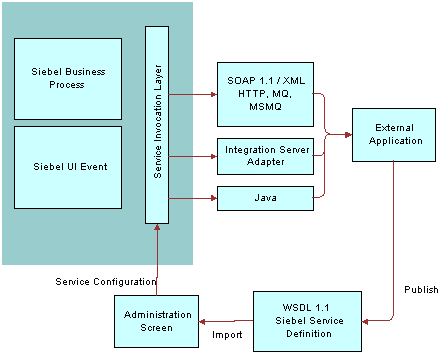
Types of ASI Interfaces
An ASI is either an inbound ASI and or an outbound ASI.
Inbound ASI
The following image illustrates how an inbound ASI is used to accept data into a Siebel application from an external system by using Siebel workflow processes, Siebel business services, and Siebel data synchronization services through the Siebel Object Manager.
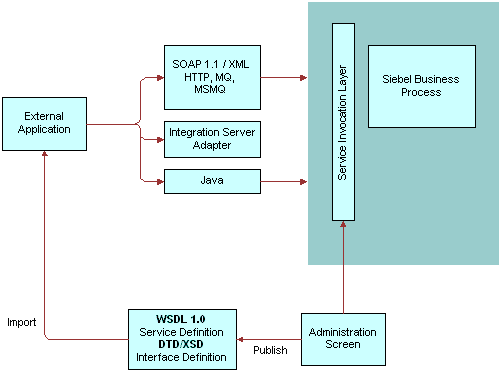
Outbound ASI
The following figure illustrates how an Outbound ASI is used to send data that is based on a UI event or a trigger in a Siebel workflow process.