/unsecured status. |
Paragraph
II-C-3(d) |
9 |
[Fed]-Non operational CF from non financial customers |
Non-operational funding received from wholesale customers who are not financial entities or consolidated entities of a financial entity and which matures beyond 6 months. |
||
10 |
[Fed]-Operational balances from wholesale customers |
Operational funding received from all types of wholesale customers and which matures within 6 months. |
||
11 |
[Fed]-Operational CF from wholesale customers |
Operational funding received from all types of wholesale customers and which matures beyond 6 months. |
||
12 |
[Fed]-Non operational balances from financial customers |
Non-operational funding received from wholesale customers who are either financial entities or consolidated entities of a financial entity and which matures within 6 months. |
||
13 |
[Fed]-Non operational CF from financial customers |
Non-operational funding received from wholesale customers who are either financial entities or consolidated entities of a financial entity and which matures beyond 6 months. |
||
14 |
[Fed]-Secured deposits and other funding from wholesale customers |
Secured funding received from wholesale customers and which matures within 6 months. |
||
15 |
[Fed]-Secured deposits and other funding from wholesale customers-CF |
Secured funding received from wholesale customers and which matures beyond 6 months. |
||
16 |
[Fed]-Long term liabilities |
Deposits and Borrowings with a remaining term to maturity of greater than 1 year as prescribed in the US NSFR guidelines. |
This assumption specifies the factor for long term funding from wholesale customers. (Maturity beyond one year). |
Paragraph II-C-3(a) and K.104 |
17 |
[Fed]-Issued Securities |
Securities issued by the covered company. |
This assumption specifies the factor for securities issued by the covered company. |
Paragraph II-C-3(a, d and e.) |
18 |
[Fed]-Trade date payables |
Trade date payables that result from purchases by a covered company of financial instruments, foreign currencies, and commodities. |
This assumption specifies the factor for trade date payables. |
Paragraph
II-C-3( e.) |
19 |
[Fed]-Deferred Tax liabilities |
Deferred Tax Liabilities. |
This assumption specifies the factor for deferred tax liabilities. |
|
20 |
[Fed]-Cash and cash items in process of collection |
Coins, banknotes, cash, restricted cash, and cash items in process of collection, such as bank drafts and cheques. |
This assumption specifies factors for coins, banknotes, cash, and restricted cash held by the bank. |
Paragraph
II-D-3(a) (i) |
21 |
[Fed]-Central bank reserves |
All central bank reserves, including, required reserves and excess reserves. |
This assumption specifies factor for Central bank reserves. |
|
22 |
[Fed]-Trade date receivables |
Trade date receivables that result from the sale of financial instruments, foreign currencies, and commodities. |
This assumption specifies the factor for trade date receivables. |
Paragraph II-D-3(a) (i) |
23 |
[Fed]-Claims on central banks |
Unencumbered loans and other claims on central banks. |
This set of assumptions specifies factors for claims on Central banks. |
Paragraph
II-D-3(a) (i) |
24 |
[Fed]-Encumbered claims on central banks |
Encumbered loans and other claims on central banks. |
||
25 |
[Fed]-Unencumbered Level 1 assets |
Unencumbered assets that qualify for inclusion in Level 1 of High quality liquid assets as defined in the LCR. |
This set of assumptions specifies factors for unencumbered and encumbered high-quality liquid assets. |
Paragraph
II-D-3(a) (ii),(iv) and (v) |
26 |
[Fed]-Unencumbered Level 2A and 2B assets |
Unencumbered assets that qualify for inclusion in Level 2A and 2B of High quality liquid assets as defined in the LCR. |
||
27 |
[Fed]-Encumbered Level 1 assets |
The encumbered portion of assets which qualify for inclusion in Level 1 of High quality liquid assets as defined in the LCR. |
||
28 |
[Fed]- Encumbered Level 2 assets |
The encumbered portion of assets which qualify for inclusion in Level 2A and 2B of High quality liquid assets as defined in the LCR. |
||
29 |
[Fed]-Loans to FI secured by Level 1 asset |
Unencumbered loans to financial institutions where the loan is secured against Level 1 assets as defined in the LCR. |
This set of assumptions specifies factors for loans to financial parties based on encumbrance and maturity. |
Paragraph
II-D-3(a) (vi), (vii) |
30 |
[Fed]-Encumbered loans to FI secured by Level 1 asset |
Encumbered loans to financial institutions where the loan is secured against Level 1 assets as defined in the LCR. |
||
31 |
[Fed]-Loans to FI secured by other assets |
Unencumbered loans to financial institutions where the loan is secured against assets belonging to levels other than Level 1, as defined in the LCR. |
||
32 |
[Fed]- Encumbered loans to FI secured by other assets |
Encumbered loans to financial institutions where the loan is secured against assets belonging to levels other than Level 1, as defined in the LCR. |
||
33 |
[Fed]-Unsecured loans to financial institutions |
Unencumbered unsecured loans to financial institutions. |
||
34 |
[Fed]- Encumbered unsecured loans to FI |
Encumbered unsecured loans to financial institutions. |
||
35 |
[Fed]-Loans to other parties maturing in 1year |
Unencumbered loans with residual maturity less than a year to other counterparties that is Nonfinancial corporates, retail and small business customers, sovereigns, Public sector enterprises, and sovereigns. |
This set of assumptions specifies factors for loans to non-financial parties based on encumbrance and maturity. |
Paragraph
II-D-3(a) (vi), (vii) |
36 |
[Fed]-Encumbered loans to other parties maturing in 1year |
Encumbered loans with residual maturity less than a year to other counterparties that is Non-financial corporates, retail and small business customers, sovereigns, Public sector enterprises, and sovereigns. |
||
37 |
[Fed]-Loans to other parties maturing beyond 1year |
Unencumbered loans with residual maturity beyond one year to other counterparties that is Non-financial corporates, retail and small business customers, sovereigns, Public sector enterprises, and sovereigns. |
||
38 |
[Fed]-Encumbered loans to others maturing beyond 1year |
Encumbered loans with residual maturity more than a year to other counterparties that is Non-financial corporates, retail and small business customers, sovereigns, Public sector enterprises, and sovereigns. |
||
39 |
[Fed]-Unencumbered residential mortgage loans |
Unencumbered residential mortgage loans which would qualify for a) 50% or lesser risk weight as per U.S. Capital Rules b) higher than 50% risk weight as per U.S. Capital Rules. |
This set of assumptions specifies factors for residential mortgage loans based on their risk weight. |
Paragraph
II-D-3(a) (vi),(vii) |
40 |
[Fed]-Encumbered residential mortgage loans |
Encumbered residential mortgage loans which would qualify for a) 50% or lesser risk weight as per U.S. Capital Rules b) higher than 50% risk weight as per U.S. Capital Rules. |
||
41 |
[Fed]-Operational balances with other banks |
Operational portion of encumbered deposits held at other financial institutions, for operational purposes. |
This set of assumptions specifies the factors for deposits held at other covered institutions. |
Paragraph
II-D-3(a) (v) |
42 |
[Fed]-Non operational balances with other banks |
The non-operational portion of operational deposits held at other financial institutions. |
||
43 |
[Fed]- Encumbered balances with other banks |
Encumbered deposits held by the covered company at other financial institutions. |
||
44 |
[Fed]-Non HQLA assets |
Unencumbered securities which do not qualify as High-Quality Liquid Assets(HQLA) under the LCR Rule. |
This set of assumptions specifies factors for unencumbered and encumbered assets which are not HQLA. |
Paragraph
II-D-3(a) (v) (vii) |
45 |
[Fed]-Encumbered non HQLA assets |
Encumbered securities which do not qualify as High-Quality Liquid Assets(HQLA) under the LCR Rule. |
||
46 |
[Fed]- Derivative liabilities |
Potential valuation changes for derivative liabilities. |
This set of assumptions specifies factors for Derivatives. |
Paragraph 107(5) |
47 |
[Fed]- NSFR Derivative liabilities |
NSFR derivative liabilities, with consideration of the variation margin, posted. |
Paragraph 107(c and d) |
|
48 |
[Fed]- NSFR Derivative assets |
NSFR derivative assets along with consideration of variation margin received as cash. |
||
49 |
[Fed]-Credit and liquidity facilities extended to customers |
Off balance sheet exposures- Irrevocable and conditionally revocable credit and liquidity facilities offered to clients by the bank. |
This assumption specifies factors for credit and liquidity facilities extended to customers. |
Paragraph II-D-3(a) (ii) |
50 |
[Fed]-Initial margin for derivatives |
Initial margin provided by the covered company and the covered company's contributions to a central counterparty (CCP) mutualized loss-sharing arrangements. |
This set of assumptions treat initial and variation margin placed and received against derivatives. |
Paragraph 107(b-6) |
51 |
[Fed]-Variation margin received |
Variation margin received by the covered company whose RSF treatment is per the type of collateral received. |
Paragraph 107(b)(4) |
|
52 |
[Fed]-Commodities |
Unencumbered commodities held by the covered company. |
This set of assumptions specifies factors for commodities based on encumbrance. |
Paragraph
II-D-3(a) (vii) |
53 |
[Fed]-Encumbered commodities |
Encumbered commodities held by the covered company. |