2. Core Maintenances
2.1 Introduction
This chapter contains the following sections:
- Section 2.2, "Bank and Branch Core Parameters Maintenance"
- Section 2.3, "Maintaining Host Code"
- Section 2.4, "Local Holiday Maintenance"
- Section 2.5, "Country Code Maintenance"
- Section 2.6, "Currency Maintenance"
- Section 2.7, "Currency Holiday Maintenance"
- Section 2.8, "Floating Rates Definition"
- Section 2.9, "External Entities Maintenance"
- Section 2.10, "External Limit Entities Maintenances"
- Section 2.11, "Settlement Details Maintenance"
- Section 2.11, "Settlement Details Maintenance"
- Section 2.12, "MIS Details Maintenance"
- Section 2.13, "User Defined Fields Maintenance"
- Section 2.14, "Generic Interface Maintenance"
- Section 2.15, "Process Definition"
- Section 2.16, "Reporting Parameters Maintenance"
- Section 2.17, "Maintaining Amount Text"
- Section 2.18, "Dynamic Package - DML Execution"
2.2 Bank and Branch Core Parameters Maintenance
This section contains the following topics:
- Section 2.2.1, "Invoking Bank Core Parameters Maintenance Screen"
- Section 2.2.2, "Invoking Branch Core Parameter Maintenance Screen"
2.2.1 Invoking Bank Core Parameters Maintenance Screen
You can invoke ‘Bank Core Parameters Maintenance’ screen by typing ‘STDCRBNK’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking on the adjoining arrow button.
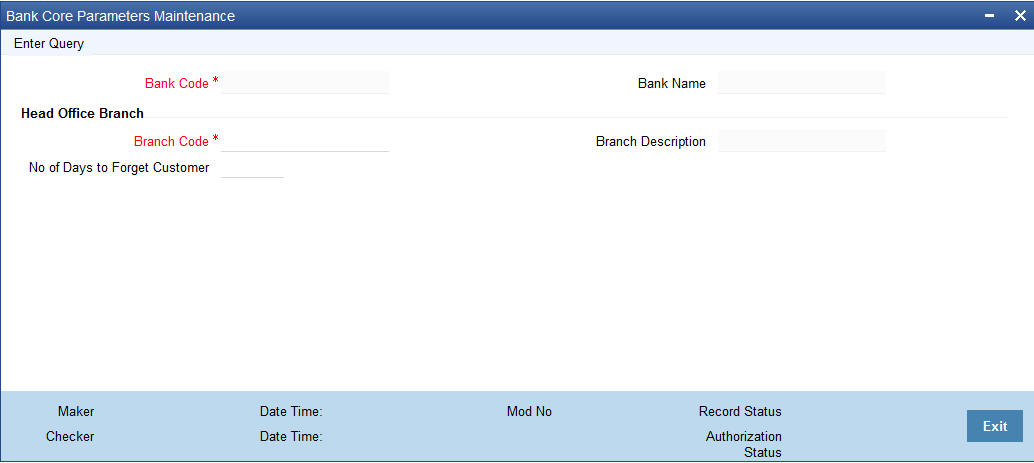
You can specify the following fields:
Bank Code
Specify the bank code.
Bank Name
The name of the bank is displayed here.
Head Office Branch
Branch Code
Specify the head office branch code.
Branch Description
The description of the branch is displayed here.
No. of days to Forget Customer
Enter the number of days, after which the system will forget the customer after they close their account. Once the customer is forgotten you can’t view the details of the customer.
Click “Execute Query”. The records matching the entered query criteria is displayed.
2.2.2 Invoking Branch Core Parameter Maintenance Screen
You can invoke ‘Branch Core Parameter Maintenance’ screen by typing ‘STDCRBRN’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking on the adjoining arrow button.
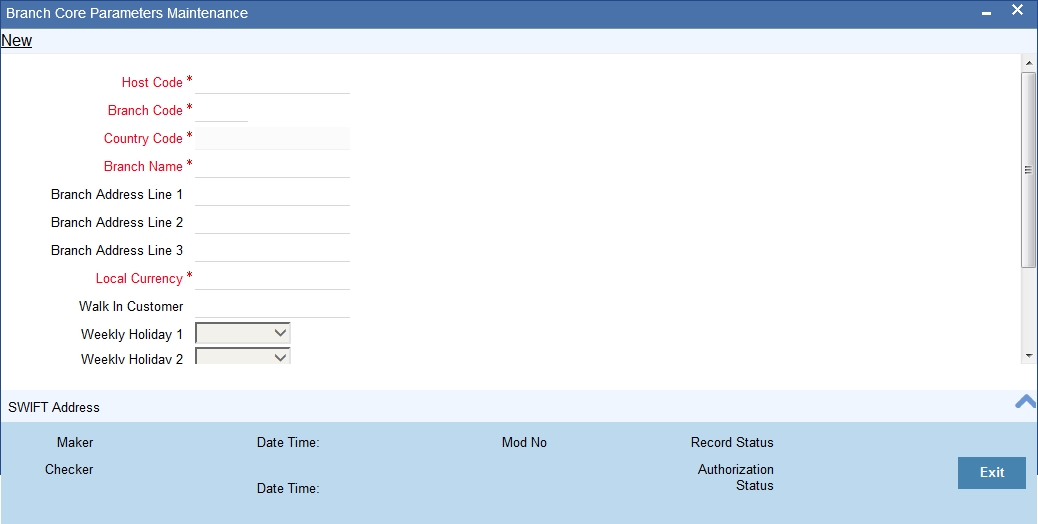
You can specify the following fields:
Host Code
Specify the host code here. Alternatively, you can also select the host code from the adjoining option list.
Branch Code
Specify the branch code here.
Country Code
Specify the country code here.
Branch Name
Specify the branch name here.
Branch Address
Specify the address of branch here.
Local Currency
Specify the local currency of the branch. Alternatively, you can also select the currency from the adjoining option list.
Walk in Customer
Specify the walking customer name here. Alternatively, you can also select the walk in customer name from the adjoining option list.
Weekly Holiday 1 & 2
Select the weekly holiday of the branch from the drop-down list. The list displays the following values:
- Sunday
- Monday
- Tuesday
- Wednesday
- Thursday
- Friday
- Saturday
Auto Authorization
Check this box to indicate that the branch allows auto authorization facility.
Host Name
Specifies the host name from which the customer is logged in.
Report DSN
Specify the Report DSN details.
Maintaining SWIFT Address Details
You can maintain SWIFT address details for the branch in the ‘SWIFT Address’ screen. Click “Swift Address” button to invoke the screen.
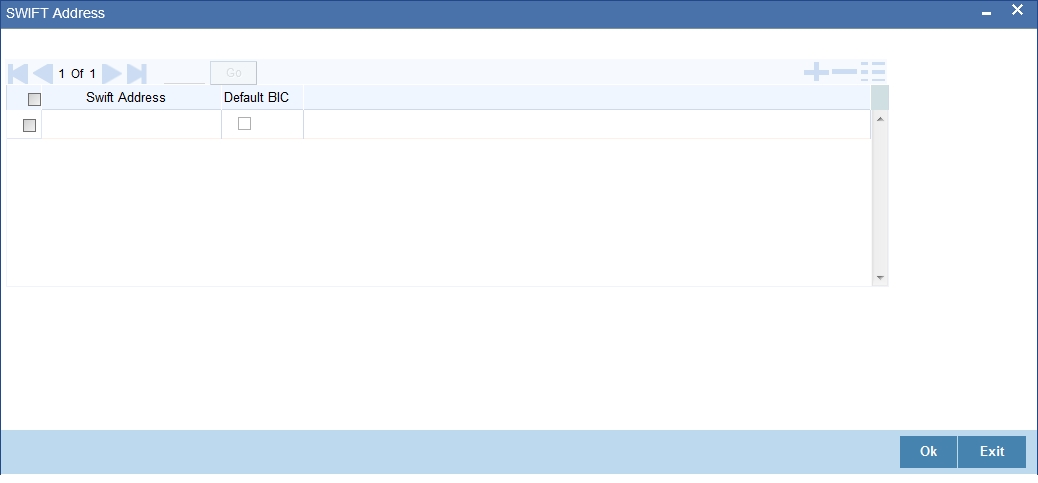
SWIFT Address
Specify the required SWIFT Address. Alternatively, you can also select the SWIFT address from the adjoining option list.
Default BIC
Check this box to use the default BIC.
2.3 Maintaining Host Code
You can group branches in the same zone or region under a Host for specific processing. You can have multiple hosts depending on processing requirements. These hosts can be maintained in Host Code Maintenance screen.
This section contains the following topics:
- Section 2.3.1, "Invoking Host Code Maintenance Screen"
- Section 2.3.2, "Viewing Host Code Maintenance Summary"
2.3.1 Invoking Host Code Maintenance Screen
You can invoke ‘Host Code Maintenance’ screen by typing ‘STDHSTCD’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking on the adjoining arrow button.
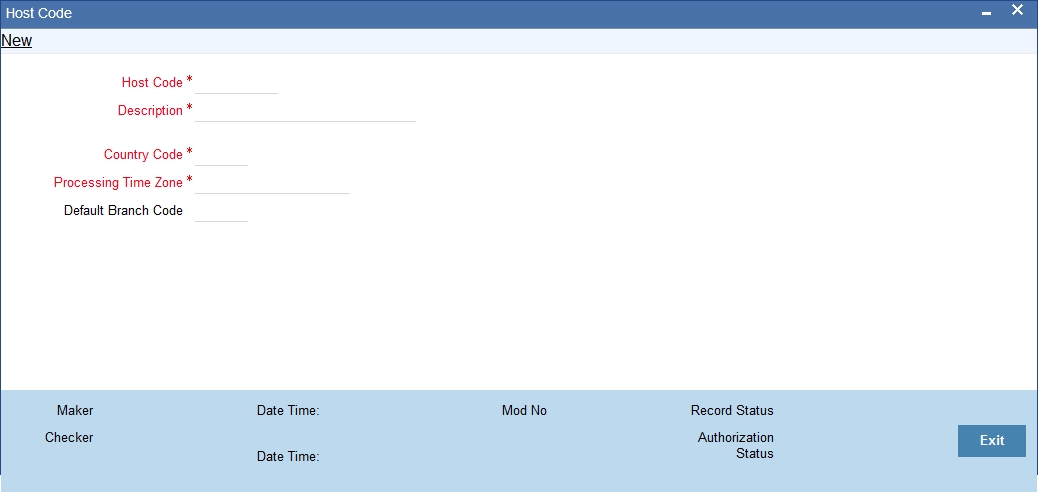
You can specify the following fields:
Host Code
Specify the processing zone that is applicable for the requests.
Host Description
Specify the description of the host code.
Country
Specify the required country code from the list.
Processing Time Zone
Specify the time zone that is used for processing the request. All open and authorized time zones are available in the list.
Default Branch
Specify the required branch code which indicates the main branch of the group of branches linked to the same host code. All valid branches are available in the list.
2.3.2 Viewing Host Code Maintenance Summary
You can invoke ‘Host Code Maintenance Summary’ screen by typing ‘STSHSTCD’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking on the adjoining arrow button.
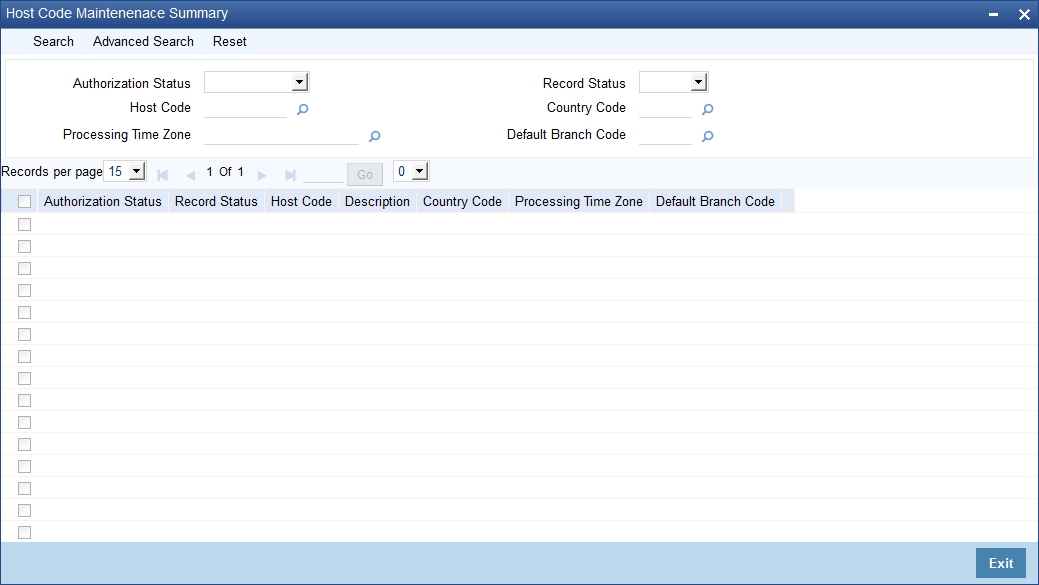
You can search using one or more of the following parameters:
- Authorization Status
- Record Status
- Host Code
- Country Code
- Processing Time Zone
- Default Branch Code
Once you have specified the search parameters, click ‘Search’ button. The system displays the records that match the search criteria for the following:
- Authorization Status
- Record Status
- Host Code
- Description
- Country Code
- Processing Time Zone
- Default Branch Code
2.4 Local Holiday Maintenance
For a year, you need to define your weekly holidays and your calendar year annual holidays. This is done in the ‘Local Holiday Calendar’ screen.
The system uses the information maintained in this screen to do the following:
- To check that the ‘value date’ of no Data Entry transaction falls on a holiday
- To check that the start date / maturing date and schedule date of a loans and deposit contract does not fall on a holiday
- To effect a date change on the system -- today’s date and the next working date
For any schedule / contract maturing at a future date, say, 5 years hence, you can input a future date, only if the calendar for that year has been maintained. It is not necessary to maintain the list of all annual holidays, for future, you can merely define all regular weekly holidays.
This screen is maintained for each branch, of your bank, from the respective branches; thus making it possible to have a different set of holidays for different branches of the bank.
This section contains the following topics:
2.4.1 Maintaining Local Holiday Calendar
Invoke the ‘Local Holiday Calendar’ screen, by typing ‘STDLOCHL’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
In this screen you can specify the weekly and also the annual holidays, for your branch, for any year between 1 AD and 4000 AD.
Steps to Define Yearly Holidays
To define holidays for a year, (for instance, for 2000) you have to do the following:
Building the calendar for the year
Step 1
Select ‘New’ from the Actions menu in the Application tool bar or click new icon
Step 2
Enter the year -- 2000 or move to the year 2000 using the arrows
Step 3
To build the calendar for the year, 2000 click the ‘Refresh’ button. This button is called the ‘refresh / build up’ button because it builds the calendar for you. Please note:
- On invoking the calendar of any year, you will notice that Saturdays and Sundays are marked as weekly holidays. This is the default setting of the system
- For identification, the working days are marked in black and the holidays in red
Defining Holidays
To define annual holidays, click on the particular date to mark the selected date as a holiday.
If you want to unmark a day specified earlier as a holiday, double click on it, once again. You will notice that the day gets marked in black.
2.4.2 Annual Holidays
These are the holidays you have defined for the year calendar on display
You will observe that all holidays are marked in red, while working days in black. (All unauthorised holiday dates appear against a blue background). To mark a date as a holiday, double click on it. In case you wish to undo a date marked off as a holiday, double click on it once again. It changes back to a working day.
With each modification you make, the Modification Number in the made by column below moves up serially.
2.5 Country Code Maintenance
This section contains the following topics:
2.5.1 Maintaining Country Name Details
You can define country name through the ‘Country Code Maintenance’ screen. You can invoke this screen by typing ‘’STDCNMNT’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
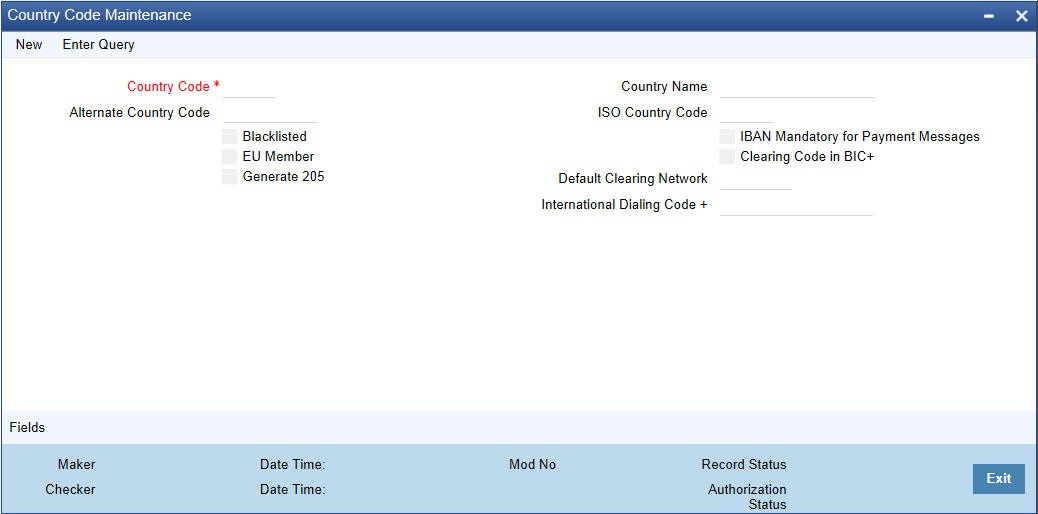
Here, you can capture the following details
Country Code
You can capture a unique three-character code to identify the country. For example: you can maintain USA as the country code for United States of America.
Alternate Country Code
You can also associate an alternate country code. This is for information purposes only and will not be printed on any customer correspondence.
For example you can have US as the alternate code for USA
Country Name
After you define an alphanumeric code to identify the country for which you would like to assign a name, you have to specify the name of the Country.
Blacklisted
Further, in the ‘Country Name Maintenance’ screen you can black list a country for further usage. You are not allowed to deal in countries that are blacklisted.
You can only deal with countries that are not blacklisted
IBAN Mandatory for Payment Messages
If this is checked, it indicates that for every payment message an IBAN is mandatory.
If this option is unchecked for a country, the system will not process the outgoing payments wherein the ordering customer or the beneficiary customer belongs to that country.
EU Member
This indicates whether the country is recognized by Swift as a part of the Intra European countries.
If you check this flag the instructed amount field should be mandatory in the generated 103, 103+ and 102 messages. The instructed amount field is mandatory in the incoming messages.
Clearing Code in BIC+
Check this box to indicate that the National ID in the BIC plus file is the clearing code. During upload of clearing codes from BIC plus file, the records that belong to countries against which this box is checked will be selected.
Generate 205
Check this box to indicate that the cover message 205COV or 205 need to be generated for transactions involving this country. If you do not select this option, RTGS, 202 or 202COV message will be generated.
For more details on 202COV and 205COV cover message formats, refer settlements user manual.
Default Clearing Network
Once the National ID from BIC plus directory is uploaded into clearing codes, the network will be populated as the default clearing network for that country. This is mandatory when clearing code in BIC+ is chosen as ‘Y’.
International Dialling Code
Specify the international dialing code associated with the country.
2.6 Currency Maintenance
This section contains the following topics:
- Section 2.6.1, "Maintaining Currency Definition"
- Section 2.6.2, "Maintaining Currency Position GL"
- Section 2.6.3, "Viewing Currency Summary Details"
- Section 2.6.4, "Maintaining Currency Pair"
- Section 2.6.5, "Viewing Currency Pair Summary"
- Section 2.6.6, "Maintaining Currency Rate Type"
- Section 2.6.7, "Maintaining Currency Exchange Rates"
- Section 2.6.8, "Viewing Exchange Rates"
2.6.1 Maintaining Currency Definition
In the ‘Currency Definition’ screen, you define the attributes of the currencies in which your bank can deal. For each currency, you can define attributes like, the SWIFT code for the currency, the country to which the currency belongs, the interest method, the spot days, the settlement days, etc.
Currencies can be maintained only at the Head Office. The list of currencies will be made available to the branches based on the currencies that have been defined for the country linked to that branch.
Invoke this screen by typing ‘ ‘CYDCDEFE’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
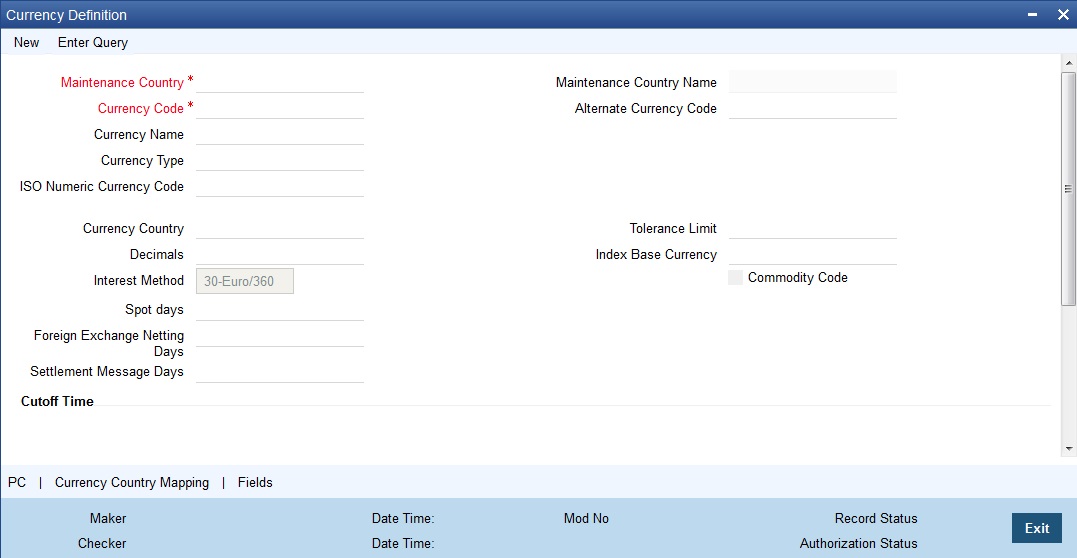
Maintaining Currency Details
Maintenance Country
Specify the country code for which the currency is maintained. Alternatively, you can select the country code from the option list. The list displays all the authorized and open country codes along with their description maintained in the system.
For example, if you maintain the country code for a bank or a branch, which is operating in Singapore for the currency USD, then you should specify the country code as SG. The system defaults the field ‘Country’ as US.
Maintenance Country Name
The system displays the name of the country for which the currency is maintained.
Currency Code
Currencies are identified in Oracle FLEXCUBE by the SWIFT codes assigned to them. The currency will be identified by this code in all transactions that involve it.
Currency Name
You can enter the detailed name of the currency in not more than thirty-five alphanumeric characters.
Currency Type
As per your bank’s requirement you can choose to classify currencies into different currency types. The bank can use its own discretion to decide the basis of classifying currencies into different currency types. A currency type can consist of a maximum of three characters.
Depending on the customer account mask maintained, the value in the currency type field would be used during the generation of customer account numbers through the Customer Accounts Maintenance screen.
If you have decided to include currency type as part of the customer account number (in the account number mask), then at the time of creating a new customer account number, you will need to select the currency of the account number being generated. In the option-list provided for currency, the currency code is displayed along with the associated currency type say, USD – 1, GBP – 2 etc. When the account number gets populated, it is the currency type that forms a part of the customer account number.
ISO Numeric Currency Code
Specify the currency code specified by the International Standardization Organization.
Country
After you have identified the currency, you should indicate the country to which the currency belongs. You can select a country code from the option list available.
Decimals
You can indicate the number of decimal units up to which the currency can be denominated. The number of decimals allowed for any amount in the currency can be:
0 - Currency with no decimals
2 - Currency with two decimals
3 - Currency with three decimals
Interest Method
You can indicate the interest rate to be used for transactions that involve this currency. The interest options available are:
- Actual/Actual
- 30(US)/360
- Actual/360
- 30(Euro)/365
- 30(US)/365
- Actual/365
- 30(Euro)/Actual
- 30(US)/Actual
- Actual/Actual
Select the interest method that should be used by default whenever the currency is used in transactions. While processing a transaction that involves this currency, the interest method defined for the currency is defaulted. You have the option to change it for a specific transaction.
However, if you do not specify an interest method for a transaction, the method defined for the currency will be used (For details refer to Annexure on Page 140).
Spot Days
The number of spot working days applicable for the currency is specified here.
For example, the tenor of an MM contract is as follows:
Value Date - 01/01/99
Maturity Date - 31/01/99
Contract Currency - USD
Contract Amount - 5000
For USD, the number of Spot Days is specified as: Spot Days - 3
For this contract, the payment advices will be sent on 28/01/96.
Foreign Exchange Netting Days
Oracle FLEXCUBE provides a facility wherein all transactions relating to a customer, meant to be settled on a particular day and are made before a specific cut off day are collated, netted and a single payment message is sent instead of individual messages for each payment. This cut off day can be parameterized and is called ‘Netting Days’. The number of FX netting days applicable for the specified currency is maintained here.
Note
The system will validate that the FX Netting days are lesser than or equal to the spot days.
Settlement Days
In this screen, you can specify the ‘Settlement Days’ for a currency. Settlement messages for the components of a contract (in the LC, BC, LD, MM, FX, and FT modules) will be generated according to the settlement days specified for the currency of the settlement account. The following example illustrates this.
For example, when maintaining the details of USD in the Currency screen, you specify the ‘Settlement Days’ as ‘2’. This implies that two working days prior to the settlement of a component through a USD account, a settlement message will be automatically generated if specified (when you run the Settlement Messages function at the end of day).
The settlement details of a contract are as follows:
Settlement Date: 06 May 1999
Settlement Account Currency: USD
Component: Principal
Settlement Message: Yes
Component Currency: GBP
When you generate the Settlement Messages function, at the end of day, on 04 May 1999, a settlement message for the Principal component of the contract will be generated.
You can run Settlement Messages function as part of EOD operations from the Application Browser to automatically generate settlement messages for contracts marked out for automatic liquidation.
The settlement day specification for a currency will determine the contracts that are picked up for settlement message generation.
Cut-off Time
The Currency Cut-off time refers to the time by which all transactions involving a currency should be generated. For a currency, you can indicate the cut-off hour and minute. This time should be expressed in the local time of the bank.
The maintenance of a cut-off time for a currency has particular reference to outgoing funds transfers involving it.
Cut-off days
You can also specify the cut-off days and time for payment transactions involving the currency.
For example, the value date of a funds transfer transaction (incoming payment) involving USD, is 3rd June 2001. The number of cut-off days specified for the currency is 2. This means that the payment must be received on or before 1st June 2001. If the payment is received on 1st June, it must be received before the cut-off time specified for USD.
If the USD cut-off time is 1200 hrs, then, if the payment is received on 1st June 2001, it must be received before 1200 hrs.
The cut-off time (in hours and minutes) that you maintain to be applicable for payment transactions involving a currency are applicable to the head office branch of your bank.
If the branches are in time zones other than the head office branch time zone, you must maintain the offset time applicable for each branch, in the Branch Parameters screen.
Note
Even when cut-off days and cut-off time for a currency have both been specified, the cut-off checks are performed for a funds transfer transaction only if specified as applicable for the product involved in the transaction.
Tolerance Limit
When you are maintaining an ‘In’ Currency, or the Euro, in the Currency Definition screen, you can define a ‘Tolerance Limit’ for it. The limit is expressed as a percentage.
The implication:
During the transition period, settlement of components in ‘In’ currencies can be made either in the same currency or in the Euro (EUR) depending on the settlement account(s) maintained. (Similarly, components in Euro can either be settled in EUR or in an ‘In’ currency.) In the settlement messages that are generated (MT 100, MT202), the settlement amount would be reported in the Settlement Account Currency. However, you can opt to additionally furnish the value of the component in Euro Related Information (ERI) currency. You have to manually specify the settlement amount value, in the ERI currency, in the Settlement Message Details screen.
When generating the message towards settlement (MT100, MT202), the system ensures that the value you specify as the ERI Amount conforms to the Tolerance Limit defined for the ERI Currency (in the Currency Definition screen). That is, the system computes the ERI equivalent of the settling amount using the pegged rates, and compares the same against the ERI amount input by the user. If the difference is within the tolerance limits defined for the ERI currency, the user specified amount is used.
If the user specified ERI amount breaches the Tolerance Limit defined for the ERI currency, the system calculates and reports the ERI Amount on the basis of the exchange rate defined for the settlement currency vis-à-vis the ERI currency.
For example, in the SWIFT messages (MT 100 and MT 202) that are generated towards settlement, the value of the component can be reported both in Nostro account currency (in Field 32A) and in an ERI currency that you specify (in Field 72). In Oracle FLEXCUBE, this information is captured in the European Related Information (ERI) fields in the Settlement Message Details screen.
Assume the following scenario:
- The settlement account is an EUR account
- You have to settle an amount of DEM 10000
- You have defined the ERI currency for DEM as DEM
- The Tolerance Limit for DEM as 0.05%
- The exchange rate: 1 Euro = 1.30 DEM
The settlement amount in Euro would therefore be 7692.36 (rounded to nearest higher cent). This amount will be reported in Field 32A of the settlement messages. Now, if you want to furnish the settlement amount in the ERI currency (in this case, DEM) you have to manually enter the DEM value in the ERI Amount field. You may enter DEM 10000. (EUR 7692.36 actually converts into DEM 10000.068.)
The value that you have entered is well within the Tolerance Limit of 0.05% defined for DEM. Therefore, this value will be reported in Field 72 of the settlement messages.
Since the Tolerance Limit for DEM is 0.05%, you can specify an ERI Amount between DEM 9995 and DEM 10005 (DEM 10000 * 0.05/100 = DEM 5). If you enter an ERI value exceeding DEM 10005 or less than DEM 9950, the system recalculates the ERI Amount at the time of generating the settlement messages. The recalculation will be on the basis of the pegged rates between the Settlement Currency and the ERI currency.
Note
The system validates the ERI amount only when generating the settlement messages. It does not validate the ERI amount at the time of input (in the Settlement Message Details screen).
Index Base Ccy
Specify the currency that should be used to handle index-based securities traded by the banks, wherein the deals are done in index currency and their settlement is done through the local currency.
Commodity Code
Check this box to indicate that maintained currency code is a commodity code which is restricted not to populate in payment messages during message generation in the currency code field.
Generate 103+
You can enable the MT 103 + format option only if you would like to generate outgoing MT 103 messages in the MT 103 + format.
If you are enabling this option for a specific currency, ensure to also enable this option:
- For your bank branch in the Branch Parameters Maintenance
- For the customer of the contract, in the BIC Code Maintenance
- For the product used by the contract, in the Product Preferences
Consequently, while processing transactions in the specified currency for such a customer, branch and product, for which the MT 103+ option is enabled, the system generates outgoing payment messages in the MT 103 + format.
Note
Since the system is also capable of processing incoming MT 103 messages in the MT 103 + format. Therefore, during the upload process for your branch, the system considers an MT 103 payment message to be of MT 103+ format for those customer, currency and product combinations, for which the MT 103+ option has been enabled.
CLS currency
To allow customers of your bank to settle their FX deals via the CLS (Continuous Linked Settlements) Bank, you can identify the currency to be a ‘CLS Currency’. FX deals in the CLS currency only will be eligible to be routed through the CLS bank.
From the available list of CLS currencies, you can further maintain a list of ‘allowed’ or ‘disallowed’ currencies for a specific customer. Every customer who is a ‘CLS Participant’ will be allowed to trade in all the available CLS currencies unless specifically mentioned.
Refer the ‘Continuous Linked Settlements’ chapter of the Foreign Exchange User Manual for details on maintaining currency restrictions and other maintenances required for processing CLS deals in Oracle FLEXCUBE.
Index Flag
Check this box to derive index rate of the currency in Lending module.
Validate Tag 50F
Check this box to indicate that validations need to be performed for the 50F details captured for the ordering customer during contract input.
For more details on 50F validations, refer the chapter titled ‘Maintaining Addresses for a Customer’ in Messaging System user manual.
Note
Customer cover messages are always generated in new format (MT202COV or MT205COV).
For more details on new cover message formats, refer settlements user manual.
Indicating Rounding Preferences
Rule
This refers to the method to be followed for rounding off fractional units of a currency. The rounding preferences available are:
- Truncate — The amount is truncated to the number of decimals specified for the currency
- Round Up — The amount is rounded up based on the number of decimals and the nearest rounding unit
- Round Down —The amount is rounded down based on the number of decimals and the nearest rounding unit
For example,
Amount before Rounding |
Rounding Method |
No. of Decimals |
Rounding Unit |
Amount after Rounding |
1234.678 |
Truncate |
2 |
- |
1234.67 |
1234.678 |
Round up to the nearest rounding unit |
2 |
.01 |
1234.68 |
1234.678 |
Round down to the nearest rounding unit |
2 |
.01 |
1234.67 |
Unit
If you have selected Round Up or Round Down in the Rule field, you need to indicate the nearest unit to which the rounding should take place. The number of units specified here should not be greater than the number of decimals allowed for the currency.
Example
The decimal points specified for currency ‘A’ is 2. Rounding unit is .05
Amount for transaction is USD 100.326, which will be rounded off depending upon the decimals specified and the rounding rule and rounding unit.
For Rounding Rule ‘Up’, the amount available for transaction would be USD 100.35. For rounding rule ‘Down’, the transaction amount would have been rounded down to 100.30
If the rounding rule was specified as ‘truncate’ then, the amount would have rounded off to 100.32 (simply, knock off all decimal points beyond the stated decimals places to be rounded off). Thus whenever you specify a ‘truncate’ option you need not state the ‘Rounding unit’.
Specifying Amount Format Mask
Specify the format in which amounts in this currency are to be displayed for contracts in this currency. Two options are available:
999,999,999
9,999, 999, 99
The system defaults to the 999,999,999 format.
Euro Type
When maintaining a currency in the Currency Definition screen, you have to specify the ‘type’ of the currency with relation to transition phase of the European Economic and Monetary Union (EMU). You can do this in the ‘Euro Type’ field.
Your specifications in this field enable you to handle the first phase of the EMU, which commenced on 01 January 1999.
For more details on the manner in which Oracle FLEXCUBE handles the Euro, refer the chapter ‘Handling the Euro’.
By choosing the appropriate option, you can indicate if the currency is:
- The Euro
- An ‘In’ currency
- An ‘Out’ currency
- ‘Euro Closed’
National currencies of ‘In’ countries are referred to as ‘In’ currencies. When maintaining other currencies, you have to choose the ‘Out Ccy’ option under Euro Type.
When the transition period ends, the national currencies of the participating countries would cease to exist as valid legal tenders. The Euro would be the only legal tender in the participating countries. Consequently, the Euro changes made to Oracle FLEXCUBE will no longer be required.
You can turn off the changes at the end of the transition period by:
- Closing all ‘In’ currencies, and
- Choosing the ‘Euro Closed’ option (for the Euro)
2.6.1.1 PC Button
Click ‘PC’ button in the Currency Definition screen to invoke ‘Limits’ screen.
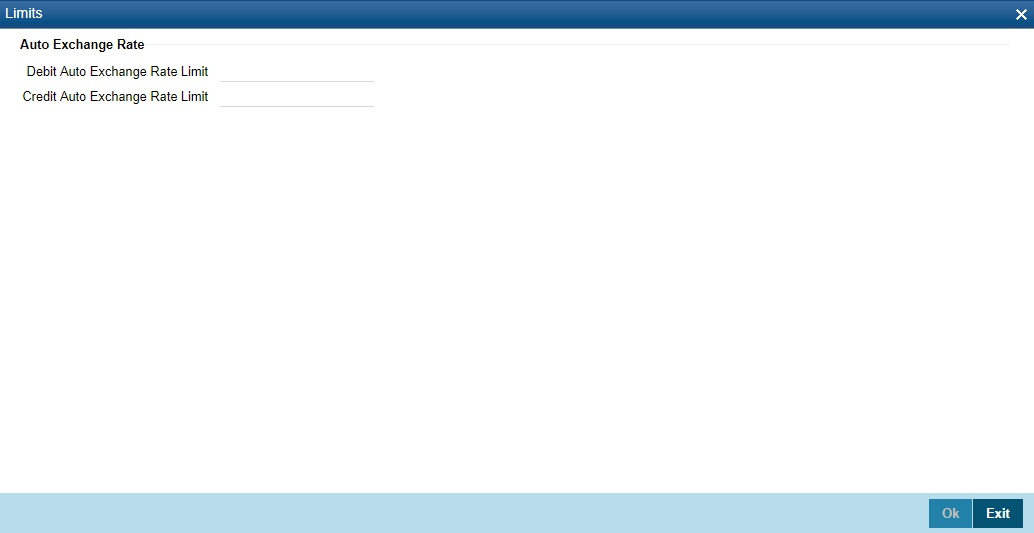
You can specify the credit limit and the debit limit for the exchange rate in this screen. The transaction amount of a PC contract must not exceed the limit specified here.
2.6.1.2 Currency Country Mapping Button
Click ‘Currency Country Mapping’ button in the Currency Definition screen to invoke ‘Clearing Zones Country Codes for Currency’ screen.
The screen appears as shown below:
You can map a currency code to a country in this screen.
Currency Code
The system displays the currency code maintained in the system.
Maintenance Country
The system displays the maintenance country for the currency.
Maintenance Country Name
The system displays the name of the country for which the currency is maintained.
Country Code and Description
Country Code
Specify the clearing zone country code. Alternatively, you can select the country code from the option list. The list displays all the country codes maintained in the system.
Country Name
The system displays the name of the clearing zone country.
2.6.1.3 Fields Button
You can associate values to all the User Defined fields created and attached to the Currency Definition Screen. You can view the list of User Defined fields associated by clicking the ‘Fields’ button.
The screen appears as shown below:
You can enter the value for the UDFs listed here in the ‘Value’ column.
For more details on how to create user Defined fields, refer chapter ‘Creating custom fields in Oracle FLEXCUBE’ in the User Defined Fields User Manual under Modularity.
2.6.1.4 Annexure
The treatment for interest calculation varies with each of the interest calculation methods. Each method is dealt with individually below:
Actual/Actual Method
10,000x10/100 x (31/365 + 84/366)
In this method, the number of days is calculated as follows:
Dec. -31 days (include from date exclude to date)
Jan -31 days
Feb.-29 days (leap year)
March - 24 days (include from date exclude to date)
Total = 31 + (31+29+24=84) =115
Note
When the interest period crosses from a non-leap year to a leap year (or otherwise), the basis of actual days has to be treated separately in each year.
Therefore, the denominator for the 31 days in December is 365 as it is a non-leap year and the denominator for the 84 days in 2000 is 366 as it is a leap year.
Actual /365 Method
10,000x10/100x115/365
In this method, the number of days is calculated as follows:
Dec. -31 days (include from date exclude to date)
Jan -31 days
Feb.-29 days (leap year)
March - 24 days (include from date exclude to date)
Total=31+31+29+24=115
Actual/360 Method
10,000x10/100x115/360
In this method, the number of days is calculated as follows:
Dec. -31 days (include from date exclude to date)
Jan -31 days
Feb.-29 days (leap year)
March - 24 days (include from date exclude to date)
Total=31+31+29+24=115
30 Euro/Actual Method
10,000x10/100 x (30/365+84/366)
In this method, the number of days is calculated as follows:
Dec. - 30 days (include from date exclude to date)
Jan - 30 days (In 30 Euro Method, all months have 30 days, February included.)
Feb. - 30 days (In 30 Euro Method, February always has 30 days, leap year or not)
March - 24 days (include from date exclude to date)
Total = 113 days
Note
When the interest period crosses from a non-leap year to a leap year (or otherwise), the basis of actual days has to be treated separately in each year.
30 Euro/365 Method
10,000x10/100x114/365
In this method, the number of days is calculated as follows:
Dec. - 30 days (include from date exclude to date)
Jan - 30 days (In 30 Euro Method, all months have 30 days, February included.)
Feb. - 30 days (In 30 Euro Method, February always has 30 days, leap year or not)
March - 24 days (include from date exclude to date)
Total = 113 days
30 Euro/360 Method
10,000x10/100x114/360
In this method, the number of days is calculated as follows:
Dec. - 30 days (include from date exclude to date)
Jan - 30 days (In 30 Euro Method, all months have 30 days, February included.)
Feb. - 30 days (In 30 Euro Method, February always has 30 days, leap year or not)
March - 24 days (include from date exclude to date)
Total = 113 days
30 US/Actual Method
10,000x10/100 x (30/365+84/366)
In this method, the number of days is calculated as follows:
Dec. - 30 days (include from date exclude to date)
Jan - 30 days (In 30 US Method, all months have 30 days, only for February are the actual number of days calculated.)
Feb. - 29 days (In 30 US Method, actual days are accounted for the leap year.)
March - 24 days (include from date exclude to date)
Total = 113 days
Note
When the interest period crosses from a non-leap year to a leap year (or otherwise), the basis of actual days has to be treated separately in each year.
30US/365 Method
10,000x10/100x114/365
In this method, the number of days is calculated as follows:
Dec. - 30 days (include from date exclude to date)
Jan - 30 days (In 30 US Method, all months have 30 days, only for February are the actual number of days calculated.)
Feb. - 29 days (In 30 US Method, actual days are accounted for the leap year.)
March - 24 days (include from date exclude to date)
Total = 113 days
30US/360 Method
10,000x10/100x114/360
In this method, the number of days is calculated as follows:
Dec. - 30 days (include from date exclude to date)
Jan - 30 days (In 30 US Method, all months have 30 days, only for February are the actual number of days calculated.)
Feb. - 29 days (In 30 US Method, actual days are accounted for the leap year.)
March - 24 days (include from date exclude to date)
Total = 113 days
2.6.2 Maintaining Currency Position GL
You can maintain the currency position GL and position eqv GL in ‘Currency Position GL Maintenance’ screen. You can invoke this screen by typing ‘CYDPOSGL’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking on the adjoining arrow button.
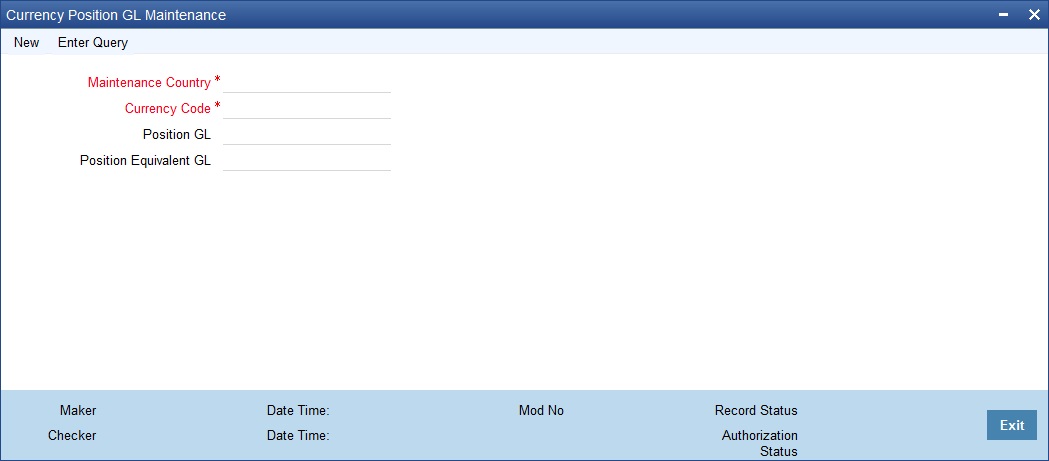
Maintenance Country
Specify the country code for which the currency is maintained. Alternatively, you can select the country code from the option list. The list displays all the authorized and open country codes along with their description maintained in the system.
Currency Code
Specify the currency code. Currencies are identified in Oracle FLEXCUBE by the SWIFT codes assigned to them. The currency will be identified by this code in all transactions that involve it.
Position or Position Equivalent GL for a currency
If you have opted for position accounting in your bank, then you need to maintain the same using CYDPOSGL to indicate the Position GL and the Position Equivalent GL.
When maintaining GLs in your bank, you can opt to link different foreign currencies, associated with GL to either of the following:
- The Position GLs that you specify here (for the corresponding currency)
- Position GLs of your choice
2.6.3 Viewing Currency Summary Details
You can view currency summary details in the ‘Currency Summary’ screen. You can invoke this screen by typing ‘CYSCDEFE’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking on the adjoining arrow button.
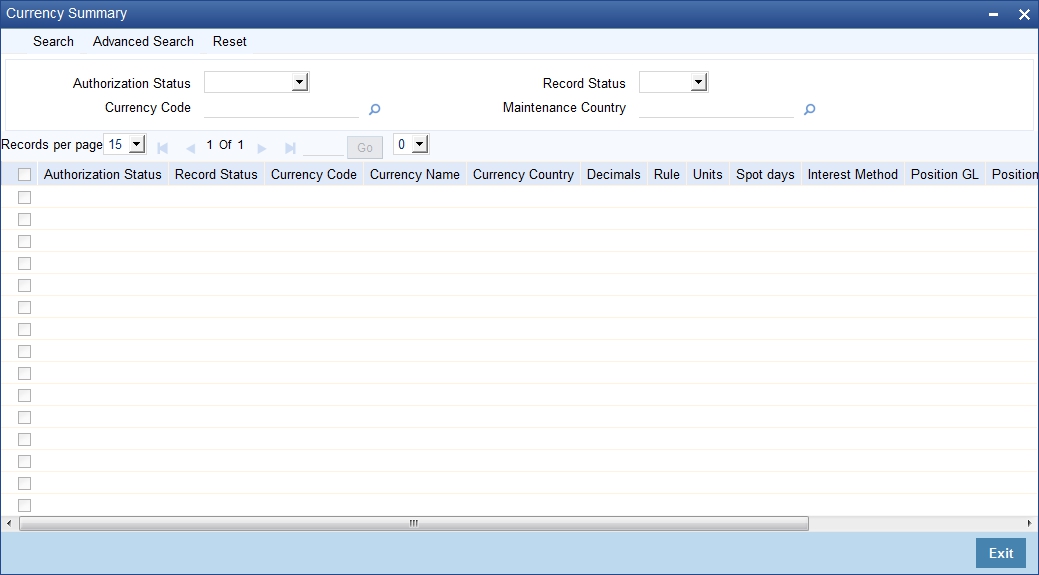
In the above screen, you can base your queries on any or all of the following parameters and fetch records:
- Authorization Status
- Currency Code
- Record Status
- Maintenance Country
Click ‘Search’ button. The system identifies all records satisfying the specified criteria and displays the following details for each one of them:
- Authorization Status
- Record Status
- Currency Code
- Currency Name
- Country
- Decimals
- Rule
- Units
- Spot days
- Interest Method
- Position GL
- Position Equivalent GL
- Maintenance Country
2.6.4 Maintaining Currency Pair
In the foreign exchange markets, the exchange rates for some currency pairs such as the USD-GBP or USD-JPY are easily obtainable, since these are frequently traded. The exchange rates of other currencies such as the ZAR-INR (South African Rand - Indian Rupee), which is not traded very often, is determined through a third currency. This third currency is usually the US dollar, since the US dollar is quoted in all trading centres.
In the Currency pair definition screen, you define the static attributes of currency pairs for which a regular market quote is readily available. For other pairs, which do not have a regular market quote, you need to specify the third currency through which the system should compute the exchange rate.
The currency pair screen is maintained at the bank level by your Head Office branch using the ‘Currency Pair Maintenance’ screen.
You can invoke this screen by typing ‘CYDCCYPR’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
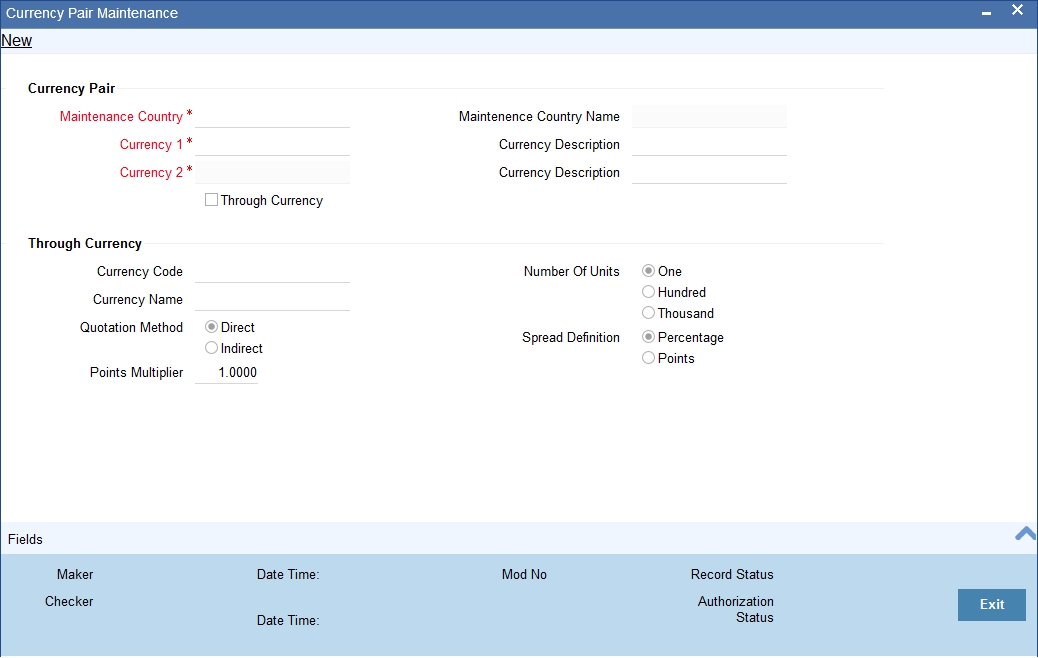
System Features
From among the currencies maintained in the currency screen, the system builds all possible combinations of currencies in pairs. For example, if you have maintained the following currency codes: USD, YEN. The system will give you a choice of defining parameters for the following pairs.
- USD-INR
- USD-YEN
- INR-USD
- INR-YEN
- YEN-USD
- YEN-INR
It is however, not obligatory to define parameters for all these pairs. A currency pair needs to be maintained only if:
- You want to define a direct exchange rate for the pair: for frequently traded currencies like INR-USD or USD-GBP or USD-JPY for which market quotes are available.
- You want to define a through currency for the pair: for those currencies which are not so well traded, market quotes may not be available. Therefore you can route the conversion rate for the pair via a ‘through currency’. For example, in the case of GBP-NLG, for which a direct exchange rate may not be available, you can define a through currency say, USD. The exchange rate between GBP-USD and NLG-USD will be picked up by the system to compute the exchange rate between GBP-NLG.
In the absence of a direct exchange rate, the system will look for a through currency to compute the rate. If a ‘through currency’ has not been maintained then the default local currency will be picked up as the through currency to compute the rate for a currency pair.
Currency Pair
Maintenance Country
Specify the country code for which the currency pair is maintained. Alternatively, you can select the country code from the option list. The list displays all the authorized and open country codes along with their description maintained in the system.
For example, if you maintain the country code for a bank or a branch, which is operating in Singapore for the currency USD, then you should specify the country code as SG. The system defaults the field ‘Country’ as US.
Maintenance Country Name
The system displays the name of the country for which the currency pair is maintained.
Currency Pair
A currency pair (specified as Currency1 and Currency2, in the Currency Pair screen) represents the two currencies for which you need to maintain exchange rates.
To specify the pair, choose from the list provided against Currency1. Select the pair for which you want to maintain parameters.
The pair should be selected according to the quotation method followed by the market, which could be direct or indirect (for details refer to the field ‘quotation method’). Exchange rates can be defined for currency1 against currency2 or currency2 against currency1.
The descriptions of the respective currencies are displayed below.
Through Currency
If the exchange rate for a particular currency pair is not to be maintained, specify the ‘Through Currency’ via which the exchange rate between the currencies should be calculated.
To maintain a through currency for a currency pair, check against the box ‘Through Currency’.
Then choose from the list codes provided against Code, Select the currency code, which you want to specify as the ‘through currency’. The exchange rate for the currencies involved in the pair will be calculated using the through currency.
Note
- While maintaining a pair involving an ‘In’ currency (‘In’ – ‘Out’ and ‘In’ – ‘In’), you can only specify the Euro as the ‘Through Currency’. Please note that you cannot maintain a ‘Through Currency’ for a pair constituted by an ‘In’ currency and the Euro.
For more details on the manner in which Oracle FLEXCUBE handles the Euro, refer the chapter ‘Handling the Euro’ in this manual.
Whenever, you define a through currency for a currency pair, you will not be allowed to specify the following for the pair:
- Number of units
- Spread definition
Quotation Method
This is the method to be followed for quoting the exchange rate. There are two methods direct and indirect.
In the Direct method the exchange rate for the currency pair is quoted as follows:
Buy rate = mid rate - buy spread
Sell rate = mid rate + sell spread
Ccy 1 = Rate x Ccy 2
In the Indirect method the exchange rate for the currency pair is quoted as follows:
Buy rate = mid rate + buy spread
Sell rate = mid rate - sell spread
Ccy 2 = Rate x Ccy 1
Example
The market follows the direct quote convention for the currency pair USD-DEM e.g., 1USD=1.6051DEM. To maintain this pair, you would specify currency 1 as USD and currency 2 as DEM, and specify “direct” in this field.
For the USD-GBP pair, which is quoted indirectly (1 GBP = 1, 5021 USD), the USD will be defined as currency 1 and the GBP as currency 2, with the quotation method “indirect”.
Number of Units
This indicates the number of units of currency to be used for currency conversion
Spread Definition
You need to indicate the method in which the spread for a currency pair needs to be defined. There are two ways of defining the spread -- in points and in percentage.
The effective spread can be calculated using any of the following two methods:
- In points — spread x points multiplier
- In percentage — spread/100 x mid rate
The method of spread definition that you specify here applies to two instances:
- While maintaining exchange rates for this currency pair
- While maintaining Customer Spread for this currency pair
2.6.4.1 Specifying Points Multiplier
Points are the smallest unit of measurement in the exchange rate of a currency pair. If you have opted for a points system of defining spread, you should specify the multiplication factor for the points to compute effective spread.
Suppose for the currency pair USD-DEM your rates are as follows:
Mid-Rate: 1.6045
Buy rate: 1.6040
Sell rate: 1.6051
The effective buy spread is 0.0005 (1.6045 - 1.6040) and the effective sell spread is 0.0006 (1.6051 - 1.6045).
In the Rates screen, where you define rates and spreads for a currency pair, you can specify the buy and sell spreads as 5 and 6 instead of as 0.0005 and 0.0006 (i.e., as spread points), and specify here the points multiplier as 0.0001.
The effective spread, buy and sell rates are then computed as follows:
Effective buy spread = Buy spread x Points multiplier = 5 x 0.0001 = 0.0005
Buy rate = Mid rate - Buy spread = 1.6045 – 0.0005 = 1.6040
2.6.5 Viewing Currency Pair Summary
You can view the summary details of currency pair in the ‘Currency Pair Summary’ screen. You can invoke this screen by typing ‘CYSCCYPR’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking on the adjoining arrow button.
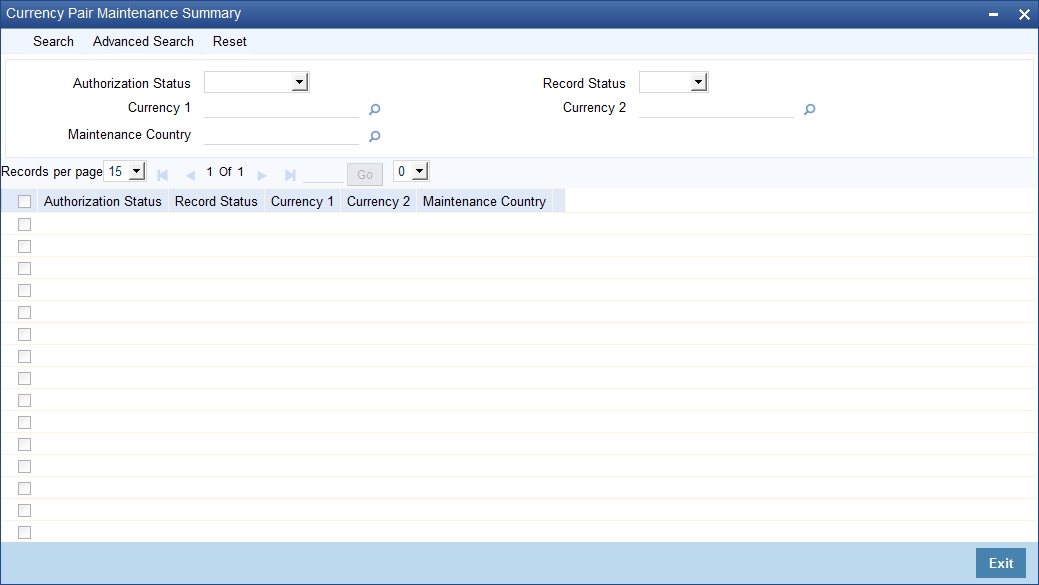
In the above screen, you can base your queries on any or all of the following parameters and fetch records:
- Authorization Status
- Currency 1
- Record Status
- Currency 2
- Maintenance Country
Click ‘Search’ button. The system identifies all records satisfying the specified criteria and displays the following details for each one of them:
- Authorization Status
- Record Status
- Currency 1
- Currency 2
- Maintenance Country
2.6.6 Maintaining Currency Rate Type
You can maintain currency rate types in this screen.
You can invoke ‘Currency Rate Type Maintenance’ screen by typing ‘CYDCRATY’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking on the adjoining arrow button.
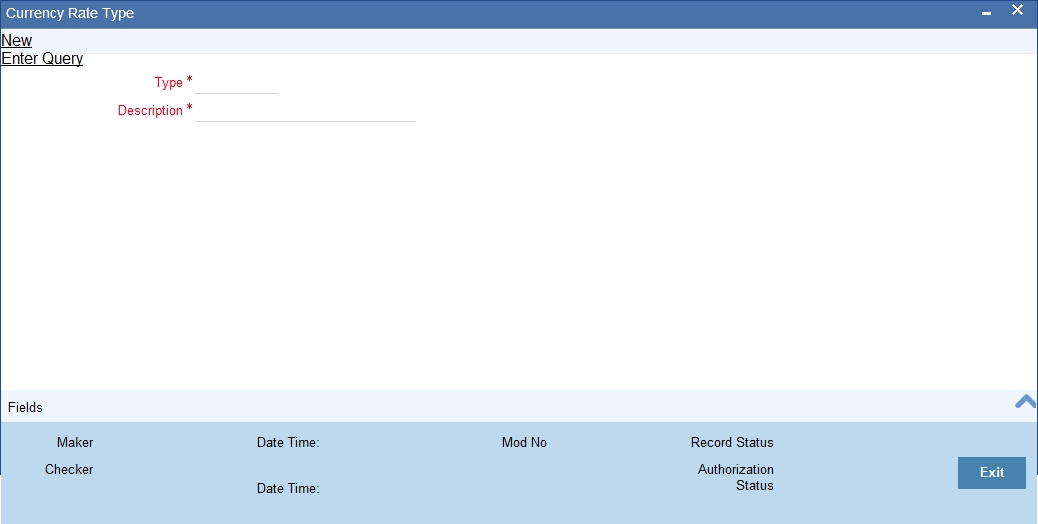
Specify the following fields
Type
Specify the currency rate type.
Description
The system displays the currency rate description.
2.6.7 Maintaining Currency Exchange Rates
In the Currency Rates screen, you can maintain exchange rates for a currency pair, the rates at which you buy and sell one currency for another.
A bank determines its buy and sell rate for a currency pair by applying a spread (i.e., its profit margin) to the mid-rate of the currency pair. Mid rate is the basic rate at which a currency pair is exchanged.
The spread applied for a currency pair varies with the transaction type, while the mid-rate usually remains constant. Consequently, different rates are applicable to different transaction types. For instance dollars in currency are purchased at a certain rate, while USD traveler’s checks are bought at a different rate. In Oracle FLEXCUBE, you can define a rate type which you would like to associate with a transaction type e.g., ‘CASH’, ‘TRAVCHKS’, etc., in the Rates screen.
In the Currency Rates Maintenance screen, you define the mid-rate, buy and sell spread applicable to each rate type; the buy and sell exchange rates are computed by the system.
Buy rates and sell rates can either be maintained by individual branches or can be input by the HO and propagated to all the branches.
If the flag ‘Copy Exchange Rates to Branches’ is set to Yes at ‘Bank Parameter Level’, then on authorization of exchange rate maintenance:
- If the branch for which the rate is being uploaded or maintained is the head office branch, then the rate would be copied to all those branches that have the same country code as the head office branch.
- If the branch for which the rate is being uploaded or maintained is not the head office branch, but it has the same country code as the head office branch, then the rate being uploaded or maintained would be specific to the branch and would not be copied to any other branch.
- If the branch for which the rate is being uploaded or maintained is not the head office branch and also does not have the same country code as the head office branch, then the rate being maintained would be copied to all the branches that has the same country code linked as the branch for which the rate is being maintained or uploaded.
In the Bank-wide Preferences screen, if you have not specified ‘copy exchange rate to branches’ then the ‘Currency Exchange Rates Input’ screen is maintained at the branch level by the different branches.
You can invoke this screen by typing ‘CYDRATEE’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.The screen appears as shown below:
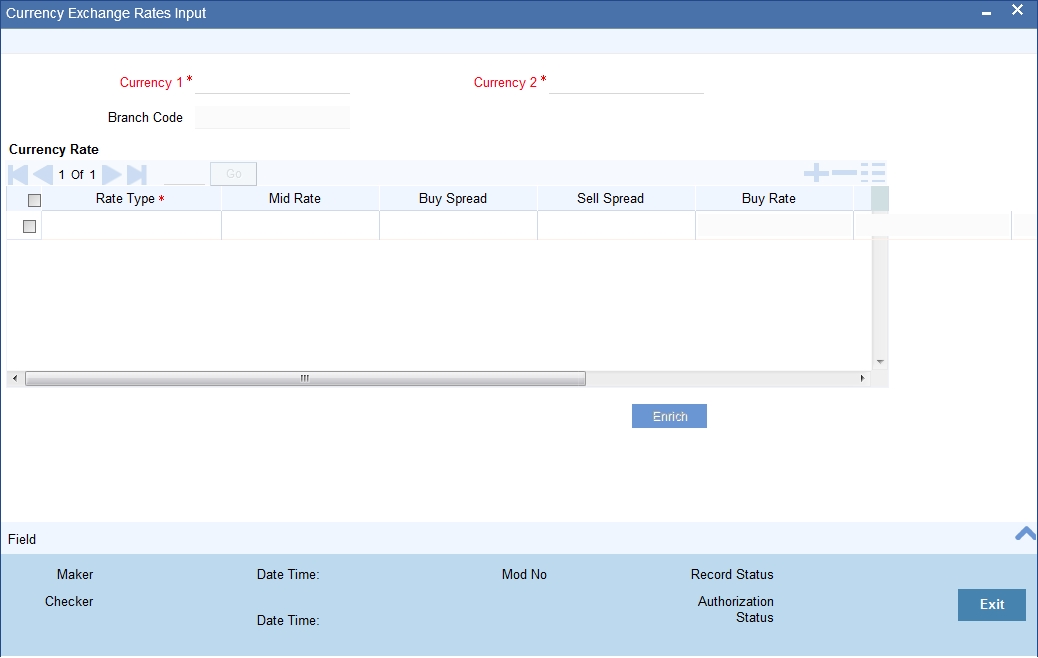
In this screen you maintain the following parameters for each rate type of a currency pair:
- Mid rate
- Buy spread and Sale spread
- Buy rate and Sale rate
Currency 1 and 2
Specify the currency pair for which you want to compute the exchange rates. The list displays the currency pair that are maintained for the country to which the branch belongs.
The pair should be selected keeping in mind the quotation method for exchange rates as followed by the market. The system offers the choice of maintaining both the currencies as currency1 or currency 2 -- USD against DEM and DEM against USD.
For the pair specified the following parameters need to be maintained to arrive at the buy and sell rate of currencies:
- Rate Type
- Mid Rate
- Buy Spread
- Sell Spread
Rate Type
This is the rate type for which you are maintaining exchange rates for a currency pair. For different transaction categories your bank would like to maintain different exchange rates. For example, traveller’s check is purchased at a certain rate whereas a bill of exchange is bought at a different rate.
In the front-end-modules, where you define products to cater to the various transaction types of your bank, you can link an appropriate rate type to the product. For instance, you create a product to cater to outgoing cross currency transfers by SWIFT. For this product, if you define the rate type to be STANDARD then for all contracts linked to this product, the Standard Rate Type would be applied.
Mid Rate
Mid rate is an indicative exchange rate for a currency pair. It is the average of the buy and sell rate quoted by the market for a currency pair.
For example,
currency 1 = USD
Currency 2 = INR
Buy rate -- 1 USD = 1.7020 INR
Sell rate -- 1 USD = 1.7040 INR
Mid-Rate = 1.7030
Buy Spread
This is the buy spread for a currency pair. It can be defined as the profit margin specified over the mid rate when you buy currency 1 for currency2. You can define the buy spread in two ways -- either in points or in percentage. The system computes the effective buy spread for you.
Sale Spread
This is the sell spread for a currency pair. It can be defined as the profit margin specified over the mid rate when you sell currency 1 for currency 2. You can define the sell spread either in points or in percentage. The system computes the effective sell spread for you.
Buy Rate
Buy rate is the rate of exchange for a currency pair, which is computed by the system based upon the mid rate, the spread specified, the spread definition and the quotation method maintained in the ‘Currency definition’ screen.
Sale Rate
Sell rate is the rate of exchange for a currency pair, which is computed by the system based upon the mid rate, the spread specified, the spread definition and the quotation method maintained in the ‘Currency definition’ screen.
You can also input the buy and sell rate for a currency pair. In which case, the system will compute the spread for the rate type.
Rate Date
This is a display field. When you enter the exchange rate for a currency pair, the system will default the Rate Date as the Application Date. The rate date will always be less than or equal to the application date.
Rate Serial
This is a running serial number for the Rate Date. You need to specify the serial number. You entry will be validated for uniqueness. For example, there could be only one exchange rate between USD and EUR for 31/07/2003 with Rate Type STANDARD with Rate Serial as 0001. Thus, this will be a unique rate serial for a currency pair, rate type combination for a given rate date.
When you enter the exchange rate for a currency pair, the system will default the Rate Date as the Application Date and the Rate Serial as the latest available serial for the currency pair + 1. The Rate Serial Number will be system generated. However, you can modify it if required. This number takes into account the Rate Serial Number present in the Currency Rates History screen too. The Rate Serial Number and the Rate Date will be displayed during authorization of the Rate in the Currency Authorization screen.
2.6.7.1 Authorizing Exchange Rates
Authorization of exchange rates is done from the Currency Exchange Rates input screen. Details like old value, new value for each field (buy rate, mid rate etc) are displayed. Click authorise icon to authorize the record.
2.6.7.2 Revising Exchange Rates
For revising the exchange rates for your bank or the branches invoke the ‘Currency Maintenance’ screen. Click the currency pair whose exchange rate you want to revise and click unlock icon on the toolbar. Input/modify the new rates for the pair.
2.6.8 Viewing Exchange Rates
You can view the exchange rates in the ‘Currency Exchange Rates View’ screen. You cannot input any values. You also have the option of specifying whether you want to view authorized rates or the unauthorized rates for any currency pair.
You can invoke this screen by typing ‘CYSRATEE’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
The screen appears as shown below:
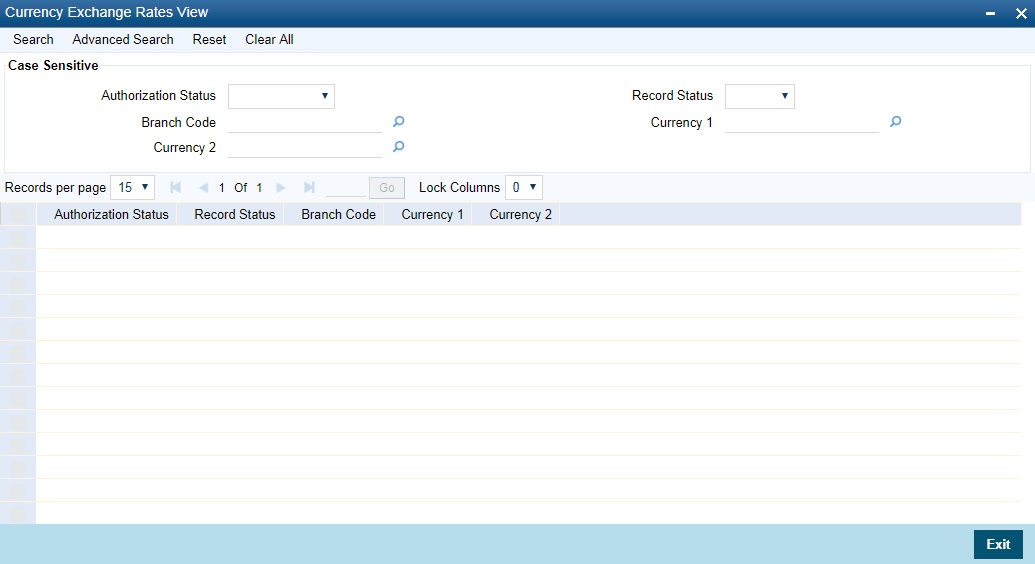
If the branches pick up the exchange rates maintained by the HO, then each time you invoke the ‘currency view’ screen from a branch it is advisable to update this screen with the latest rate input, from the HO. To do this, click on ‘Refresh’. Refresh updates the screen with the last exchange rates input.
2.6.8.1 Currency Rate Notification
You can update the exchange rates in the screen or upload through XML or upload through generic interface. The system generates a notification on authorization of the modified exchange rates.
If the parameter ‘Copy Exchange Rates to Branches' at bank parameter level is selected, then the rates will be populated and notifications will be generated in all the branches.
2.7 Currency Holiday Maintenance
This section contains the following topics:
- Section 2.7.1, "Maintaining Currency Holiday Calendar"
- Section 2.7.2, "Steps to Define Currency Holidays"
- Section 2.7.3, "Defining Currency Holidays"
2.7.1 Maintaining Currency Holiday Calendar
You need to maintain a yearly list of holidays, for the currencies, defined in the currency screen. This is done in the ‘Currency Holiday Calendar’ screen.
The system uses the information maintained in this screen to check whether any settlement, involving a foreign currency (in the foreign Exchange, Money market, Funds Transfer, Loans & Deposit modules) falls on that currency’s holiday. If yes, then the system will display a message stating so, and ask the user for an override
For any schedule or contract maturing at a future date say, 5 years hence, you can input the future date, only if the calendar for that year has been maintained.
The currency holiday screen is maintained at the Bank Level by the Head Office
You can maintain holiday calender for a currency in this screen. You can invoke the ‘Currency Holiday Calender Maintenance’ screen by typing ‘STDCCHOL’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking on the adjoining arrow button.
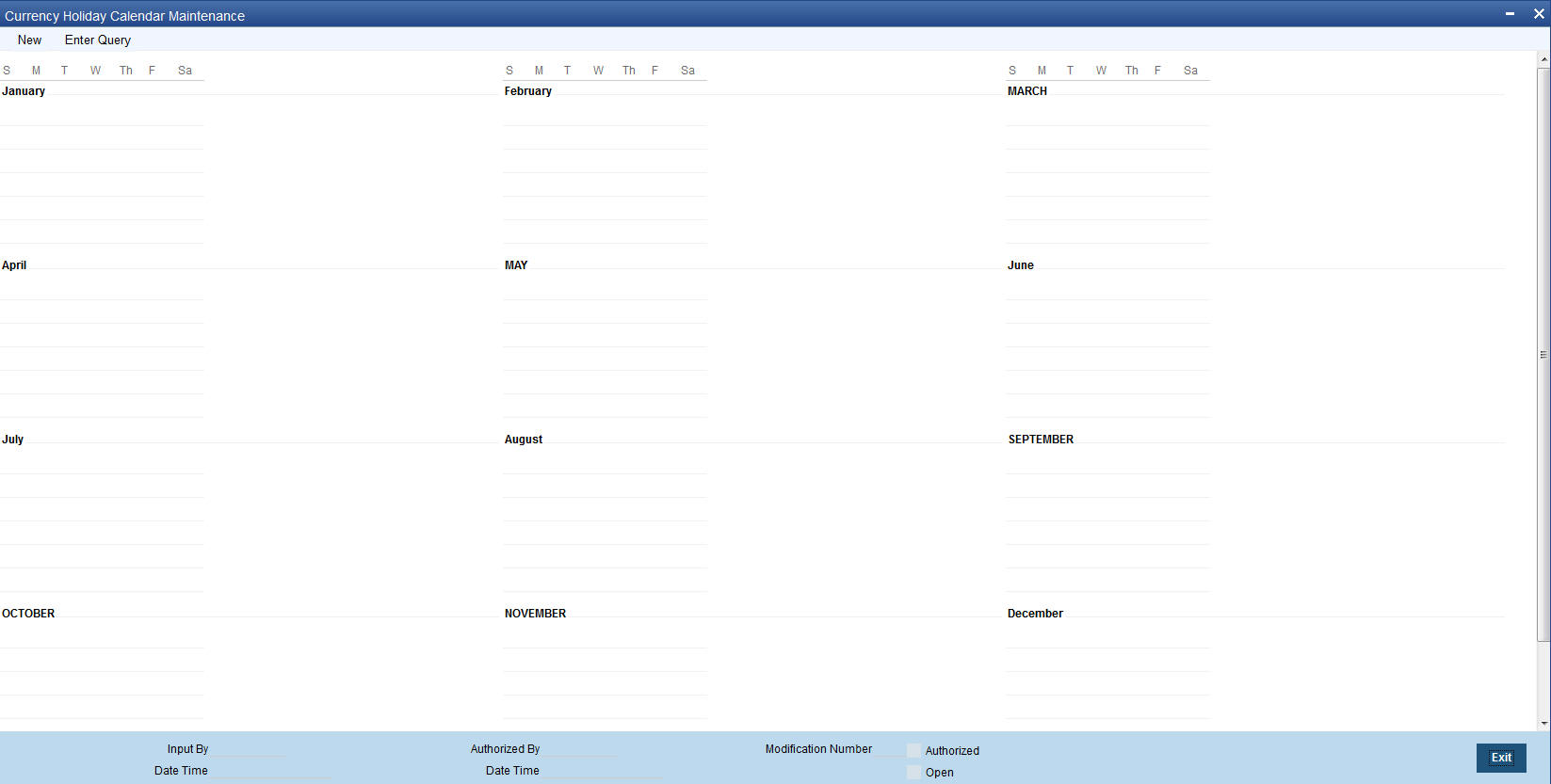
Specify the following fields:
Currency code
Specify the currency code. Alternatively, you can select the currency code from the option list. The list displays all valid currency codes maintained in the system.
Year
Select the year.
In this screen, you can maintain a list of holidays for each of the currencies maintained in the ‘currency screen’, for any year between 1 AD and 4000 AD.
2.7.2 Steps to Define Currency Holidays
To define currency holidays for a year, (for instance, for 2000) you have to do the following:
Building the calendar for the year
Step 1
Select ‘new’ from the Actions menu in the Application tool bar or click new icon. A blank screen appears and the cursor moves to the field ‘Year’
Step 2
Enter the year -- 2000 or move to the year 2000 using the arrows
Step 3
To build the calendar for the year, 2000 click on the ‘Refresh’ button. This button is called the ‘refresh / build up’ button because it builds the calendar for you
Step 4
Select the currency for which you are defining holidays. Please note:
- On invoking the calendar of any year, you will notice that Saturdays and Sundays are marked as weekly holidays for the currency. This is the default setting of the system.
- For identification, the working days are marked in black and the holidays in red.
2.7.3 Defining Currency Holidays
To define any other weekly holiday for the currency, other than the default, double click the day of the week, listed on the top row of the screen. For instance, if you double click ‘F’, all Fridays in the year would be marked as holidays.
To clear off the default weekly holidays — Saturdays and Sundays, double click on ‘sa’ and ‘s’ written on the top row.
To define annual holidays, click on the particular date to mark the selected date as a holiday.
If you want to unmark a day specified earlier as a holiday, double click on it, once again. You will notice that the day gets marked in black.
2.8 Floating Rates Definition
This section contains the following topics:
- Section 2.8.1, "Invoking LD MM Floating Rate Input Screen"
- Section 2.8.2, "Invoking Rate Code Definition Screen"
- Section 2.8.3, "Capturing Currency Details"
- Section 2.8.4, "Specifying Effective Date and Amount Slab Details"
- Section 2.8.5, "Tenor and Interest Rate Details"
- Section 2.8.6, "Rate Code Usage"
2.8.1 Invoking LD MM Floating Rate Input Screen
The Interest Rate Type of a product can be one of the following:
- Fixed
- Floating
- Special
A Floating Rate corresponds to the market rates for the day. These rates are maintained and updated daily (or whenever they change) in the Floating Rates Table. The rates can be applied on a contract with or without a spread.
You can define Floating Interest Rates through the ‘LD MM Floating Rate Input’ screen. You can invoke this screen by typing ‘CFDFLTRI’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
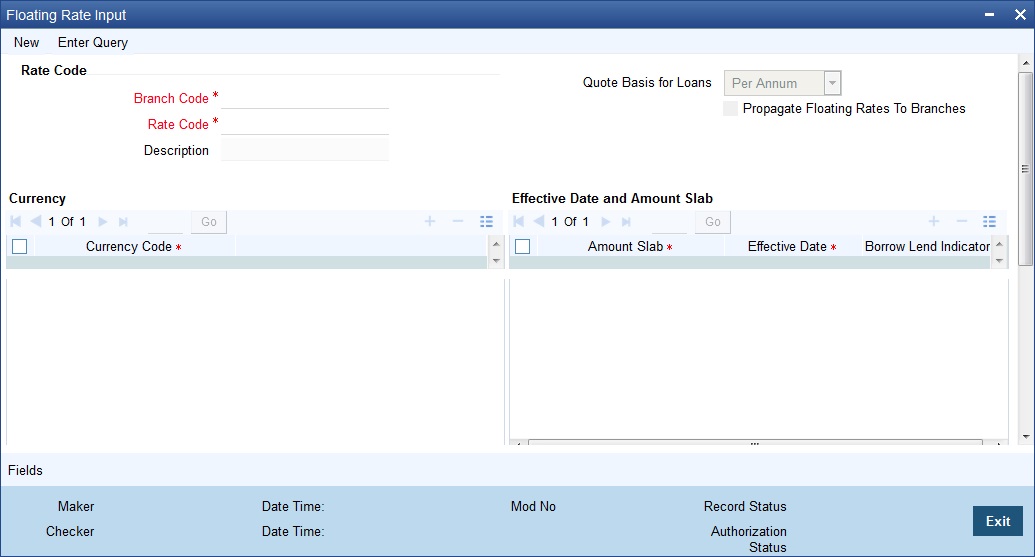
Rate Code
Specify the rate code to identify the Floating Rate you are defining. Alternatively, you can select the rate code from the list of values. The list displays all valid rate codes maintained in the ‘Rate Code Definition’ Screen (CFDFRTCD)
2.8.2 Invoking Rate Code Definition Screen
A Rate Code identifies a set of rates defined for a combination of Currency, Amount Limit (optional), Tenor and Effective Date. You can define rate codes through the ‘Rate Code Definition’ screen. You can invoke this screen by typing ‘CFDFRTCD’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
Rate Code
Specify a code to identify the Floating Rate you are defining. You can associate several currencies to the rate code and specify rates for each currency. While processing a contract, you need to indicate this code to make the rate applicable to the contract.
Description
Specify a unique description for the rate code.
2.8.2.1 Viewing Rate Code Definition Summary
You can view the Rate Code Definition details using ‘Rate Code Definition Summary’ screen. You can invoke this screen by typing ‘CFSFRTCD’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
This summary screen can be used to search for external systems which match the data specified for any of the following criteria:
- Authorization Status
- Record Status
- Rate Code
- Description
For each record fetched by the system based on your query criteria, the following details are displayed:
- Authorization Status
- Record Status
- Rate Code
- Description
2.8.3 Capturing Currency Details
Each Rate Code is associated with a currency. You can define rates for the same Rate Code in different currencies.
For example, you can have a Rate Code TERMDEP45 (with a description of Rates for a Term Deposit of 45 days). Thus, you can define a set of rates for contracts in U S Dollar and another set for contracts in Great British Pounds.
When you link a contract in US Dollars to the Rate Code TERMDEP45, the rates defined for this currency will be applied. Similarly, if the contract is in Great Britain Pounds, the rates defined for that currency will be applied.
2.8.4 Specifying Effective Date and Amount Slab Details
Amount Slab
For a specific Rate Code and Currency combination, you can define an amount slab structure for application of interest rates. You should specify the upper limit of the slab to which a particular rate should be applied. A rate that has been defined for an Effective Date - Amount Slab combination will be applicable to an amount less than or equal to the specified amount. You can thus define interest rates for a slab structure.
Let us extend the example we discussed for Rates and Effective Dates to include amount limits.
Amount (USD) |
Effective Date |
Interest Rate |
10,000 |
01 January ‘97 |
12.5% |
50,000 |
01 January ‘97 |
13.0% |
999.9 million |
01 January ‘97 |
14.0% |
If the rates have to be applied on 01 January ‘97, they will be picked up as follows:
- For a deposit with an amount less than or equal to USD 10, 000, the rate will be 12.5%.
- For a deposit with an amount greater than USD 10,000 and less than or equal to 50,000, the rate will be 13%.
- For a deposit with an amount greater than USD 50,000 and less than or equal to USD 999.9 millionth, the rate applied will be 14%.
Note
Notice that a huge amount (999.9 million) has been given as the last amount limit. This denotes that after 50,000 there is no upper limit in the slab. Further, if the component amount is greater than the highest slab, the appropriate rate for highest amount slab will be applied. Similarly, if the component amount is lesser than the lowest amount slab, the appropriate rate for lowest slab will be applied.
Effective Date
Each rate that you define for a Rate Code and Currency combination should have an Effective Date associated with it. This is the date on which the rate comes into effect. Once a rate comes into effect, it will be applicable till a rate with another Effective Date is given for the same Rate Code and Currency combination.
The following example illustrates this point:
Rate Code: TERMDEP45
Currency: US Dollar
Effective Date |
Interest Rate |
01 January ‘97 |
12.5% |
14 January ‘97 |
12.0% |
31 January ‘97 |
13.0% |
These rates will be applicable as follows:
Period |
Interest Rate |
01 January to 13 January ‘97 |
12.5% |
14 January to 30 January ‘97 |
12.0% |
31 January to one day before the next date |
13.0% |
Note
The rates will be applied to a contract depending on whether it has been defined with Auto Rate Code Usage or Periodic Rate Code Usage. You can specify this in the Product ICCF Details screen.
Borrow/Lend Rate Indication
For every Amount Limit - Effective Date combination, you should define the rate to be applied as a borrow rate or a lend rate. You also have the option to specify the mid rate.
2.8.5 Tenor and Interest Rate Details
The rates that will be applied for a given combination of Amount Slab – Effective Date – Lend/Borrow Indication can be tenor based. In the table, you can define tenors and indicate the rates applicable to each tenor. The rate will be applied to contracts based on the slab into which it falls and the reset tenor defined for the component.
2.8.6 Rate Code Usage
If you specify Auto Rate Code usage, all the rate changes made during the liquidation or accrual period will be considered. If you specify periodic rate code usage, the rates will be periodically refreshed and the rates as of a specific frequency will be applied.
This frequency is specified in the Contract Schedules screen while the Rate Code Usage is specified in the Product ICCF Details screen. The following example illustrates the concept:
For example, you have a deposit that has a Start Date as 1 October 1997 and a Maturity Date as 30 November 1997. The interest payment frequency is to be monthly. The contract has been defined with a floating rate.
The rates in the floating rate table change in the following manner:
Effective Date |
Rate |
1 October ‘97 |
12 |
12 October ‘97 |
11.5 |
25 October ‘97 |
11 |
15 November ‘97 |
12 |
30 November ‘97 |
12.5 |
If you want the floating rates to be applied automatically every time they change, you should specify Auto Rate Code usage in the Product ICCF screen. When you do this, if the first interest payment is to be done on 31 October, all the rate changes between 1 October and 31 October will be considered automatically.
The rates will be applied for the number of days for which they remained unchanged in the rate table, as follows:
From |
To |
Rate |
1 October |
11 October |
12 |
12 October |
24 October |
11.5 |
25 October |
31 October |
11 |
If you want the floating rates to be refreshed periodically, you should first specify the rate code usage as periodic, through the Product ICCF Details screen.
Next, you should define the rate revision schedules to specify when these rates should be applied on the deposit (that is, the frequency at which rates should be refreshed).
To do this, through the Contract Schedules screen, mark the component as a revision schedule by checking the Rev box. Then, specify the component (for example, INTEREST). Specify the frequency at which the interest rate has to be refreshed, say every fortnight. Specify the Start Date as, say, 15 October. That is, for a deposit defined with periodic rate code application, the rates prevailing on the dates at the frequency you have specified will be used for accruals and liquidation.
In the deposit we are discussing, with the frequency at which the rates should be refreshed defined as fortnightly and the Start Date as 15 October, the rate applied for the payment on 31 October will be as follows:
From |
To |
Rate |
1 October |
15 October |
11.5 |
16 October |
31 October |
11 |
Note
Rev schedules are applicable only for contracts where the Rate Type is Floating and the Code Usage is Periodic. If the Code Usage is Automatic the system applies the effective rate whenever the underlying Rate gets updated.
2.9 External Entities Maintenance
This section contains the following topic:
- Section 2.9.1, "Maintaining External Chart of Accounts"
- Section 2.9.2, "Maintaining External Transaction Code"
- Section 2.9.3, "Maintaining External Credit Approval"
- Section 2.9.4, "Maintaining External Customer Input"
- Section 2.9.5, "Viewing External Customer Summary"
- Section 2.9.6, "Maintaining External Customer Account"
- Section 2.9.7, "Mapping External Multi Currency Accounts"
- Section 2.9.8, "Maintaining External Consumer Loan Account"
2.9.1 Maintaining External Chart of Accounts
You can invoke ‘External Chart of Accounts’ screen by typing ‘STDCRGLM’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking on the adjoining arrow button.
You can specify the following fields:
GL Code
Specify a code for the General Ledger.
General Ledger Description
Specify a description for the General Ledger code.
GL Category
Select the category of the General Ledger from the drop-down list. The list displays the following values:
- Asset
- Liability
- Income
- Expense
- Contingent Asset
- Contingent Liability
- Memo
- Position
- Position Equivalent
Blocked
Check this box to block the GL for accounting entries.
2.9.2 Maintaining External Transaction Code
You can invoke ‘External Transaction Code Maintenance’ screen by typing ‘STDCRTRN’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking on the adjoining arrow button.
You can specify the following fields:
Transaction Code
Specify the transaction code of the external transaction.
Transaction Code Description
Specify the description of the transaction code.
Source System
Specify the source system of the transaction code.
Source Transaction Code
Specify the source of the transaction code.
2.9.3 Maintaining External Credit Approval
You can invoke ‘External Credit Approval System’ screen by typing STDECAMT’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking on the adjoining arrow button.
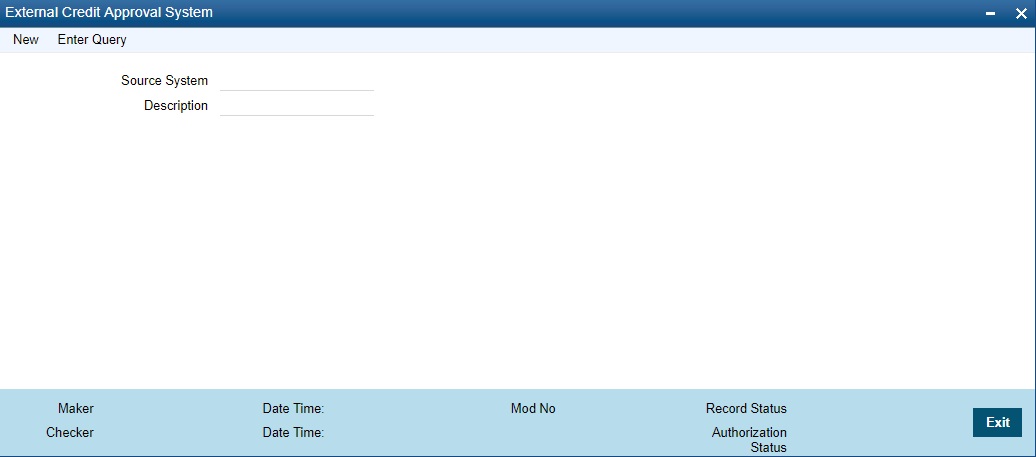
You can specify the following fields:
Source System
Specify the source system.
Description
Specify the description of the source system.
2.9.4 Maintaining External Customer Input
You can invoke ‘External Customer Input’ screen by typing ‘STDCIFCR’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking on the adjoining arrow button.
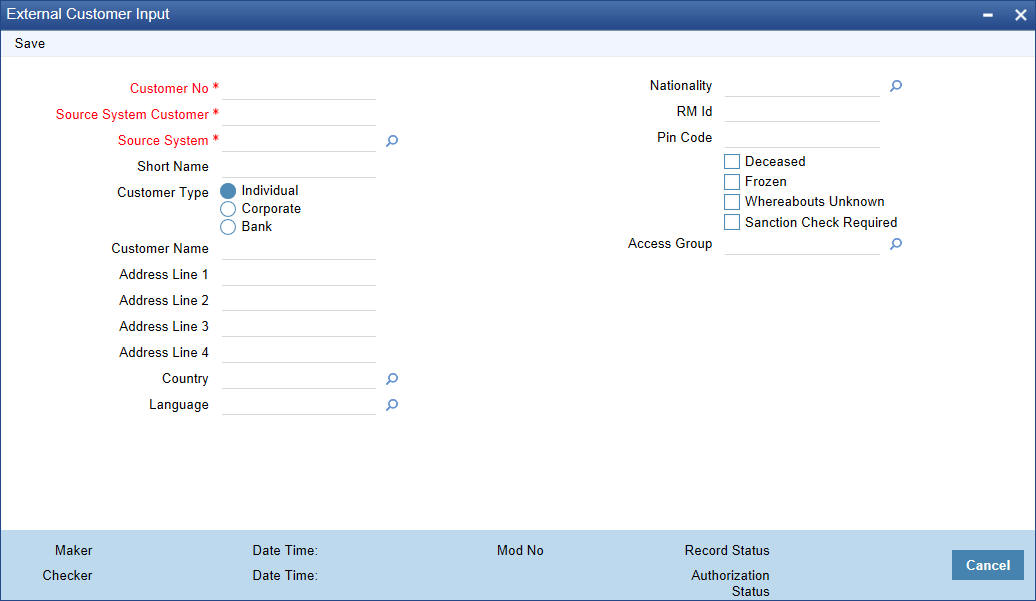
You can specify the following fields:
Customer Number
Specify the customer number.
Source System
Specifies the source system.
Source Customer ID
Specify the customer identification details as per the source system.
Short Name
Specifies the short name of the customer.
Customer Type
Select the required type of customer. Choose any of the following:
- Individual - Click this button if the customer is an individual customer.
- Corporate - Click this button if the customer is a corporate customer.
- Bank - Click this button if the customer is a bank employee.
Address Line 1
Specify the first line of the customer’s address.
Address Line 2
Specify the second line of the customer’s address.
Address Line 3
Specify the third line of the customer’s address.
Address Line 4
Specify the fourth line of the customer’s address.
Pin code
Specifies the pin code of the customer’s address.
Country
Select the country of the customer’s address.
Language
Select the language of customer’s preferred language of communication.
Nationality
Specify the nationality of the customer.
Customer Category
Specify the required category of customer.
Deceased
Check this box if the customer is deceased.
Frozen
Check this box if the customer’s account is frozen.
Whereabouts Unknown
Check this box of the customer’s whereabouts are not known.
RM ID
Specify the relationship id of the customer’s relationship manager.
Access Group
Specify the access group. Alternatively, you can select the access group from the option list. The list displays all valid access group maintained in ‘Customer Access Group Maintenance’ screen (STDACGRP).
Note
When you try viewing details of a customer whose data is forgotten, the system displays an error message.
For more information on forgetting customers refer Core Services - Security Management System user guide.
2.9.5 Viewing External Customer Summary
You can view the uploaded data in the ‘Customer Summary’ screen.You can invoke the ‘Customer Summary’ screen by typing ‘STSCIFCR’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
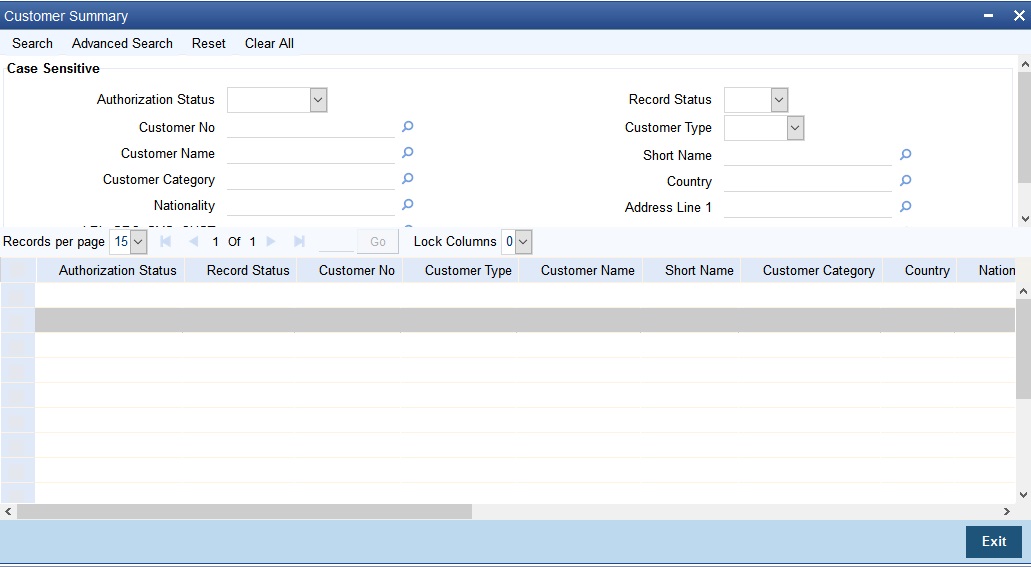
The query option is available on the following fields in this screen:
- Authorization Status
- Record Status
- Customer No.
- Customer Type
- Customer Name
- Short Name
- Customer Category
- Country
- Nationality
- Address Line 1
- Source System Customer
- Source System
Note:
When you try viewing details of a customer whose data is forgotten you see a message saying that no record exists.
For more information on forgetting customers refer Core Services - Security Management System user guide.
2.9.6 Maintaining External Customer Account
You can invoke ‘External Customer Account’ screen by typing ‘STDCRACC’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking on the adjoining arrow button.
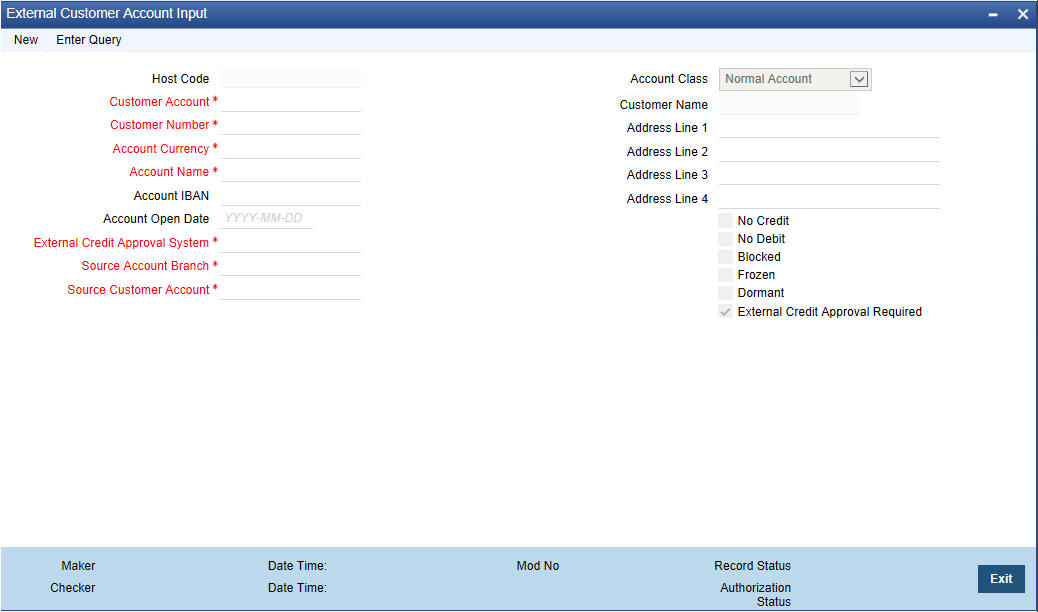
You can specify the following fields:
Customer Account
Specify the customer account number.
Customer Number
Specify the required customer number. Alternatively, you can select the customer number from the option list. The list displays all valid customer numbers maintained in the system.
Account Branch
Specify the account branch.
Account Currency
Specify the required currency of the external customer. Alternatively, you can select the currency from the option list. The list displays all valid currencies maintained in the system.
Account IBAN
Specify the IBAN that is linked to the customer.
Account Name
Specify the name of the account holder.
Host Code
Specify the host code that is linked to the logged in user of the branch.
External Credit Approval System
Specify the External Credit Approval System for which accounts are mapped. Alternatively, you can select the ECA from the option list. The list displays all valid ECA systems maintained in the system.
Account Class
Select the required account class of the external customer account. Choose between the following:
- Normal Account
- Nostro Account
- Multi Currency Account
The account currency should be null if account class is selected as multi currency account. The system throws an error message if the account class is selected as multi currency account and the account currency is specified.
No Credit
Check this box to indicate that the account does not have any credit facility.
No Debit
Check this box to indicate that the account does not have any debit facility.
Blocked
Check this box to indicate that the account status is blocked.
Frozen
Check this box to indicate that the account status is frozen.
Dormant
Check this box to indicate that the account status is dormant.
External Credit Approval Required
Check this box to indicate that ECA check is required for the external customer account.
Note
When you try viewing details of a customer whose data is forgotten, the system displays an error message.
For more information on forgetting customers refer Core Services - Security Management System user guide.
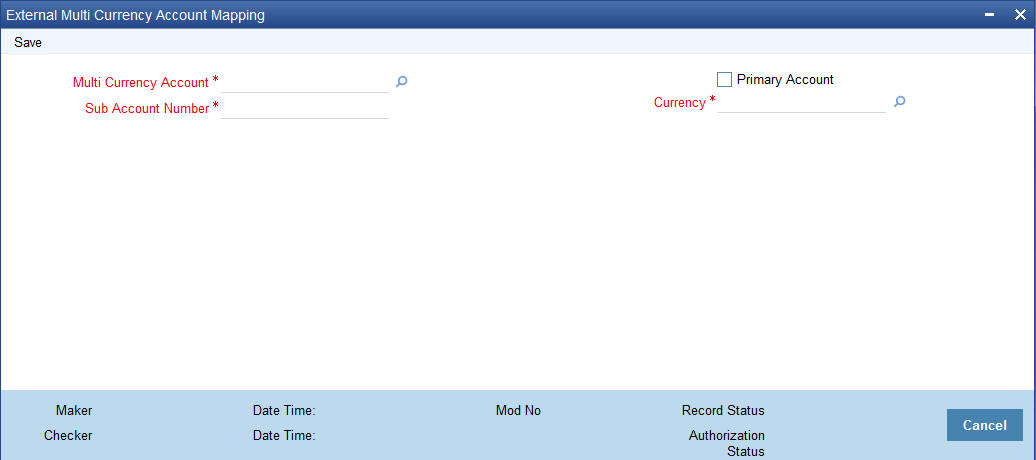
2.9.7 Mapping External Multi Currency Accounts
You can map multi currency accounts and their currency with real accounts using ‘External Multi Currency Account Mapping’ screen. You can invoke this screen by typing ‘STDCRMCA’ in the top right corner of the Application toolbar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
You can maintain the following in this screen:
Multi Currency Account
Specify the multi currency account. Alternatively, you can select the multi currency account from the option list. The list displays all the external multi currency accounts.
Sub Account Number
Specify the sub account number.
Primary Account
Check this box to indicate that the selected sub account number is the primary account. You can mark only one account under a multi currency account as primary account.
Currency
Specify the currency of the sub account number. Alternatively, you can select the currency from the option list. The list displays all valid currencies maintained in the system.
2.9.8 Maintaining External Consumer Loan Account
You can capture consumer loan account details in the ‘External Consumer Loan Account Input’ screen. You can invoke this screen by typing ‘STDCRCLN’ in the top right corner of the Application toolbar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
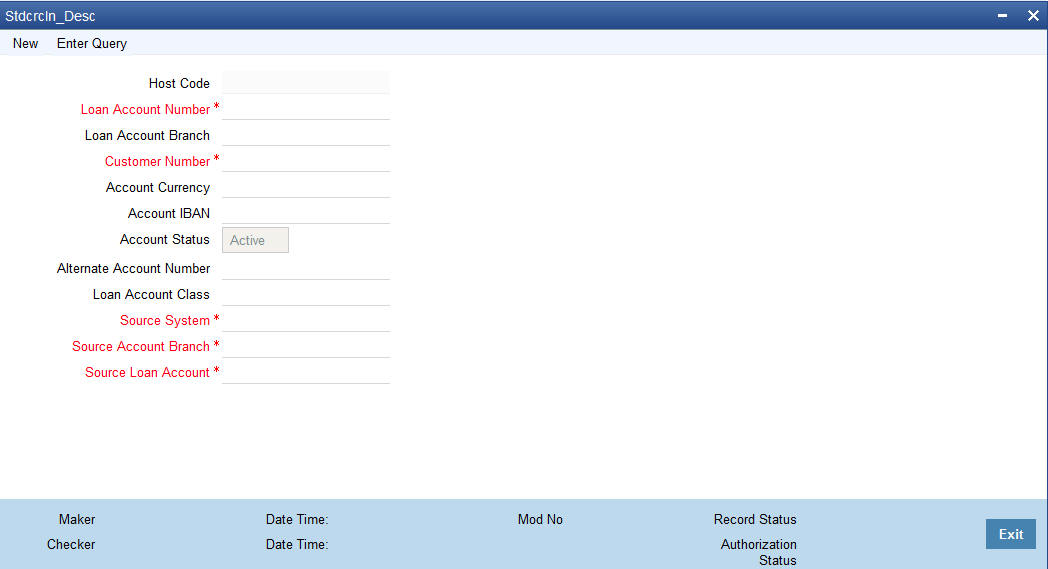
Specify the following details:
Host Code
Specify the host code of the external consumer loan account.
Loan Account Number
Specify the consumer loan account number.
Loan Account Branch
Specify the consumer loan branch.
Customer Number
Specify the customer number of the external consumer loan account.
Account Currency
Specify the currency of external consumer loan account.
Account IBAN
Specify the IBAN of external consumer loan account.
Account Status
Select the account status from the drop-down list. The list displays the following options:
- A-Active
- Y-Inactive
- L-Liquidated
- R- Reversed
Alternate Account Number
Specify the alternate account number consumer loan account.
Loan Account Class
Specify the loan account class.
Source System
Specify the source system.
Source Account Branch
Specify the source system account branch.
Source Loan Account
Specify the source loan account.
2.10 External Limit Entities Maintenances
This section contains the following topics:
- Section 2.10.1, "Maintaining External Collaterals"
- Section 2.10.2, "Maintaining External Collateral Pools"
- Section 2.10.3, "Maintaining External Facilities"
- Section 2.10.4, "Maintaining External Liability Linkage"
- Section 2.10.5, "Maintaining External Liability"
2.10.1 Maintaining External Collaterals
You can maintain external collateral details in ‘External Collateral Maintenance’ screen You can invoke this screen by typing ‘STDCRCOL’ in the top right corner of the Application toolbar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
You can specify the following in this screen:
Collateral Details
Host Code
Specify the host code. Alternatively, you can select the host code from the option list. The list displays all valid values.
Branch Code
Specify the branch code in which the collateral is created.
Available
This check box will be checked by default, indicating that the collateral is available for linking to the collateral pool. You can uncheck this so as to manually freeze this collateral.
Liability No
Specify the liability Number for which the collateral is linked.
Customer No
Specify the customer number. Alternatively, you can select the customer number from the option list. The list displays all valid values.
Collateral Code
Specify the Collateral Code here. A maximum of 20 alphanumeric characters are allowed in this field. There should be only one Collateral code for a given Liability.
Collateral Description
Give a brief description of the collateral here.
Collateral Type
Indicate the type of collateral. The options are
- Property
- Vehicle
- Marketable Securities
- Plant and Machinery
- Precious Metal
- Guarantee
- Miscellaneous
- Policy
Interest Rate
Specify the interest rate of the collateral.
Collateral Currency
Specify the currency in which the Collateral has to be maintained. Once authorized you cannot change this entry.
Collateral Value
The collateral value depends on whether the security is Market Value based or Non-Market Value based.
If it is market value based then the collateral value is calculated as shown in the following examples.
Example
Input in case of a nominal quoted security:
Nominal Amount |
Price Code |
Market Price |
Collateral Value [(Market price/100) * Nominal Amount] |
10,00,000 |
BOM1 |
65 |
(65/100) * 10,00,000=650000 |
5,00,000 |
BOM2 |
70 |
(70/100) * 5,00,000= 350000 |
7,00,000 |
BOM3 |
80 |
(80/100) * 7,00,000= 560000 |
Input in case of a unit quoted security:
Number of Units |
Price Code |
Market Price |
Collateral Value (Number of Units x Market price) |
65 |
BOM1 |
120 |
7800 |
70 |
BOM2 |
130 |
9100 |
40 |
CAL1 |
95 |
3800 |
If it is Non-Market Value based then the user has to enter the collateral value manually.
Limit Contribution
Specify the final amount contribution that will be applicable for a Limit.
Example
Collateral is valued at $1000, and you wish to offer the customer credit only worth $ 980. This amount is 98% of the collateral contribution.
(1000 - 980) / 1000 = 2 % is the Hair cut percentage
This means you want to have a lendable margin of 98%.
For instance, if you enter the lendable margin percentage, then based on the value you enter, the hair cut will be calculated as described above and the limit contribution will be calculated.
Start Date and End Date
Specify the tenor of the collateral using the Start Date and End Date fields. The collateral is considered effective only during this period.
The start date indicates the date from which the collateral becomes effective. The end date that you specify indicates the date on which the collateral ceases to exist. On the end date, the credit limit, of the credit line backed by the collateral, will be reduced by the amount that the collateral contributes to the credit line.
Liability Name
Specify the liability name.
Source Liab ID
Specify the source liability ID.
Source Collateral Code
Specify the source collateral code.
Taken Over
Taken Over collateral is checked if the collateral linked to CI/CL account is taken over.
Source System
Specify the source system. Alternatively, you can select the source system from the option list. The list displays all valid options.
2.10.2 Maintaining External Collateral Pools
You can maintain external collateral pools in ‘External Collateral Pools Maintenance’ screen. You can invoke this screen by typing ‘STDCRPOL’ in the top right corner of the Application toolbar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
You can specify the following in this screen:
Host Code
Specify the host code. Alternatively, you can select the host code from the option list. The list displays all valid values.
Liability No
Specify the liability to which the collaterals need to be linked.
Liability Branch
The system displays the liability branch.
Liability Name
Specify the liability name.
Branch Code
The branch code for the branch where the collateral is maintained in the 'External Collateral Maintenance' screen gets defaulted here.
Pool Code
Specify the Pool Code here. The pool code assigned to each collateral pool can be linked to a Liability while creating credit limits.
Pool Description
Specify a brief description of the collateral pool here.
Pool Currency
Specify the currency in which the Collateral Pool has to be maintained.
Pool Amt
The system computes and displays the utilization amount to the Collateral Pool, if a collateral Pool is attached to a contract or account and not through a facility.
Source Liab ID
Specify the source liability ID.
Source Pool Code
Specify the source pool code.
Source System
Specify the source system. Alternatively, you can select the source system from the option list. The list displays all valid options.
2.10.3 Maintaining External Facilities
You can maintain external facilities in ‘External Facilities Maintenance’ screen. You can invoke this screen by typing ‘STDCRFAC’ in the top right corner of the Application toolbar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
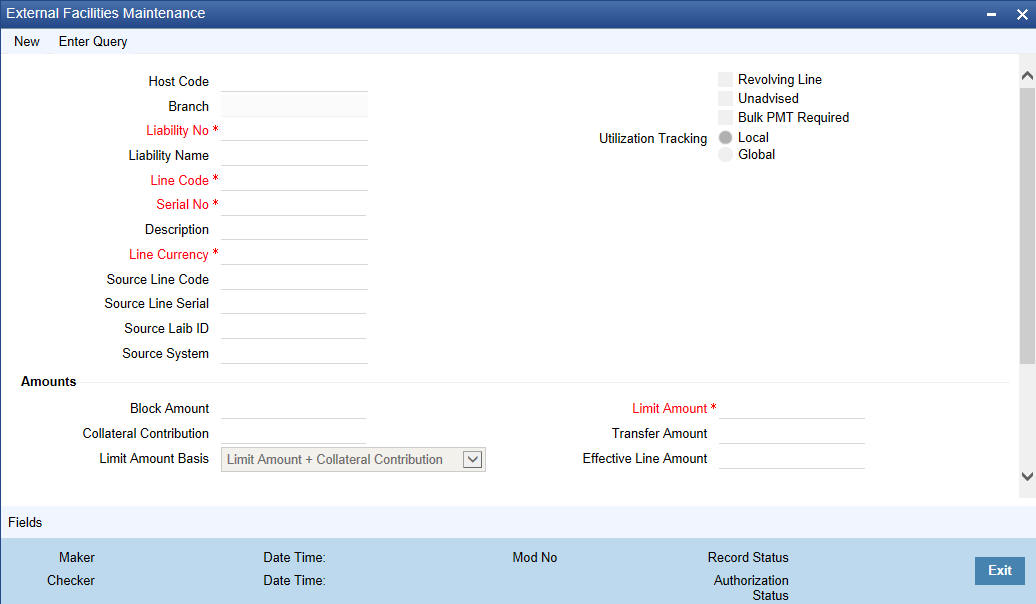
You can specify the following here:
Host Code
Specify the host code. Alternatively, you can select the host code from the option list. The list displays all valid values.
Branch
Specify the facility branch. Alternatively, you can select the branch code from the option list. The list displays all valid values.
Liability No
Specify the Liability number here. Alternatively, you can select the liability number from the option list. The list displays all valid values maintained in the system.
Liability Name
Specify the liability name.
Line Code
Specify the Line Code to which the liability ID is to be associated with. Allocating credit limits for the Line-Liability combination can be done. The customer(s) who fall under this Liability Code will in turn avail credit facilities under this Credit line.
By linking a Credit Line to a Liability code the customer also gets linked to the Credit Line. This is true because a Liability code has been assigned to every credit seeking customer and the credit facilities granted to the customer are defined and tracked against this code.
Serial No
Each time a customer - line code combination is specified, LCM module assigns a unique serial number to the combination. This serial number is unique to the line-liability code combination. Thus, for every new record entered for a Line-Liability combination, a new serial number is generated. The Line - Liability - Serial number forms a unique combination.
Description
Give a brief description of the facility here.
Line Currency
Specify the currency in which the facility is defined. The currency that has been selected will have the following implications:
- The limit amount that has been specified for this Line-Liability combination is taken to be in this currency.
- The line that has been defined will be available for Utilization only in the line currency, unless specified otherwise under Currency Restrictions in this screen.
Once the entry is authorized you cannot change the currency.
If the limit allotted to this Line-Liability combination can be utilized by accounts and transactions in currencies other than the limit currency, the limit utilization will be arrived at by using the mid rate for the currency pair as of that day.
Source Line Code
Specify the source line code.
Source Line Serial
Specify the source line serial.
Source Liab ID
Specify the source liability ID.
Source System
Specify the source system. Alternatively, you can select the source system from the option list. The list displays all valid values.
Revolving Line
Select this check box to indicate that the credit line is revolving. A revolving credit line indicates that a repayment of the utilized credit should reinstate the credit limit of the customer.
Unadvised
Select this check box if the Liability is unadvised.
Bulk PMT Required
Check this box to indicate that bulk PMT is required.
Utilization Tracking
It signifies if the utilization tracking of the facility is done locally or globally.
Amounts
Block Amount
Specify the block amount.
Collateral Contribution
The collateral amount which has been maintained is displayed when a collateral code has been picked.
Limit Amount Basis
The value for Limit Amount can be maintained as the following:
- Limit Amount Basis
- Limit Amount + Collateral Contribution Limit Amount
- Min (Limit Amount, Collateral Contribution)
Limit Amount
Specify the limit for the facility. If you have maintained schedules for limits, the system automatically updates the limit amount here on the dates specified for each limit in the schedule.
Transfer Amount
System displays the transfer amount resulting from 'Facilities Amount Transfer' transactions. The value displayed has either the sign "-" or "+", indicating whether the amount is transferred from or to the line. If the sign is "-", then the amount is transferred from the line and if it is "+", then the amount is transferred to the line.
Effective Line Amount
The system displays the effective line amount.
Availability
Line Start Date
Specify the line start date. If not specified, system defaults the line start date as the current application date.
Availability Flag
If the Line facility is available then this check box will be checked.
Line Expiry Date
The system displays line final expiry date. This is derived by adding the line grace days with the line expiry date. If ‘Line Grace Days’ is null, then system considers the limit expiry date as the final expiry date.
Facility Fee Preference
Interest Required
Select this check box to indicate the facility is applicable for interest calculation.
Interest Calc AC
Specify the interest calculation account. Alternatively, you can select the interest calc account from the option list. The list displays all valid values.
2.10.4 Maintaining External Liability Linkage
You can link customers to liabilities using the ‘External Liability Linkage Maintenance’ screen. You can invoke this screen by typing ‘STDCRLIK’ in the top right corner of the Application toolbar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
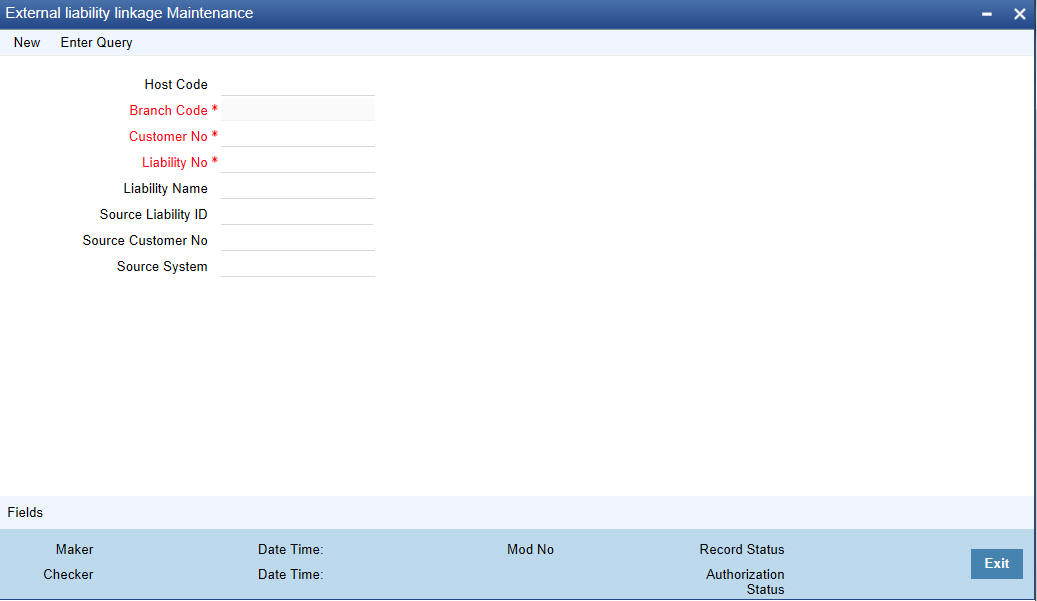
You can specify the following in this screen:
Host Code
Specify the host code. Alternatively, you can select the host code from the option list. The list displays all valid values.
Branch Code
The system defaults the branch code.
Customer No
Specify customer’s number to whom the liability has to be linked.
Liability No
Specify the liability number. Alternatively, you can select the liability number from the option list. The list displays all valid values.
Liability Name
Specify the liability name.
Source Liab ID
Specify the source liability ID.
Source Customer No
Specify the source customer number.
Source System
Specify the source system. Alternatively, you can select the source system from the option list.
2.10.5 Maintaining External Liability
You can maintain liability details in ‘External Liability Maintenance’ screen. You can invoke the screen by typing ‘STDCRLIB’ in the top right corner of the Application toolbar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
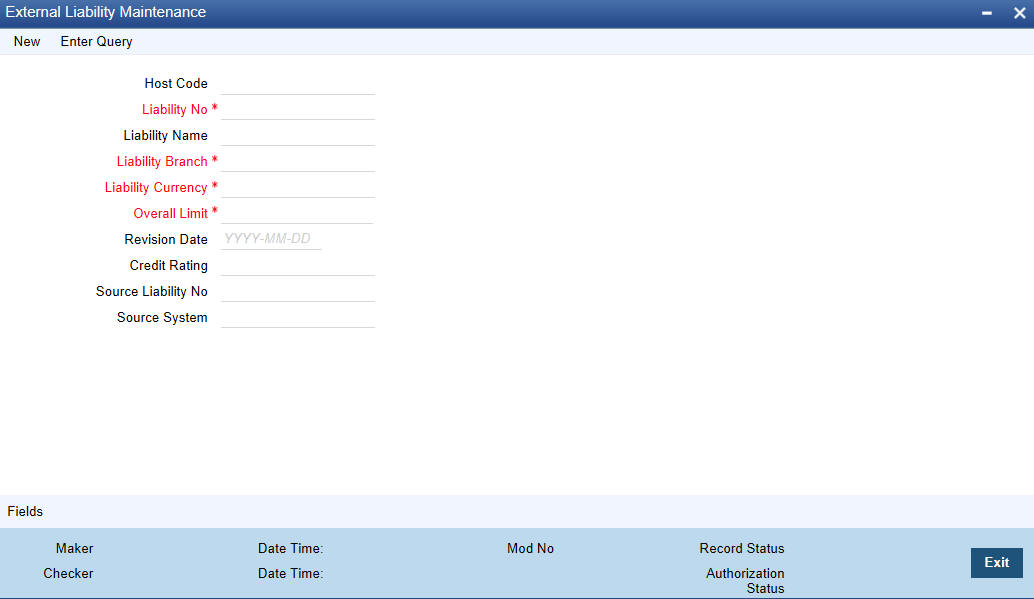
You can specify the following in this screen:
Host Code
Specify the host code. Alternatively, you can select the host code from the option list. The list displays all valid values.
Liability No
Specify the Liability Number. If the Liability Number is customer group then all customers under this group should have same Liability Number.
Liability Name
Specify the Liability Number. If the Liability Number is customer group then all customers under this group should have same Liability Number.
Liability Branch
Specify the branch in which liability is associated.
Liability Currency
Specify the currency with which the liability is associated. If Liability currency is different from Limit currency specified in Global Exposure Parameter then the Liability amount is converted to the limit currency.
Overall Limit
Specify the overall limit amount for that liability. Value entered in the field will be in the currency stated above. If liability is of customer group then overall limits stated will be common to all the customers.
Revision Date
Specify the date on which your bank would wish to revise the limit for the liability. The limit check will continue irrespective of the date maintained here. The revision date must be greater than the start date and can also be left blank.
Credit Rating
The primary credit rating maintained in the credit rating sub screen is displayed here.
Source Liab No
Specify source liability number.
Source System
Specify the source system. Alternatively, you can select the source system from the option list. The list displays all valid values.
2.11 Settlement Details Maintenance
This section contains the following topic:
- Section 2.11.1, "Capturing the BIC Code of a Customer"
- Section 2.11.2, "Viewing BIC Codes"
- Section 2.11.3, "Operations on a BIC Record"
- Section 2.11.4, "Maintaining Bank Directory Plus"
- Section 2.11.5, "Viewing Bank Directory Plus Details"
- Section 2.11.6, "Maintaining IBAN Plus"
- Section 2.11.7, "Viewing IBAN Plus Details"
- Section 2.11.8, "Maintaining BICPlusIBAN"
- Section 2.11.9, "Viewing BICPlusIBAN"
- Section 2.11.10, "Maintaining IBAN Information"
- Section 2.11.11, "Viewing IBAN Information"
- Section 2.11.12, "Uploading BIC Files "
- Section 2.11.13, "IS File Upload"
2.11.1 Capturing the BIC Code of a Customer
As part of setting up some basic information for the functioning of Oracle FLEXCUBE, you should maintain Bank Identifier Codes (BIC).
You can define bank codes through the ‘BIC Code Details’ screen. You can invoke this screen by typing ‘ISDBICDE’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button. If you are maintaining details of a new bank code, select ‘New’ from the Actions Menu in the Application toolbar or click new icon.
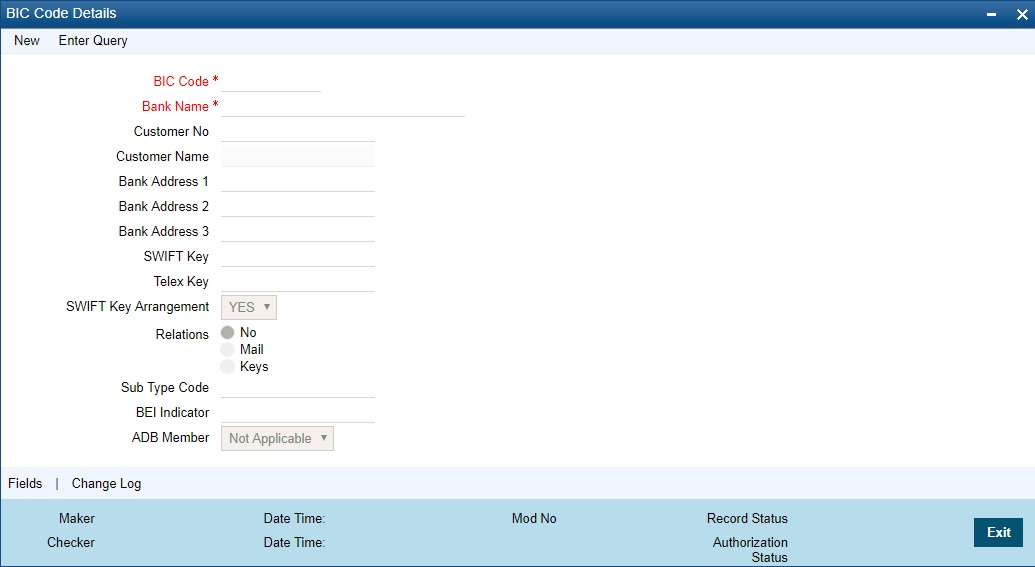
BIC codes can be maintained manually or uploaded from an external source onto Oracle FLEXCUBE.
BIC Code
You need to indicate the code by which the bank is identified by SWIFT. On indicating the Bank Identifier Code, you should indicate the detailed name of the bank. If the bank is a customer of your bank, you can select the CIF ID assigned to the bank from the option list.
Once you select the CIF ID, the name of the bank will be displayed in the Bank Name field. If the bank is not a customer of your bank, you will have to manually enter the name and address of the bank.
Note
The country information is captured to enable Mantas to analyse the transactions for possible money laundering activities.
For more details on Mantas, refer 'Mantas' interface document.
Customer Name
The system displays the name of the specified customer ID based on the details maintained at ‘Customer Maintenance’ level.
Relationship
You have to identify the kind of relationship that exists between your bank and the BIC entity.
Select any one of the following options to indicate the same:
- No – to indicate that the BIC Entity is not a customer of your bank
- Mail – select this option if the BIC entity is not a recognized SWIFT entity but an address internal to you bank. In such cases all correspondence directed to the particular BIC entity will be sent as mail messages.
- Keys – If a SWIFT /Telex connectivity exists between your bank and the bank for which you are maintaining details you can select this option. Subsequently, you will have to specify the SWIFT/Telex Key in the adjacent field.
SK Arrangement
Indicate whether a SK arrangement exists between your bank and the BIC entity. If an arrangement does exist you can select the Yes option from the option list.
Sub-Type Code
Select the appropriate sub-type code to be mapped to the BIC. The adjoining option list offers the following factory-shipped codes:
- BANK - SWIFT Member/Sub member
- BEID - Business Entity Identifier
- BROK - Brokers-Dealers
- COOP - Co-operative Agreement with SWIFT
- CSDS - Clearing Houses, Central Depositories
- CUST - Subsidiary Providers of Custodian and Nominee Services
- ETCP - Electronic Trade Confirmation Providers
- EXCH - Recognized Exchanges
- FUAD - Fund Administrators
- IMIS - Investment Management Institutions
- MCFI - Financial Institution in a MA-CUG
- MCCO - Non-Financial Institution Participant in a MA-CUG
- MONE - Money Brokers
- NSFI - Non-Shareholding Financial Institutions
- NSWB - Non SWIFT BIC's
- PRXY - Securities Proxy Voting Agency
- PSPA - Payment System Participants
- REGI - Registrars and Transfer Agents
- SSPA - Securities System Participants
- TESP - Treasury ETC Service Provider
- TRAD - Trading Institutions
- TRAV - Travellers¿ Cheques Issuers
- TRCO - Treasury Counterparty
- TRUS - Trustees, Fiduciary Service Companies
- ZZZZ - Undefined Institutions
Choose the appropriate one. In case of upload, the system automatically updates this field with the sub-type code corresponding to the BIC.
BEI Indicator
The system identifies whether the BEI status for the chosen sub-type code is ‘Yes’ or ‘No’ from the back-end maintenance in the ‘ISTM_SUBTYPE_CODE’ table. It checks this option whenever the status in the table for the sub-type code is ‘Yes’. You cannot modify this field.
ADB Member
Select a value to indicate membership of the specified BIC code in Asian Development Bank (ADB), from the adjoining drop-down list. This list displays the following values:
- Yes – Select if the BIC code holds a membership in ADB.
- No – Select if the BIC code does not hold a membership in ADB.
- Not Applicable – Select if the membership is not applicable for this BIC code.
Note
- The system maintains ‘Not Applicable’ as the default value.
- If ‘Not Applicable’ is maintained as the status, then the system will not consider the status for validation.
Payment Message
You can indicate whether your counterparty whose BIC Code details you are capturing is capacitated to receive payment messages in the MT 103 format. If so, enable the ‘Generate MT 103 as Payment Message’ option by checking the box.
Note
However, the Counterparty bank will still receive the payment messages in the MT103 format if you do not enable the box ‘Generate MT 103 as Payment Message’
If you have chosen the MT 103 option, you can enable the MT 103 + format option if you would like to generate outgoing MT 103 messages in the MT 103 + Format. Enable the MT 103+ option by checking the ‘MT 103+ Preferred’ box.
You will be allowed to choose the MT 103+ option only if you have enabled the generation of MT 103 messages as Payment Messages. Moreover, you should also ensure that you have also enabled this option:
- For your bank branch in the Branch Parameters Maintenance
- By choosing the Generate 103+ option for currency in the Currency Definition
- For the product used by the contract, in the Product Preferences
The ‘other’ preferences that you need to specify for each BIC entity are as follows:
- CUG Member – enable this option by checking the box positioned next to this field to indicate that the BIC entity is a Closed User Group member
- Update During Upload
- Black-Listed – this indicates that the BIC entity is also black listed
- Remit Member - This indicates that the customer is registered with MT 103 Extended Remittance Information Multi User Group.
Multi Customer Credit Transfer
This option is to indicate whether or not a Multi Credit Transfer Feature [MT102 support] exists between your bank and the BIC entity.
Maximum Size
Indicate the maximum size in bytes, agreed upon between the two parties for transmitting a MT102 message. A null value in this field signifies that there is no limit set on the size of the message.
Whenever the queue exceeds the maximum size specified in the BIC maintenance, the system automatically splits the queue into multiple queues to contain the message within the specified limits.
Generate MT102+
Check this box to process MT102+ messages. Selecting this check box also required the ‘Multi Customer Credit Transfer’ checkbox to be selected.
Generate MT101
This field indicates whether an MT101 can be sent/received from this BIC. Select this option to generate MT101 message.
Note
This is a primary selection criterion. A separate maintenance for agreements has to be maintained in the function ISDCCYRS to generate the MT101.
No of Transaction per Message
Here you can indicate the no of transactions to be included in an MT101 message. If you do not specify a value it will be defaulted to 10.
Note
The system generates notification on authorization of any modification, addition or deletion of BIC code.
2.11.2 Viewing BIC Codes
Oracle FLEXCUBE allows you to store SWIFT BIC in the database. You can directly transfer data from the SWIFT BIC directories to the Oracle FLEXCUBE tables. You can view the uploaded data in the ‘BIC Code Summary’ screen.
You can invoke the ‘BIC Code Summary’ screen by typing ‘ISSBICDE’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
The query option is available on the following fields in this screen:
- BIC Code
- National ID (Only BIC Database plus)
- CHIPS UID (Only BIC Database plus)
- Institution name
- Tag (To identify either FI or AM record type)
- City
- Location
- Country Name
- New BIC
- New Branch Code
- Modification
The BIC Code Summary screen operates as an upload table. The data is entered into Oracle FLEXCUBE using these tables.
2.11.3 Operations on a BIC Record
On an existing BIC code record, you can perform any of the following operations (if a function under the Actions Menu is disabled, it means that the function is not allowed for the record):
Apart from defining a new BIC code record you can perform any of the following operations on an existing record (if any function under the Actions Menu is disabled, it means that the function is not allowed).
- Amend the details of a record
- Authorize a record
- Copy the details of the record
- Close the record
- Reopen the record
- Delete the details of a record
Refer to the User Manual on Common Procedures for details of these operations.
It is assumed that the upload source contains details of all relevant BIC codes. The BIC records that are uploaded to Oracle FLEXCUBE should contain the following tags:
- U - If records do not exist in the Oracle FLEXCUBE BIC directory, the same would be inserted. For a record that already exists, it will be updated with that of the BIC upload.
- M - If there is no existing record in the Oracle FLEXCUBE BIC directory, the same would be inserted. Otherwise the record will be updated with the one in the BIC upload.
- A - For an existing record in the Oracle FLEXCUBE BIC directory, an error will be logged and the upload will continue. If no records exist, then a new record will be updated with the one in the BIC upload.
- D - If there is no existing record in the Oracle FLEXCUBE BIC directory, an error will be logged and the upload will continue. If there is any record existing, then it will be marked as ‘CLOSED’.
- AM- For an existing record in the BIC file or AM file, BIC code would be renamed in the upload file
BIC addresses that have changed will be appropriately updated. Addresses bearing the tag D will be automatically deleted. New BIC records will be created for records that bear the tag N.
The network codes that are marked for exclusion in the ‘BIC Upload Maintenance’ screen will not be uploaded.
The upload sequence is based on the modification tags in the BIC records. The sequence will occur in the following order:
- Deletion
- Modification
- Addition
- Unchanged
The file upload is processed in an asynchornous manner. The system prompts the user to check the logs.
Note
The logs can be viewed by visiting Batch Operations -> Intra Day Batch -> Monitor (Fast Path: BASIDMTR). The function field can be given as ISDBICPU% for searching the upload logs
Click ‘Exit’ or ‘Cancel’ button to exit the screen without initiating the upload process.
2.11.4 Maintaining Bank Directory Plus
You can view the details of each BankDirectoryPlus file record in the ‘Bank Directory Plus Maintenance’ screen. To invoke this screen type ‘ISDBKDPL’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and click on the adjoining arrow button.
Record Key
Specify the record key.
The system displays the following based on the record key specified:
Unique Details
- Office Type
- Parent Office Key
- Head Office Key
- Legal Type
- Legal Parent Key
Group Details
- Group Type
- Group Parent Key
- Institution Status
- Cooperative Group Key
- ISO LEI Code
Address Details
- Institution Name
- Branch Info
- POB Number
- Street Address 1, 2,3 & 4
- City
- CPS
- ZIP Code
- Country Name
- ISO Country Code
- Time Zone
BIC Details
- BIC8
- Branch BIC
- BIC Code
- Chips ID
- National ID
- National ID Type
- Connected BIC
Other Details
- Subtype Indicator
- Network Connectivity
- Branch Qualifiers
- Service Codes
- SSI Group Key
- IBAN Key
2.11.5 Viewing Bank Directory Plus Details
You can view the details maintained in the 'Bank Directory Plus Maintenance' screen using the 'Bank Directory Plus Summary' screen. You can invoke this screen by typing 'ISSBKDPL' in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking on the adjoining arrow button.
In the above screen, you can base your queries on any or all of the following parameters and fetch records:
- Record Key
- Parent Office Key
- Legal Type
- Office Type
- Head Office Key
- Legal Parent Key
Select any or all of the above parameters for a query and click ‘Search’ button. The records meeting the selected criteria are displayed.
- Record Key
- Office Type
- Parent Office Key
- Head Office Key
- Legal Type
- Legal Parent Key
- Group Type
- Group Parent Key
- Institution Status
- Cooperative Group Key
- ISO LEI Code
- BIC8
- Branch BIC
- BIC Code
- Chips ID
- National ID
- Connected BIC
- Institution Name
- Branch Info
- POB Number
- Street Address 1,2. 3 & 4
- City
- CPS
- ZIP Code
- Country Name
- ISO Country Code
- Time Zone
- Subtype Indicator
- Network Connectivity
- Branch Qualifiers
- Service Codes
- SSI Group Key
- IBAN Key
2.11.6 Maintaining IBAN Plus
You can view the details of each IBANPlus file record in the ‘IBAN Plus Maintenance’ screen. To invoke this screen type ‘ISDIBNPL’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and click on the adjoining arrow button.
Record Key
Specify the record key.
The system displays the following based on the record key specified:
- Institution Name
- Country Name
- ISO Country Code
- IBAN ISO Country Code
- IBAN BIC
- Routing BIC
- IBAN National ID
- Service Context
2.11.7 Viewing IBAN Plus Details
You can view the details maintained in the 'IBAN Plus Maintenance' screen using the 'IBAN Plus Summary' screen. You can invoke this screen by typing 'ISSIBNPL' in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking on the adjoining arrow button.
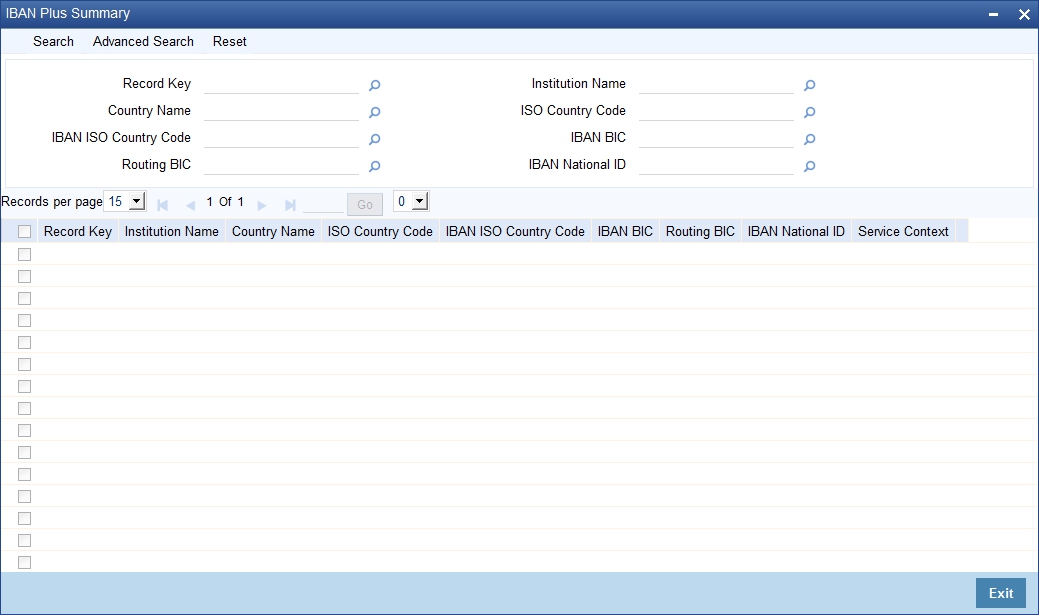
In the above screen, you can base your queries on any or all of the following parameters and fetch records:
- Record Key
- Country Name
- IBAN ISO Country Code
- Routing BIC
- Institution Name
- ISO Country Code
- IBAN BIC
- IBAN National ID
Select any or all of the above parameters for a query and click ‘Search’ button. The records meeting the selected criteria are displayed.
- Record Key
- Institution Name
- Country Name
- ISO Country Code
- IBAN ISO Country Code
- IBAN BIC
- Routing BIC
- IBAN National ID
- Service Context
2.11.8 Maintaining BICPlusIBAN
Oracle FLEXCUBE supports the Upload of BICPlusIBAN directory.
BICPlusIBAN is a SWIFT directory that lists institution identifiers recognized by the financial industry, for example, Bank Identifier Codes, CHIPS UIDs, national clearing codes, and IBAN-related information. It also provides name and addresses of the corresponding entities.
BICPlusIBAN is used to identify correspondents and counterparties accurately, and to allocate the correct code when sending messages, thus improving Straight Through Processing (STP). Initiators of cross-border payments within Europe are required to submit the BIC and IBAN codes to the receiver in order to benefit from reduced payment transaction charges.
You can invoke the ‘BIC and IBAN Summary’ screen by typing ‘ISSEBANP’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
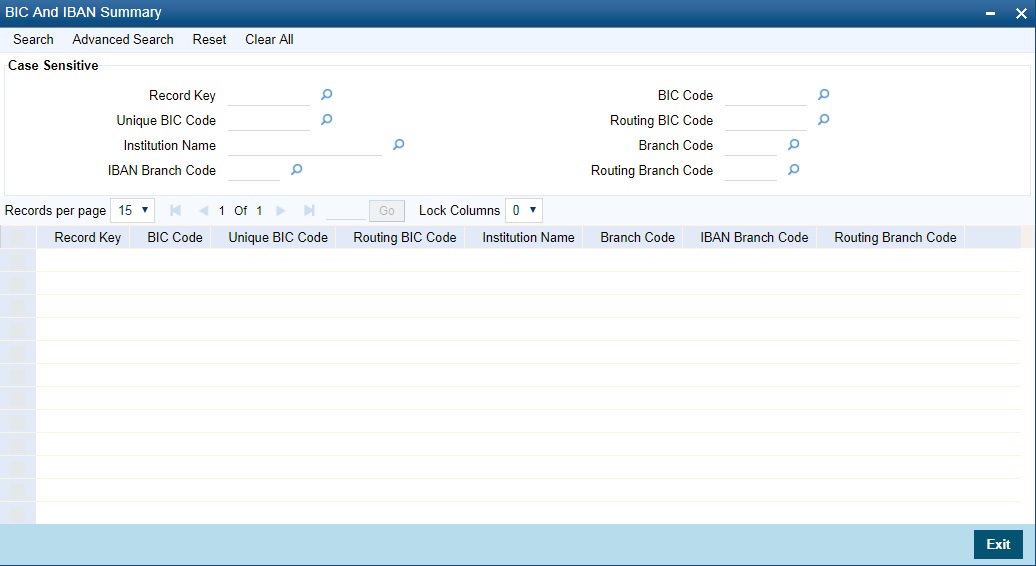
2.11.9 Viewing BICPlusIBAN
You can invoke the ‘BIC and IBAN Summary’ screen by typing ‘ISSEBANP’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.

Unique Key for Record
Specify the unique key of the record in the file. This consists of ISO country code and sequential number of six digits.
2.11.10 Maintaining IBAN Information
Invoke the ‘IBAN Information Maintenance’ screen by typing ‘ISDESBAN’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
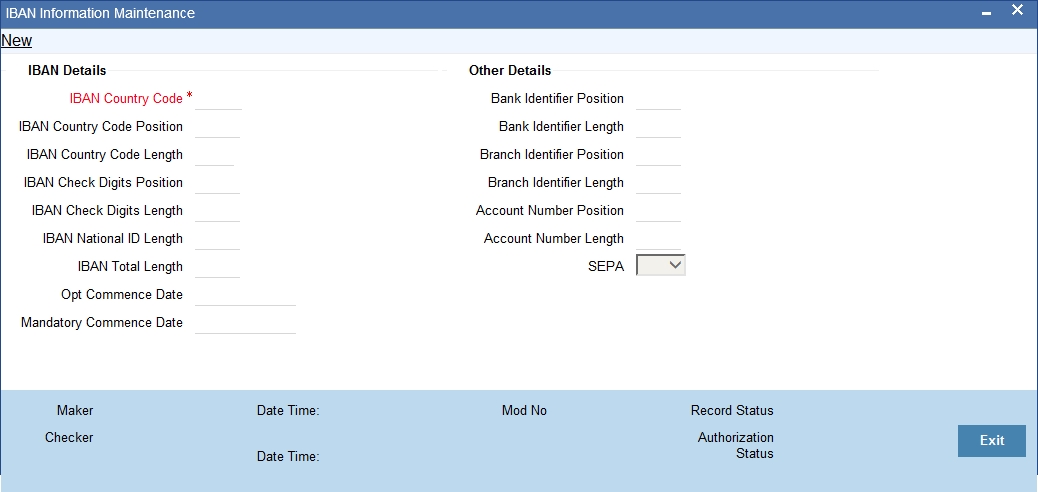
Here you can specify the details of the following:
IBAN Country Code
Specify the ISO country code prefix in the IBAN.
IBAN Country Position
Specify the position of the country code in IBAN.
IBAN Country Code Length
Specify the number of characters of the country code in the IBAN.
IBAN Check Digits Position
Specify the start position of check digits in the IBAN
IBAN Check Digits Length
Enter the Number of check digits in the IBAN
Bank Identifier Position
Enter the Start position of bank identifier in the IBAN
Bank Identifier Length
Specify the Number of characters of bank identifier in the IBAN
Branch Identifier Position
Specify the Start position of the branch identifier in the IBAN (value is empty if the branch identifier is not applied in the country's IBAN format)
Branch Identifier Length
Specify the Number of characters of the branch identifier in the IBAN (value is 0 if the branch identifier is not applied in the country's BAN format)
IBAN National ID Length
Specify the Number of significant characters of the National ID value that are used by SWIFT to populate the IBAN NATIONAL ID, and that are sufficient to derive the IBAN BIC correctly.
This number can be different from (that is, smaller than) the length of the national bank/branch identifier defined in the IBAN Registry.
SWIFT refines its IBAN to BIC translation algorithms, this number may change from release to release.
Account Number Position
Specify the Start position of the account number in IBAN.
Account Number Length
Specify the Number of characters of account number in IBAN
IBAN Total Length
Specify the total number of characters of the IBAN.
Optional Commence Date
Specify the date from when the IBAN structure is an optional requirement.
Mandatory Commence Date
Specify the date from when the IBAN structure is a mandatory requirement.
SEPA
Select the SEPA from the adjoining drop-down list. The options are:
Y - Select ‘Y’ if the IBAN is used in any of the SEPA schemes.
N- Select ‘N’ if the IBAN is not used in the SEPA schemes.
2.11.11 Viewing IBAN Information
Invoke the ‘IBAN Information Summary’ screen by typing ‘ISSESBAN’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
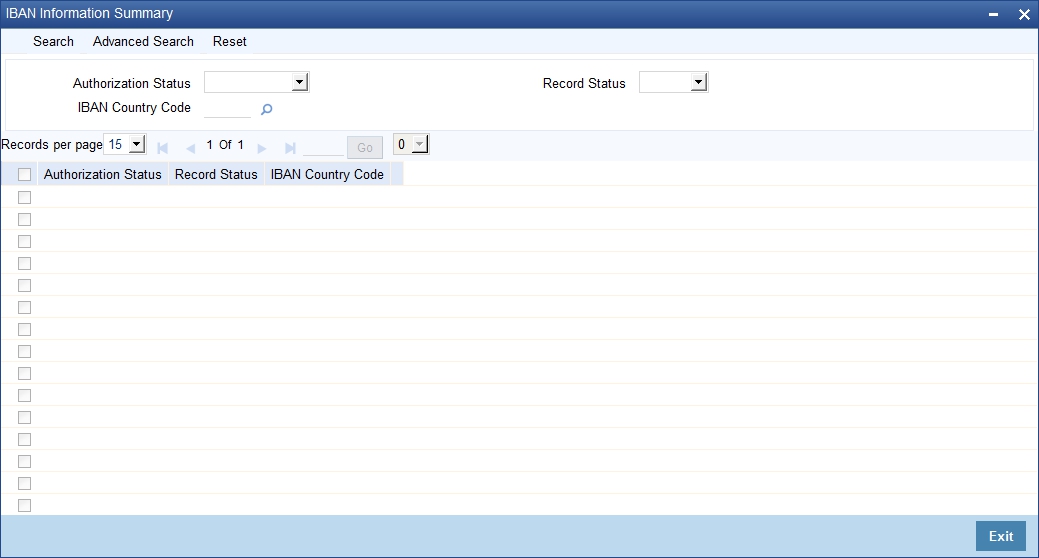
In the above screen, you can base your queries on any or all of the following parameters and fetch records:
- Authorization Status
- IBAN Country Code
- Record Status
Select any or all of the above parameters for a query and click ‘Search’ button. The records meeting the selected criteria are displayed.
- Authorization Status
- Record Status
- IBAN Country Code
The IBAN Check Digit and IBAN Check National ID validations are applicable only if the IBANPLUS_REQD global parameter value is 'Y'.
2.11.12 Uploading BIC Files
SWIFT allows you to upload the entire BIC file or individual records like Amendments (AM) and File Instructions (FI) record files within the BIC upload file, on to the BIC directory. You can perform this through the ‘BIC Upload’ screen.
The BICPlusIBAN directory consists of the following files:
- BI file (BICPlusIBAN Information)
- IS file (IBAN Structure information)
- The BICPlusIBAN directory should be used to
- Translate beneficiary bank’s BIC into national (clearing, sort) code
- Show banks’ participation in RTGS system
- Show banks’ details (name, address & so on)
- BICPlusIBAN Directory can also be used as an enquiry tool
- SEPA Related:
- Derive BIC from the IBAN, if missing
- Validate IBANs and BICs
On successful upload of BIC Plus IBAN, system populates the SWIFT BIC directory and the clearing codes automatically.
2.11.13 IS File Upload
This file forms the part of the BICPlusIBAN package. This contains information about the IBAN structure applicable in the countries.IS File forms are stored in a new data store and are used for IBAN structure validations. Invoke the ‘BIC Upload’ screen by typing ‘ISDBICPU’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
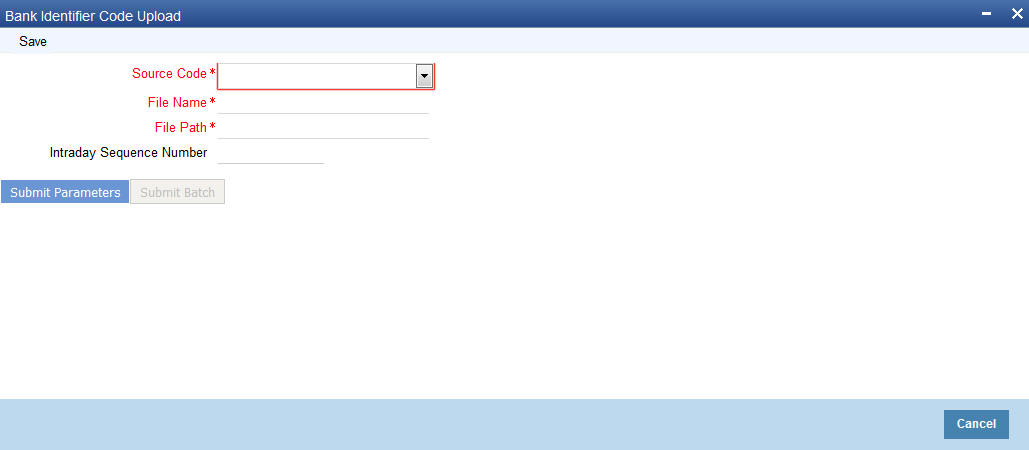
Here you can specify the following details:
Source Code
Specify the source from which you want to upload details. You can select the appropriate source code from the drop-down list displaying the following values:
- BIC - Select this to upload the BIC file
- CCH File - Select this to upload the country-wise holiday file
- BIC Plus IBAN - Select this to upload BIC plus IBAN file.
- BICPlusIBANIS - Select this to upload IBAN structure file
- BankDirectoryPlus - Select this to upload Bank Directory Plus file.
- IBANPlus - Select this to upload IBAN Plus file
- IBANStructure - Select this to upload IBAN structure file
- IBAN EXCLUSION LIST - Select this to upload IBAN exclusion list
- SEPA Plus - Select this to upload SEPA Plus file
- BICPLUS2018 - Select this to upload BIC Plus 2018 file
- BICPLUS2018 Country - Select this to upload BIC Plus 2018 country file
- BICPLUS2018 Currency - Select this to upload BIC Plus 2018 currency file
- BICPLUS2018 Holiday - Select this to upload BIC Plus 2018 holiday file
- BICPLUS2018 Holiday Services - Select this to upload BIC Plus 2018 holiday services file
- BICPLUS2018 TimeZone - Select this to upload BIC Plus 2018 time zone file
File Path
State the path in the database server where the uploaded file should be stored.
File Name
Specify a name for the uploaded file. The file name should bear the extension ‘.DAT’.
Intraday Sequence Number
The system generates an intraday sequence number when ‘Submit Parameters’ or ‘Submit Batch’ is clicked.
Click ‘Submit Params’ button and ‘Submit Batch’ button to start the upload process.
2.11.14 BIC Record File Formats
The file formats for the FI and AM records is as under:
FI record
Position |
Description |
Length |
Type |
Mandatory |
Data |
1 |
Tag Identifier |
2 |
VARCHAR2 |
Y |
‘FI’ |
3 |
Modification Flag |
1 |
VARCHAR2 |
Y |
‘A’ addition ‘M’ modification ‘D’ deletion ‘U’ unchanged |
4 |
BIC (Bank, Country & Location Code) |
8 |
VARCHAR2 |
Y |
Bank code (4 char) Country code (2 char) Location code (2 char) |
12 |
BIC (Branch code) |
3 |
VARCHAR2 |
Y |
Branch code, with - ‘XXX’ if no branch code exists |
15 |
Institution Name |
35 |
VARCHAR2 |
Y |
Name (first part) |
50 |
Institution Name |
35 |
VARCHAR2 |
N |
Name (second part) |
85 |
Institution Name |
35 |
VARCHAR2 |
N |
Name (third part) |
120 |
Branch Information |
35 |
VARCHAR2 |
N |
Branch specification (first part) |
155 |
Branch Information |
35 |
VARCHAR2 |
N |
Branch specification (second part) |
190 |
City Heading |
35 |
VARCHAR2 |
Y |
City name |
225 |
Subtype indication |
4 |
VARCHAR2 |
Y |
A subtype can be bank, broker, etc. |
229 |
Value Added Services |
60 |
VARCHAR2 |
N |
20 x 3 char. Fields indicating the Value-added Service Code |
289 |
Extra Information |
35 |
VARCHAR2 |
N |
Specific information |
324 |
Physical address |
35 |
VARCHAR2 |
N |
Physical address (first part) |
359 |
Physical address |
35 |
VARCHAR2 |
N |
Physical address (second part) |
394 |
Physical address |
35 |
VARCHAR2 |
N |
Physical address (third part) |
429 |
Physical address |
35 |
VARCHAR2 |
N |
Physical address (fourth part) |
464 |
Location |
35 |
VARCHAR2 |
N |
Location (first part) |
199 |
Location |
35 |
VARCHAR2 |
N |
Location (second part) |
534 |
Location |
35 |
VARCHAR2 |
N |
Location (third part) |
569 |
Country name |
35 |
VARCHAR2 |
N |
Country name (first part) |
604 |
Country name |
35 |
VARCHAR2 |
N |
Country name (second part) |
639 |
POB Number |
35 |
VARCHAR2 |
N |
Post Office Box number |
674 |
POB Location |
35 |
VARCHAR2 |
N |
POB Location (first part) |
709 |
POB Location |
35 |
VARCHAR2 |
N |
POB Location (second part) |
744 |
POB Location |
35 |
VARCHAR2 |
N |
POB Location (third part) |
779 |
POB Country name |
35 |
VARCHAR2 |
N |
POB Country name (first part) |
814 |
POB Country name |
35 |
VARCHAR2 |
N |
POB Country name (second part) |
AM record
The AM record would consist of only the tag identifier, old BIC and the new BIC. The file format is as follows:
Position |
Description |
Length |
Type |
Mandatory |
Data |
1 |
Tag Identifier |
2 |
VARCHAR2 |
Y |
‘AM’ |
3 |
Old BIC |
11 |
VARCHAR2 |
Y |
Old BIC |
14 |
New BIC |
11 |
VARCHAR2 |
Y |
New BIC |
2.12 MIS Details Maintenance
This section contains the following topics:
- Section 2.12.1, "Maintaining MIS Class"
- Section 2.12.2, "Saving the Record"
- Section 2.12.3, "Maintaining MIS Group"
- Section 2.12.4, "Operations on the MIS Group Record"
- Section 2.12.5, "Maintaining MIS Cost Codes"
- Section 2.12.6, "Operations on the MIS Cost Code Record"
- Section 2.12.7, "Maintaining MIS Pool"
2.12.1 Maintaining MIS Class
In order to maintain MIS classes, you need to invoke the ‘MIS Class Maintenance’ screen by typing ‘GLDCLSMT’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking on the adjoining arrow button. In this screen, you can define various categories based on which reports on general ledgers should be classified. To maintain details of a new MIS class, click new icon.
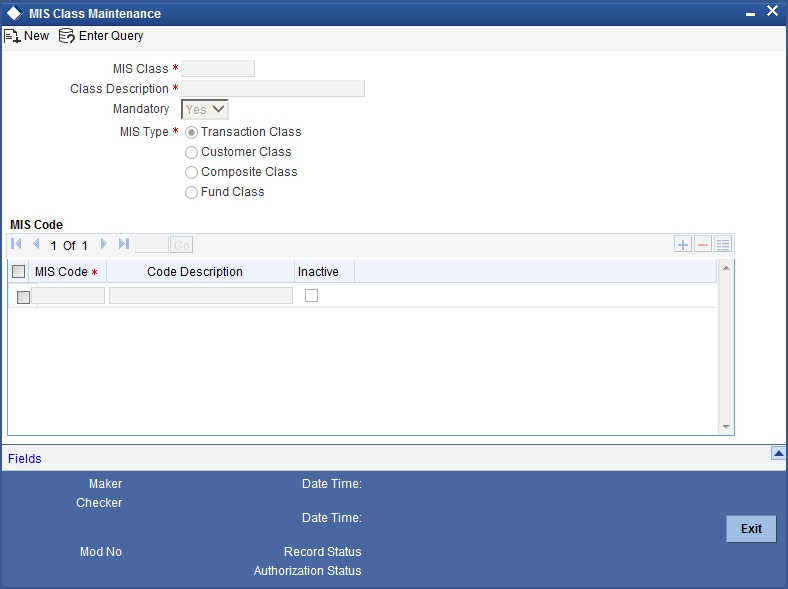
Here you can maintain the following details:
MIS class
In Oracle FLEXCUBE, each MIS class that you maintain is identified by a unique nine-character code called a Class Code. You can follow your own convention for devising this code.
Description
You can specify a short description that will enable you to identify the MIS class quickly. The short description that you specify is for information purposes only and will not be printed on any customer correspondence.
An important detail in defining an MIS class is to specify the type of class that you are creating. The MIS class type identifies the basic nature of the class. In Oracle FLEXCUBE you can set up the following type of MIS classes:
- Transaction class — A transaction class refers to all transactions that have taken place through any of the front-end modules like foreign exchange, money market etc. Customer Class relates to customer accounts.
- Customer class — Select this option if you are defining a customer-based classification.
- Composite class — Choose this option to indicate that the MIS class can be used both at customer definition and at the time of processing a transaction.
- Fund class — Refer to the Core Services User manual for details on setting up a Fund MIS class
This is the basic feature of a class and will determine the type of MIS codes that can constitute the class. For each of these MIS types you can create a maximum of ten classes.
Mandatory
Using this field, you can indicate whether entering an MIS code is mandatory for a particular MIS class or not. Whenever any transaction is stored, the system checks if an MIS code is supplied for this MIS class invoked in the transaction.
MIS Codes
Under a class, you can indicate the sub-divisions that should be reported under the class. Each of the sub-classes is given unique code identifiers.
The MIS codes that you associate with a class will fall under the class at the time of reporting or consolidation.
Click add icon to associate an MIS code to a class. To remove an MIS class from the list, place your cursor in that row and click delete icon.
The MIS codes that you associate will depend on the Type of MIS Class that you are creating. While setting up the details of a customer, you can associate the customer to a customer type MIS Code. Therefore the set up serves more for management purposes and makes the management of GLs simple and easy.
2.12.2 Saving the Record
Click save icon to save the record. Click delete icon to exit without saving the details that you entered. An MIS Class that you have created will be available for use only after it has been authorized by a user bearing another ID.
Similarly, you cannot make any modifications to a Class or Category until the previous modification made, has been authorized. After you have made the required entries, click ‘Exit’ button to exit the screen. You will be returned to the Application Browser.
2.12.3 Maintaining MIS Group
You can invoke the ‘MIS Group Maintenance’ screen by typing ‘MIDGRPMT’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking on the adjoining arrow button.
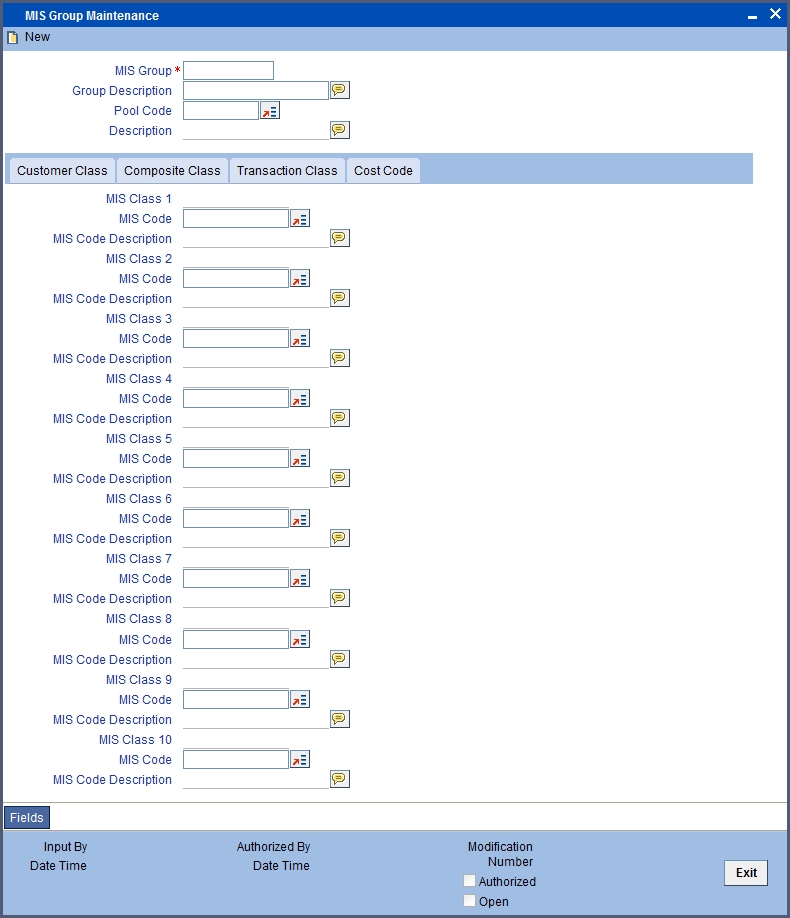
If you are creating a new MIS Group, select ‘New’ from the Actions Menu in the Application toolbar or click new icon. The ‘MIS Group Definition’ screen is displayed without any details.
If you are calling an MIS Group that has already been defined, double-click an MIS Group from the summary screen.
2.12.4 Operations on the MIS Group Record
On an existing MIS Group record, you can perform any of the following operations (if any function under the Actions Menu is disabled, it means that the function is not allowed for the record):
- Amend the details of an MIS Group
- Authorize an MIS Group
- Copy the details an MIS Group on to a new one
- Print the details of an MIS Group
- Delete an MIS Group
Please refer to the manual on Procedures for details of these operations.
2.12.5 Maintaining MIS Cost Codes
An MIS cost code represents the notional cost incurred for a transaction. An MIS cost code can be attached either to an account or to a contract, in the following manner:
- You can link a Cost Code to an account class. This will default to the accounts maintained under the account class. You can change this default. Alternatively, you can link an MIS Cost Code to an account when maintaining it.
- When creating a product, you can identify the Cost Codes against which contracts involving the product should be reported.
- When processing a contract, the Cost Codes identified for the product (the contract involves) will automatically default. These defaults can be changed. If cost codes have not been identified for the product, you can identify one for the contract.
The notional cost will be reported in the profitability report.
You can invoke this screen by typing ‘MIDXCODE’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application toolbar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
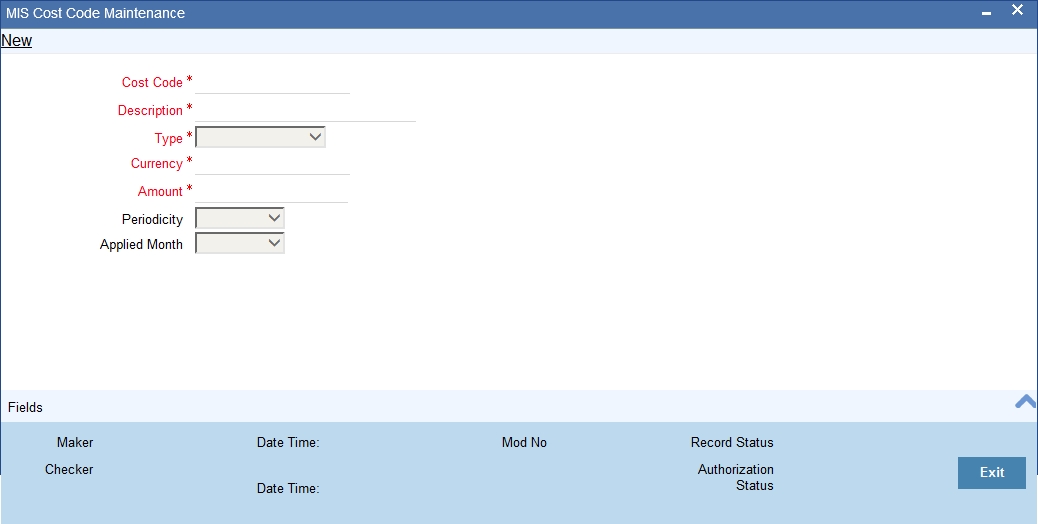
If you are creating a new MIS Cost Code, select ‘New’ from the Actions Menu in the Application toolbar or click new icon. The ‘MIS Cost Code Maintenance’ screen is displayed without any details.
If you are calling an MIS Cost Code that has already been defined, double-click on an MIS Cost Code from the summary screen.
Type
The MIS Cost Code can belong to one of the following types:
Number of Transactions
This typically applies for calculating the cost of processing a transaction involving an account.
You can indicate the amount to be considered as the notional cost for each transaction.
For example, you may incur a certain amount for every transaction you process of a savings account a particular category. This cost could be different for processing transactions in a different type of savings account or for current accounts. You should define different MIS Cost Codes and link them to the appropriate account classes.
Event based Charges
The notional cost applicable for processing an event can be defined as a cost code. Typically, this applies for a contract.
For example, for processing an event in the life-cycle of a loan, you may want to attach a certain cost. You can define a cost code for it and link it to the product.
Similarly, you can define a different notional cost for different events in the life-cycle of a contract. Thus, you can have a cost code for initiating a loan, one for liquidating interest, and so on, and link them to the product with the appropriate event codes.
The notional cost that you define will be taken as the cost per event.
Duration based charges
These changes are applied typically for a contract. The notional cost in this case, is calculated on the basis of a specific duration. This notional cost is defined for a cost code. The following example illustrates how this cost is applied on a contract.
For example, if a loan is live for a month, the notional cost you incur is a specific amount. You would define a duration based cost code, define the periodicity as 'monthly'. For every month a loan linked to the cost code is live, the notional cost will be applied.
Cost
The notional cost, along with the currency in which it is expressed should be indicated for the cost code. The cost will be applied based on the Cost Code type, as follows:
Cost Code Type |
Description |
Number of Transactions |
The amount is taken as the cost per transaction |
Event |
The amount is taken as the cost per event |
Duration |
The amount is taken as the cost for the period defined as the periodicity, for the cost code |
If a currency conversion is involved during reporting, the prevailing conversion rate will be used.
Periodicity
This is the periodicity at which the costs defined have to be applied. In the profitability report, the notional cost reported would depend on the periodicity defined for the cost code.
For a quarterly, half-yearly or yearly periodicity, you should also indicate the first month of application. The subsequent application months would be computed based on this.
2.12.6 Operations on the MIS Cost Code Record
On an existing MIS Cost Code record, you can perform any of the following operations (if any function under the Actions Menu is disabled, it means that the function is not allowed for the record):
- Amend the details of an MIS Cost Code
- Authorize an MIS Cost Code
- Copy the details an MIS Cost Code on to a new one
- Print the details of an MIS Cost Code
- Delete an MIS Cost Code
Please refer to the manual on Common Procedures for details of these operations.
2.12.7 Maintaining MIS Pool
You can invoke the ‘MIS Pool Code Maintenance’ screen by typing ‘MIDXPOLD’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking on the adjoining arrow button.
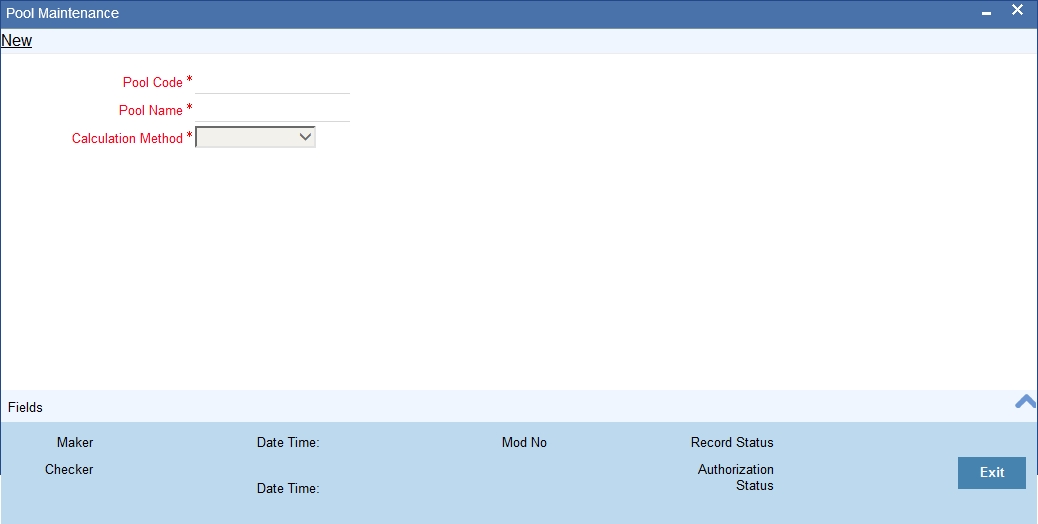
If you are creating a new MIS Pool Code, select ‘New’ from the Actions Menu in the Application toolbar or click new icon. The ‘MIS Pool Code Definition’ screen is displayed without any details.
If you are calling an MIS Pool Code that has already been defined, double-click on an MIS Pool Code from the summary screen.
2.13 User Defined Fields Maintenance
This section contains the following topics:
- Section 2.13.1, "Invoking the User Defined Fields Maintenance Screen"
- Section 2.13.2, "Mapping UDF Function Field"
2.13.1 Invoking the User Defined Fields Maintenance Screen
Based on your requirement and the nature of the field, you can specify default values and validations for the field. Oracle FLEXCUBE will validate all entries made to the field against the validations you define for a field. You can invoke the ‘User Defined Fields Maintenance’ screen by typing ‘UDDUDFMT’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking on the adjoining arrow button.
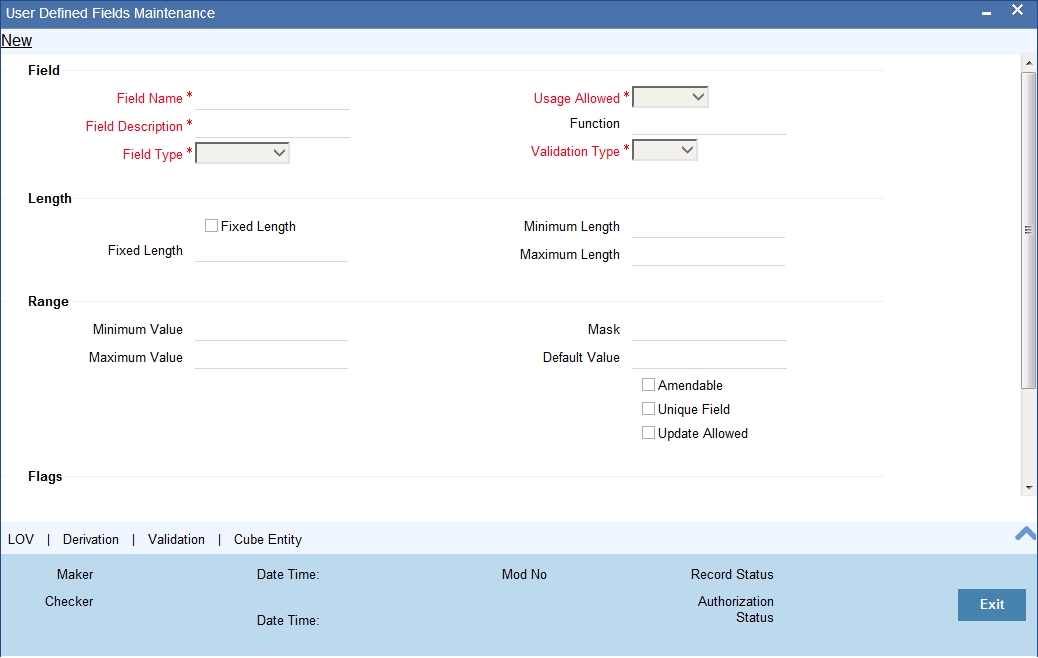
A field that you have created will become operational in Oracle FLEXCUBE only after it is authorized. A user bearing a different Login ID can authorize a field definition record that you have created.
2.13.2 Mapping UDF Function Field
You can maintain the user defined fields function mapping in the User Defined Fields Function Field Mapping Maintenance screen. To invoke this screen type ‘UDDFFLMT’ in the top right corner of the application toolbar and click the adjoining arrow button.
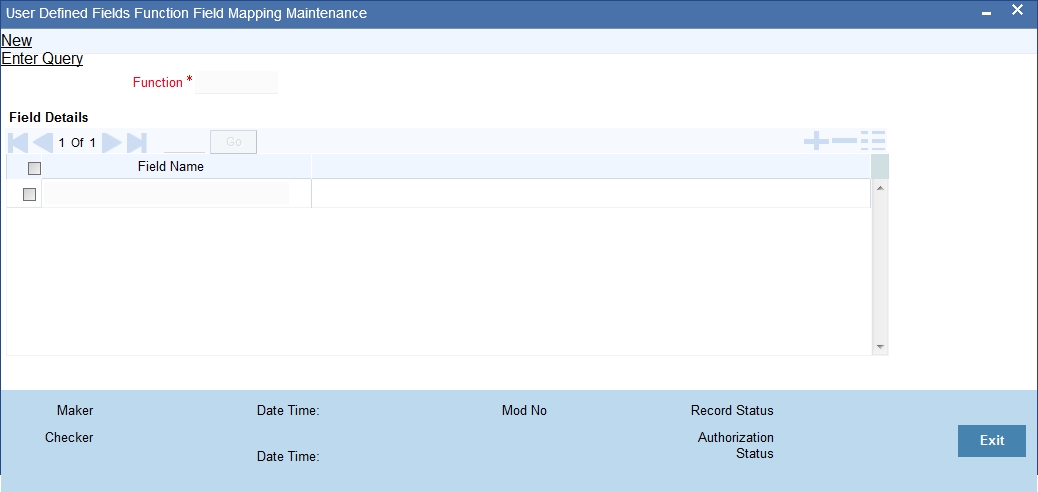
You can specify the following in this screen:
Function
Specify the function ID. Alternatively, you can select the function from the option list. The list displays all valid functions maintained in the system.
Field Name
Specify the name of the field. Alternatively, you can select the field name from the option list. The list displays all valid fields maintained in the system.
2.14 Generic Interface Maintenance
This section contains the following topics:
- Section 2.14.1, "Invoking GI Process"
- Section 2.14.2, "Viewing Error Details of Individual Record"
- Section 2.14.3, "Specifying Interface Definition Details"
- Section 2.14.4, "Viewing Interface Definition Summary"
- Section 2.14.5, "Maintaining AUDF (ASCII User Defined Function) Details"
- Section 2.14.6, "Viewing AUDF Summary Details"
2.14.0.1 Maintaining GI Parameter
You can set the parameters for the framework of Generic Interface processing in the following screen ‘Parameters’ screen invoked from the Application Browser. You can invoke this screen by typing ‘GIDPARAM’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
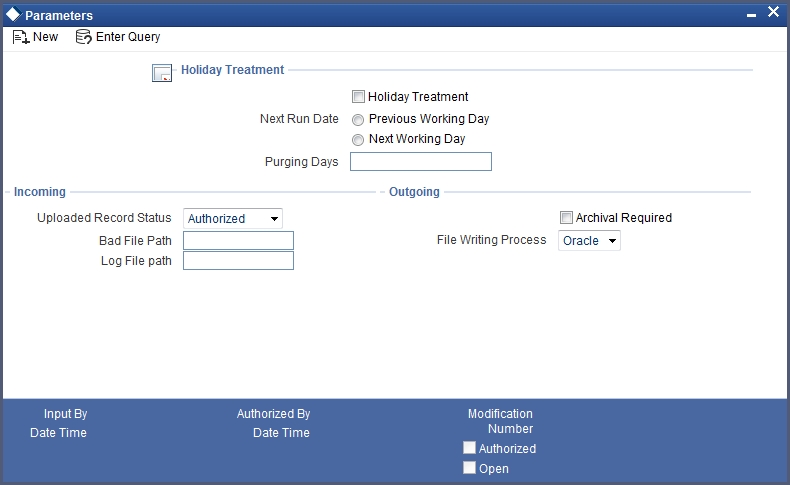
You can maintain the following parameters for generic interface here.
Holiday Treatment
You can specify the parameters for interface processing if the schedule date falls on a holiday.
Holiday Treatment
Check this box to indicate your preference for interface processing on a holiday.
Next Run Date
Specify how the system should process if the schedule date falls on a holiday. You can select the options as either move the interface processing to previous working date or next working date if the interface processing day falls on a holiday.
Note
The default holiday treatment is movement to ‘next working date’.
Purging Days
Specify the purging days if you want to maintain any days to be purged while processing interface.
Incoming
You can specify the parameters for interface processing for the incoming files.
Uploaded Record Status
Select the input status of the transaction record after upload as:
- Authorized
- Unauthorized
Note
By default ‘Authorized’ option is selected.
Bad File Path
Specify the path where the external tables should write the bad records, while reading from the Incoming file.
Log file Path
Specify the path where the external tables should write the Log file, while reading from the Incoming file.
Outgoing
You can specify the parameters for interface processing for the outgoing files.
Archival Required
Check this box to specify if the upload table data and file log data should be archived at the time of EOD or before deleting the same.
File writing process
Select the tool to write the data into output file from the following options:
- Oracle - This component uses ORACLE UTIL packages to write the data into output file.
- Java - This component uses java libraries ages to write the data into output file
Note
By default ‘Oracle’ option is selected.
You need to note the following details while selecting the tool for file writing:
- This feature is applicable only for the outgoing process
- Low volume sites are recommended to use Oracle tool only in case of high volume Java tool is recommended.
- If Java tool is selected then the necessary Java software/component should be installed in the database server and jvm is enabled in database.
2.14.1 Invoking GI Process
You can trigger the process of Generic Interface using Gateway Messages, EOD run or through ‘Interface Trigger’ screen. You can invoke this screen by typing ‘GIDIFPRS’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
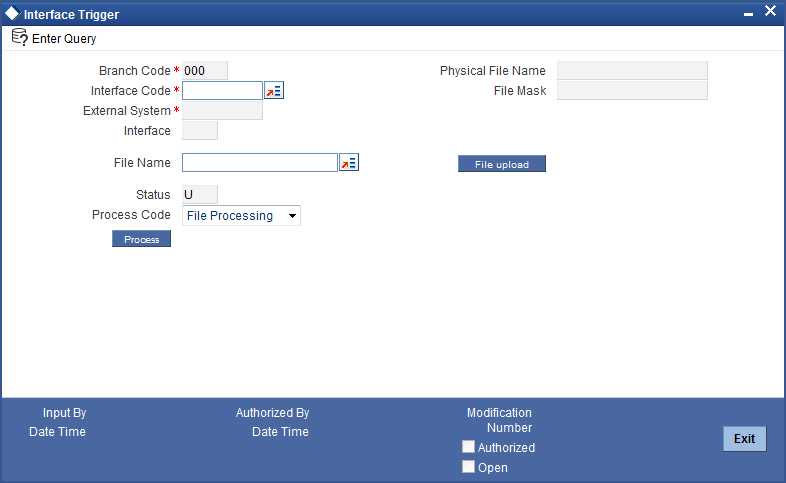
You can provide the following details here to invoke the GI routing package.
Branch Code
Specify the branch code from where the GI file process has to be initiated.
Interface Code
Select the Interface Code that has to be processed.
Based on the selected interface code, system defaults external system and interface type.
File Name
Specify the file name if the selected Interface Code is Incoming.
Process Code
Select the process code from the drop-down list, if the selected Interface Code is Incoming. The options available are:
- FP – Populating the Upload tables using the file data.
- DP – Populating the Base tables from the Upload tables.
- AL – This is will trigger ‘FP’ and ‘DP’ processes one after another.
- RT – This is Retry operation the previous process that failed is triggered.
- RE – This will rerun the ‘DP’ process for error records.
Physical File Name
A physical file name is applicable if you are processing a file that is uploaded through the ‘Interface Trigger’ screen.
When the file upload is successful, the system will display the name of the file in this field.
File Mask
The system displays the incoming file mask specified during interface definition.
2.14.2 Viewing Error Details of Individual Record
You can view the individual record error details of the uploaded file in the ‘View Error Details’ (GIDFILOG) screen. From the summary screen (GISFILOG), double click the selected record to view the error details screen.
You can invoke View Error Details screen by typing ‘GIDFILOG’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
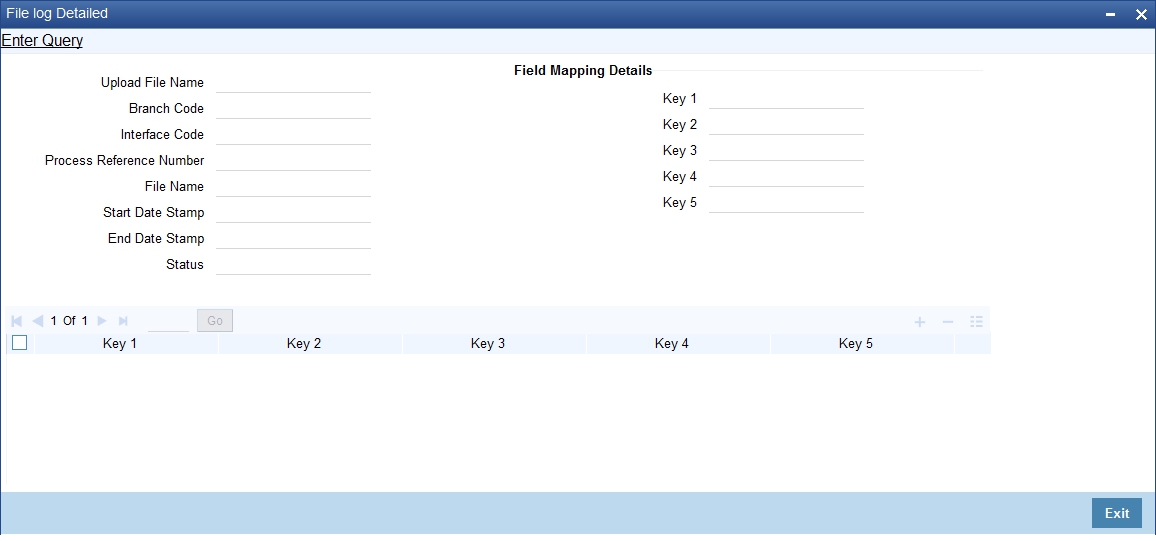
Based on the upload file name and process reference number, system displays the error details here:
- Upload File Name
- Branch code
- Interface Code
- Process Reference Number
- File Name
- Started Time
- Ended Time
- Status
Following field mapping details are also displayed
- Key 1
- Key 2
- Key 3
- Key 4
- Key 5
- Error Code
- Error Description
2.14.3 Specifying Interface Definition Details
You can define the format details and properties associated with interface file in the ‘Interface Definition’ screen. You can invoke this screen by typing ‘GIDIFTDF’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
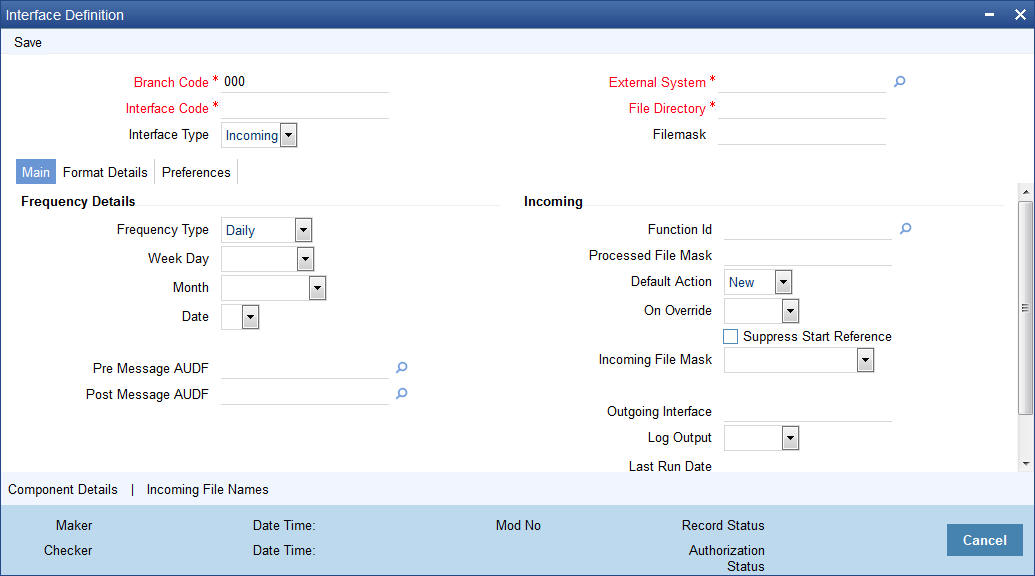
You can define the following interface file properties, formats and components here.
Branch Code
Specify the code of the branch to which the interface belongs.
Interface Code
Specify a unique interface code to identify the interface as incoming or outgoing.
Interface Type
Select the interface type from the following options:
- Incoming - Select this option if the file data needs to be uploaded into Oracle FLEXCUBE
- Outgoing - Select this option if data from Oracle FLEXCUBE needs to be written into file
External System
Specify the external system with which Oracle FLEXCUBE is interfacing.
File Directory
Specify the Oracle directory name. All the incoming/outgoing files will be copied to the path specified for this Oracle directory name. The name of the Oracle directory specified here should correspond to the path ending with 'ready' folder.
Data Controller (Bank) can use the OS features to manage and control access to the data files.
File Mask
Specify the file mask for the outgoing interface file.
2.14.3.1 Main Tab
Frequency Details
Frequency Type
Select the frequency type for interface file processing from the following drop-down options:
- Daily
- Weekly
- Fort Nightly
- Monthly
- Quarterly
- Half-yearly
- Yearly
- Adhoc
Note
If Adhoc is specified it will override any existing restrictions.
Week Day
If you select frequency type as ‘Weekly’, select the day from the drop-down list for processing the interface file. The options available are:
- Sunday
- Monday
- Tuesday
- Wednesday
- Thursday
- Friday
- Saturday
Month
If you select frequency type as ‘Quarterly, Half Yearly and Yearly’, select the month for the interface file execution from the drop-down list. The options available are:
- January
- February
- March
- April
- May
- June
- July
- August
- September
- October
- November
- December
Date
If you select frequency type as ‘Monthly, Quarterly, Half Yearly and Yearly’, select the date of the month for the interface file execution from the drop-down list.
Pre Message AUDF
Specify the AUDF that needs to be invoked before triggering the interface. You can use this to add additional functionality required at the message level.
Post Message AUDF
Specify the AUDF that needs to be invoked after triggering the interface. You can use this to add additional functionality required at the message level.
Incoming
You can specify the interface details applicable for incoming file details here.
Function ID
Specify the function id for which the incoming data need to be sent.
Processed File Mask
Specify the file mask for renaming the incoming file after uploading the data.
Default Action
Select the default action which needs to be invoked to process the uploaded data in the upload table from the drop-down list below:
- New
- Modify
- Close
On Override
Select the action to be taken if an override occurs from the drop-down list below:
- Reject
- Continue
- Skip
Suppress Start Reference
Check this box to indicate that the start reference number should be suppressed.
If the checkbox is selected and start reference element is defined in the component definition, system raises an error message while saving the interface. System validates the start reference check for Header, Body and Footer.
For a given interface, mask and suppress start reference are applicable to all the file names configured for that interface
Incoming File Mask
Specify the file mask for selecting the incoming files from the file directory. System supports four types of file masking:
- Date and Time mask (YYYYMMDDHHMISS) – (year, month, date, hours, minutes and second)
- Sequence number based mask(nnn) – 3 digit numeric numbers
- File names starting with a specific signature. (Upload all files which are starting with incoming File name)
- Exact File Name (File Names which are exact match with the file name in interface definition)
System searches all the files which are matching the mask criteria and process the files one by one “_” as the split separator for the file name and the mask criteria.
Note
System will continue or break the uploading of records based on the error handling defined in the 'On Override' field. If it is Continue, then the system will ignore the current record and continue with the next record. If it is Reject, then the system will stop the execution of the file and start executing the next available incoming file.
Note
By default system append the Incoming File Mask type to the file name while searching the physical file name. If an interface supports for multiple type incoming files, then same file mask is applicable for all type of incoming files.
Outgoing Interface
Specify the corresponding outgoing interface file for the above incoming file.
Log Output
Select the type of details to be updated in the log file from the adjoining drop-down list. This list displays the following values:
- Error
- Success
- Both
While processing the interface file, system verifies the log output value and the below details:
- If the value of “Log Output” is “Error”, then, system creates an error file (<INTERFACE_NAME>_ FILENAME>_ERR_<ProcessRefNo>.dat) in Log_Failure folder and update the primary key elements and the corresponding error details (error code and message).
- If the value of “Log Output” is “Success”, then, system creates a data file (<INTERFACE_NAME>_ FILENAME>_SUC_<ProcessRefNo>.dat) in Log_Success folder and update the primary key elements. “
- If the value of “Log Output” is “Both”, then, system creates both error file and data file in log folder.
During the interface configuration, log_failure and log_success folders are created in the interface configured folder.
Last Run Date
The last run date gets displayed here.
Next Run Date
The day on which the interface can be triggered gets displayed here.
2.14.3.2 Format Details Tab
Data Alignment
Date
Select the justification type for date field from the drop-down list. The options are:
- Right
- Left
Number
Select the justification type for number field from the drop-down list. The options are:
- Right
- Left
Text
Select the justification type for text field from the drop-down list. The options are:
- Right
- Left
Note
Default justification type for text and date field type is Left and number field type is right.
Padding Character
You can specify the padding character of fixed length format type interface file here. All the data types can have the same padding character
Date
Specify the padding character for date field.
Number
Specify the padding character for number field..
Text
Specify the padding character for text field.
Note
All the data types can have the same padding character.
Format Type
Format Type
Select the type of data length in the interface from the following options:
- Fixed – Select this option if the file data has to be in fixed width.
- Delimited - Select this option if the file data has to be in delimited format.
Delimiting Character field gets enabled for you to specify the delimiting character if you select the format type of definition as ‘Delimited’.
Delimiting Character
Specify the delimiting character if you select the format type of definition as ‘Delimited’.
Date Format
Specify the date format for the interface file.
2.14.3.3 Preferences Tab
Preferences
CRC Required
Check this box if you want to check the CRC while transferring the data.
In case of incoming interface, system checks for the CRC value in the file name maintained in ‘CRC file mask’. For outgoing interface, system generates the CRC value in a CRC file.
CRC Algorithm
Specify the CRC algorithm which has to be used to calculate the CRC Value.
CRC File Mask
The path of CRC File mask gets displayed here.
CRC File Directory
The directory of CRC file gets displayed here. However you can modify it. If the file directory is modified, the path for this directory should end with ‘ready’ folder.
Confirmation File Required
Check this box to indicate if confirmation is required for an incoming file. If this box is checked then when incoming file is processed, system checks whether confirmation file is available in the folder specified. If the file is not available then incoming file processes will raise an error indicating the confirmation file is not available.
Confirmation File Mask
The path of confirmation file mask gets displayed here.
Confirmation File Directory
The directory of confirmation file gets displayed here. However, you can modify it. If the file directory is modified, the path for this directory should end with ‘ready’ folder.
Data Log Required
Check this box to indicate if the confirmation details are required in the log file.
When to Run
Select the stage of application the interface has to be triggered.
Mandatory
Check this box to indicate that the interface has to be mandatorily processed before moving on to the next stage of EOD. If this box is checked system checks if the interface has been processed or not and if it is not processed system will not allow movement to the next EOD stage.
Trigger Type
Select an appropriate option to indicate how the interface should be triggered. The options available are:
- Manual – Select this option if the interface has to be triggered manually.
- System – Select this option if the interface has to be triggered automatically.
During EOD if there are any mandatory unprocessed interfaces and if the triggering type is selected as ‘System’ then the interface is triggered automatically. In case of Incoming interface if triggering type is selected as ‘System’ then system checks if the file is available in the ‘ready’ folder for that interface. If the file is present the system will process it. In case of outgoing interface if triggering type is selected as ‘System’ then, system will automatically trigger the Outgoing interface.
Note
If the interface is mandatory, the triggering type must be system. Even if the triggering type is mentioned as System, you can manually trigger the interface whenever required through Interface triggering screen.
No of Executions/Day
If you select frequency type as ‘Daily’, specify the total number of interface file processing executions in a day.
This field is applicable only for incoming interface file process.
Commit/Fetch Frequency
Specify the number of transaction committed or fetched at a given point of time.
Duplication File Check Required for Current Date
Check this box to indicate that the duplicate files should not be added for the current date.
Parallel Process
You can specify the parallel process details here.
Parallel Process Required
Check this box to indicate if parallel processing is required if multiple interface files has to be processed at a given time.
When you select parallel process required parallel process type field gets enabled.
Parallel Process
Select the type of parallel process you want to keep for the interface processing:
- Record Based – Select this option if you want parallel processing to be based on the number of records you maintained.
- Process Based – Select this option if you want parallel processing to be based on the number of parallel processes that you maintained.
No of Records
Specify the number of records of parallel process can be performed at a given time. This field gets enabled only if you select the parallel process type as ‘Record based’.
No of Parallel Process
Specify the number of parallel process can be performed at a given time. This field gets enabled only if you select the parallel process type as ‘Process based’.
2.14.4 Viewing Interface Definition Summary
You can view the interface details maintained in the system using ‘Interface Definition Summary’ screen. You can invoke this screen by typing ‘GISIFTDF’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
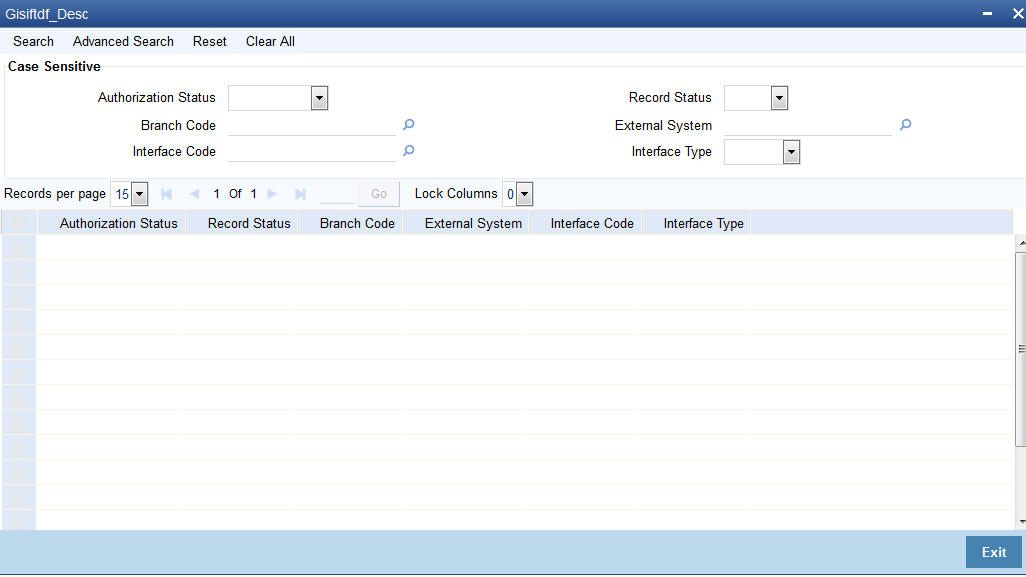
You can click ‘Search’ button to view all the interface records of your bank. You can filter your search based on any of the following criteria:
Authorization Status
Select the authorization status of the Interface definition you want to view the details from the drop-down list. The options are:
- Authorized
- Unauthorized
Branch code
Select the branch code belonged to the interface details from the option list.
Interface code
Select the interface code belonged to the interface details from the option list
Record Status
Select the record status of the interface details from the drop-down list. The options are:
- C – Closed
- O - Open
External System
Select the name of the external system belonged to the interface details from the option list.
Interface Type
Select the type of interface from the option list as incoming or outgoing.
When you click ‘Search’ button the records matching the specified search criteria are displayed. For each record fetched by the system based on your query criteria, the following details are displayed:
- Authorization Status
- Record Status
- Branch Code
- External System
- Interface Code
- Interface Type
2.14.4.1 Search Functionalities
The search functions available are:
- Advanced – Click Advanced to specify queries with logical operators such as AND, OR and NOT.
- Reset – Click Reset to empty the values in the criteria fields, so that you may begin a new search.
- Query – After specifying your search criteria click Query to view the list of results which match your search criteria.
- Refresh – Click Refresh to refresh the list of results.
2.14.5 Maintaining AUDF (ASCII User Defined Function) Details
You can maintain the AUDF (ASCII User Define Function) details in the ‘AUDF Maintenance’ screen. You can invoke this screen by typing ‘GIDAUDFM’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
Specify the following AUDF details in this screen.
AUDF Name
Specify the name of the AUDF here.
Description
Specify a description for the AUDF here.
Unit Name
Specify the invoked function name here.
AUDF Type
Select the AUDF types from the drop-down list. The following options are available:
- Message
- Component
- Record
- Field
2.14.6 Viewing AUDF Summary Details
You can view AUDF details maintained in the system using ‘AUDF Summary’ screen. You can invoke this screen by typing ‘GISAUDFM’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
You can click ‘Search’ button to view all the AUDF records of your bank. You can filter your search based on any of the following criteria:
Authorization Status
Select the authorization status of the AUDF you want to view the details from the drop-down list. The options are:
- Authorized
- Unauthorized
Record Status
Select the record status of the AUDF from the drop-down list. The options are:
- C – Closed
- O - Open
AUDF Name
Select the name of the AUDF from the option list.
Description
Select the description of the AUDF from the option list.
When you click ‘Search’ button the records matching the specified search criteria are displayed. For each record fetched by the system based on your query criteria, the following details are displayed:
- Authorization Status
- Record Status
- AUDF Name
- Description
2.14.7 Maintaining Translation Details
You can maintain translation details required between the external system values to Oracle FLEXCUBE Values and vice Versa in the ‘Translation Definition’ screen. You can invoke this screen by typing ‘GIDTRANS’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
You can capture the following details here:
Translation Name
Specify the translation name you want to keep for the set. The translation name gets linked to the interface field whose value needs to be translated during Interface Processing.
Translation Parameters
The following details are specified here:
In Param
Specify the system value for the corresponding external systems value.
Out Param
Specify the external system’s value for the corresponding Oracle FLEXCUBE value.
2.14.8 Viewing Translation Summary Details
You can view the translation details maintained in the system using ‘Translation Summary’ screen. You can invoke this screen by typing ‘GISTRANS’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
You can click ‘Search’ button to view all the translation records of your bank. You can filter your search based on any of the following criteria:
Authorization Status
Select the authorization status of the translation you want to view the details from the drop-down list. The options are:
- Authorized
- Unauthorized
Record Status
Select the record status of the translation from the drop-down list. The options are:
- C – Closed
- O - Open
Translation Name
Select the name of the translation from the option list.
When you click ‘Search’ button the records matching the specified search criteria are displayed. For each record fetched by the system based on your query criteria, the following details are displayed:
- Authorization Status
- Record Status
- Translation Name
2.14.8.1 Search Functionalities
The search functions available are:
- Advanced – Click Advanced to specify queries with logical operators such as AND, OR and NOT.
- Reset – Click Reset to empty the values in the criteria fields, so that you may begin a new search.
- Query – After specifying your search criteria click Query to view the list of results which match your search criteria.
- Refresh – Click Refresh to refresh the list of results.
2.14.9 Maintaining CRC Algorithm Details
Generic Interface supports CRC-32 and Adler-32 Checksum algorithms for generating CRC value of the file. Other CRC components which are developed in Java and PL/SQL are also supported by GI using the ‘CRC Maintenance’ screen.
You can invoke this screen by typing ‘GIDCRCFN’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
You can write the invocation stub along with the CRC component details here:
CRC Name
Specify the CRC Algorithm used to calculate the CRC value for the file.
Description
Specify the description of the CRC Algorithm here.
Invocation Stub
Specify the stub to invoke the CRC generation component.
2.14.10 Viewing CRC Summary Details
You can view the CRC details maintained in the system using ‘CRC Summary’ screen. You can invoke this screen by typing ‘GIDCRCFN’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
You can click ‘Search’ button to view all the CRC records of your bank. You can filter your search based on any of the following criteria:
Authorization Status
Select the authorization status of the CRC algorithm from the drop-down list. The options are:
- Authorized
- Unauthorized
CRC Name
Select the name of the CRC algorithm from the option list.
Record Status
Select the record status of the CRC algorithm from the drop-down list. The options are:
- C – Closed
- O - Open
Description
Select the description of the CRC algorithm from the option list.
When you click ‘Search’ button the records matching the specified search criteria are displayed. For each record fetched by the system based on your query criteria, the following details are displayed:
- Authorization Status
- Record Status
- CRC Name
- Description
2.14.10.1 Search Functionalities
The search functions available are:
- Advanced – Click Advanced to specify queries with logical operators such as AND, OR and NOT.
- Reset – Click Reset to empty the values in the criteria fields, so that you may begin a new search.
- Query – After specifying your search criteria click Query to view the list of results which match your search criteria.
- Refresh – Click Refresh to refresh the list of results.
2.15 Process Definition
This section contains the following topics:
2.15.1 Maintaining Process Codes
You can maintain the process codes using the ‘Process Definition’ screen. You can invoke this screen by typing ‘SMDPRCDE’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking on the adjoining arrow button.
You can specify the following here:
Process Code
Specify a unique code for the process.
Description
Enter an appropriate description of the process.
After entering the details, click the ’Save’ button.
2.16 Reporting Parameters Maintenance
This section contains the following topic:
2.16.1 Maintaining Report Spool Path
You can maintain a location to spool the reports for a specific branch using ‘Reporting System – Parameters’ screen. You can invoke this screen by typing ‘RPDRPRAM’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking on the adjoining arrow button.
Here, you need to specify the following details:
Branch
The system displays the branch for which you are maintaining the spool path. However, you cannot modify it.
Spool Path
Specify the location to which the reports should be spooled. The system stores the generated reports into this location, if you have selected ‘Spool’ in the ‘Printing Preferences’ screen.
Spool History Path
Specify the spool history path. This is the generation where the system saves the generated report. It is usually the same as the spool path.
Time Out
Specify the time span within which you wish to complete the process. The system reports if it takes longer time to generate it.
Server Report Path
This is the location where the system stores the report, if you have selected the option ‘View’ in the ‘Printing Preferences’ screen.
2.17 Maintaining Amount Text
You can describe the amounts printed on account statements, messages, advices, etc., in words, for the benefit of your customers. To describe ‘amounts’ in a specific language, you have to maintain the verbal equivalents of numerals in the language. You can maintain verbal equivalents of numerals in the ‘Amount Text Maintenance’ screen.
You can invoke this screen by typing ‘STDAMTMN’ in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking the adjoining arrow button.
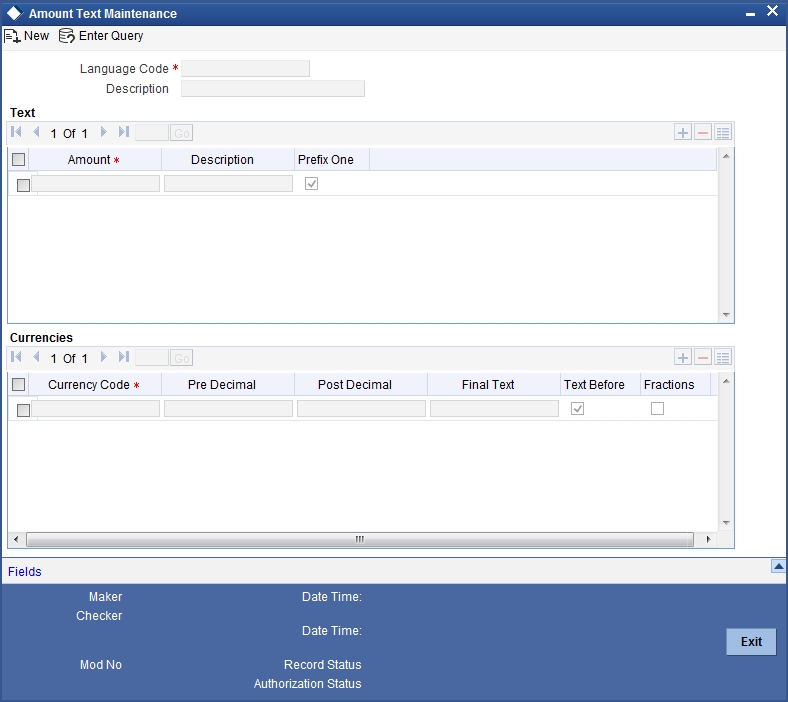
Amount translation details can be maintained as one time maintenance at the time Oracle FLEXCUBE is installed at your bank. Once maintained, the amount descriptions printed on account statements, and other messages, will be described according to your specifications in this screen.
Language
You can maintain verbal equivalents of numerals in any language that Oracle FLEXCUBE supports. This means that you can maintain the verbal equivalents of numerals in as many languages as you generate messages.
Text
You must describe the following numerals in the Description field (in the language that you specify in the Language field):
- 1, 2, 3, upto 10
- 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, and 90
- 100
- 1,000
- 10,000
- 100,000
- 1,000,000
- 10,000, 000, and so on
In certain languages, One thousand, One million, and so on are expressed, simply, as ‘thousand’, and ‘million’. If you are defining verbal equivalents of amounts in such a language, do not choose the ‘Prefix One’ option. Statements and messages printed in such a language will describe amounts such as ‘1000’, simply, as ‘thousand’.
Choose the ‘Prefix One’ option, if you would like amounts such as ‘1000’ described as ‘One thousand’.
Currencies
In this screen, you can also describe the pre-decimal and the post-decimal units of a currency in different languages. Enter the verbal equivalent of the ‘pre’ and ‘post’ decimal units of a currency in the Pre-Decimal and Post-Decimal fields respectively. For example, if you would like to describe the decimal units of USD, enter:
- The currency in the Currency field
- The pre-decimal description as ‘Dollars’
- The post-decimal description as ‘Cents’
- Final Text to be attached to the currency.
You can opt to prefix, or suffix, an amount with its currency. If you would like the suffix an amount with its currency, do not choose the ‘Text Before’ option. If you would like to prefix an amount with its currency, choose the ‘Text Before’ option.
For example, if you would like to describe USD 1000, as Dollars One Thousand, choose the ‘Text Before’ option.
2.18 Dynamic Package - DML Execution
You can synchronize the dynamic packages and DML statements which have to get propagated to the PDBs from Approot through 'Dynamic Package - DML Execution Screen'. You can invoke this screen by typing 'CODDYNCL' in the field at the top right corner of the Application tool bar and clicking on the adjoining arrow button.
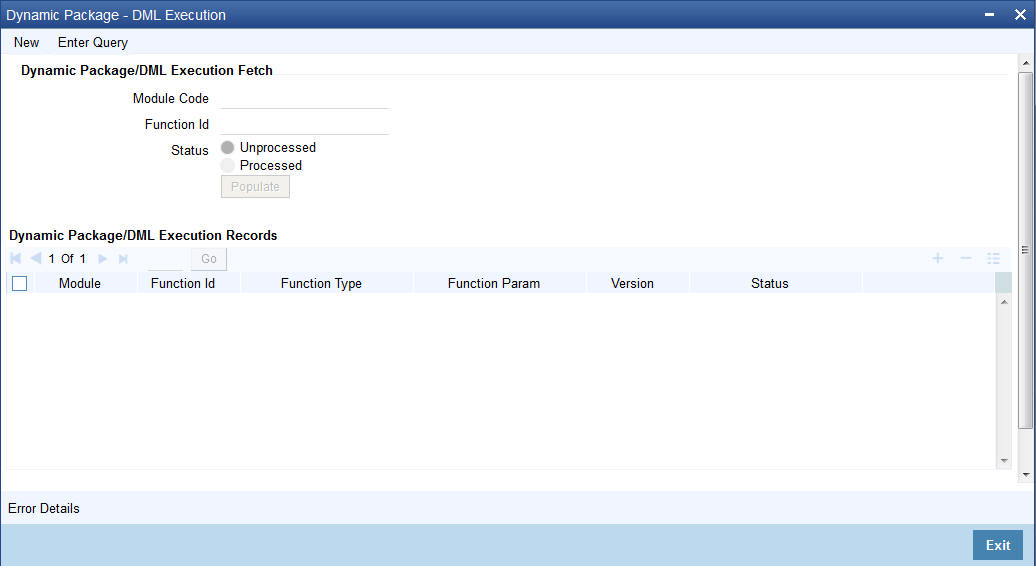
You can specify the following here:
Module Code
Specify the module code for which the dynamic packages and DML statements have to get propagated to the PDB from Approot. Alternatively, you can select the module code from the option list. The list displays all valid module codes maintained in the system.
Function Id
The system displays the function ID based on the module code selected.
Status
Select any of the following options:
- Unprocessed - Select this to fetch the unprocessed records in the PDB and proceed with processing.
- Processed - Select this to view the recent synchronized records in PDB.
After selecting the status, click 'Populate' button to fetch the list of records to be processed or records that are already processed based.
On selecting the status as 'Unprocessed' and upon clicking the 'Populate' button, you can view the list of records which are yet to be compiled in the PDB. These records can be processed on clicking the button 'Process All Records'. The system displays an information message once processing of all the records are completed. You cannot do any other operation after processing the records. The action buttons will be disabled.
You can select the Status as 'Processed to view the list of processed records. Status column will depict the processed status of the records. Error records can be viewed from the sub screen 'Error Details' available in the main screen.