G-Flex Call Flows
Several types of subscriber numbers can be used as a basis for routing messages to HLRs: IMSI, MSISDN, MIN, and MDN.
- IMSI routing that uses the actual IMSI (an E.212 number)
- IMSI routing that uses the Mobile Global Title (MGT), which is an E.214 number derived from the IMSI
G-Flex also handles the MSISDN/MIN/MDN cases, which use the E.164 numbering plan. The call flows in this section address these three cases.
The call flows in this section show only one possible scenario for how messages are routed in the network and where various stages of GTT are performed. G-Flex C7 Relay may perform intermediate or final GTT and/or replace the SCCP (Signaling Connection Control Part) CdPA (Called Party Address) with the HLR entity address, depending on the message received and provisioned data. All call flows here assume that G-Flex C7 Relay is integrated with the vSTP.
Note:
In GSM networks, each network entity (for example, MSC, HLR, VLR [Visitor Location Register]) is identified by an E.164 entity address. GSM networks also route messages based on E.164 entity addresses when those addresses are known by the sender. While the routing of these messages must also be handled by G-Flex C7 Relay, this function is not considered to be a core part of G-Flex. Because these numbers are not expected to be populated in the G-Flex data, messages routed using these addresses should fall through to normal or enhance) GTT (Global Title Translation). Therefore, call flows for this type of routing are not described here.MGT (E.214) Routing
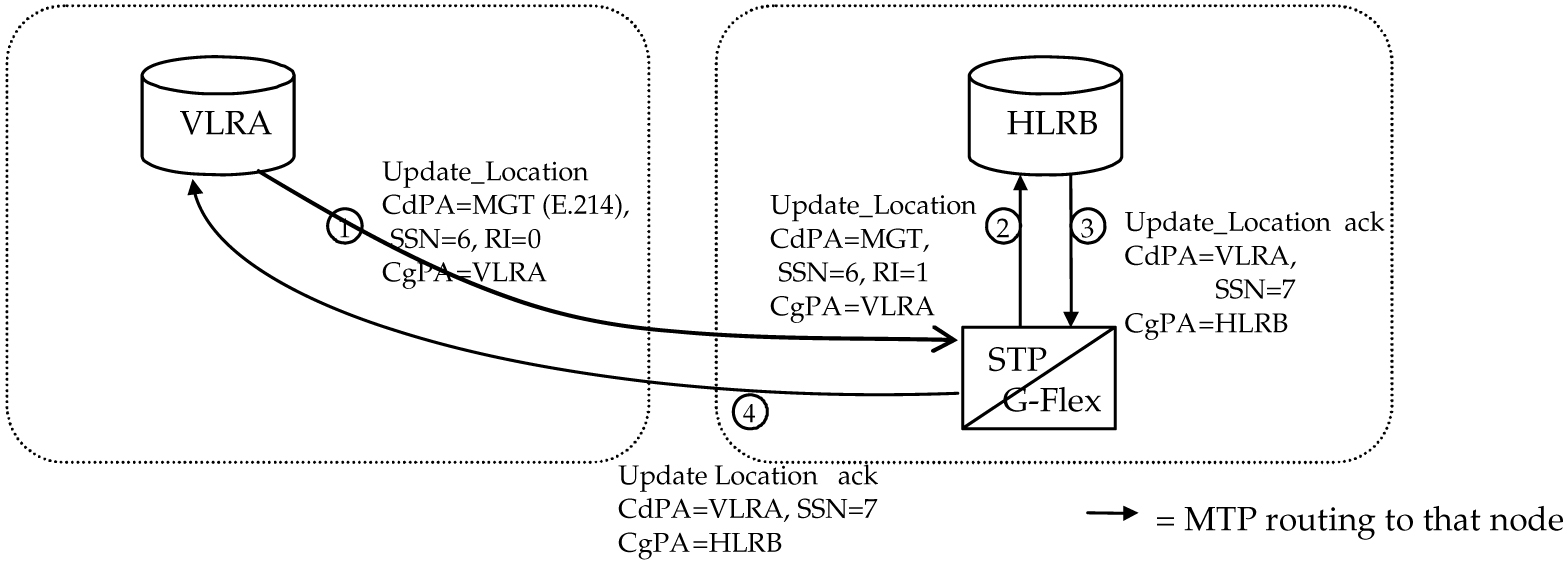
The partial Update Location procedure shown in unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-36B73513-74F6-4526-AC76-4074AD5382CF__42421 is an example of E.214 mobile global title routing. MGT is employed in situations where the E.164 address of the receiving node (labeled HLRB) is not yet known by the sending node (labeled VLRA).
In order to update information about the subscriber's location, VLRA sends a MAP (Mobile Application Part) Update_Location message to the G-Flex Relay (possibly through a Gateway Mobile Switching Center).
The steps in unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-36B73513-74F6-4526-AC76-4074AD5382CF__42421 are cross-referenced in the following procedure.
-
The message is received at the G-Flex Relay. Global title information triggers G-Flex processing. Because the SCCP CdPA contains an E.214 number, G-Flex first converts the E.214 number to an international E.212 number before searching the vSTP Real Time Database (UDR) with the E.212 number (Step 1). G-Flex also handles the case where an E.212 number is received in the SCCP CdPA. In this case, the database is searched directly using the E.212 number.
-
G-Flex finds a match with HLR GT information and routes the message to the designated DPC (HLRB) (Step 2).
-
HLRB responds to VLRA with an Update_Location
ack. This message has the E.164 address of VLRA in the SCCP CdPA and is routed by normal or enhanced GTT, not G-Flex (Step 3). -
The message is relayed to VLRA (Step 4).
Figure 6-1 E.214 (E.212) Routing Example - Location Updating
There are other MAP messages from VLR to HLR that also fall into this category of requiring E.214 global title routing. All of these messages are handled the same way by G-Flex, using the process described above.
IMSI (E.212) Routing
G-Flex processing for a message routed with an E.212 number in the SCCP CdPA GTA (Global Title Address) is essentially the same as the processing for a message routed with an E.214 number. The only difference is that the number does not have to be converted to E.212 (since it is already E.212) before doing the database lookup. Therefore, those call flows are not shown here.
MSISDN/MIN/MDN (E.164) Routing
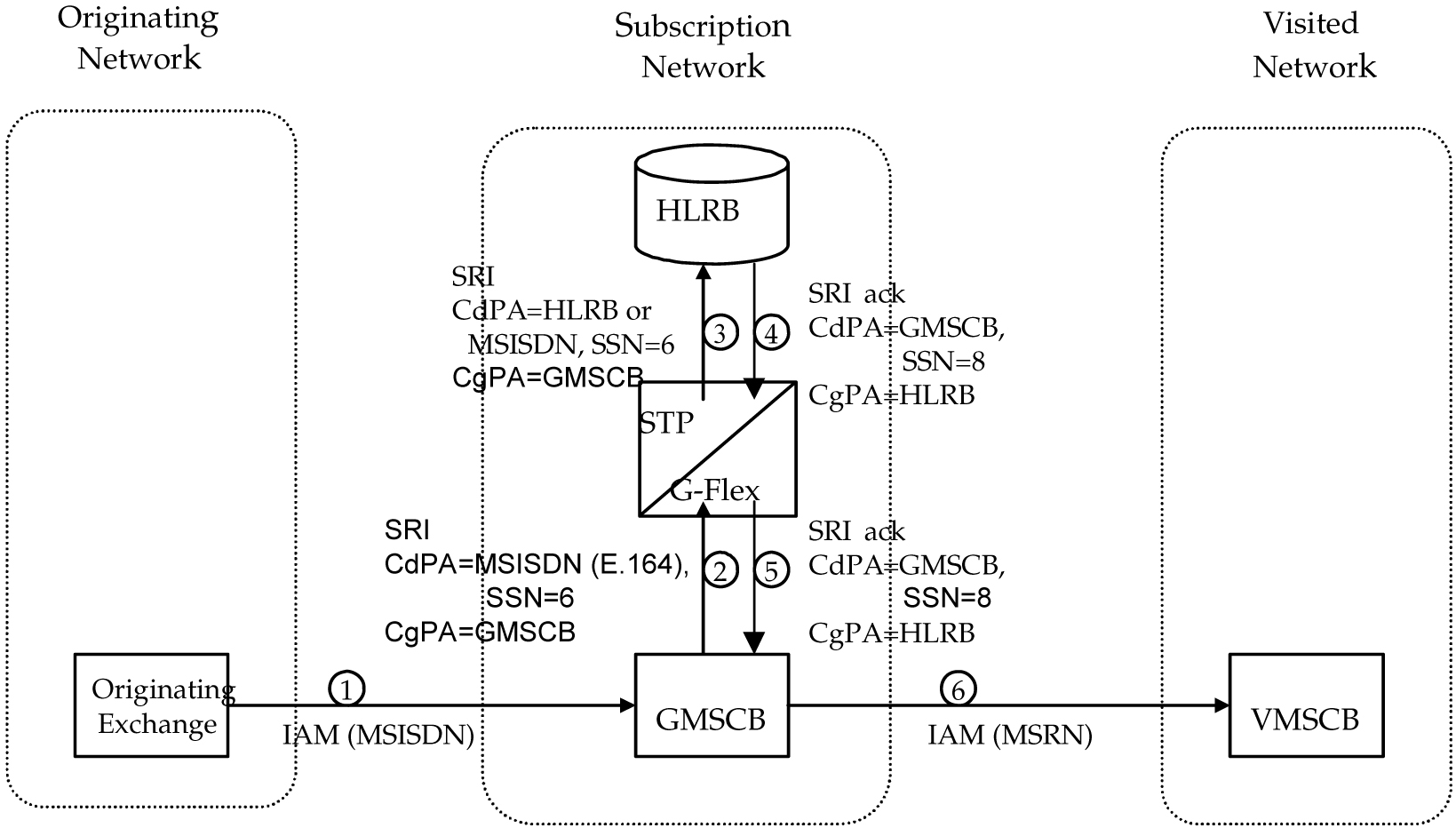
A mobile terminated call results in the GMSC (Gateway Mobile Switching Center) querying the HLR through the use of the called number as a GTA. G-Flex is used to locate the appropriate HLR. The partial mobile terminated call procedure shown in unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-36B73513-74F6-4526-AC76-4074AD5382CF__25969 is an example of MSISDN global title SCCP addressing. This applies to MIN and MDN routing numbers as well.
The steps in unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-36B73513-74F6-4526-AC76-4074AD5382CF__25969 are cross-referenced in the following procedure.
-
A call is originated and an IAM (Initial Address Message) is sent from the originating network to the subscription network (Step 1).
-
Digit analysis at GMSCB detects a mobile terminated call to a mobile station and generates a MAP Send_Routing_Info (SRI) message to the G-Flex Relay (Step 2).
-
The vSTP receives the message. Global title information triggers G-Flex processing. Since the SCCP CdPA contains an E.164 number, G-Flex searches the UDR with the E.164 number, which must be converted to an international number if it is not one already. The G-Flex finds a match with HLR GT information and routes the message to the designated DPC (HLRB) (Step 3).
-
HLRB responds to GMSCB with an SRI
ack. This message has the E.164 address of GMSCB in the SCCP CdPA, and is routed by normal or enhanced GTT, not G-Flex (Step 4). -
The message is relayed to GMSCB (Step 5).
-
GMSCB sends an IAM containing the MSRN (Mobile Station Roaming Number) to the visited network (Step 6).
Figure 6-2 Mobile Terminated Call
Other MAP messages that are routed using MSISDN/MIN/MDN global title routing to an HLR are handled the same way by G-Flex. This includes mobile terminated short messages.