Creating and Populating Multi-Dimensional Arrays
You can create arrays with more than one dimension. Each element in a multi-dimensional array is itself an array. For example, a two-dimensional array is really an array of arrays. Each subarray has to be created and populated as an array.
Each subarray in a multi-dimensional array must be of the same type. For example, you can’t create a two dimensional array that has one subarray of type string and a second subarray of type number.
The following example creates an array of array of string, then reads two files, one into each "column" of the array. The CreateArrayRept function call creates an empty array of string (that is, the Len property is 0) but with two dimensions (that is, with two subarrays, Dimension is 2). The first Push method adds elements into the first subarray, so at the end of that WHILE loop in the example, &BOTH has Len larger than 0. The other Push methods add elements to the second subarray.
Local array of array of string &BOTH;
Local File &MYFILE;
Local string &HOLDER;
/* Create empty &BOTH array */
&BOTH = CreateArrayRept(CreateArrayRept("", 0), 0);
/* Read first file into first column */
&MYFILE = GetFile("names.txt", "R");
While &MYFILE.ReadLine(&HOLDER);
&BOTH.Push(&HOLDER);
End-While;
/* read second file into second column */
&MYFILE = GetFile("numbers.txt", "R");
&LINENO = 1;
While &MYFILE.ReadLine(&HOLDER);
If &LINENO > &BOTH.Len Then
/* more number lines than names, use a null name */
&BOTH.Push(CreateArray("", &HOLDER));
Else
&BOTH[&LINENO].Push(&HOLDER);
End-If;
&LINENO = &LINENO + 1;
End-While;
/* if more names than numbers, add null numbers */
for &LINENO = &LINENO to &BOTH.Len
&BOTH[&LINENO].Push("");
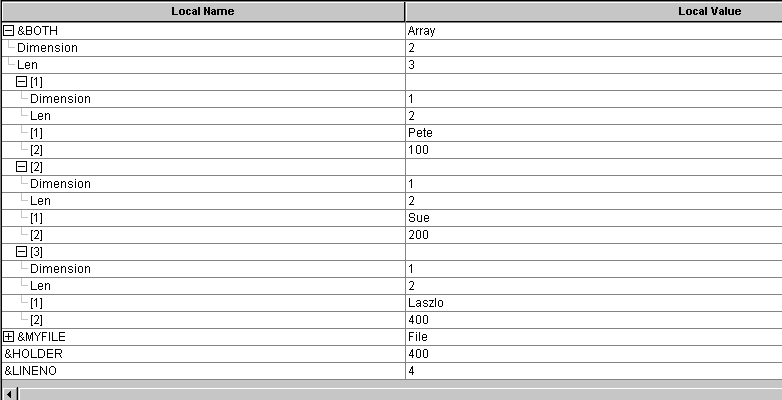
End-For;Image: &BOTH array expanded in PeopleCode debugger at program end
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the &BOTH array expanded in PeopleCode debugger at program end. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
The following code reads from a two-dimensional array and writes the data from the each subarray into a separate file.
Local File &MYFILE1, &MYFILE2;
Local string &STRING1, &STRING2;
Local array of array of string &BOTH;
.
/* code to load data into array would be here */
.
/* open files to be written to */
&MYFILE1 = GetFile("names.txt", "A");
&MYFILE2 = GetFile("numbers.txt", "A");
/* loop through array and write to files */
For &I = 1 To &BOTH.Len
&J = 1;
&STRING1 = &BOTH[&I][&J];
&MYFILE1.writeline(&STRING1);
&J = &J + 1;
&STRING2 = &BOTH[&I][&J];
&MYFILE2.writeline(&STRING2);
End-For;
&MYFILE1.Close();
&MYFILE2.Close();The following example populates a multi-dimensional string array using SQL. This could be used for reading small tables.
Component array of array of string &ArrRunStatus;
&ArrRunStatus = CreateArrayRept(CreateArrayRept("", 0), 0);
&ArrRunStatusDescr = CreateArrayRept("", 0);
&SQL = CreateSQL("SELECT FIELDVALUE, XLATSHORTNAME FROM XLATTABLE WHERE FIELDNAME = 'RUNSTATUS'");
&LineNo = 1;
While &SQL.Fetch(&FieldValue, &XlatShortName)
&ArrRunStatus.Push(&FieldValue);
&ArrRunStatus[&LineNo].Push(&XlatShortName);
&LineNo = &LineNo + 1;
End-While;To search for a particular element in this array, use the following:
&iIndex = &ArrRunStatus.Find(&RunStatusToGet);&RunStatusDescr = &ArrRunStatus[&iIndex][2];The following example shows how to create a two-dimension array using CreateArrayRept and Push. In addition, it shows how to randomly assigns values to the cells in a two-dimension array.
Local array of array of string &ValueArray;
&Dim1 = 10;
&Dim2 = 5;
&ValueArray = CreateArrayRept(CreateArrayRept("", 0), 0);
For &I = 1 To &Dim1
&ValueArray.Push(CreateArrayRept("", &Dim2));
End-For;
&ValueArray[1][1] = "V11";
&ValueArray[2][1] = "V21";
WinMessage("&ValueArray[1][1] = " | &ValueArray[1][1] | " " | "&ValueArray[2][1] = " | &ValueArray[2][1], 0);