This module describes the procedure for working with and managing Pricing Margin Rules.
This chapter covers the following topics:
· Overview of Pricing Margin Rules
· Creating Pricing Margin Rules
· Defining Pricing Margin Rules
· Defining a Pricing Margin Rule: An Example
In BSP, Pricing Margin Rules allow users to define default pricing margins (or spreads) for their products. Pricing margins are defined period by period based on your active Time Bucket definition, for each product and, potentially, each currency. Pricing margins work together with an underlying Base Interest Rate Curve to determine note rate pricing for new business volumes defined through BSP's Planning User Interfaces. New Business Assumptions are defined based on the combined inputs from the following three forecast related Business Rules:
· Product Characteristics
· Forecast – Maturity Mix
When you require more complex definitions of pricing margins to model unique account pricing details, user-defined repricing patterns can be used. For more information, see User-defined Repricing Patterns
The procedure for working with and managing Pricing Margin Rules is similar to that of other Oracle Balance Sheet Planning Business Rules. It includes the following steps:
· Searching for Pricing Margin rules. For more information, see the Searching for Rules Section.
· Creating Pricing Margin Rules. For more information, see Creating Rules Section.
· Viewing and Editing Pricing Margin rules. For more information, see the Viewing and Editing Rules Section.
· Copying Pricing Margin rules. For more information, see the Copying Rules Section.
· Deleting Pricing Margin rules. For more information, see Deleting Rules Section.
As part of creating and editing Pricing Margin rules, you assign Pricing Margins to applicable products. See Defining Pricing Margin Rules
You create Pricing Margin rules to assign pricing margins (or spreads) to be used in pricing new volumes defined through Forecast Balances Business Rules.
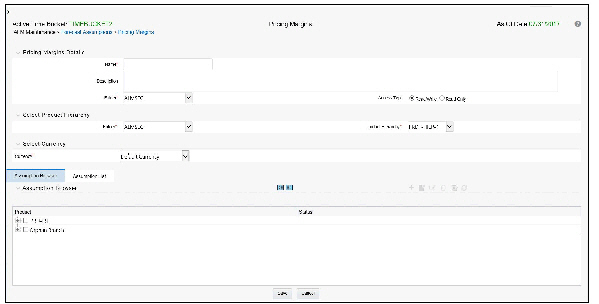
1. Navigate to the Pricing Margins Rule Summary Page.
2. Complete standard steps for this procedure.

NOTE:
In addition to the standard steps for creating rules, the procedure for creating a Pricing Margins Rule involves one extra step. After Standard Step 6, you need to select a Product Hierarchy. You can define methodologies at any level of the Hierarchical Product Dimension. The Hierarchical Relationship between nodes allows the inheritance of methodologies from Parent Nodes to Child Nodes.
Oracle Balance Sheet Planning provides you with the option to copy, in total or selectively, the product assumptions contained within BSP Business Rules from one currency to another currency or a set of currencies or from one product to another product or a set of products.
The definition of a Pricing Margins rule is part of the Create or Edit Pricing Margins Rule Process. When you click Save in the Create Pricing Margins Rule Process, the rule is saved and the Pricing Margins Rule Summary Page is displayed. However, Pricing Margin Assumptions have not yet been defined for any of your products at this point. Typically, you would start defining your Pricing Margin Assumptions for product-currency combinations before clicking Save.
Node Level Assumptions allow you to define assumptions at any level of the Product Dimension Hierarchy. The Product Dimension supports a hierarchical representation of your chart of accounts, so you can take advantage of the Parent-Child Relationships defined for the various nodes of your product hierarchies while defining rules. Children of Parent Nodes on a hierarchy automatically inherit the assumptions defined for the Parent Nodes. However, assumptions directly defined for a Child take precedence over those at the Parent Level.
Performing basic steps for creating or editing a Pricing Margins Rule.
Defining Pricing Margins has two primary steps:
1. Choosing your Rate Dependency Option.
2. Inputting Pricing Margin details for the selected products.
NOTE:
Using the default currency to set up assumptions can save data input time. At Run time, the calculation engine uses assumptions explicitly defined for a product currency combination. If assumptions are not defined for a currency, the engine uses the assumptions defined for the product and the default currency. If the assumptions are the same across some or all currencies for a specific product, you can input assumptions for the default currency. Be careful using this option on screens where an Interest Rate Code is a required input.
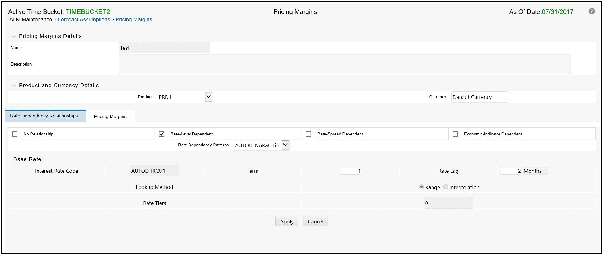
Rate Dependency Relationships utilized within ALM but are not supported in BSP. For BSP, you must select No Relationship.
· No Relationship
· Rate Level Dependent
· Rate Spread Dependent
· Economic Indicator Dependent
If one of the Rate Dependency options, other than No Relationship, is selected, the Rate Dependency Pattern drop list becomes active. The list of available patterns is limited to those which apply to the selected Rate Dependency Relationship type.
In an income simulation scenario, you may want to price new business for an account at a margin above or below a market interest rate code. For example, you can model a premium paid on CDs in relation to a market yield curve by adding a pricing margin to the interest rate code assigned to the product in the Product Characteristics Rule. If you want a rate that is 25 bps above the Market Yield Curve, you will type “0.25" as the pricing margin for the appropriate Modeling Period.
The Pricing Margin Rule uses the Modeling Period defined in the “active” Time Bucket Rule. You should always verify that your modeling horizon and related assumptions are consistent with the As of Date and active Time Bucket Rule before processing.
Rate Tiers reflect the Rate Dependency Pattern details from the selected Rate Dependency Pattern. You define Pricing Margin Assumptions for each rate tier. The application will automatically determine which set of assumptions to apply for a given scenario based on the relationship between the Rate Tier and the related Forecast Rate Assumption Value.
This option allows you to enter the Margin as Rate (fixed rate) or Percent (percentage of forecast Rate). By default, it is set to Rate.
· If Margin Type is selected as Rate, provided Margin is used as a fixed spread.
· If Margin Type is selected as Percent, Margin needs to be provided as Percentage of Forecast Rate. If the margin is 10% of the forecast rate, 10 needs to be provided. Margin is calculated as:
Margin = Margin % * Raw Rate
For more information, see the Cash Flow Reference Guide on OTN.
Once you change from Rate to Percent, all unsaved margin data will be deleted.
A warning message is displayed: All entered values will be lost. Do you want to proceed?
The bucket number input allows you to select a range of buckets over which the pricing margin assumption will apply. Start Date and End Date values are updated automatically based on the Bucket Number input for each row.
When the Pricing Margins detail page opens, the Start Date (min value) and End Date (max value) columns are automatically populated and are read-only values. The date ranges represent the Income Simulation Date buckets as defined in the “active” Time Bucket Rule. See Time Buckets for more information. Any new business that originated within these dates is modeled using the pricing margins defined in the Pricing Margin Rule. The new business added for each date bucket will have the same net and gross margin for its life. The margins for a particular instrument will not change as the instrument ages.
The Gross Margin you define is added to the Interest Rate Code specified in the Product Characteristics Rule to define the Gross Rate on new business.
NOTE:
BSP supports only Net Margins.
The Net Rate is affected by setting the Net Margin Flag in the Product Characteristics Rule. If Net Margin Flag is set to Floating Net Rate, then Net Rate is equal to the Interest Rate Code plus Net Margin.
If the Net Margin Flag is set to Fixed Net Rate, then Net Rate is equal to Net Margin.
NOTE:
If Margin Type is selected as Percent and Net Margin Flag is set to Fixed Net Rate, provided Margin as Percent is treated as Rate.
Apply Defined Buckets to all Rate Tiers
This option allows you to copy the bucket setup from one page to all other Rate Tiers when using Rate Dependent Assumptions.
Define a Pricing Margin Rule using a Rate Dependency Pattern.
1. From the Assumption Browser, select Currency (US Dollar) and a product from the Hierarchy Browser.
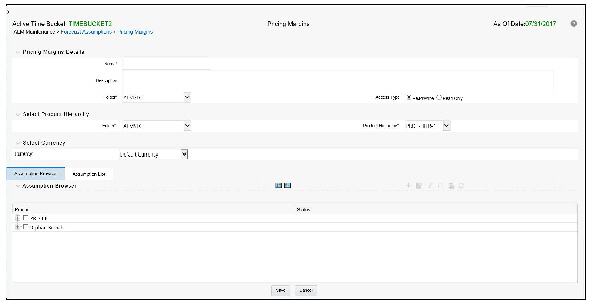
2. Select the “Add New” icon to enter the Assumption Details Page.
3. Select the Rate Level Dependent – Rate Dependency Option.
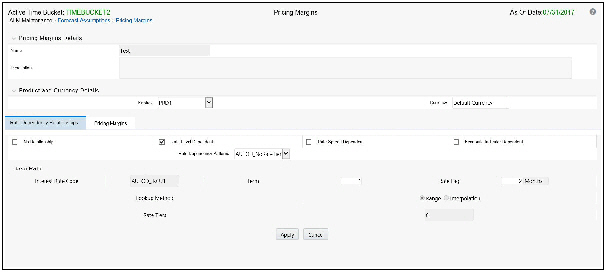
4. Select the Rate Level – Rate Dependency Pattern from the drop list.
5. Select Apply to navigate to the Pricing Margin Tab where you can define assumptions for each rate tier.
6. Add bucket ranges to the page as needed. Optionally, select the “Apply Defined Buckets to All Rate Tiers” check box to copy the bucket structure across all Rate Tier pages.
7. Input Rate Spreads for each Bucket Range that you define.
NOTE:
You may want to utilize the Data Input Helper to copy an assumption from a row where you have already defined a value or apply a fixed amount down the page. The following optional steps describe how to use this feature.
a. Select the check boxes next to the rows that you want to work with or use the “Select ALL” option by selecting the check box on the header row.
b. Select the Data Input Helper icon.
c. From the Data Input Helper – popup screen, select Method – “Keep Current Values” or some other appropriate method.
d. Select the Frequency and/or Multiplier from the left side of the shuttle box.
e. Select APPLY to copy assumptions to the selected rows.
8. You can also use the Excel import/export feature to add the Date Buckets/Margins information in the Pricing Margins Tab.
9. Select Apply to commit your assumptions for each Rate Tier. Repeat the process for each rate tier. After you have defined assumptions for all Rate Tiers, you will return automatically to the Assumption Browser Page.
NOTE:
You can select more than one product at a time from the Assumption Browser Page.
· When Pricing Margin Assumptions are defined for all required product/currency combinations, select SAVE from the Assumption Browser Page.