Rate Table Formats
The Rules Palette rate upload process provides a user friendly mechanism to upload rates, even multiple sets of rates and multiple rate groups in a single session, via Excel spreadsheets with nominal set up in Palette required. The import and export functions will handle hundreds of thousands of rates. A set of rates with 3 criteria easily approaches 170,000 rates. The ability to overwrite rate sets for existing rate groups is also available.
General Information
An insured has an issue age and an attained age. The issue age is based on the person's age at the time the insurance policy goes into force. The insured's actual age, their age at their nearest birthday or their age at their last birthday are typically used to determine their issue age. The attained age is calculated at the policy’s anniversary, and is the issue age plus the years in force (based on the number of anniversaries passed). The attained age is usually kept on the policy or segment, although it may be calculated throughout. At time of issue, an insured's issue age equals their attained age.
A number of criteria are used in setting rates. The number of criteria used and the basis for distinction will vary by insurance company. Criteria commonly used include, but are not limited to:
- Gender
- Smoker status
- Underwriting status
- Band (based on premium, face, cash value, or other method)
- Rider/benefit combination
- Multiple policy discount
The table format selected for rate upload will impact the values required in the wizard. Below are brief explanations of the three defined table formats.
A set of rates for any rate group can be imported/exported in one of three formats
Aggregate Rates
Aggregate rates group more individuals to a single rate than select rates, and are typically attained age-based. This means that a person’s rate, for a given set of criteria, is determined only by their attained age. For example, a person with Issue Age 40 will have the same rate for a person in duration 5 with an Issue Age of 35, since the attained age in duration 5 would be 40.
To create the rates, then, all the rates for a given criteria combination will be held in a single row or column with the key “attained age.” The system will navigate down a given row or column for the duration indicated. Once one row/column is complete, that criteria combination is done, and the system would then move to the next row/column for the next criteria combination.
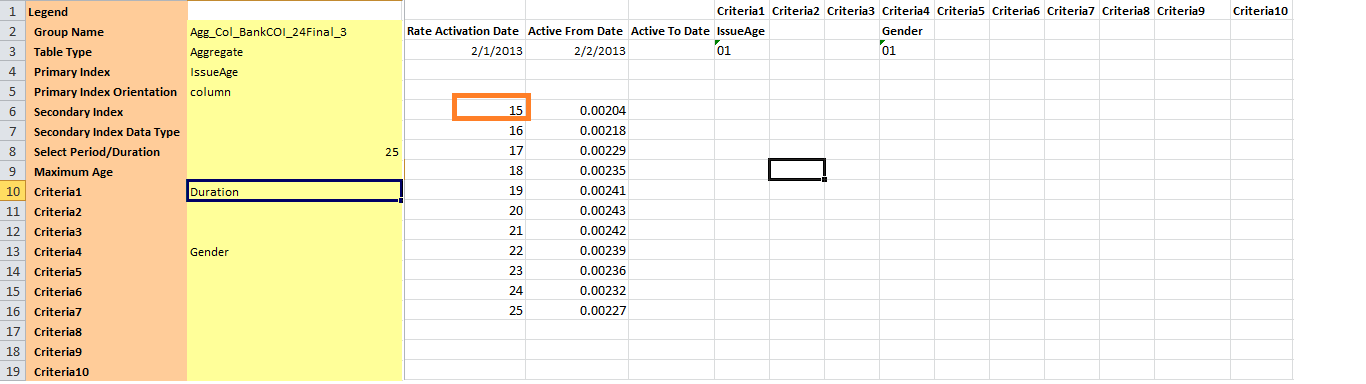
Data representation in the worksheet for Aggregate table type:
- In Aggregate table type data is represented as a single dimensional table.
- There is no secondary index so all criteria data are placed in the worksheet's cells as saved in AsRateGroup and AsRates.
- Primary index orientation is column.
- The integer data is placed vertically starting as shown in the below screen shot and arranged in ascending order. Each integer criteria value in column A is associated to a rate which in column B.
Select Rates
Select rates are typically issue age- and duration-based, where duration is determined by a maximum age (e.g. 121). This means that a person’s rate for a given set of criteria is determined by both the issue age and the policy’s current duration. As an example, because of the way select rates are calculated, the insured is typically going to have a lower rate for attained age 40 if the policy was purchased at Issue Age 35 than at Issue Age 40.
Because both issue age and duration are used in setting select rates, each criteria combination will have multiples rows and columns to traverse to complete a single combination. For example, to create the rates, the issue ages are in a row and the duration is in a column. Starting with the initial age, the system will traverse through the column for all applicable durations. Once one issue age is complete, the system must process the next issue age in the same manner. The system would continue in this manner until all issue ages are complete. Only after that is the criteria combination done, and the next criteria combination can begin.
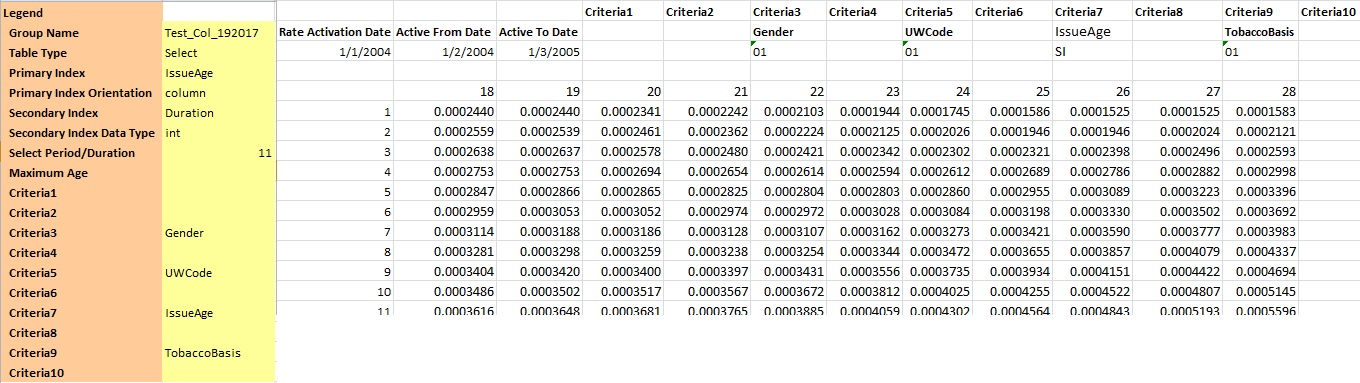
Data representation in the worksheet for Select table type:
- Data in select type is represented as a two dimensional table.
- The secondary index is available and data is identified uniquely based on secondary index. And is one among the criterion’s.
- In the worksheet the criteria which is used as secondary index is marked as 'SI'.
- Primary index orientation is column.
- The Integer Criteria data are placed vertically starting in "A10" and listed in ascending order.
- The values for "SI" criteria data are placed horizontally in ascending order starting at "B9".
One rate is associated to each intersection of "SI" and Integer Criteria. The appropriate rate is placed in each of these cells.
Note: because select rates are based on issue age and duration to a max age, it is likely that not all issue ages will have the same number of rates populated.
Ultimate Rates
Ultimate rates are a combination of the above two rate types: they are select rates up to a given duration, and then the rates switch to aggregate rates. These rates may be used for Term policies that are guaranteed for X years, where there is an option to renew after X years at aggregate rates. For X duration, the rates are loaded just as for select processing, where there will be a difference for rates between attained ages with different issue ages. For X+ years, the rates for attained age will be the same for the given criteria combination.
For example, to create the rates, the issue ages are in a row, the duration is in a column and the Term period is 10 years, during which time select processing will be used. Starting with the initial age, the system will traverse through the column for 10 durations. After that, it will find the attained age. Once one issue age is complete, the system must process the next issue age in the same manner. The system will continue in this manner until all issue ages are complete. Only after that is the Criteria Combination finished, and the next Criteria combination can begin.
Data representation in the worksheet for Ultimate table type:

