2 Virtual Network Functions Manager Overview
A VNFM automates lifecycle operations for VNFs. Since, each VNF is managed independently, to deploy a DSR it requires creating and instantiating at least two VNFs (one for the network OAM VNF and one for the signaling VNF). Signaling VNFs can be instantiated any time after the network OAM has been instantiated.
The main objective of the DSR VNFM is to provide an ETSI-compliant VNFM manager. The VNFM would be helpful by:
- Automating lifecycle management (LCM) operations for DSR VNFs. Automation of these operations can reduce their execution time.
- Providing a standardized interface to easily integrate with automation clients, especially ETSI-compliant NFVOs. The DSR VNFM provides a REST API that complies with ETSI NFV-SOL 003.
The VNFM is also helpful in responding quickly to changing customer requirements and delivers solutions for those requirements in a very short time.
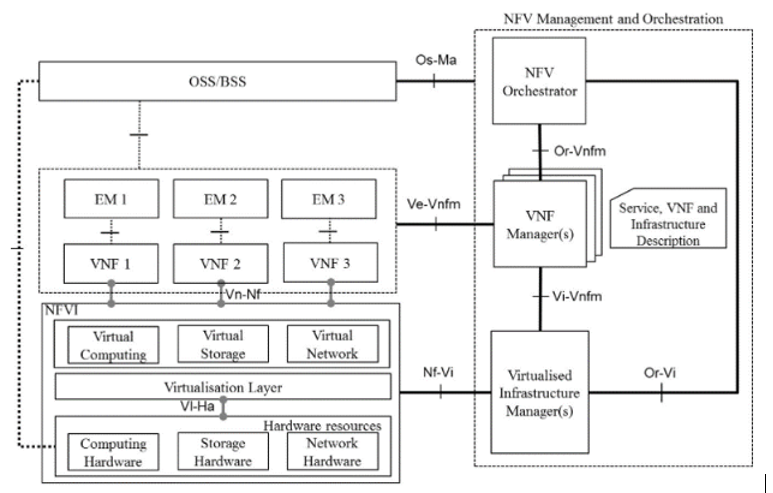
The following figure illustrates the interaction between various components of DSR and VNFM:
Figure 2-1 ETSI MANO Specification
Advantage of Using VNFM
Deployment of Virtual DSR (vDSR) was performed using the following methods that required manual processing:
- VM creation and installation process
- HEAT Template based installation (HEAT templates require manual updates)
The manual deployment consumes multiple hours to deploy a fully operational DSR and the HEAT template based installation needed more caution since it requires more manual work.
Using DSR VNFM, users can deploy an operational DSR on OpenStack within 20 minutes.
This application benefits both the internal and external customers by reducing operating expenses associated with the implementation and by reducing human errors by eliminating manual intervention.