2.8.3 Velocity Check
The Velocity Check use case uses the information stored in HLR about the current VLR and the age of location parameter to identify if the new VLR is reachable from the current VLR stored in HLR.
This
use case is dependent on the validity of the information stored in the VLR and
the T3212 timer (periodic update location timer). This timer governs the rate
at which the mobile subscriber autonomously updates their location. In case the
time distance between two networks is less than the value of T3212 timer
configured for the network, this use case test would provide false positives
since the location age information would not have been properly updated in the
VLR.
The assumption for successful execution of this use case are:
The vSTP Call flow for Velocity Check, first lookup the Common DB
that is UDR, for IMSI. If the record is available in UDR, then the ATI is not
sent to HLR and the UDR information is used further. But, in case the record is
not available in UDR, then ATI is sent to HLR.
- The First location update can be identified using the IMSI only in the address.
- The Age of Location provided by HLR is accurate.
- The quantum of information (Age of Location) will not be less than the time to get travel.
In both the scenarios, the UDR is updated in case of successful validation. If record is not found in UDR and validation is successful through ATI, then a new record is created in UDR with that IMSI. In case the IMSI record is available in UDR and validation is successful, then the last updated time of the record is updated in UDR.
Both the scenarios of vSTP call flow for VLR Validation are described below:- vSTP Call Flow for Velocity
Check - When no IMSI record is found in Common DB
The following figure shows the vSTP call flow when there is no record available in Common DB:
Figure 2-11 Velocity Check - vSTP Call Flow when IMSI Record is not Found in UDR
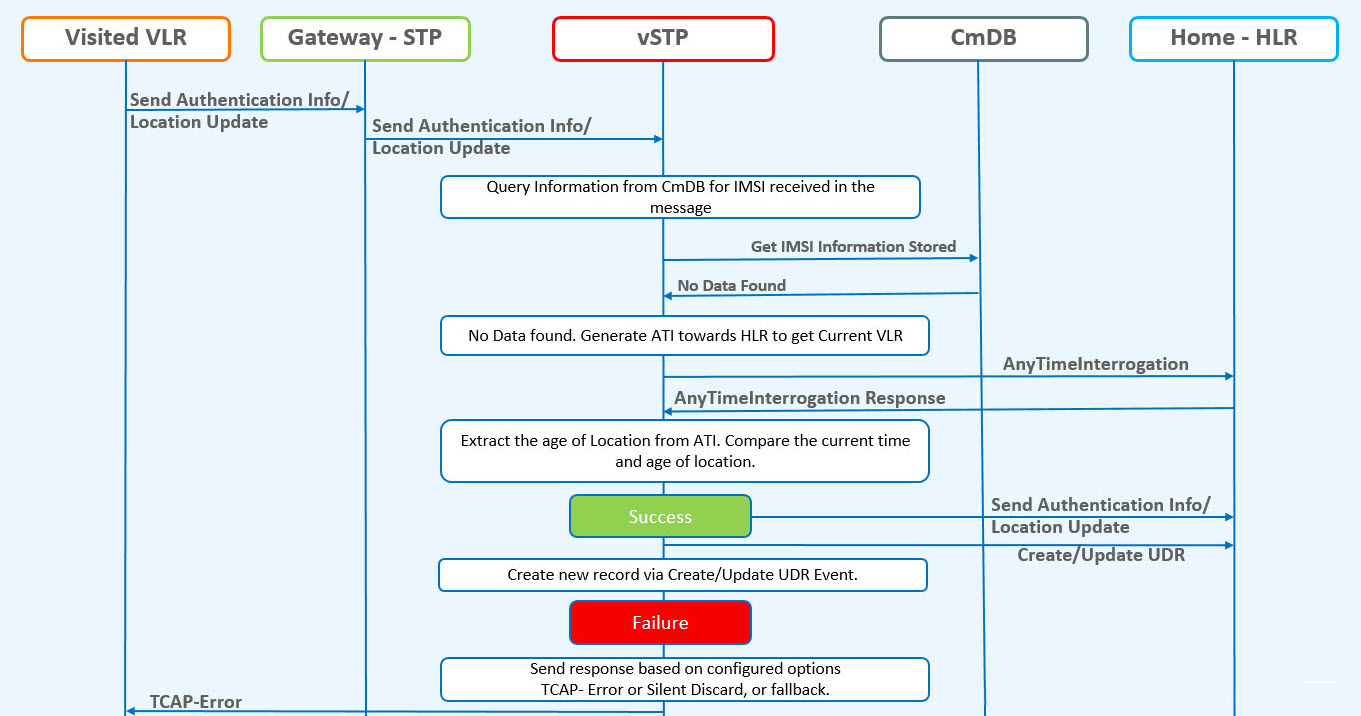
- A local database on vSTP will be configured to identify the network locations (using country codes for VLR addresses) and the shortest amount of time it may take to travel between them.
- The incoming message
will be decoded:
- An Error will be generated in case of decode failure.
- A Measurement will be pegged for the decode failure with OpCode and CgPA.
- The message information will be stored in the local database.
- The request to get the IMSI information is generated towards UDR.
- If the IMSI record is not found in UDR, the ATI request will be generated toward the HLR identified in the CdPA of the incoming message. The ATI request will be coded so that it is received on the same MP, as DB is local.
- In case the HLR sends
a failure in the ATI response:
- A measurement will be pegged to identify HLR error corresponding message from CgPA (VLR).
- For a success response, extract the Age of Location from the ATI Response message and the VMSC address in the HLR.
- A record is created in UDR for the IMSI after successful validation.
- In case the VLR from which the SAI/LU was received matches the VLR in the ATI response, do nothing.
- In case the VLR
addresses do not match:
- Calculate the time difference between the current time and the Age of Location.
- Verify the Age of Location is less than the travel time configured in the local database.
- Calculate the distance between two country codes using Havrshine Formula. Longitude/Latitude values are retrieved from database for corresponding entries.
- In case the time
value is not within limits:
- The validation gets failed.
- A measurement will be pegged.
- Response will be generated based on the configured option.
- If validation is successful, forward message to HLR and update the UDR with relevant data with VLR number, last updated Network, last update time.
- vSTP Call Flow - When IMSI
record is found in Common DB
The following figure shows the vSTP call flow when the IMSI record is available in Common DB:
Figure 2-12 Velocity Check - vSTP Call Flow when IMSI Record Found in UDR
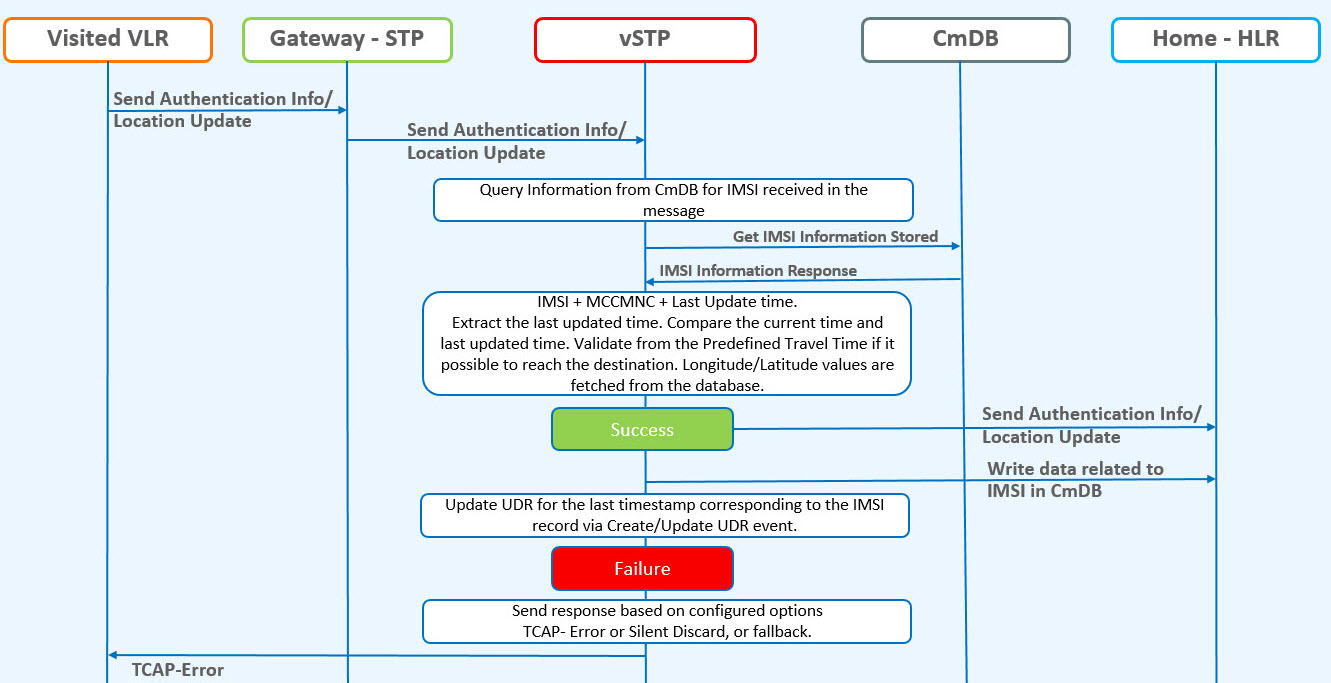
- A local database on vSTP will be configured to identify the network locations (using country codes for VLR addresses) and the shortest amount of time it may take to travel between them.
- The incoming message will
be decoded:
- An Error will be generated in case of decode failure.
- A Measurement will be pegged for the decode failure with OpCode and CgPA.
- The message information will be stored in the local database.
- In case VLR address do
not match:
- Lookup into SfappCCMCCMap table and for corresponding country codes and retrieve the MCC.
- The exception or neighboring list table is checked for with old MCC, if it is available in neighboring list then do nothing. Else, the following step will be performed.
- The exception or neighboring list table is checked for with old MCC, if it is available in neighboring list then the process ends. Else, the following step will be performed.
- The distance between 2 country codes is calculated using Havrshine Formula. Use Longitude/Latitude values from database.
- The Time ( = Distance / Velocity) shall be calculated and used to authenticate the subscriber location.
- Validate the last time distance check based on last location with the VLR address received in the incoming message.
- In case the VLR addresses
do not match:
- Calculate the distance between 2 country codes using Havrshine Formula using longitude and latitude values (from SfappLongLat MO).
- Calculate the time using distance calculated from above point and travel_velocity value from vSTPSccpOptions MO.
- Verify that Time calculated in point b is less than the (current time -last update time from UDR).
- If validation is successful forward message to HLR and update the UDR with relevant data with VLR number, last updated Network, last update time.
- In case the validation
failed,
- A measurement will be pegged.
- Response will be generated based on the configured option.
Note:
- The T3212 timer is responsible for periodic location update for subscribers. If the timer is set to a value greater than the shortest travel time value between two network locations, then the location validation in the use case fails.
- Results of the use cases depends on the pre-configured values of SfappCCMCCMAP, SfappCountryLongLat, SfappCountryCodes, and SfappNeighboringCountries entries.