Topics:
· Adjustment Auto Approval Concept
· Data Model and Metadata Extensions
· Procedure to Add Optional Dimensions
· Optimization of GL Reconciliation Processing Package
· Map Level Recon Parent Node Selection
· Creating Filter for Load Run ID
· VPAT-keystrokes and access keys
The following provides a brief description of the various tables:
Name |
Comment |
Download or DT |
|---|---|---|
GL Master |
This table stores a list of all available GL codes. Select a subset of GL codes that is to be considered for the GL Reconciliation. |
Partly DL & Partly Setup |
Product Processors |
This table stores a list of all PPs supported by the GBS data model. Select a subset of Product Processors for which GL Recon is required. |
DL |
Setup GL Balances |
This table stores the table name of the table which stores the GL data along with the mapping of various columns within that table. |
DL |
Stage GL Data |
This table stores the values of each of the GL codes which is present in the table GL Master. |
DL |
GL Mapping Master |
This table stores the information about mapping for its reconciliation treatment and any thresholds that must be applied at a mapping level during the GL Reconciliation. |
Setup |
GL PP Map |
This table stores the mapping between a GL and a PP and the associated granularity of the GL that must be reconciled with a certain granularity in the PP. The same GL can be mapped to multiple PPs and conversely, a PP can be mapped to multiple GLs. The mapping stored in this entity drives all other processes for GL Reconciliation. |
Setup |
PP Default Values |
This table stores the default values that must be used for mandatory columns within the PP in the event an adjustment entry is to be posted into the corresponding PPs. |
Setup |
Product Processor(s) |
It receives for every processing period, the account level information across various products. |
DL |
GL Adjustment Entries |
This table stores the information about the adjustment entries after the differences are found out. |
Processing |
GL Execution Master |
This table stores the information on each execution. |
Processing |
GL Threshold Breaches |
This table stores the breaches from the thresholds as specified in the Rule Configuration, if any. |
Processing |
GL Recon Audit Trail |
This table stores a trace of all add, modify or delete operations performed through User Interfaces. |
Log |
GL Execution Info |
At the time of batch execution, this table gets updated and it checks if the mapping which is chosen for GL Reconciliation pertains to the entity which is selected |
Processing |
Dynamic SQL error log |
This table stores the processing specific dynamic SQL queries as well as Error details if any. |
Log |
Fact Reconciliation Difference |
This table stores the results of executing a defined reconciliation, that is, it stores the reconciliation difference amount if any. |
Processing |
The requirement for Purging or Archiving FACT tables must be analyzed, developed, and executed as per the implementation site requirements; for better performance and space management.
GL or Map level Reconciliation (In Reconciliation Management page) |
Allocation required (In Reconciliation Management page) |
Auto Approval (In PMF Execution Parameter) |
Result - Auto Approval (Y, N) of Adjustment Entry |
|---|---|---|---|
GL |
N |
N |
N - GL Code where Auto Approval flag is N will not be used for reconciliation and no adjustment entry is passed against it. Allocation required and auto-approval will not be considered for the GL code. |
GL |
N |
N |
N - The difference for the GL code is taken to the FCT_RECONCILIATION_DIFFERENCE and a threshold check is performed. No impact on FCT_GL_ADJUSTMENT_ENTRIES. |
GL |
N |
Y |
N - GL Code where Auto Approval flag is N is not used for reconciliation and no adjustment entry is passed against it. Allocation required and auto-approval is not considered for the GL code. |
GL |
N |
Y |
N - The difference for the GL code is taken to the FCT_RECONCILIATION_DIFFERENCE.Auto Approval (In Run Management Screen) will not be considered. |
GL |
Y |
N |
N - GL Code where Auto Approval flag is N is not used for reconciliation and no adjustment entry is passed against it. Allocation required and auto-approval is not considered for the GL code. |
GL |
Y |
N |
N - The adjustment entry for the GL code is in FCT_GL_ADJUSTMENT_ENTRIES. |
GL |
Y |
Y |
Y - The adjustment entry for the GL code is taken to the target entity or PP. |
GL |
Y |
Y |
N - GL Code where Auto Approval flag is N will not be used for reconciliation and no adjustment entry is passed against it. Allocation required and auto-approval will not be considered for the GL code. |
Map |
N |
N |
N - GL Code where the Auto Approval flag is N will not be used for reconciliation. |
Map |
N |
N |
N - Accounts having such GL codes will participate in map level reconciliation. The difference is taken to the FCT_RECONCILIATION_DIFFERENCE and a threshold check is performed. No impact on FCT_GL_ADJUSTMENT_ENTRIES. |
Map |
N |
Y |
N - GL Code where the Auto Approval flag is N will not be used for reconciliation. Auto Approval (in PMF Execution Framework) will not be considered. |
Map |
N |
Y |
N - Accounts having such GL codes will participate in map level reconciliation. The difference for the GL code is taken to the FCT_RECONCILIATION_DIFFERENCE and a threshold check is performed. No impact on FCT_GL_ADJUSTMENT_ENTRIES. Auto Approval (in the PMF Execution Framework page) will not be considered. |
Map |
Y |
N |
N - GL Code where the Auto Approval flag is N will not be used for reconciliation. The adjustment entry is in FCT_GL_ADJUSTMENT_ENTRIES with status as pending for approval. It'll not be taken to the target entity or PP. |
Map |
Y |
N |
N - Accounts having such GL codes will participate in map level reconciliation. The adjustment entry for the GL code is in FCT_GL_ADJUSTMENT_ENTRIES with status as pending for approval. It'll not be taken to the target entity or PP. |
Map |
Y |
Y |
Y - Accounts having such GL codes will not participate in map level reconciliation. The adjustment entry for the rest of the reconciliation is taken to the target entity or PP. |
Map |
Y |
Y |
Y - Accounts having such GL codes will participate in map level reconciliation. The adjustment entry for the rest of the reconciliation is taken to the target entity PP. |
Topics:
· Steps to Configure an Additional Table in the Application
To add a Ledger entity, Product Processor entity, or Dimension table in OFS Analytical Application Reconciliation Framework, follow these steps.
For example, to add a GL Entity for General Ledger to General Ledger reconciliation, perform the following steps:
1. Open the OFS_GLRECON.erwin file in Erwin Data Modeler.
2. Change the view mode to Physical.
3. If Target ledger Structure is different than STG_GL_DATA:
a. Place the cursor on the tables in OFSAA Tree View, right-click, and select New. This creates a new table. Rename it to the required table name.
b. Expand the table and click the + icon to view the columns mapped against the tables.
c. Place the cursor on the columns mapped against the tables, right-click, and select New. It adds a new column to that table. Rename it to the required column name.
d. Repeat the above-mentioned steps to add multiple tables and columns.
e. Navigate to Logical View and provide the logical table name and logical column names to the added columns.
4. If Target ledger Structure is the same as STG_GL_DATA:
a. In the OFSAA tree view, you can see Tables.
b. Navigate to STG_GL_DATA in OFSAA tree view; right-click and select Go to Diagram.
c. Press CTRL+C (to copy) and then CTRL+V (to paste), to create a new table with the same name as STG_GL_DATA. Rename the table name in both the Physical View and Logical View.
d. Rename the constraints and index names on the newly added table.
5. Save the newly added tables as .xml file. Choose save as type to XML Types (*.xml).
6. Select option AllFusion Repository Format in the dialog box. Click OK to generate a new .xml file.
7. Copy that XML file to server for fast processing under ftpshare/<<infodom>>/erwin/erwinXML
8. Navigate to the OFSAAI UI and log in. Select an appropriate infodom and navigate to Unified Analytical Metadata. To process further see the following steps:
9. Click Import Model.
10. Select Incremental Changes or Sliced Model in Choose Type to Upload.
11. Select the file from the server. It will list out the files present in the path.
12. Select your XML file and click upload to begin the process to upload the data model. On successful upload, a dialog box pops up.
13. Similarly, follow the steps mentioned above to add a Stage General Ledger Master (STG_GL_ACCOUNT_MASTER ), General ledger account dimension (Example DIM_GL_ACCOUNT), or Product processor (Example STG_CARDS).
14. Perform the following steps to continue further (these steps are not applicable for a Product Processor entity):
15. Insert a new unique map_ref_num in two tables SYS_TBL_MASTER and SYS_STG_JOIN_MASTER for creating SCD for data movement from new Stage general ledger master to new General ledger account dimension.
16. Example: SYS_TBL_MASTER Table contains table level information Stage to Dimension. Table names must be changed according to the new stage general ledger master (STG_TBL_NM) to the new General ledger account dimension (TBL_NM).
MAP_REF_NUM |
TBL_NM |
STG_TBL_NM |
SRC_PRTY |
SRC_PROC_ SEQ |
SRC_TYP |
DT_OFFS ET |
SRC_KEY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
491 |
DIM_GL_ACCOUNT |
STG_GL_ACCOUNT_MASTER |
|
8 |
MASTER |
0 |
|
17. Example: SYS_STG_JOIN_MASTER Column level mapping information from Stage to Dimension. Column names and data types must be modified according to the new Stage general ledger master (STG_COL_NM) to the new General ledger account dimension (COL_NM).
MAP_RE F_NUM |
COL_NM |
COL_TYP |
STG_COL_NM |
SCD_T YP_ID |
PRTY_LOOKUP_REQD_FLG |
COL_DA TATYPE |
COL_F ORMAT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
491 |
D_END_DATE |
ED |
31-Dec-99 |
|
N |
DATE |
|
491 |
D_START_DATE |
SD |
SD |
|
N |
DATE |
|
491 |
F_DIFF_AUTO_AP PROVE_FLAG |
DA |
F_DIFF_AUTO_APP ROVE_FLAG |
2 |
N |
VARCHAR |
|
491 |
F_INTRA_GROUP |
DA |
F_INTRA_GROUP |
2 |
N |
CHAR |
|
491 |
F_LATEST_RECO RD_INDICATOR |
LRI |
Y |
|
N |
CHAR |
|
491 |
N_GL_ACCOUNT_I D |
SK |
SEQ_DIM_GL_ACC OUNT.CURRVAL |
|
N |
NUMBER |
|
491 |
N_GL_ACCOUNT_ SKEY |
SK |
SEQ_DIM_GL_ACC OUNT.NEXTVAL |
|
N |
NUMBER |
|
491 |
V_GL_ACCOUNT_ CODE |
PK |
V_GL_CODE |
|
N |
VARCHAR |
|
491 |
V_GL_ACCOUNT_ NAME |
NN |
V_GL_NAME |
2 |
N |
VARCHAR |
|
491 |
V_GL_BOOK_COD |
DA |
V_GL_BOOK_CODE |
2 |
N |
VARCHAR |
|
491 |
V_GL_PARENT_A CCOUNT_CODE |
DA |
V_PARENT_GL_CO DE |
2 |
N |
VARCHAR |
|
491 |
V_GL_TYPE |
DA |
V_GL_TYPE |
2 |
N |
VARCHAR |
|
18. Navigate to Operations and see the following steps:
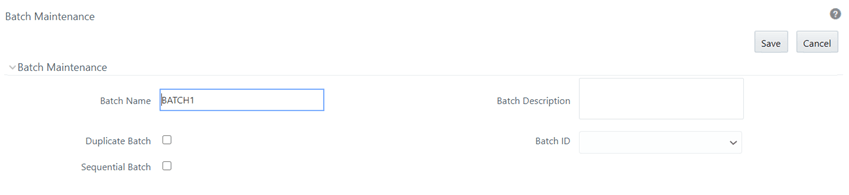
a. Click Batch Maintenance.
b. Add a new batch, provide an appropriate name and description, and click Save.
Figure 84: Batch Maintenance Window

c. Add a task to the newly created batch.
d. Select Run Executable under Components.
e. Select appropriate Datastore type, Datastore Name, IP Address.
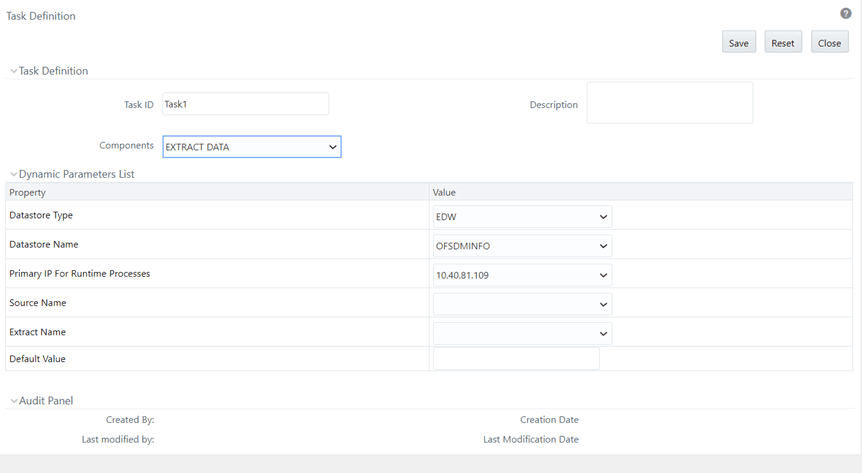
f. Update scd,<<MAP_REF_NUM>> in the executable with the unique number which is provided while inserting in SYS_TBL_MASTER and SYS_STG_JOIN_MASTER. Select Wait as N and Batch Parameter as Y. Click Save as shown in the following figure:
Figure 85: Task Definition Window
Navigate to Unified Analytical Metadata and see the following steps to proceed further:
a. Click Data Sets under Business Metadata Management.
b. Add a new dataset and provide code, short description, and long description.
c. Select the entities that are participating in the Dataset.
d. Define Ansi join.
19. Example: where STG_GL_DATA is your Ledger table and DIM_GL_ACCOUNT is your General ledger account dimension.
STG_GL_DATA
INNER JOIN DIM_CURRENCY ON DIM_CURRENCY.V_ISO_CURRENCY_CD = STG_GL_DATA.V_CCY_CODE
INNER JOIN DIM_ORG_STRUCTURE ON DIM_ORG_STRUCTURE.V_ENTITY_CODE =
STG_GL_DATA.V_LV_CODE AND DIM_ORG_STRUCTURE.f_latest_record_indicator='Y'
INNER JOIN DIM_DATES ON DIM_DATES.D_CALENDAR_DATE = STG_GL_DATA.FIC_MIS_DATE INNER JOIN DIM_GL_ACCOUNT ON DIM_GL_ACCOUNT.V_GL_ACCOUNT_CODE =
STG_GL_DATA.V_GL_CODE AND DIM_GL_ACCOUNT.f_latest_record_indicator='Y'
INNER JOIN DIM_GAAP ON DIM_GAAP.V_GAAP_CODE = STG_GL_DATA.V_GAAP_CODE AND
DIM_GAAP.f_latest_record_indicator='Y' LEFT OUTER JOIN DIM_BUSINESS_UNIT ON DIM_BUSINESS_UNIT.V_BUSINESS_UNIT_CODE = STG_GL_DATA.V_BUSINESS_UNIT_CODE AND
DIM_BUSINESS_UNIT.f_latest_record_indicator='Y'
LEFT OUTER JOIN DIM_ORG_UNIT ON DIM_ORG_UNIT.V_ORG_UNIT_CODE =
STG_GL_DATA.V_ORG_UNIT_CODE AND DIM_ORG_UNIT.f_latest_record_indicator='Y'
LEFT OUTER JOIN DIM_GEOGRAPHY ON DIM_GEOGRAPHY.V_ACCT_BRANCH_CODE =
STG_GL_DATA.V_BRANCH_CODE AND DIM_GEOGRAPHY.f_latest_record_indicator='Y'
LEFT OUTER JOIN DIM_PRODUCT ON DIM_PRODUCT.V_PROD_CODE = STG_GL_DATA.V_PROD_CODE
AND DIM_PRODUCT.f_latest_record_indicator='Y'
20. Click Save.
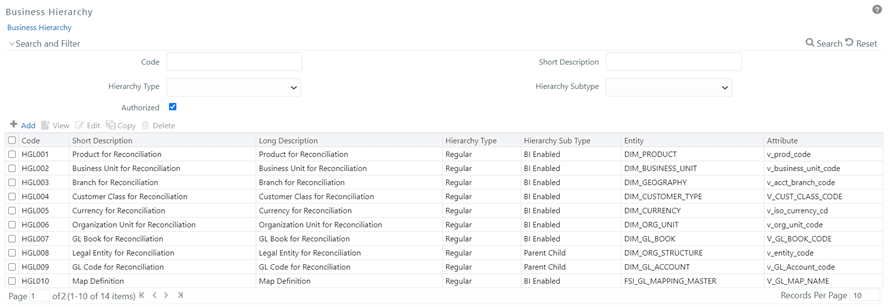
21. Navigate to Unified Analytical Metadata and click Business Hierarchy under Business Metadata Management.
22. Add two new Hierarchies on new Ledger Account Dimension, for GL Code, and GL Type and shown in the following figures:
Figure 86: GL Code Example
23. Perform an excel upload for table SETUP_GLSOURCE_HIERARCHY
§ V_GL_HCY_CODE Hierarchy code which is created, as on GL code for new general ledger account dimension.
§ V_GL_HCY_DIM_TABLE_NAME General ledger account dimension table name.
§ V_GL_HCY_INTRA_GROUP_COL_NAME Intragroup Column name.
§ V_GL_HCY_GL_TYPE_COL_NAME GL Type column name.
Example:
V_GL_HCY_CODE |
V_GL_HCY_DIM_TABLE_NAME |
V_GL_HCY_INTRA_GROUP_COL_NAME |
V_GL_HCY_GL_TYPE_COL_NAME |
|---|---|---|---|
HGL009 |
DIM_GL_ACCOUNT |
F_INTRA_GROUP |
V_GL_TYPE |
1. Create a dimension table in the model if required.
2. Add the table (where the dimension is defined) in the join condition of the GL dataset & Product Processor dataset.
3. Create a Hierarchy with metadata authorization.
4. Add a field from the respective dimension table which is used to join with stage product processor tables in the following tables:
a. FCT_RECONCILIATION_DIFFERENCE
b. FCT_GL_ADJUSTMENT_ENTRIES
c. FCT_GL_CORRECTION_ENTRIES
d. FSI_TMP_TARGET_BALANCE
e. FSI_TMP_SOURCE_BALANCE
f. FSI_GL_THRESHOLD_BREACHES
5. Add a field from respective dimension table which is used to join with stage product processor tables in the unique index of the following tables:
a. FCT_RECONCILIATION_DIFFERENCE
b. FCT_GL_ADJUSTMENT_ENTRIES
c. FCT_GL_CORRECTION_ENTRIES
d. FSI_TMP_TARGET_BALANCE
e. FSI_TMP_SOURCE_BALANCE
6. Upload the customized data model to see the changes reflected in the database.
This section is only applicable for RDBMS installation mode.
Parallel Hint for SELECT statements:
The use of a parallel hint is optional in the queries. Perform the following steps to use the parallel hint in SELECT clause of the queries generated during execution:
Insert a record into the GL_SETUP_CONFIGURATION table and provide a parallel hint in the V_COMPONENT_VALUE column.
For example, insert into GL_SETUP_CONFIGURATION (V_COMPONENT_CODE, V_COMPONENT_DESC, V_COMPONENT_VALUE) values ('GLRECON_SEL_PARALLEL_HINT', 'To use Parallel hint in GL Recon Application.', '/*+ parallel */').
In case a parallel hint is not required then the previous step is not required. The usage of a parallel hint is optional for the GL Processing package.
Parallel Hint for CREATE TABLE statements:
The use of parallelism during intermediate table creation is optional. Perform the following steps to use parallelism to CREATE TABLE clause during execution:
Insert a record into the GL_SETUP_CONFIGURATION table and provide a parallel hint in the V_COMPONENT_VALUE column.
For example, insert into GL_SETUP_CONFIGURATION (V_COMPONENT_CODE, V_COMPONENT_DESC, V_COMPONENT_VALUE) values ('CREATE_TABLE_PARALLEL_HINT', 'To use parallelism while creating intermediate tables', 'PARALLEL').
NOTE:
HINT can be used with a combination of - NOLOGGING and PARALLEL with different degrees of parallelism as follows:
1. PARALLEL
2. NOLOGGING PARALLEL
3. PARALLEL (DEGREE i*)
4. NOLOGGING PARALLEL (DEGREE i*)
*Any positive integer based on available system resources.
To select the Map Level Recon parent node, perform the following steps:
1. Ensure that the General Ledger Product Processor (GL PP) Definition has the following settings:
a. Reconciliation Definition Type as Manual
b. Consolidation Type as Solo
c. Reconciliation Definition as Map Level Recon.
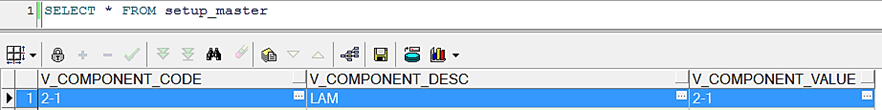
2. Create an entry in the SetUpMaster as LAM, for the corresponding Map ID and Version Number.
Figure 87: LAM entry in SetUpMaster
a. The parent-child hierarchy for the legal entity selected in the definition is considered for filtration.
In case the GL nodes exceed 2024 then use the following configuration to support the hierarchy browser of GL:
1. Change <PARAMETER NAME=PC_NONBI_BI_SWITCH VALUE=<PARAM>/> in $FIC_HOME/conf/DynamicServices.xml and deployed location <CONTEXT_PATH>/CONTEXT_NAME/conf/DynamicServices.xml
2. <PARAM>: Parameter value to be chosen based on no total number of nodes in a hierarchy (OOB: 2048) For example, if hierarchy nodes are 9000, then VALUE must be 9500.
3. After taking backup of these tables, delete the data from rev_bihier,rev_locale_hier for the respective hierarchy code.
4. Restart the web and app servers by clearing the work/cache/tmp folder.
5. Resave the respective hierarchy, and verify whether the data is populated into the rev_bihier table with version 0.
6. Clear browser cache and create the definition from the start.
Topics:
· Problem
· Solution
For a GL Recon Rule running in production, one of the legal entities has a new parent node in the underlying data and the Legal Entity Hierarchy is refreshed with an automatic batch. Because of this change in the legal entity structure, the GL Recon Rule, where the hierarchy is used, is broken.
GL Recon Rule did not fail, it is executed successfully without returning any results. Hence, there is no way for any user to know that there is an issue. When the GL Recon Rule is opened in the front end, the legal entity field is displayed as blank.
Ideally, any changes to the underlying data of the hierarchy must be automatically reflected in the GL Recon Rule.
A batch has to be executed with the FIC_MIS_DATE that will refresh all hierarchies used in the existing rule. Before executing the batch, check the entries in the table:
FSI_GL_HIERARCHY_CONFIGURATION
The following batch has to be executed with proper FIC_MIS_DATE and the updated hierarchies will be saved in an Audit Table: FSI_GL_HIER_REFRESH_AUDIT_DDL for tracking purposes.
Batch: ##INFODOM##REFRESH_HIERARCHY
You can filter the load Run ID value and process reconciliation accordingly. One load Run ID in the product processor table can be filtered and reconciled with the respective ledger data. When load Run ID filtration is enabled, adjustments automatically get updated with the filtered load Run ID value, irrespective of the value given in default values.
The following is the procedure to filter load Run ID, reconcile, and default the same:
· Add the following entry in GL_SETUP_CONFIGURATION table:
V_COMPONENT_CODE |
V_COMPONENT_DESC |
V_COMPONENT_VALUE |
|---|---|---|
GLPPLOADRUNIDFILTER |
Flag to set parametrized Load Run filter |
N |
To enable load Run ID filtration, change the flag to Y in the column V_COMPONENT_VALUE.
· Add the following entry in RUN_EXE_PARAMETERS table for the corresponding RunSkey
N_RUN_SKEY |
V_PARAM_ID |
V_SEGMENT_CODE |
V_PARAM_VALUE_CODE |
V_HIER_NODE_CODE |
V_LEAF_CONDITION |
V_HIER_NODE_DESC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
53 |
GLPPLOADRUNIDFILTER |
GLSEG802 |
1 |
|
|
|
· RunSkey: RunSkey value can be fetched from the table DIM_RUN.
· The rule must be executed once, before updating the previous tables and V_COMPONENT_VALUE must be N. You must go the DIM_RUN table and fetch the corresponding Skey for the definition you like to filter with load Run ID.
· V_PARAM_ID: This must have a value GLPPLOADRUNIDFILTER.
· V_SEGMENT_CODE: This value must be updated with the corresponding application segment.
· V_PARAM_VALUE_CODE: This column must have the value of load Run ID based on which filtration happens in the target data for the selected RunSkey rule.
· Once these tables and values are updated, you can run the batch from the Operations tab and check the results. Adjustments that are created with these changes displays the load Run ID value specified in the V_PARAM_VALUE_CODE.
There is an option to include the adjustments as any other normal account information into the reconciliation process.
The following are the steps you must follow to include the adjustments into the reconciliation process:
· You must make an entry in the GL_SETUP_CONFIGURATION table as follows.
V_COMPONENT_CODE |
V_COMPONENT_DESC |
V_COMPONENT_VALUE |
|---|---|---|
IGNORE_DEFAULT_ADJUSTMENT_ENTRY |
Flag to ignore default adjustment entries for further calculations |
Y |
· By default V_COMPONENT_VALUE value is set to Y.
· Once the Reconciliation Difference process is executed, the differences between source and target are identified and captured in the table - FCT_RECONCILIATION_DIFFERENCE.
Based on Adjustment entry floor, dummy adjustment entries are generated in table - FCT_GL_ADJUSTMENT_ENTRIES with dummy account number - GL_<MAP_ID>_<Sequence> (GL_45_1).
· If V_COMPONENT_VALUE is set to N then during the next execution of the same definition or any definition which results in the same granularity, the dummy account numbers are considered for calculation and differences are adjusted accordingly.
NOTE:
While executing multiple rules together in one run, definitions with different dimensional granularity or similar definitions with different filters have to be carefully executed in a single run as the system randomly allocates the map ID for the order of execution and not for the order of UI rule addition.
Voluntary Product Accessibility Template (VPAT) is a document that mentions how to access the User Interface elements. Unique keystrokes and Access keys move the focus to a specific UI element (and trigger the command). They are usually a button, link, or control that triggers the command. Access keys relocate cursor or selection focus to specific interface components. Every component on the page with definable focus is accessible by tab traversal (using Tab and Shift+Tab); however, access keys provide quick focus to frequently used components. Access keys must be unique within a page. Oracle Financial Services Reconciliation Framework requires to use the additional below mentioned keys.
Target |
Key |
Action |
|---|---|---|
Add Filter |
Enter |
Opens the panel. |
Dropdown |
UpArrow or DownArrow |
Highlight the option item in the direction of the arrow. |
Dimension cards |
Enter |
To select the card |
|
Q or q |
If the focus is on a card, pressing Q will make its contents accessible using TAB |
|
X or x |
When Q mode is enabled, press X to exit Q mode |
|
Tab |
Navigates to next card |
Button on card |
Space |
Activates the button |
|
Tab |
When Q mode is activated, the tab is used to move focus to the next button |
Target |
Key |
Action |
|---|---|---|
Dropdown |
UpArrow or DownArrow |
Highlight the option item in the direction of the arrow. |
Measures/Dimension cards/Filter cards |
Enter |
To select the card |
|
Q or q |
If the focus is on a card, pressing Q will make its contents accessible using TAB |
|
X or x |
When Q mode is enabled, press X to exit Q mode |
|
Tab |
Navigates to next card |
Buttons on card |
Space |
Activates the button |
|
Tab |
When Q mode is activated, the tab is used to move focus to the next button |