3. Administration User
In the Administration > User, you can record setup data that define your organization structure and its users. Information in this link is more “data” related, whereas the information stored on the System drop-down link functions more like switches that control system behavior.
Navigating to Administration User
- On the Oracle Financial Services Lending and Leasing home screen, click Setup > Setup > Administration > User.
The User drop-down link records the following data:
- Organization
- Companies
- Access
- Users
- General Ledger
- Printers
- Intelligent Segmentation
- Bank Details
- Check Details
- Standard Payees
- Currencies
- ZipCodes
- Payment Hierarchy
3.1 Organization
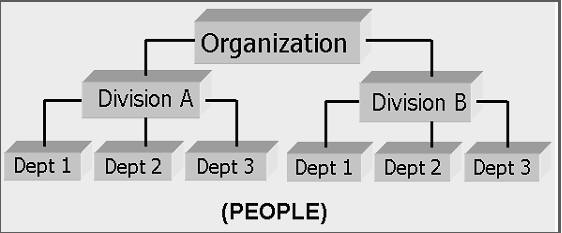
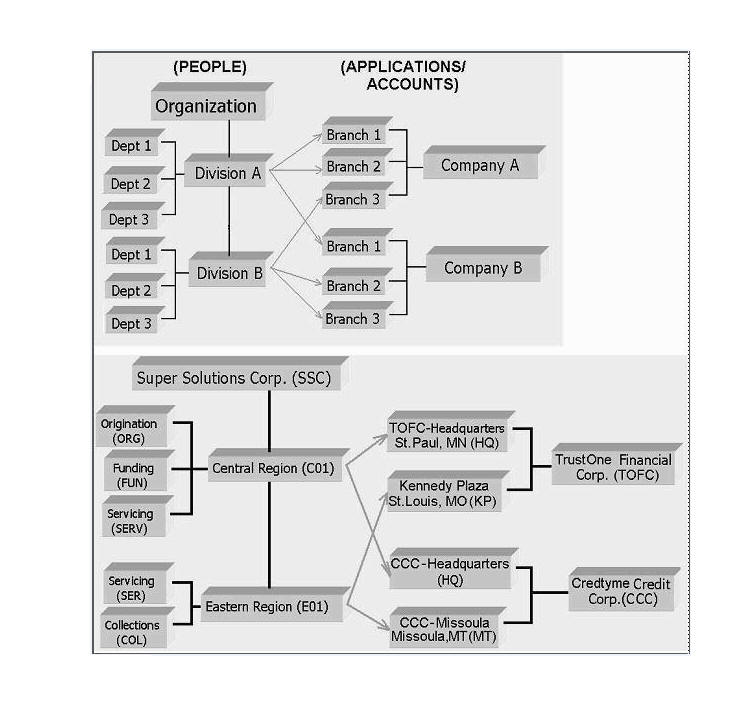
The Organization screen records the operational hierarchy of your business in terms of people. It groups the human resources of your business in three categories: organization, division, and department. The system uses this data to control access of users to applications and accounts.(The Companies screen allows you to setup the location of these applications and accounts.)
Note
You can have only one active organization, so use the Organization field to define your organization at its highest level.
Divisions are groups within your organization that will have access to the same applicationsand accounts. Larger organizations often define their divisions by region. Smaller organizations may define division as branch offices or even departments, and might only have one division defined.
Departments are smaller units within a division. They expand on who is in the corresponding Division field. The system uses this sub screen, for example, when setting up the Services screen on the Utility form. At least one department must be defined for each division.
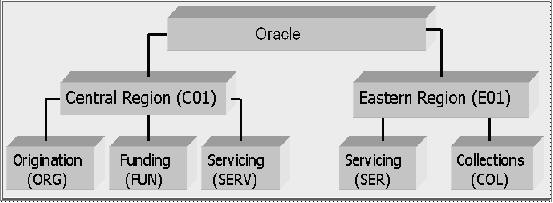
As an example of an organization setup, Oracle Corp. might be defined as:
Organization: O-0001 Oracle Corp. ORA
Division: OD-001 Central Region C01
Department: ODD-01 Origination ORG
Department: ODD-02 Funding FUN
Department: ODD-03 Servicing SER
Division: OD-002 Eastern Region E01
Department: ODD-11 Servicing SER
Department: ODD-12 Collection COL
Note
The Short Name field on the Organization screen allows you to create the ID that Oracle Financial Services Lending and Leasing will use when referring to the organization, division, and department throughout the system.
To setup the Organization screen
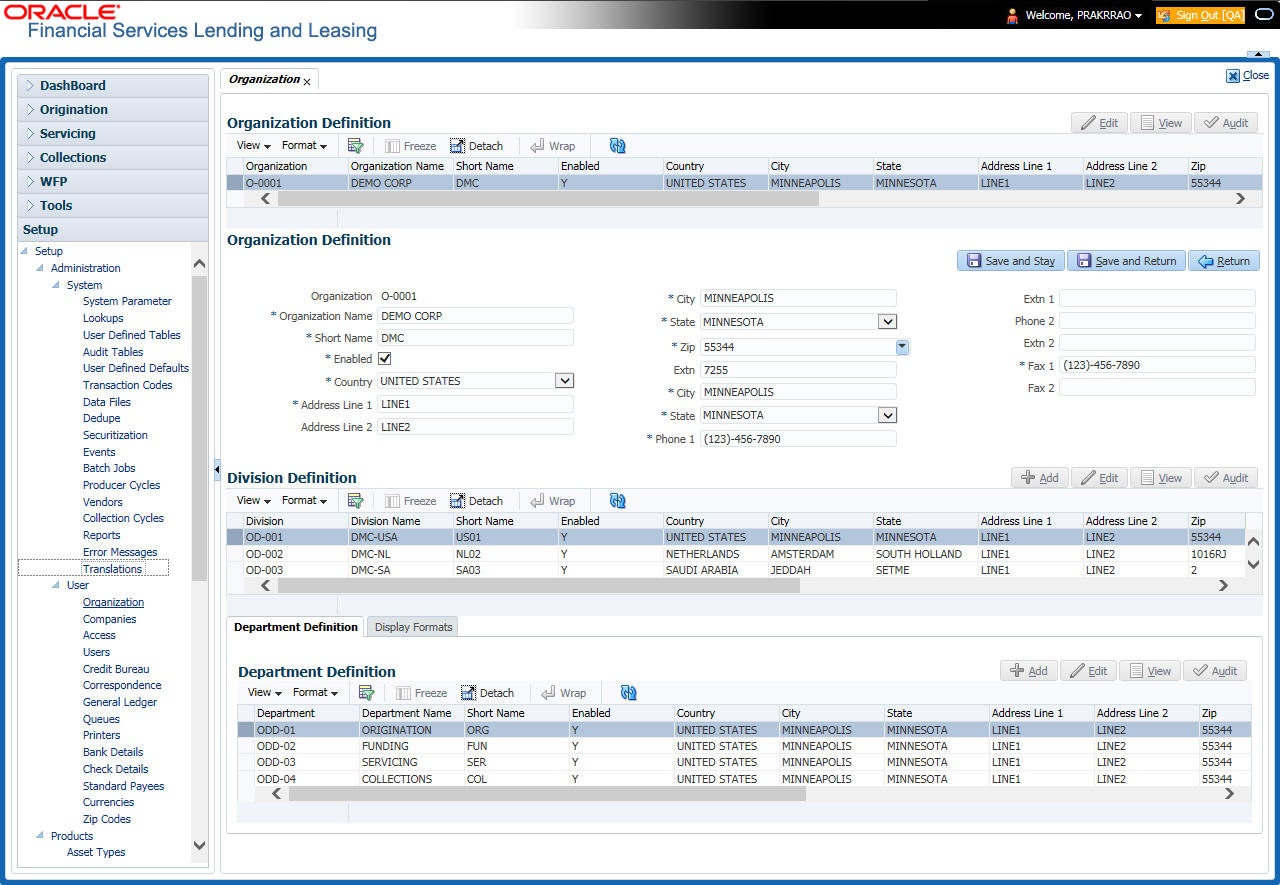
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Organization.
- In the Organization Definition section, there can be only one active entry, so use this screen to define your organization at its highest level. Perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Organization |
Specify the organization ID (the ID is the unique identifier used internally by Oracle Financial Services Lending and Leasing to represent your organization). Note: Do not edit this field. |
Organization Name |
Specify the organization name. |
Short Name |
Specify the short name for the organization. Note: This ID represents this organization throughout the system. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the organization. Note: Only one enabled organization is currently allowed by Oracle Financial Services Lending and Leasing. |
Country |
Select the country where the organization is located from the drop-down list. |
City |
Specify the city where the organization is located. |
State |
Select the state where the organization is located from the drop-down list. |
Address Line 1 |
Specify the address line 1 for the organization. |
Address Line 2 |
Specify the address line 2 for the organization. |
Zip |
Select the zip code of the location where the organization is located from the drop-down list. |
Extn |
Specify the extension of the selected zip code. |
Phone 1 |
Specify the primary phone number for the organization. |
Extn 1 |
Specify the phone extension for the primary phone number. |
Phone 2 |
Specify the alternate phone number for the organization . |
Extn 2 |
Specify the phone extension for the alternate phone number, if specified. |
Fax 1 |
Specify the primary fax number for the organization. |
Fax 2 |
Specify the alternate fax number for the organization. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- In the Division Definition section, you can setup the information for the groups within your organization that will have access to the same applications and accounts. Perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Division |
Specify the division ID. The ID is the unique identifier used internally by the system to represent the division within the organization. Note: Once specified, do not edit this field. |
Division Name |
Specify the division name. |
Short Name |
Specify the short name for the division. Note: This ID represents this division throughout the system (required). |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the division. |
Country |
Select the country where the division is located from the drop-down list. |
City |
Specify the city where the division is located. |
State |
Select the state where the division is located from the drop-down list. |
Address Line 1 |
Specify the address line 1 for the division. |
Address Line 2 (unlabeled) |
Specify the address line 2 for the division. |
Zip |
Select the zip code of the location where the division is located from the drop-down list. |
Extn |
Specify the extension of the selected zip code. |
Phone 1 |
Specify the primary phone number for the division. |
Extn 1 |
Specify the extension for the primary phone number. |
Phone 2 |
Specify the alternate phone number for the division. |
Extn 2 |
Specify the extension for the alternate phone number . |
Fax 1 |
Specify the primary fax number for the division. |
Fax 2 |
Specify the alternate fax number for the division. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Organization > Department Definition.
- On the Department Definition section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Department |
Specify the department ID. Note: The ID is the unique identifier used internally by the system to represent the department within the division. |
Department Name |
Specify the department name. |
Short Name |
Specify the short name for the department. Note: This is the ID that appears throughout the system to represent this department. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the department. |
Country |
Select the country where the department is located from the drop-down list. |
City |
Specify the city where the department is located. |
State |
Select the state where the department is located from the drop-down list. |
Address Line 1 |
Specify the address line 1 for the department. |
Address Line 2 |
Specify the address line 2 for the department. |
Zip |
Select the zip code where the department is located from the drop-down list. |
Extn |
Specify the zip extension where the department is located. |
Phone 1 |
Specify the primary phone number for the department. |
Extn 1 |
Specify the phone extension for the primary phone number. |
Phone 2 |
Specify the alternate phone number for the department. |
Extn 2 |
Specify the phone extension for the alternate phone number. |
Fax 1 |
Specify the primary fax number for the department. |
Fax 2 |
Specify the alternate fax number for the department. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Organization > Display Format.
- On the Display Format section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Format Type |
Select the type of format from the drop-down list. |
Format Sub Type |
Select the sub type of the format from the drop-down list. The format sub type will be displayed based on the format type selected. |
Format |
Specify or select the format based on the format type and format sub type selected. For Date and Time Zone format, select the required option from the drop-down list. |
Format Mask |
Specify the format mask. |
Format Filler |
Specify the format filler. |
Special Data |
Specify the special data, if any. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the display format. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.2 Companies
The Companies screen records the hierarchical structure of your portfolio companies and their branches. Just as Oracle Financial Services Lending and Leasing uses the Organization screen to determine the location of people, it uses the information on the Companies screen to determine the location of applications and accounts. In completing the Companies screen, there can be more than one company, and each company can have more than one branch.
Accounting is performed at the company level. Accounts and applicationscan be sorted down to the branch level. For this reason, branches are set up to reflect different business practices. You would set up different branches if, for example:
- The General Ledger (GL) differs between branches
- The branches work with different accounts
- There is a difference between branches in terms of the tasks they perform (loan origination, servicing, collections, and so on)
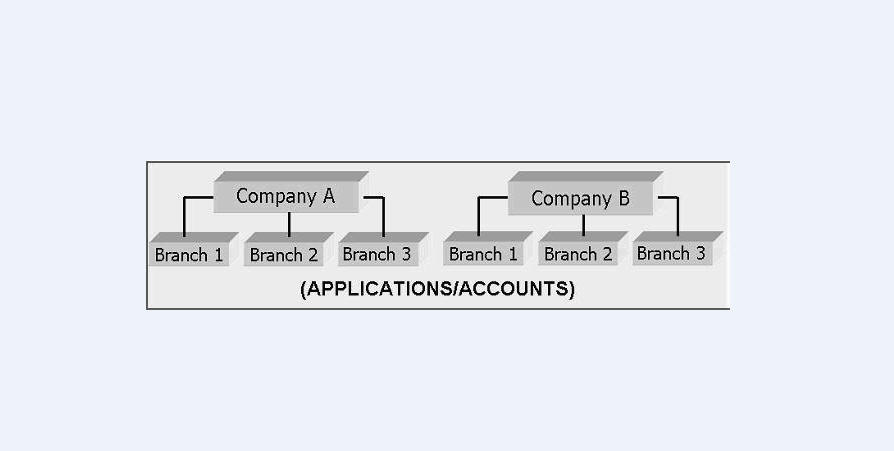
As an example of the companies setup, Oracle Corp. might have the following companies and branches defined as:
Company: C-0001 TrustOne Financial Corp TOFC
Branch: CB-01 TOFC - Headquarters HQ
Branch: CB-02 Kennedy Plaza KP
Company: C-0002 Credtyme Credit Corp CCC
Branch: CB-11 CCC - Headquarters HQ
Branch: CB-12 CCC - Missoula MT
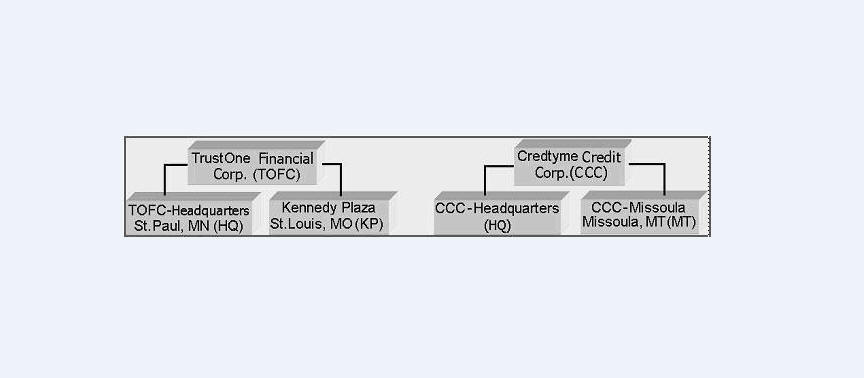
Note
- The system does not limit the number of companies or associated branches with the company you can enter.
- The Short Name field on the Companies screen allows you to create the ID that the system will use while referring to the company and branch.
Key concept: Note the difference between the Company screen and the Organization screen:
- On the Organization screen, Oracle Financial Services Lending and Leasing users belong to an organization and division.
- On the Companies screen, creditapplications and accounts belong to a company and branch.
As you can see in the following Access screen section, the information on the Organization and Companies screens define the operational hierarchy of your companies in terms of which Oracle Financial Services Lending and Leasing users will have access to which applications and accounts.
To setup the Companies
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Companies. The Companies screen defines entities within your organization that originate and/or service Loans.
- In the Company Definition section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
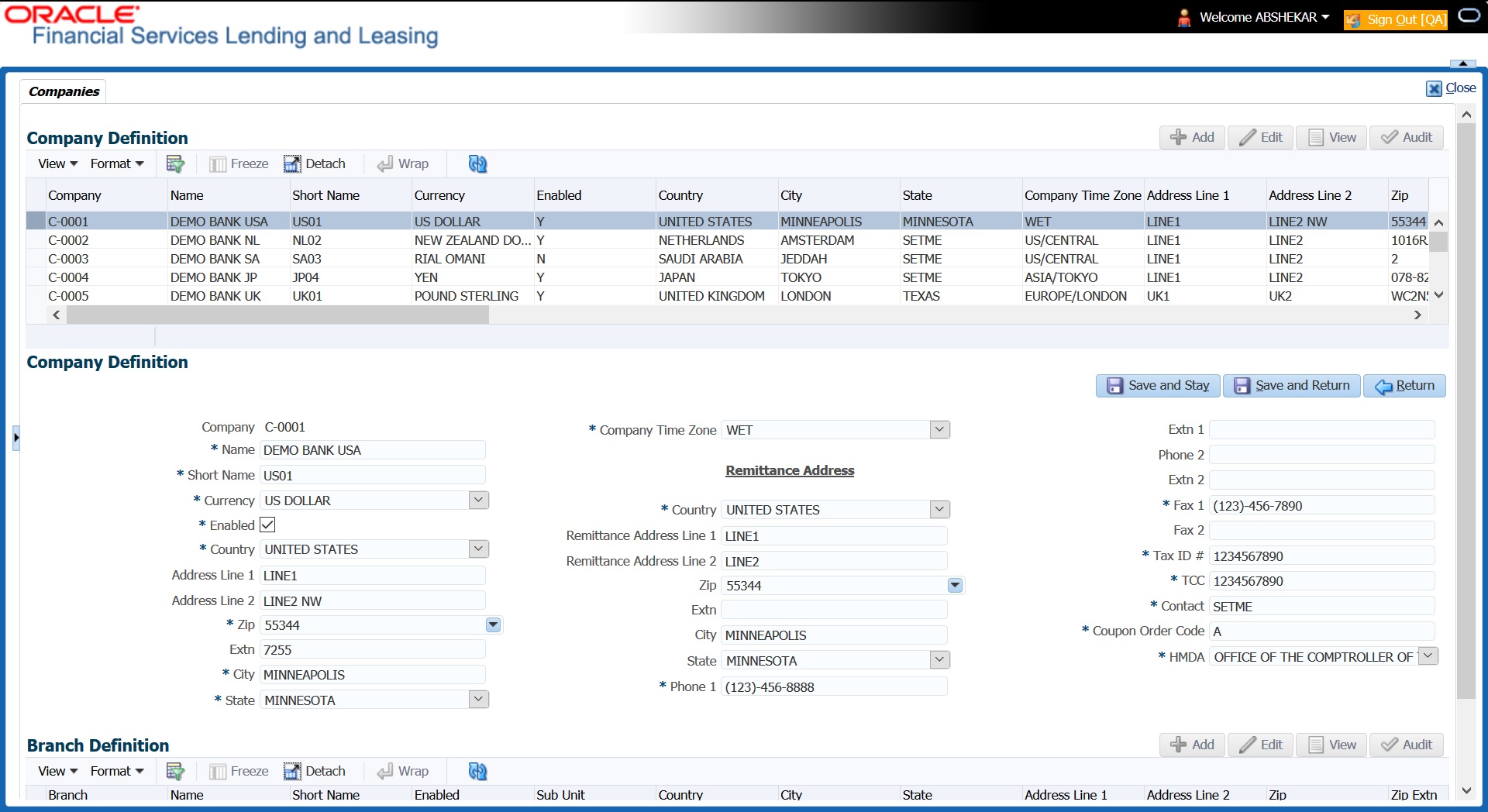
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Company |
Specify the portfolio company ID. (This ID is the unique identifier used internally by the system to represent the company). |
Name |
Specify the name of the portfolio company (required). |
Short Name |
Specify the short name for the portfolio company (ID displayed to represent the company). |
Currency |
Select the currency of the portfolio company from the drop-down list. The system displays the default value as ‘US DOLLAR’. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the portfolio company. |
Country |
Select the country where the portfolio company is located from the drop-down list. The system displays the default value as ‘UNITED STATES’. |
Address Line 1 |
Specify the address line 1 for the portfolio company. |
Address Line 2 |
Specify the address line 2 for the portfolio company. |
Zip |
Select the zip code of the location where the portfolio company is located from the drop-down list. |
Extn |
Specify the extension of the zip code where the portfolio company is located. |
City |
Specify the city where the portfolio company is located. |
State |
Select the state where the portfolio company is located from the drop-down list. |
Company Time Zone |
Select the time zone in which the company operates using the drop-down list. This time zone is considered if system is setup to process GL at Company level. For more information, refer to ‘Appendix - Configuration at Company Level’ chapter. |
Remittance Address section |
|
Country |
Select the remittance address country from the drop-down list. The system displays the default value as ‘UNITED STATES’. |
Remittance Address 1 |
Specify the remittance address line 1, if it is different from the company address. This address is included as the remittance address on statements. |
Remittance Address 2 |
Specify the remittance address line 2. |
Zip |
Select the zip code of the remittance address line 1 from the drop-down list. |
Extn |
Specify the extension of the remittance address zip code. |
City |
Specify the remittance address city. |
State |
Select the remittance address state from the drop-down list. |
Phone 1 |
Specify the primary phone number for the portfolio company. |
Extn 1 |
Specify the phone extension for the primary phone number. |
Phone 2 |
Specify the alternate phone number for the portfolio company. |
Extn 2 |
Specify the phone extension for the alternate phone number. |
Fax 1 |
Specify the primary fax number for the portfolio company. |
Fax 2 |
Specify the alternate fax number for the portfolio company. |
Tax ID # |
Specify the tax identification number for the portfolio company. |
TCC |
Specify the transmitter control code for the portfolio company (1098 Electronic Filing). |
Contact |
Specify the contact information about the portfolio company. |
Coupon Order Code |
If you are using coupons, Specify the coupon order code to be used by a third party printing the coupons for billing statements. |
HMDA |
Select the HMDA agency (Home Mortgage Disclosure Act reporting agency for the company). |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- On the Branch Definition section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Branch |
Specify the portfolio branch ID. (This ID is the unique identifier used internally by the system to represent the branch within your company). |
Name |
Specify the name of the portfolio branch (required). |
Short Name |
Specify the short name for the portfolio branch (ID displayed to represent the branch) (required). |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the portfolio branch. |
Sub Unit |
Select the Sub Unit from the drop-down list. Sub Unit refers the entity which is the source of funds for the credit application/Account. System associates the selected sub unit with the particular company/branch combination and displays by default when the same is selected during an application/Account creation. |
Country |
Select the country from the drop-down list. The system displays the default value as ‘UNITED STATES’. |
City |
Specify the city where the portfolio branch is located. |
State |
Select the state from the drop-down list. |
Address Line 1 |
Specify the address line 1 for the portfolio branch. |
Address Line 2 |
Specify the address line 2 for the portfolio branch. |
Zip |
Select the zip code of the location where the portfolio branch is located. |
Zip Extn |
Specify the extension of the zip code, where the portfolio branch is located. |
Phone 1 |
Specify the primary phone number for the portfolio branch. |
Extn 1 |
Specify the phone extension for the primary phone number. |
Phone 2 |
Specify the alternate phone number for the portfolio branch. |
Extn 2 |
Specify the phone extension for the alternate phone number. |
Fax 1 |
Specify the primary fax number for the portfolio branch. |
Fax 2 |
Specify the alternate fax number for the portfolio branch. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.3 Access
Using the organizations, divisions, companies, and branches created on the Organization and Companies screens, you can control the access privileges of applications and accounts. On the Access screen, you define which organization/division (users) can gain access to which company/branch (applications and accounts) locations.
Normally, for each division within an organization, you would define a record with Company value of ALL and a Branch value of ALL, then select the Allowed box. You then define other records for the same Organization and Division for other Company and Branch combinations with the Allowed box cleared to restrict access.
To setup the Access
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Access. The system displays the Access screen. In this screen, you can control the access privileges of the user for the following categories:
- Data
- Screen
- Reports
- Correspondence
- Transaction
- Webservice
3.3.1 Data
The Data screen allows you to restrict access to different data.
To setup the Data
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Access > Data.
- In the Access Grid section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
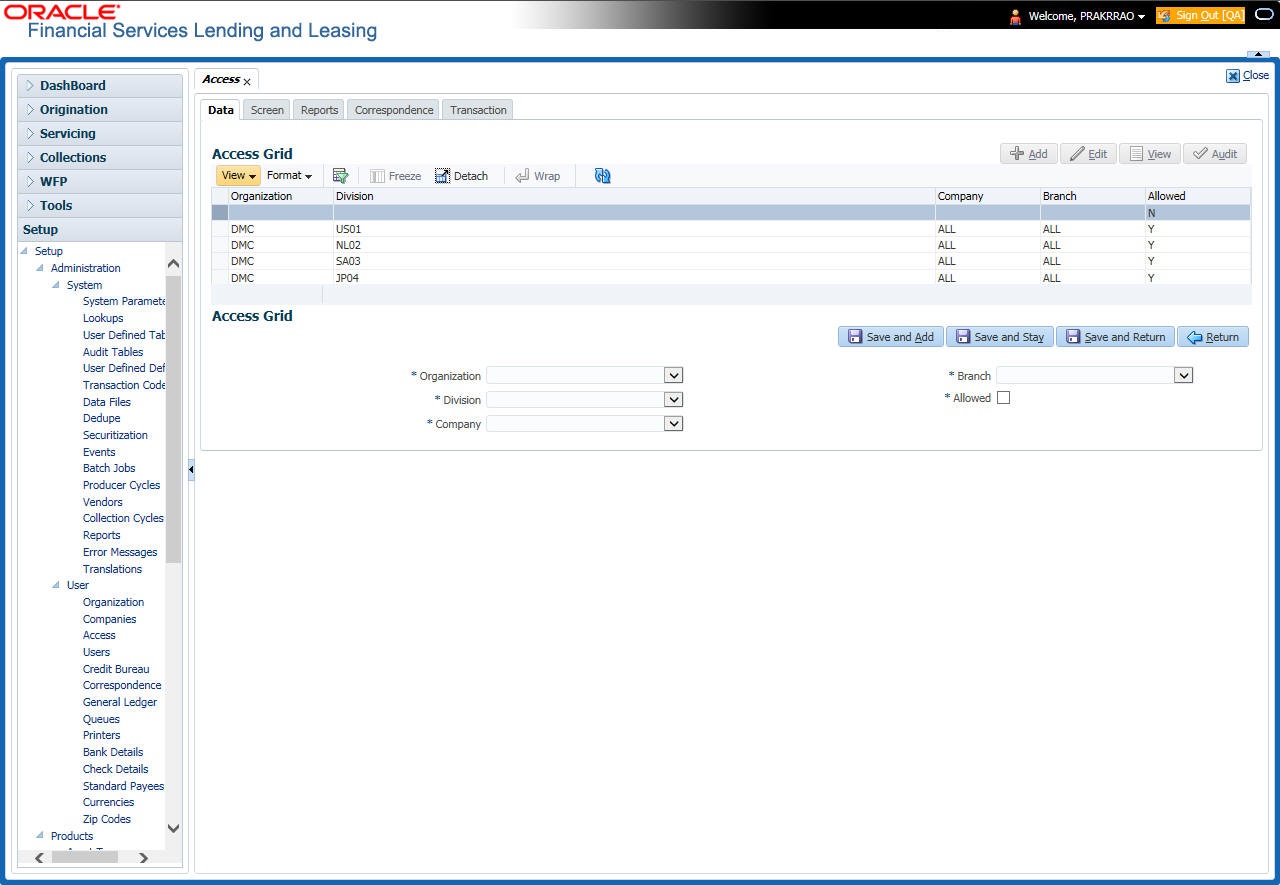
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Organization |
Select the organization for which you are defining access privileges from the drop-down list. |
Division |
Select the division within the organization for which you are defining Access privileges from the drop-down list. |
Company |
Select the portfolio company to which you are defining access privileges for the organization and division specified from the drop-down list. |
Branch |
Select the portfolio branch of the company to which you are defining access privileges for the organization and division specified from the drop-down list. |
Allowed |
Check this box to provide access to the data pertaining to the company and branch, for the organization and division specified. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.3.2 Screen
In the screen, you can control the access to the following:
- Menu – Control access at the application menu level. For example, for Setup menu you can provide access only to an Administrator.
- Screens – Control access to the screens available in the application.
- Buttons – Control access based on the stage.
- Fields - Control access to base and user defined fields.
For example, Add and Edit buttons can be disabled once an application is funded.
If you want to restrict updating the Applicant details, then edit button has to be disabled for the stage.
The screen allows you to restrict access to different screens and fields using the following tabs:
- Security Access Definition
- Field Access Definition
3.3.2.1 Security Access Definition
To set the Screen Security
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Access > Screen.
- In the Security Super Group section, you can view the details of the super group you want to work with.
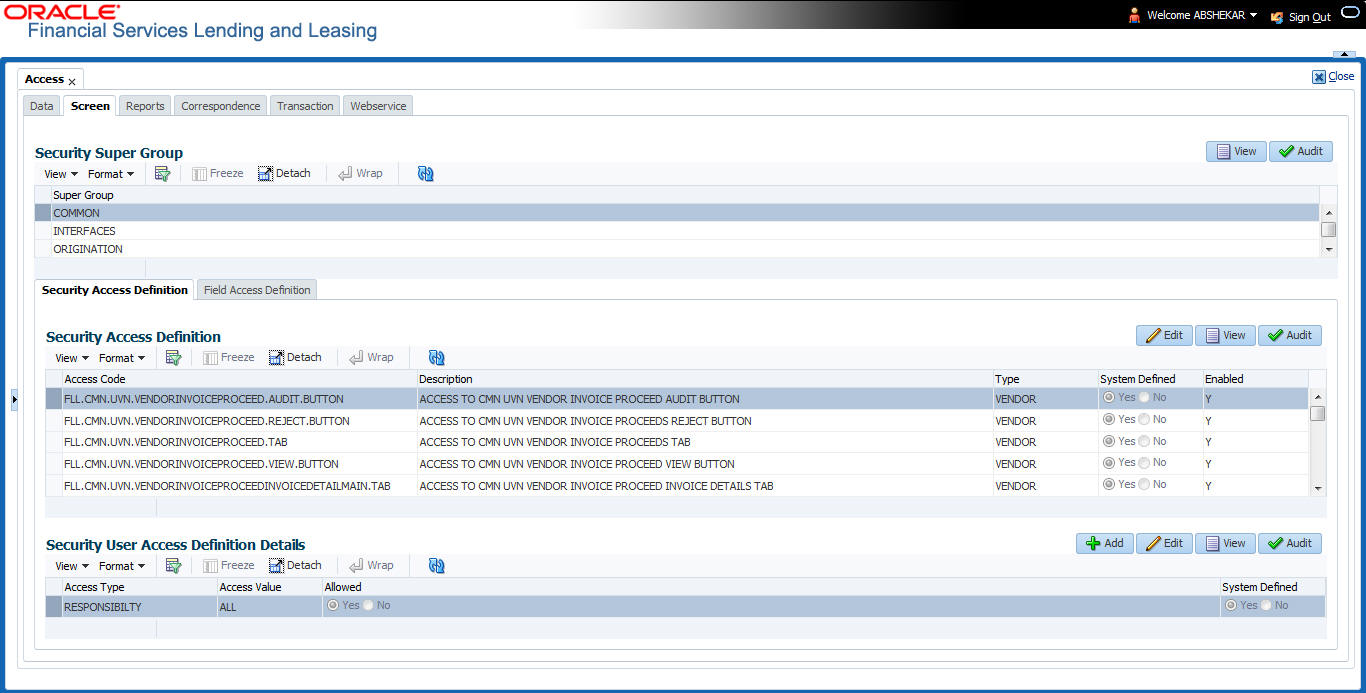
- In the Security Access Definition section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
Note
You can not add a new record
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Access Code |
The system displays the selected access code. |
Description |
Modify the description of the access code. |
Type |
The system displays the type of security access definition. |
System Defined |
If ‘Yes’ is selected, the security access definition entry is system defined. If ‘No’ is selected, the security access definition entry is manually defined. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the security access definition entry is enabled. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- In the Security User Access Details section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Access Type |
Select the access type of the user who will have access to this screen from the drop-down list. |
Active Value |
Select the active value of the user who will have access to this screen from the drop-down list. |
Allowed |
Select ‘Yes’ to allow access to this screen or ‘No’ to deny access to this screen. |
System Defined |
Select ‘Yes’, if the screen user access definition entry is system defined. Select ‘No’, if the screen user access definition entry is manually defined. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.3.2.2 Field Access Definition
The Field Access Definition tab facilitates for field customization in the User Interface (UI) screen. In this tab, you can do the following:
- Enable User Defined Fields (UDFs) to be displayed in respective UI which are provided as part of product installation/upgrade
- Allow or restrict user access to base non-mandatory fields and UDFs maintained in the system
- Regroup base fields to another section in UI
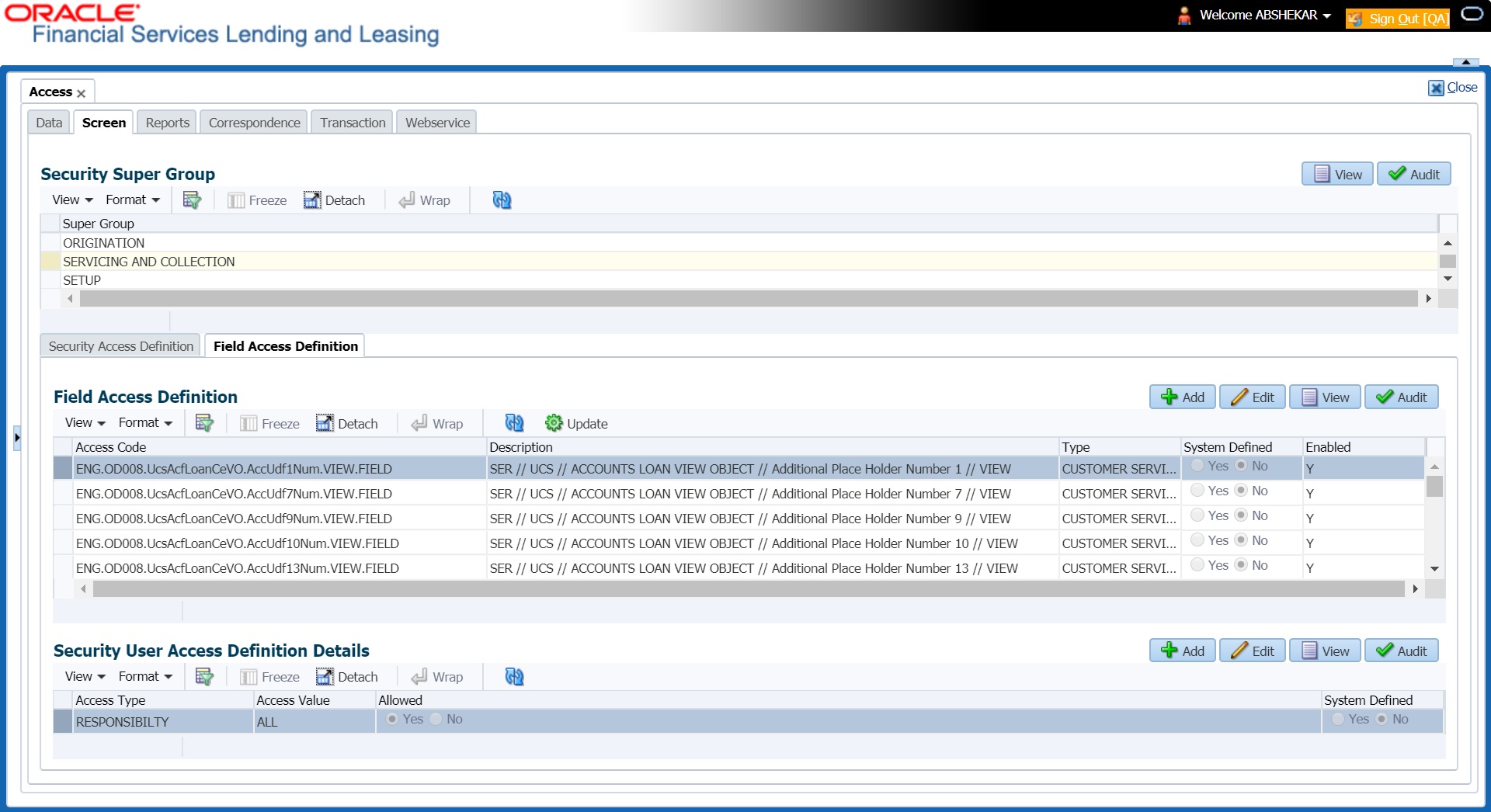
Note the following:
- The Field Access Definition tab displays User defined Fields maintained in the system for which you can specifically define access permissions based on user responsibility.
- The base mandatory fields are loaded automatically and Access Responsibility is set to ALL by default during product installation/upgrade. The same cannot be modified and hence are not displayed in this tab.
- Field access and customizations are to be performed at your sole discretion and OFSLL is not responsible for any impact/damage/mismatch in the data being represented or resulting out of this change.
- Field labels can further be customized in Administration > System > Label Configuration screen.
Before defining field access, refer to the table below which indicates the possible combinations of a particular field being displayed and allowed to edit in UI.
View Type |
Access |
Result |
VIEW |
NO |
NON VIEWABLE |
VIEW |
YES |
VIEWABLE AND EDITABLE |
LOCK |
NO |
READONLY |
LOCK |
YES |
VIEWABLE AND EDITABLE |
To add/enable new User Defined Fields
- In the ‘Field Access Definition’ section, click ‘Add’ and populate the following details:
Field:
Do this:
Language
Select the language of the user(s) who will have access to this field from the drop-down list.
Division
Select the division or group within the organization to which the user belongs from the drop-down list.
Object Name
Select the Object Name from the drop-down list. You can use the search option to query based on specific name. The list is populated based on the combination of Language and Division selected above.
Field Name
Select the field to be updated from the drop-down list. The list is displayed based on the object selected.
Access Type
Select the access type as one of the following from the drop-down list.
View - to display and make the field editable.
Lock - to only display the field.
Note: Option defined here takes precedence with the display (Y/N) option selected in Setup > Administration > System > Label Configuration tab.
System Defined
Select ‘Yes’, if the field access definition is system defined.
Select ‘No’, if the field access definition is manually defined.
Enabled
Check this box to enable the field access definition.
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- Click ‘Update’. System refreshes the cache and automatically updates the Field Access Details from database to display in header section.
After updating the required changes in screen, you need to logout and re-login for changes to be effective. This is basically to refresh session cache and update Field Access information from database server. Though, there is ‘Update’ option, clicking on the same only refreshes the cache and reloads the record.
To enable/disable Base fields
- In the ‘Field Access Definition’ section, click ‘Edit’ and populate the following details::
Field:
Do this:
Access Code
View the access code defined for the field.
Description
View the access code description. You can modify the details if required.
Type
By default, system displays the name of the group inside which the field is displayed in UI. To move the field to a different group, select the required type from the drop-down list.
System Defined
Select ‘Yes’, if the screen field access definition is system defined.
Select ‘No’, if the screen field access definition is manually defined.
Enabled
Check this box to enable the field access definition.
3.3.2.3 Security User Access Definition Details
The ‘Security User Access Definition Details’ sub tab is available only for base - non mandatory fields and user defined fields. In the ‘Security User Access Definition Details’ sub tab you can defined field access and set restrictions to specific user responsibility.
- In the ‘Security User Access Definition Details’ section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Access Type |
Select RESPONSIBILTY as the access type from the drop-down list since access to field is based on responsibility by default. This field is disabled during edit. |
Active Value |
Select the user role who needs to have access to this field from the drop-down list. |
Allowed |
Select ‘Yes’ to allow access to this field or ‘No’ to deny access to this field. |
System Defined |
Select ‘Yes’, if the field user access definition is system defined. Select ‘No’, if the field user access definition is manually defined. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.3.3 Reports
In the Reports screen you can control access to generate certain reports.
To set up Reports
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Access > Reports.
- In the Reports section, you can view the following information:
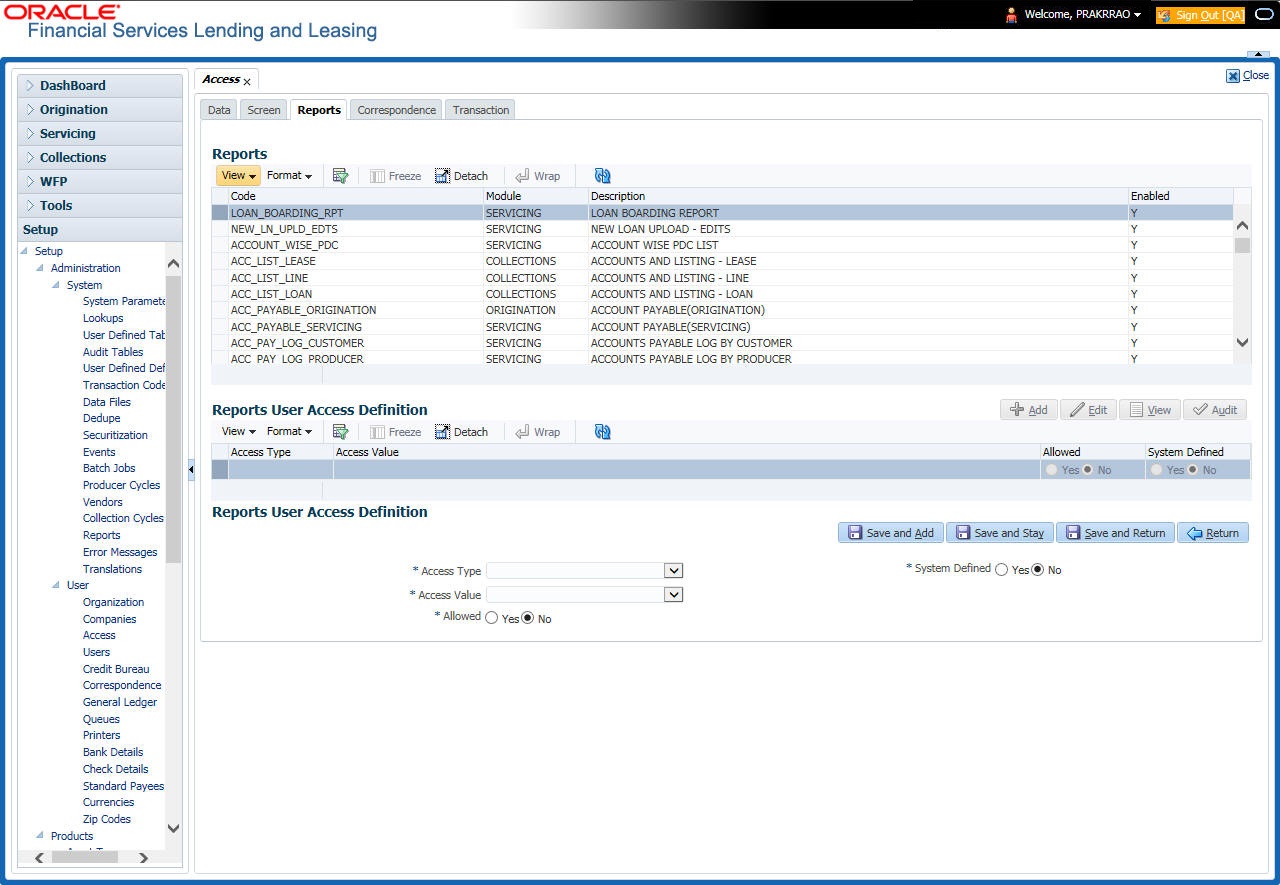
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field |
View this: |
Code |
Displays the code of the report. |
Module |
Displays the code of the report from the drop-down list. |
Description |
Displays the description of the report. |
Enabled |
Displays whether the report definition is enabled or not. |
- In the Reports User Access Definition section, you can set the access rights for the report selected in the Reports section. Perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Access Type |
Select the access grid function type from the drop-down list. |
Access Value |
Select the access function grid value from the drop-down list. |
Allowed |
Select ‘Yes’ to allow access or ‘No’ to restrict access to the entry based on the access type and value. |
System Defined Yes/No |
Select ‘Yes’, if the report user access definition entry is system defined. Select ‘No’, If the report user access definition entry is manually defined. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.3.4 Correspondence
The Correspondence screen allows you to restrict access to different correspondence commands on the Letters menu, thus restricting your ability to generate certain correspondence.
If you do not have the responsibility to create a type of correspondence, the corresponding command on the Letters menu is unavailable (dimmed).
To setup the Correspondence
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Access > Correspondence.
- In the Correspondence Codes section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
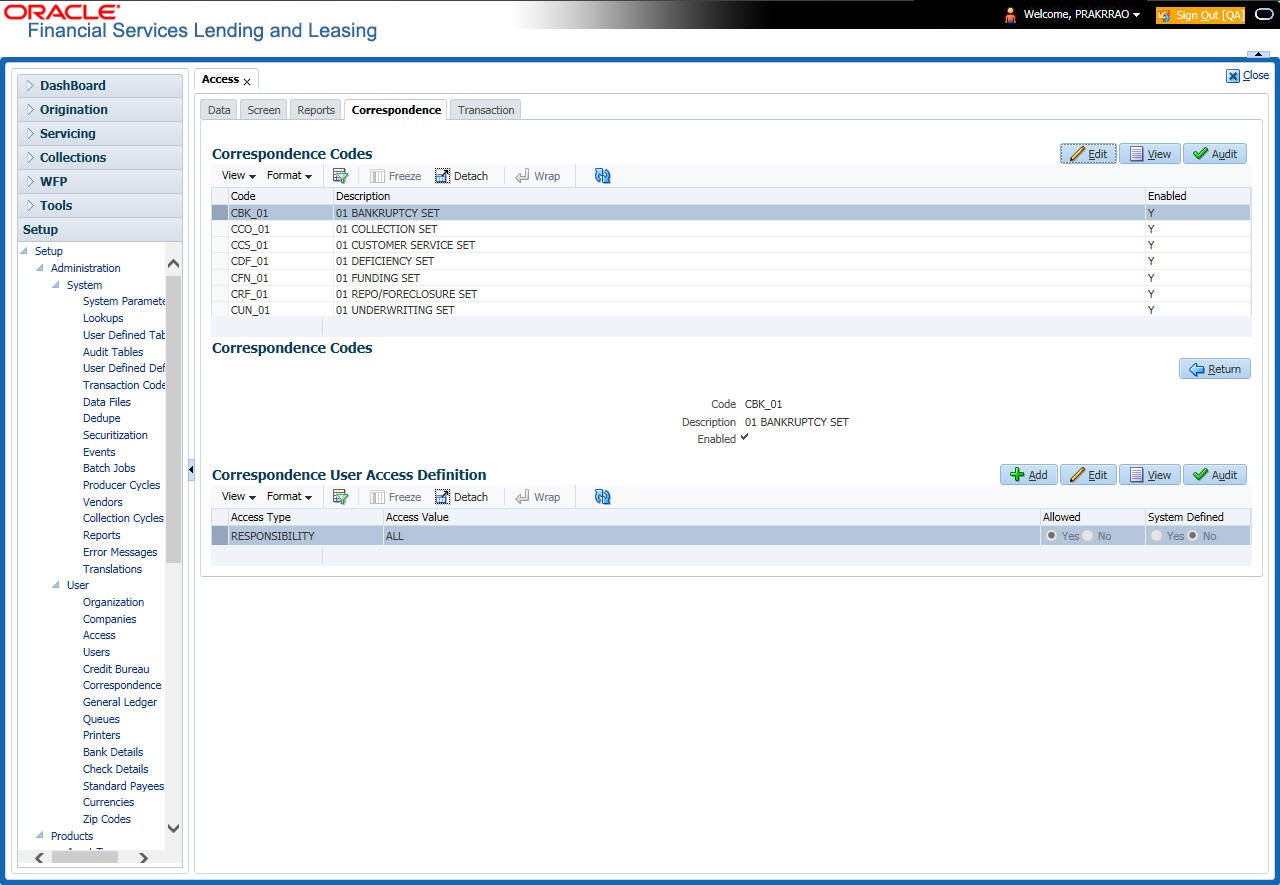
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Code |
The system displays the correspondence code name you want to work with. |
Description |
The system displays the description for the correspondence code (display only). |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the selected correspondence code entry. |
- In the Correspondence User Access Definition section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Access Type |
Select the access grid function type from the drop-down list. |
Access Value |
Select the access function grid value from the drop-down list. |
Allowed |
Select ‘Yes’ to allow access or ‘No’ to restrict access to the entry based on the access type and value. |
System Defined Yes/No |
Select ‘Yes’, if the correspondence user access definition entry is system defined. Select ‘No’, If the correspondence user access definition entry is manually defined. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.3.5 Transaction
The transaction screen allows you to view and restrict access to the following account transactions maintained in the system.
- ACCOUNT MONETARY TXN
- ACCOUNT NON MONETARY TXN
- PRODUCER MONETARY TXN
- ACCOUNT CONDITION TXN
- SECURITIZATION TXN
- ESCROW MONETARY TRANSACTIONS
- ESCROW NON MONETARY TRANSACTIONS
- FEE ASSESSMENTS
- ESCROW ANALYSIS AND DISBURSEMENTS
Along with restricting access, you can also define authorization permissions for monetary transactions. While defining authorization permissions, you can allow transactions to Authorize through assigned Maker/Check responsibilities with/without having specific authorization criteria defined. However, authorization criteria can be defined only for monetary transactions which needs authorization.
To define access/authorization rights for Transaction
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Access > Transaction.
- In the Transaction Super Group section, select the super group you want to work with.

- In the Transaction Codes section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Code |
The system displays the transaction code you want to work with. |
Description |
Specify/Edit the description for the transaction. |
Authorize |
Check this box to enable authorization by another user. Such transactions can be authorized on the Authorization tab of Transaction Authorization screen in Servicing Module. Note: For monetary transactions, system allows you to define both Maker and Checker authorization in the Maker and Checker Responsibility tabs respectively. For non-monetary transactions, you can define maker responsibility for authorization. When the Authorization check box is not selected, any new transactions posted will not go for authorization. For more information, please refer the Transaction Authorization (Maker-Checker) chapter in the Oracle Financial Services Lending and Leasing User Guide. |
Enabled |
Select this box to enable the transaction. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
You can define the authorization restrictions using the following sub tab:
- Maker Responsibility
- Checker Responsibility
- Authorization Criteria
Note
‘Checker Responsibility’ and ‘Authorization Criteria’ tabs are available only for monetary transactions (i.e. Authorize flag set to ‘Y’).
To define Maker Responsibility
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Access > Transaction.
- In the Transaction Super Group section, select the super group you want to work with.
- In the Maker Responsibility section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Access Type |
Select ‘RESPONSIBILITY’ as the access type from the drop-down list. |
Access Value |
Select the user responsibility from the drop-down list. |
Allowed |
Select ‘Yes’ to allow access or ‘No’ to restrict access to the entry in the Transaction Codes section, based on the access type and value. |
System Defined |
Select ‘Yes’, if the transaction user access definition entry is system defined. Select ‘No’, if the transaction user access definition entry is manually defined. |
Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
To define Checker Responsibility
When a particular monetary transaction needs checker authorization you can define the same in ‘Checker Responsibility’ tab and also specify the Authorization Criteria for the transaction.
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Access > Transaction.
- In the Transaction Super Group section, select the super group you want to work with.
- In the Transaction Codes section, select the monetary transaction with the Authorize flag as ‘Y’.
- In the Checker Responsibility section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Access Type |
Select ‘CHECKER RESPONSIBILITY’ as the access type from the drop-down list. |
Access Value |
Select the user responsibility from the drop-down list. |
Allowed |
Select ‘Yes’ to allow access or ‘No’ to restrict access to the entry in the Transaction Codes section, based on the access type and value. |
System Defined |
Select ‘Yes’, if the transaction user access definition entry is system defined. Select ‘No’, if the transaction user access definition entry is manually defined. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
To define Authorization Criteria
You can define conditional authorization by creating a sql statement based on required criteria. For example, you can define a condition to allow transaction authorization in an account for amount greater than 500.
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Access > Transaction.
- In the Transaction Super Group section, select the super group you want to work with.
- In the Transaction Codes section, select the monetary transaction with the Authorize flag as ‘Y’.
- In the Authorization Criteria section, you can add/edit the following details in the ‘Criteria Name’ and ‘Criteria Details’ section.
- In the Criteria Name section perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Name |
Specify a name for the criteria. |
Description |
Specify a description for the criteria. |
Authorization Level |
Specify the level of authorization responsibility in numeric value. Note: You will need to specify the same value as defined for each user within ‘Checker Responsibility’ Lookup Type (CHECKER_RESPONSIBILITY_CD) in Setup > Administration > System > Lookups screen. |
Enabled |
Select this box to enable the criteria. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- In the Criteria Details section perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
Note
Although system allows to define customized selection criteria, the execution of additional selection criteria requires additional processing at server level and can have significant performance impact delaying the EOD processing/web services. Hence it is recommended to have careful consideration while defining the additional selection criteria (like using user-defined tables and columns) and/or get approval from your database administrator before using any selection criteria.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Seq |
Specify a sequence number. |
( |
Specify the open/entry criteria. |
Parameter |
Select the transaction parameter from the drop-down list. The list displays transaction parameters for the selected transaction and the parameters in user defined table ‘INP_BMP_ACC’. |
Comparison Operator |
Select the comparison operator from the drop-down list. |
Criteria Value |
Specify the required criteria value for validation. |
) |
Specify the close/exit criteria. |
Logical Expression |
Select the logical operator from drop-down list. |
Enabled |
Select this box to enable the criteria. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- Click Check Criteria to validate the correctness of the statement and to resolve errors, if any.
You can add multiple checker responsibility and define multiple selection criteria for each checker responsibility.
3.3.6 Webservice
The Webservice screen in Access setup allows you to configure access to the available RESTful webservices in the system. The associated seed data for all the RESTful webservices are loaded during product installation and process of installing the same is detailed in the Installation guide.
As an administrator/superuser, you can Enable/Disable Web Service access to users based on their responsibility and ensure that only authorized user have access to specific type of data in the system. Following list indicates some of the available RESTful webservices in the system and the complete list is made available in swagger JSON file shared in OTN library:
- Generic Post Transaction Service
- Call Activity Service
- Scheduler Service
- Account Search Service
- Account Boarding Service
- Payment Posting Service
- Account Detail Service
- Calculator Service
- Application Search Service
- Get Scenario Analysis Service
- Post Scenario Analysis Service
- Lookup Service
- Dialer Integration Service
- Application GET Service
- Application Entry service
- Application Update Service
- Application Status Change
- Application Checklist
- Application ACH GET Service
- Application ACH POST Service
- Application Comment GET Service
- Application Comment POST Service
- Application Document GET Service
- Application Document POST Service
- Account Comment GET Service
- Account Comment POST Service
- Account Document GET Service
- Account Document POST Service
- Process File Upload Service
- Process File Download Service
- Process File List Service
- Product Service
- Asset Service
- Asset Sub-Type Service
- Scheduler Force ReSubmit
- Remarketing GET Service
- Remarketing POST Service
- Invoice GET Service
- Invoice POST Service
To setup the Webservice access
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Access > Webservice. The screen consists of the following tabs:
- Security Super Group
- Security Access Definition
- Security User Access Definition Details
- Security Access Definition Details (This sub tab is available only for ‘SERVICING AND COLLECTION’ Super Group.
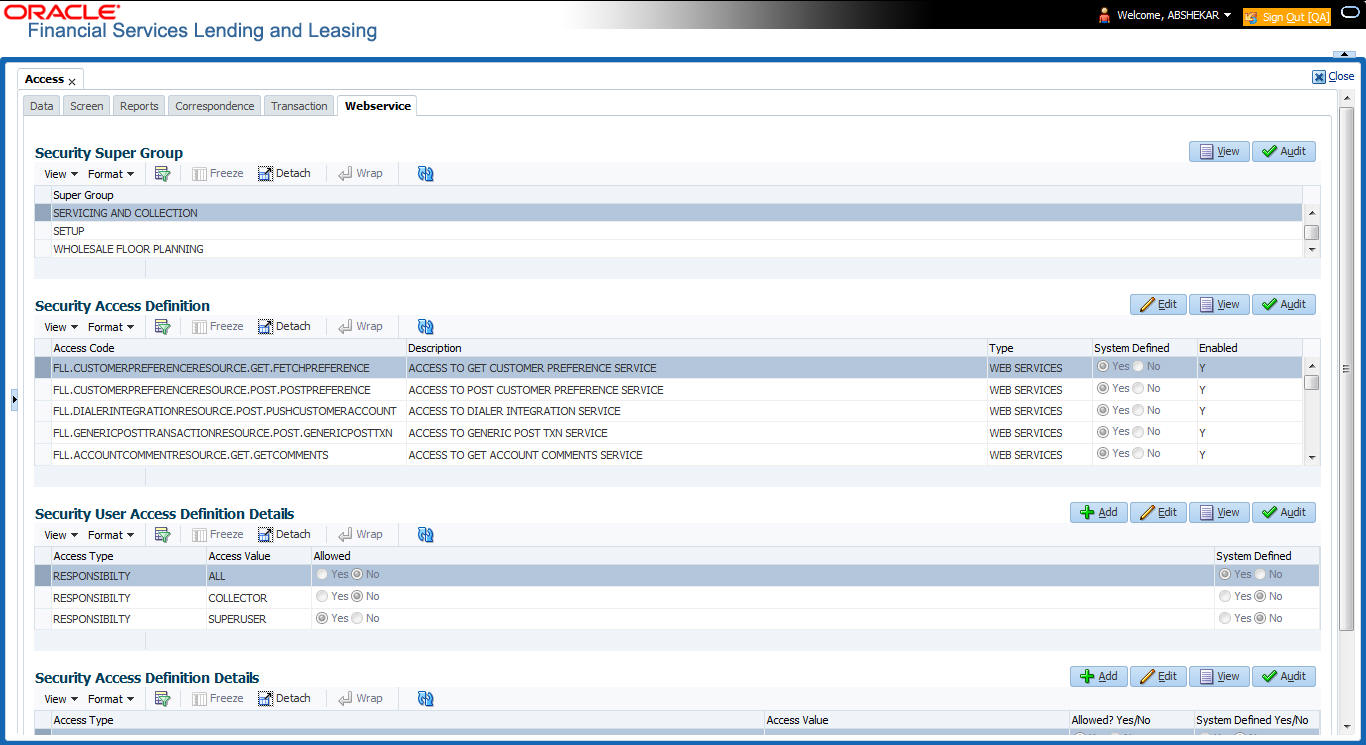
- The ‘Security Super Group’ section, contains the following super group categories for selection:
- COMMOM
- INTERFACES
- ORIGINATION
- SERVICING and COLLECTIONS
- SETUP
- WHOLESALE FLOOR PLANNING
- Select the required Super Group and the associated data in sub tabs are categorized accordingly.
- In the ‘Security Access Definition’ section, you can view the following field details and edit only the ‘Description’ and ‘Enabled’ status of selected Security Access Definition.
Field:
Do this:
Access Code
The system displays the webservice access code.
Description
The system displays the description of the associated webservice access code and can be edited for required changes.
Type
The system displays the type of security access definition.
System Defined
If selected as ‘Yes’, the security access definition entry is system defined. If selected as ‘No’, the security access definition entry is manually defined.
Enabled
Check this box to enable the selected webservice access code.
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- In the Security User Access Details section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields are given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Access Type |
Select ‘Responsibility’ (default) as the access type from the drop-down list. For this access type to be available in the drop-down list, ensure that the Lookup Type ‘ACCESS_GRID_TYPE_CD’ is maintained in the system. |
Access Value |
This field is ‘Read-only’ for ‘System Defined’ Security Access Definitions which are loaded as part of seed data during installation. For non-system defined Security Access Definitions, select the access value which is the user responsibility who needs to have access to this webservice from the drop-down list. For user responsibilities to be populated in the drop-down list, ensure that the Lookup Type ‘RESPONSIBILITY_CD’ is maintained in the system. |
Allowed |
Select ‘Yes’ to allow user access to this webservice or ‘No’ to deny access. By default, No’ is selected. |
System Defined |
Select ‘Yes’, if the webservice user access definition entry is system defined. Select ‘No’, if the webservice user access definition entry is manually defined. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
Security Access Definition Details
If you have selected the Security Super Group as ‘SERVICING and COLLECTIONS’, there is an additional sub section ‘Security Access Definition Details’ enabled. This sub tab facilitates you to further restrict and control access to specific type of data within the accessible RESTful web services. The restriction can be defined based on specific ‘Account Condition’ or ‘Account Status’.
For example, out of all the account types maintained in the system you can restrict data access to only delinquent account(s) to a particular user responsibility by selecting Access Type as ‘Account Condition’ and Access Value as ‘Delinquent’,
Controlling web service data access to permitted user(s)
For any user to access web service data, you need to define atleast one positive (allowed) definition defined in 'Security Access Definition Details' section. Else, webserivce data is not displayed for that particular user even if that user responsibility has permissions to access web service.
OFSLL supports multiple user conditions on an Account and system requires to have atleast one account condition defined as ‘Allowed’ in setup to display the data. In case, even if any one of the account condition is defined as ‘Not Allowed’ in setup, then system does not allow to access the data.
During the following scenarios, data is either displayed/not displayed in Webservice screen:
Scenario |
Data displayed |
No condition is available on the account and also no condition defined in setup |
Data is displayed since there is no restriction. |
Condition is available on the account but not defined in setup |
Data is not displayed since restriction is applied |
Multiple conditions are available on the account and one condition is defined in setup as ‘Allowed’ |
Data is displayed |
Multiple conditions are available on the account and one condition is defined in setup as ‘Not Allowed’ |
Data is not displayed |
Whenever user with specific responsibility tries to access the restricted data, following type of error messages are displayed:
- For POST/PUT service, system displays error as ‘Access denied’ with HTTP Error Code 401.
- For GET service with single account record, system displays error message as ‘No data found’ with http error code 400.
- For GET service with multiple account records, of which some have access restriction and other don’t, then system displays only the unrestricted records and does not display the restricted records. In such a case, error message is not displayed.
Note
When multiple user access definitions are defined in the system, while processing the data access request to a web service OFSLL first validates for any access restrictions on the user responsibility. If not, then validates the same against 'ALL' responsibility before displaying the data in Webservice screen.
For example, if data access restriction is defined for ALL and SUPERUSER responsibilities. when logged in with SUPERUSER responsibility, the data restriction of SUPERUSER is applied. In case, if the user logs in with any other responsibility other than SUPERUSER, then restriction defined for ‘ALL’ is applied.
To define Security Access Definition Details
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Access > Webservice tab.
- Select the module in Security Super section as ‘SERVICING and COLLECTIONS’.
- Select the user responsibility in ‘Security User Access Definition Details’ section.
- In the Security Access Definition Details section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields are given below:
Field |
Do this: |
Access Type |
Select the access function type (as either ACCOUNT CONDITION or ACCOUNT STATUS) that is being used to control the user access from the drop-down list. |
Access Value |
Select the access value from the drop-down list. The list is sorted based on the Access Type selected. Also, based on a lookup associated with the Access Type multiple entries for each access type can be created as long as each has a different access value. |
Allowed? Yes/No |
Select ‘Yes’ if the access is allowed and ‘No’ if the access is not allowed. This indicates whether the selected combination of Access Type and Access Value is allowed to access the data. |
System Defined Yes/No |
Select ‘Yes’, if you wish to maintain access type as system defined and ‘No’, if you do not want to maintain it as system defined. However, system defined entries cannot be modified. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.4 Users
The Users screen allows you to create and set up an user. In the User Definition section, you can assign a user an identification name and password to log on to the system. You can also assign the organization, division, and department where each user is located. Additional fields allow you to record information for contacting the user. You can also define the time frame within which a user has access to the system to ensure compliance to the company’s schedule. This is a very useful feature to prevent logins during scheduled maintenance.
The Responsibility field records the job function of the user and defines the level of access that user has within the system; in particular:
- What menu items does the user have access to?
- What transactions can the user perform on the Maintenance screen on the Customer Service screen?
- What edits can the user perform on the Verification link during origination?
Note
The system’s SUPERUSER responsibility grants access to the entire system. Give careful consideration to the number and type of users who receive this responsibility.
To set up the Users screen
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Users. The system displays the Users screen.
- In the User Definition section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
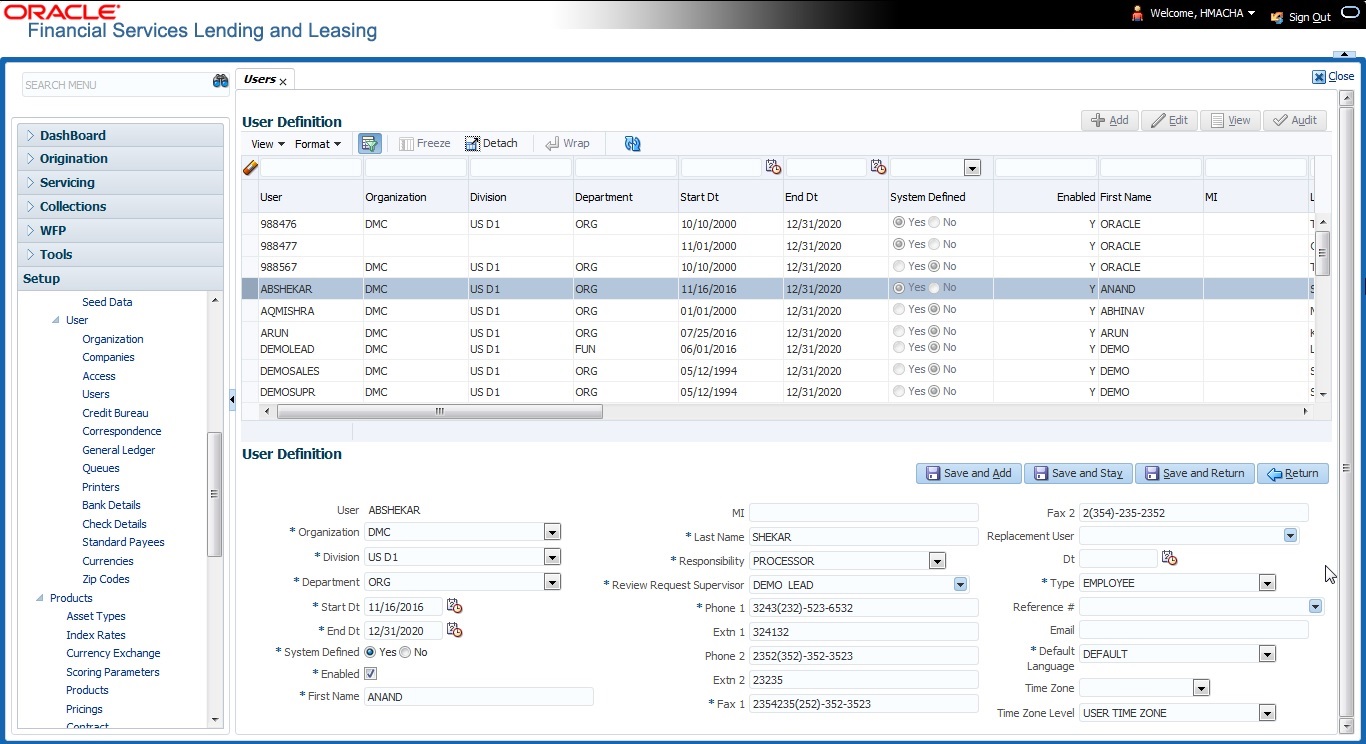
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
User |
Specify the user ID. Note: This field is a unique indicator and cannot be updated, edited, or deleted once saved. |
Organization |
Select the organization to which the user belongs, from the drop-down list. |
Division |
Select the division to which the user belongs, from the drop-down list. |
Department |
Select the department to which the user belongs, from the drop-down list. |
Start Dt |
Specify the start date for the user. You can also select from the adjoining calender icon. |
End Dt |
Specify the end date for the user. You can also select from the adjoining calender icon. |
System Defined |
Select ‘Yes’, if the entry is system defined. System defined entries cannot be modified. Select ‘No’, if the entry is not system defined and it can be modified. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the user. |
First Name |
Specify the first name of the user. |
MI |
Specify the middle initial of the user. |
Last Name |
Specify the last name of the user. |
Responsibility |
Select the responsibility for the user from the drop-down list. Note: The users mapped to the role ‘Responsibility’ can only view the screens. |
Review Request Supervisor |
Select the supervisor responsibility who can also review and respond to review requests from the drop-down list. The list displays the corresponding Review Request Supervisors who are either one or more levels higher from the above selected user ‘Responsibility’ as maintained in ‘RESPONSIBILITY_CD’ lookup code. |
Phone 1 |
Specify the user’s primary phone number. |
Extn 1 |
Specify the phone extension for the primary phone number. |
Phone 2 |
Specify the user’s alternate phone number. |
Extn 2 |
Specify the phone extension for the alternate phone number. |
Fax 1 |
Specify the user’s primary fax number. |
Fax 2 |
Specify the user’s alternate fax number. |
Replacement User |
Select the user ID of the replacement user from the drop-down list. |
Dt |
Specify the date from when the replacement is effective. You can also select from the adjoining calender icon. Note: These two fields allow you to create a replacement user for the current user. This is particularly useful when a new employee assumes the duties of a former. By completing the Replacement User and Replacement Dt field, the system recognizes the replacement user as the current user on the effective date. For more information, refer the section, ‘Replacement Users’. |
Type |
Select the user type from the drop-down list. |
Reference # |
Specify the reference number for the user from the drop-down list. |
Specify user’s email address. |
|
Default language |
Select the default language from the drop-down list. |
Time Zone |
Select the required Time Zone from the drop-down list, The specified time zone would be applicable at company level. |
Time Zone Level |
Select the time zone level (Organization, Company or User) that would apply by default, when specific time zone is not specified at Company and User level. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.4.1 Replacement users
By completing the Replacement User and Dt fields on the Users screen, you can replace an existing user with a new user. The system assigns all responsibilities of the original user to the new user as of the date of the replacement.
The Replacement User and Dt fields allow you to designate a replacement for the current user in the User ID field. When you complete the Replacement User and Dt fields, save your entry, and then enable the record, the system replaces the original user. The system changes the End Dt field to the date when the original user was replaced (the same date in the Dt field).
The system assigns the queues of the original user to only those replacement users who have the same user responsibilities (or Super User responsibility) as set in the system.
The system updates the following when replacing users:
- Assigns all applications in the replaced user’s underwriting queue with the status New to the replacement user’s queue.
- Assigns all applications in the replaced user’s funding queue with a status other than Funded to the replacement user’s queue. The system currently stores the collector name in the back end tables, which are updated with the replacement users ID in the case of the replacement of any user.
- Also updates the Producer Management screen with the replacement user in the Underwriter and Collector fields. The system assigns all applications routed to the original user to the replacement user. This also includes any future applications for the replaced user.
- The system automatically updates the Collector ID field in all accounts to the replacement user and routes all accounts assigned to the original user to the replacement user.
Note
The system will not update the replacement user ID for accounts that are closed.
- On the queue setup of Customer Service screen’s Responsibilities sub screen, the record for the original user will be disabled and a new record will be created for the replacement user. If the replacement user already exists in the setup, The system will not create a new record. It updates the user ID and routes all accounts that were assigned to the original user, based on the account condition, to the replacement user.
3.4.2 Application and Oracle Identity Manager Synchronization
Oracle Identity Manager is for user administration. Oracle Financial Services Lending and Leasing has been developed in such a way that it can be implemented with or without Oracle Identity Manager. In case OID has been employed, the user definition is done in OID and then synchronized to the Oracle Financial Services Lending and Leasing Users table using a utility JAR called OID Synchronization JAR. In OID, users are defined across various groups belonging to a realm which is nothing but the directory structure in OID. A user can be configured to belong to multiple groups in a realm. Every time the user tries to login to Oracle Financial Services Lending and Leasing or OBIEE, the system validates the login ID and the password with OID and provides access to those applications.
3.5 Correspondence
The Correspondence screen enables you to setup the system’s correspondence.
The system provides two types of correspondence: predefined and ad hoc. The following chart provides a quick summary of both:

This chapter explains how to setup ad hoc correspondence with the Correspondence form.
The Correspondence screens provide a cost-effective and easy to use method to build custom documents that draw information from the system’s database without additional programming. You can choose what to include in a letter, create a template, and then use this template to produce a letter.
The core of the Correspondence module is the document element -- the information stored in the database merged into the correspondence. The system has document elements defined for commonly used data elements in correspondence, such as account numbers, account balances, customer addresses, telephone numbers, and due dates.
Correspondence consists of a document file with text of your choice and the document elements from the system’s database.
You can create a correspondence set that consists of one or more documents. If a correspondence set consists of more than one document, such as the account details letter and a payment overdue letter, it prints both documents every time the system generates correspondence for a customer.
The Correspondence module creates the following standard ad hoc correspondence:
- Microsoft Word (rtf)
- Adobe Acrobat (pdf/xfdf)
Note
In this document and in the system, the term bankers system is synonymous with Adobe Acrobat.
3.5.1 Correspondence
The Correspondence screen contains the following sub screens:
- System Functions
- Elements
- E-Form Elements
- Documents
- Correspondence
Navigating to Correspondence
- On the Oracle Financial Services Lending and Leasing home screen, click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Correspondence.
3.5.1.1 System Functions
The System Functions screen enables you to view the predefined functions for the appropriate Loan product in the system. These are attributes from the database.
Functions define how the system retrieves data to include in correspondence. The data is retrieved as elements which are either specific database columns or calculated values. Elements are recorded on the Elements screen.
To view the predefined system functions
- Click Setup > Setup > Correspondence > Loan > System Functions.
- In the Function Definition section, you can view the following information.
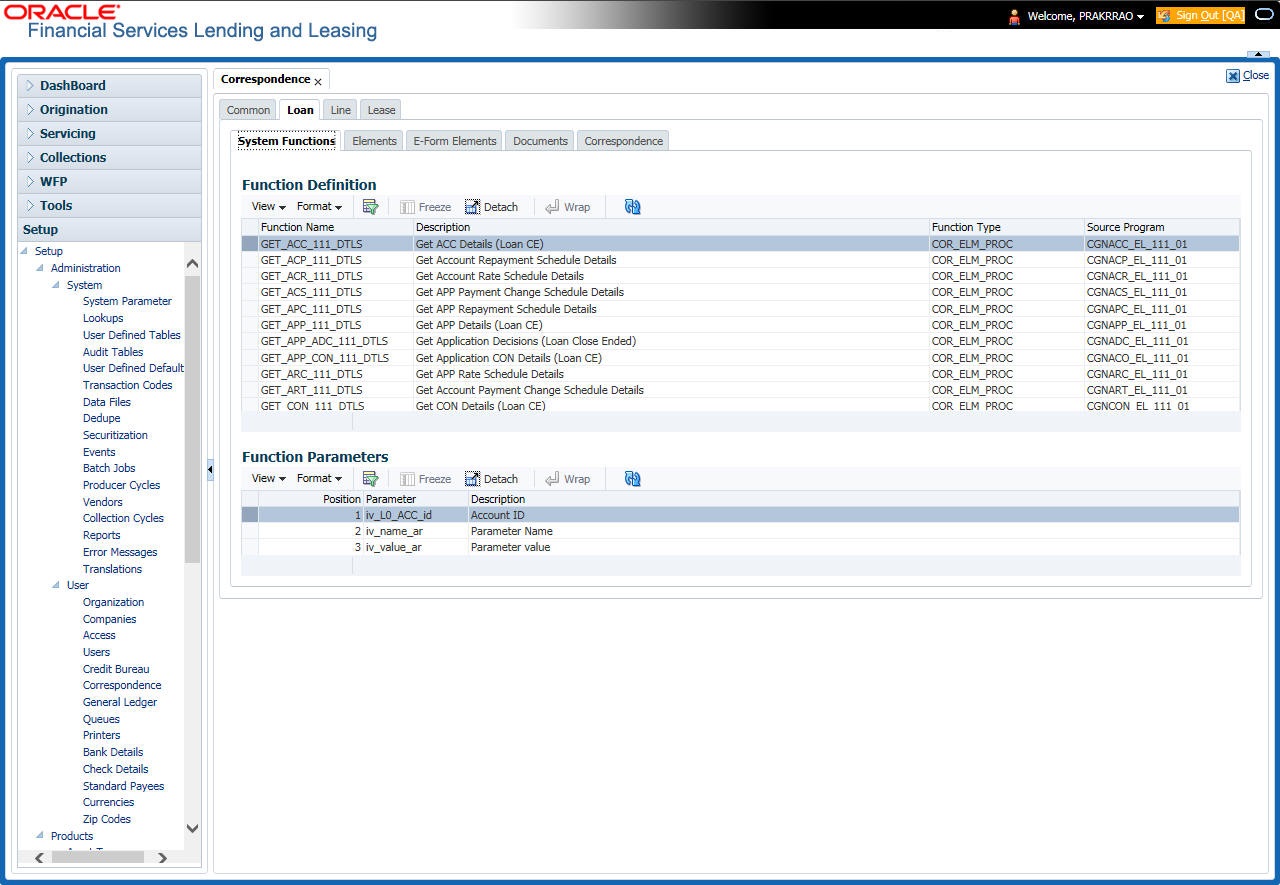
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
View this: |
Function Name |
Displays the function name. |
Description |
Displays the function description. |
Function Type |
Displays the function type. |
Source Program |
Displays the source program. |
- In the Functions Parameters section, you can view the following information.
A brief description of the fields is given below::
Field: |
View this: |
Position |
Displays the parameter position. |
Parameter |
Displays the function parameter. |
Description |
Displays the function parameter description. |
3.5.1.2 Elements
The Elements screen displays the predefined document elements retrieved from the database when the correspondence is generated.
In the Element Definitions section, you can update or edit only the Description field.
To view the Elements
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Correspondence > Loan > Elements
- On the Element Definitions screen, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter. You cannot add a new record.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Level0 Type |
Displays the element Level0 type. |
Element Name |
Displays the element name. |
Element Type |
Displays the element type. |
Description |
Specify the element description. |
Data Type |
Displays the element data type. |
Source Function |
Displays the element function. |
Enabled |
Displays if the element is enabled or not. |
Default Value |
Displays the default value. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.5.1.3 E-Form Elements
The E-forms Elements screen defines elements included when the system generates online correspondence with a browser. The E-forms screen is set up only for PDF elements using the XFDF format. These definitions translate the external element required by the vendor to a systems correspondence element.
For example,
Type |
Details |
Vendor Element |
AllBorrowers.FullNameStreetCityStateZip (Contains names of all borrowers with address of primary customer) |
The system’s Elements |
PRIM_APL_NAME SPOUSE_APL_NAME PRIM_APA_ADDRESS1 PRIM_APA_ADDRESS2 PRIM_APA_ADDRESS3 |
Translation: |
PRIM_APL_NAME || ', ' || SPOUSE_APL_NAME || ', ' || PRIM_APA_ADDRESS1 || '; ' ||PRIM_APA_ADDRESS2 || '; ' || PRIM_APA_ADDRESS3 |
To setup the E-forms Elements
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Correspondence > Loan > E-Form Elements
- In the E-form Elements Definitions section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Level0 Type |
Select the element Level0 type from the drop-down list. |
Source Code |
Select the element e-form source code from the drop-down list. |
Element Name |
Specify the element name (the name used in the external form). |
Description |
Specify the element description. |
Data Type Code |
Select the element data type code from the drop-down list. |
Translation |
Select the translation for the e-form element (SQL statement fragment defining the element data), from the drop-down list. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the e-form element. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.5.1.4 Documents
The Documents screen enables you to set up the various documents and the data fields that the system compiles together when creating a correspondence. The system provides two different document formats: Word or XFDF: XML-based form.
Note
Oracle Financial Services Software assumes that the user is familiar with Word and the Merge Document command. If the user is creating e-form documents with XFDF, then Oracle Financial Services Software assumes that person is familiar with Adobe forms.
To setup documents to be compiled in correspondence
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Correspondence > Loan > Documents.
- In the Document Definition section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Code |
Specify the document code to define the name for the new document. |
Description |
Specify the document description for the new document. This entry appears in the Correspondence section on the Request screen, when you generate an ad hoc correspondence. |
File Name |
Specify the document file name for the resulting file (Word or XFDF document). Ensure that the name specified here is same as the BIP Template name since system refers to this file name for generating the correspondence. |
Level0 Type |
Select the level0 type from the drop-down list. |
E-form Source |
Select the element e-form source from the drop-down list. |
Product |
Select the document product from the drop-down list. |
Source |
Select the document source type from the drop-down list. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the document definition. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- In the Document Elements section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Seq |
Specify the sequence number to order the document elements. |
Type |
Select element type from the following from the drop-down list. This list provides the following options: System-defined – If you select, the value is supplied by the system and cannot be changed in the Correspondence Request screen. Constant. User Defined Element – If you select, you can choose the value and change it in the Correspondence Request screen. User Defined Constant – If you choose, you can choose the value, but you cannot change it in the Correspondence Request screen. Translated Element – If a document contains an e-form element and you do not select this option, then the value will not be translated. |
Element Name |
Select the element name from the drop-down list. |
Description |
Specify element description. Notes: 1. Check that the element name does not have blank spaces or special characters, such as the forward slash “/” or backward slash “\”. 2. If the element is system-defined, then the system will automatically complete this field. |
Data Type |
Select the element data type from the drop-down list. |
Format Mask |
Select the element format mask from the drop-down list. |
Default Value |
Specify the element default value. |
Enabled |
Check this box to include the element in the document. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- In the Document Template section, you can set the information about the template which is attached to the correspondence documents. The template thus saved is similar to the template functionality available in MS word. Perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
File Name |
Specify the file name to define the name for the new template. |
Product |
Select the product for which the template is valid, from the drop-down list. |
Customer State |
Select the customer state for which the product is valid, from the drop-down list. |
Producer State |
Select the Producer state for which the product is valid, from the drop-down list. |
App/Acc St |
Select the Applicant/Account state for which the product is valid, from the drop-down list. |
New Template |
Check this box to load the template as a new template. |
Loaded |
Check this box to indicate that the template is loaded. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the template. |
Note
You can define multiple templates for each document and the template file name (BIP template) is picked based on following criteria – Product and Producer / Account / Customer State.
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
The Document Elements sub screen records the system’s application or account information that appears in the ad hoc correspondence
To generate a data file for a document
- In the Document Definition section of Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Correspondence > Loan > Documents, select the record for which you want to generate a data file.
- Click Gen. Data File button.
The system displays a new screen with the following options:
- Open with – Select to view the data file in the format you want. The adjacent drop-down list provides a list of formats compatible with the system. The system downloads the file and displays it.
- Save File – Select to save the data file on your system.
- Check the box Do this automatically for files like this from now on to apply selected properties for the files which are similar to the current one.
3.5.1.5 Correspondence
The Correspondence screen enables you to define who will receive the documents you created on the Document Definition screen by creating correspondence sets. Each document must belong to a set, and a set can have more than one document.
To set up a correspondence set
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Correspondence > Loan > Correspondence. The correspondence setup is classified into two:
- Documents
- Functions
- In the Correspondence section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
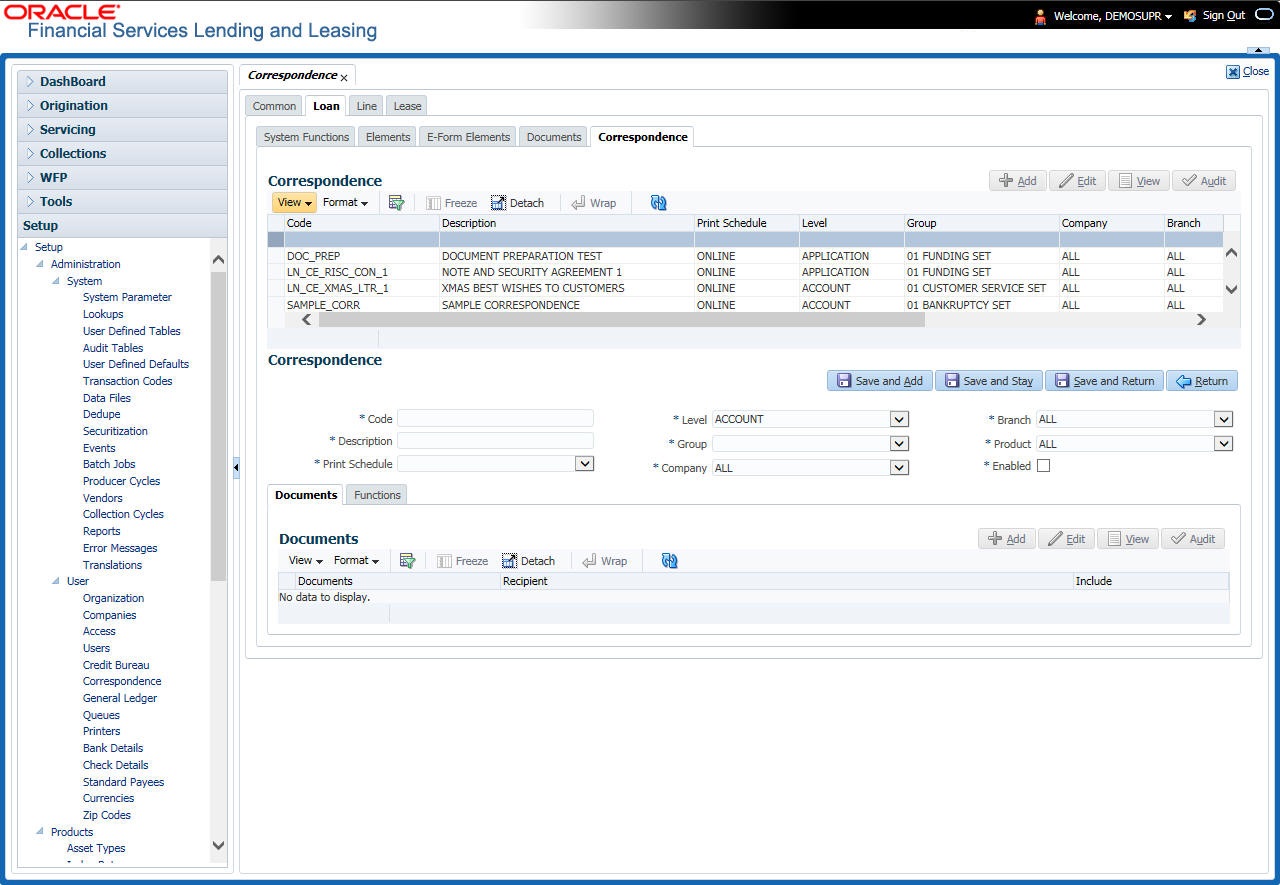
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Code |
Specify the correspondence code. |
Description |
Specify the correspondence description (required). |
Print Schedule |
Select the correspondence output schedule type from the drop-down list. |
Level |
Select the correspondence level type from the drop-down list. |
Group |
Select correspondence group from the drop-down list. |
Company |
Select the correspondence company from the drop-down list. |
Branch |
Select the correspondence branch from the drop-down list. |
Product |
Select the correspondence product from the drop-down list. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the correspondence. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Correspondence > Loan > Correspondence > Documents.
- In the Documents section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Document |
Select the correspondence document from the drop-down list. |
Recipients |
Select the recipients for the document from the drop-down list. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the recipient selected. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- Click Setup > Setup > Correspondence > Loan > Correspondence > Functions.
- In the Functions sub screen, you can define the functions that should be executed before or after correspondence is generated. Perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Function |
Select the correspondence functions from the drop-down list. |
Execute When? |
Select when to execute the correspondence function from the drop-down list. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.5.2 Creating Correspondence
- To create a correspondence add a record in the document definition block. For example: SAMPLE_LOAN_APP
- In the Document Elements section, add the elements required in the correspondence.
- Click on Gen.Data File to generate PDF file of the report.

- Copy and save the content in the pdf file as an xml file. The saved xml file should have the same name as entered in the Code column of Document Definition section. For Example: SAMPLE_LOAN_APP.xml.
- Open MS Word.
Note
Oracle Financial Services Software assumes that BIP Desktop Tool is installed and the user is familiar with the BIP Report Tool.
- In BI Publisher Tab in MS Word, click on Sample XML and import the saved xml file. For Example: SAMPLE_LOAN_APP.xml.
- Create the template by inserting required elements tag.
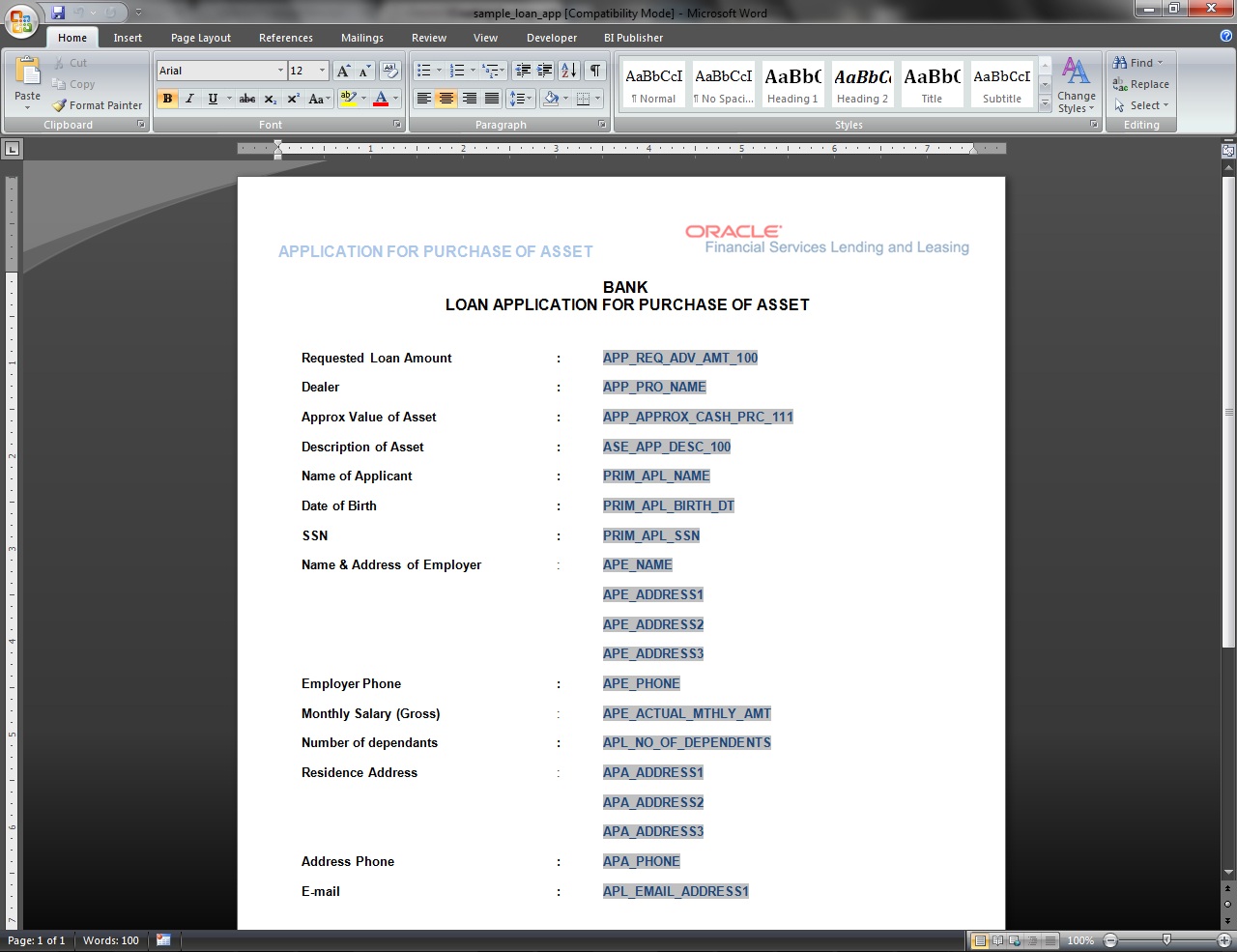
- The template created in MS Word should be saved with .rtf extension. For Example: SAMPLE_LOAN_APP.rtf
Note
The .xml and .rtf file should be saved with the same name as entered in the ‘Code’ column of Document Definition section.
- Upload the rtf template in the BIP and create the data model with SQL query as “select CDO_XML_DOCUMENT from correspondence_docs where cdo_id = :docId”.
- After the data model creation, launch the correspondence screen and click Correspondence tab.
- You can setup a correspondence with the created doc.
3.5.3 Generating Correspondence
- To generate a correspondence open the application for which the correspondence should be generated.
- Click Correspondence tab. In the Correspondence section, click on Add.
- Select the created Correspondence. Click Save and Add to save and add a new record. Click to Save and Return save and return to main screen. Click Return to return to main screen without modifications.
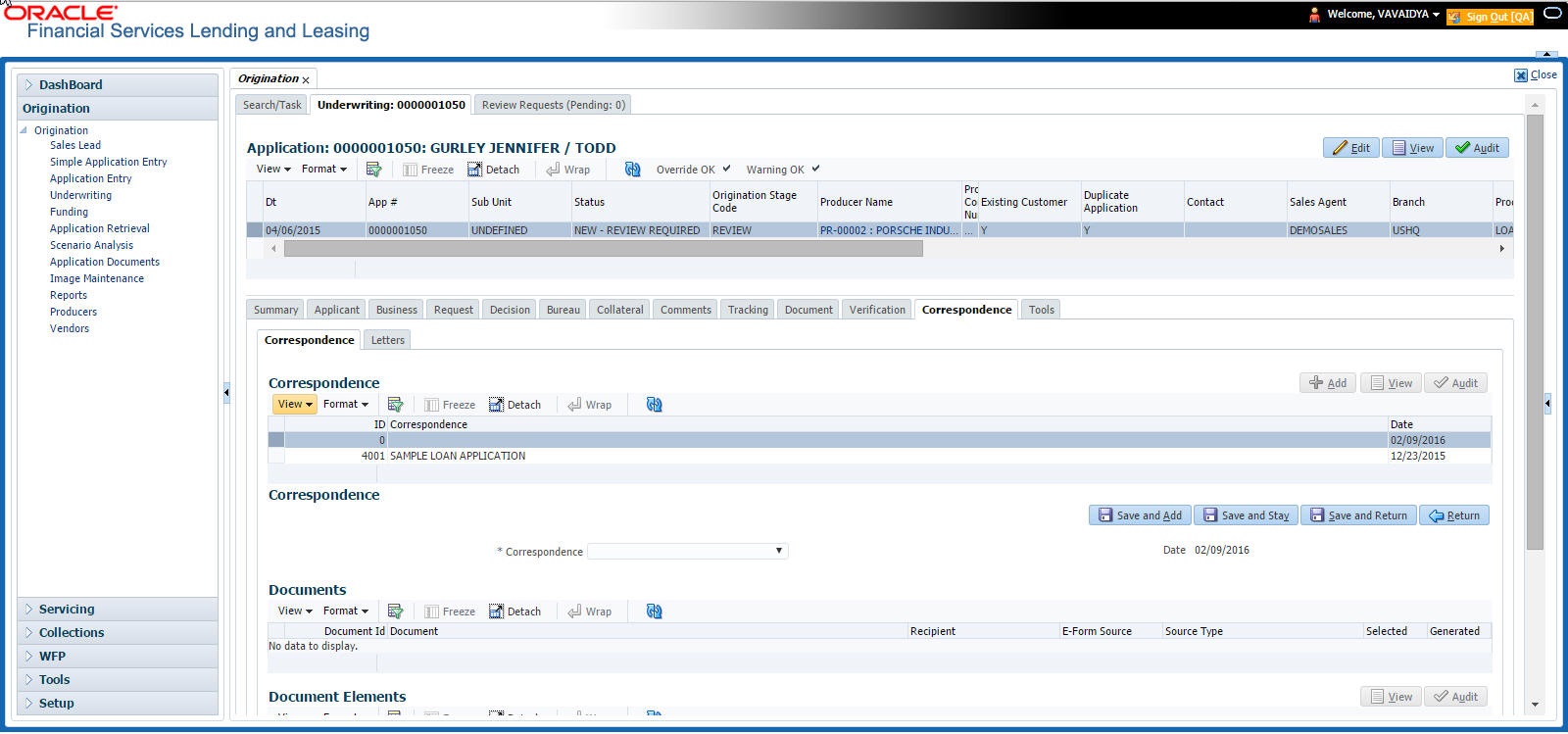
- Click Generate to generate the selected correspondence and View Correspondence to view the Correspondence in PDF format.

3.6 General Ledger
The application’s General Ledger Setup screen can generate and transfer transactions to the accounting software your company uses. It is the interface that transfers all financial transactions to the accounting system. It provides your accounting software with an ASCII data file containing the GL (general ledger) entries for the process date.
This chapter explains the General Ledger form - the system interface that enables you to:
- Map system transactions to your GL transactions.
- Define the requirements for header and derived segments
The system supports the bulk uploading of general ledger setup data. This enables you to upload multiple setup data, avoid reentering setup data, and more importantly, reduce data entry mistakes. The system currently supports uploading using a fixed-length format only, where each data is at a pre-fixed position only. You can run batch jobs with the Set Code SET-BLK to upload pricing and GL data.
Accounting Company Definition
The “accounting company” is the entity for which the financial statements are prepared for legal reporting. You must define your accounting company when implementing Oracle Financial Services Lending and Leasing GL Interface. The accounting company is based upon the portfolio company set up in the system. For example, if there are two companies set up within one organization, the two portfolio companies will be used as accounting companies. Each of these companies will have its own GL set up.
3.6.1 General Ledger
In Setup > Setup > Administration > User > General Ledger > General Ledger, you can setup data that needs to be setup in the system to export transactions to the user’s general ledger application.
The system uses segments to create the complete GL account to which the amount is to be posted. The defined segments are linked together to create the GL account. One of the segments is bound to be the natural account. The other segments could be direct values (like the natural account) or derived values. The segment is grouped into four categories:
- Translation Definition
- Attribute Definitions
- Transaction Definition
- Transaction Links
Navigating to General Ledger
- On the Oracle Financial Services Lending and Leasing home screen, click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > General Ledger > General Ledger.
- In the Company section of the General Ledger screen, select the portfolio company you want to work with.
3.6.1.1 Translation Definition
GL segment values are defined on the Translation Definition.
To setup the Translation Definition
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > General Ledger > General Ledger > Translation Definition.
- In the Segment Definitions section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.

A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Segment # |
Select the segment number. the system can support up to 10 segments, from the drop-down list. Valid values range from 01 to 10. |
Source |
Specify the Source to record a “direct value” or “translated value”. Direct Value: In case the segment value is not a derived value (more on derived segments later), the Source field contains the same value as the “Translated Value” field. This would contain a list of all the valid values for each segment (for example, GL account number). Translated Value: In case the segment value is a derived value, the Source field is used to store the value of the condition string that will be applicable for the particular segment. For example, if the value 02 value in the Segment # field is derived using the branch of the customer as a source criteria, then the entry would read as: Segment #: 02 Source: CB-001 Translated Value: HQ Description: HEADQUARTERS Therefore, for all accounts in branch CB-001 for segment 02, the translated value of HQ will be used in the GL account number (required). |
Translated Value |
Specify the actual segment value. All valid segment values for all segments are defined here. |
Description |
Specify the description of the segment. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.6.1.2 Attribute Definitions
The General Ledger interface uses two types of segments:
- Header segment types
- Detail segment types
The Attributes Definitions screen records the Header and Detail segments. Both are recorded on the Attribute Definitions screen in the Segment Type field.
Note
The Header and Detail segment attributes that you configure should be part of accounts or transactions table as configured in the following views - TXN_ACC_EVW and TXN_TXN_EVW.
Header segment types
The header segment types are the account attributes used as selection criteria to map a transaction to GL segments. The system supports 10 configurable header segments. For each header segment, you can defined specific Account and Transaction attributes which are used as the criteria to categorize the transactions to GL segment. However, note that a header segment must be an account attribute.
By default, the first five header segments (1 to 5) are updated with sample data provided as part of seed data during the base installation / upgrade.
The first five sample segments are:
Segment # |
Attribute Name |
Description |
01 |
ACC_PRODUCT_TYPE_CD |
Product Type |
02 |
TXN_BACKDATE_IND |
Backdated Transaction |
03 |
ACC_PRD_PRODUCT |
Product Code |
04 |
ACC_STATUS_CD |
Account Status |
05 |
ACC_NON_PERFORM_TYPE_CD |
Account Non-performing Indicator |
This means that the system will allow the account attributes listed above to be used as criteria for categorizing the transactions. Here header segment name defined can be either from Accounts/Transactions table (TXN_ACC_EVW/TXN_TXN_EVW). Segment selections depend on the values in the header segment fields. You can define all the 10 header segments.
Detail segment types
Detail segment types allow you to set up components of the GL account number. A GL account number can be composed of multiple segments that are combined to create the composite GL account number. The detail segments can be configured to direct values (like the natural account) or derived values. Natural account here can be a constant value which is not part of any existing Account or Transaction table.
By default, the first four detail segments (1 to 4) are updated with sample data provided as part of seed data during the base installation / upgrade. Following are the sample detail segments provided in the system:
Segment # |
Attribute Name |
Description |
01 |
ACC_CONSTANT_GL_ATTR |
The natural account number in the GL for the transaction |
02 |
ACC_PCB_BRANCH |
Customer Branch |
03 |
ACC_POO_POOL |
Account Pool |
04 |
ACC_SUBUNIT_CD |
Account Sub Unit |
All the 10 available detail segments can be defined. One of the segments can be the “natural account.” (A natural account is an account from the client’s master listing of all general ledger accounts, or “chart of accounts”) The Details segment Attribute name defined can be either from Accounts/Transactions table or a constant value (ACC_CONSTANT_GL_ATTR).
Note
Ensure to have careful consideration while adding a header or detail segment. For any additional programming support, consult Oracle Financial Services Software.
To setup the Attribute Definitions
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > General Ledger > General Ledger > Attribute Definitions.
- In the Attribute Definitions section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Segment Type |
Select the segment type from the drop-down list. |
Segment # |
Select the required segment out of 10 segments from the drop-down list. |
Attribute Name |
Select the attribute name from the drop-down list to indicate the value is to be populated in attributes. The list is populated with only ‘Enabled’ attributes and based on account parameters maintained in User Defined Table GL ATTRIBUTES available in Setup > Administration > System > User Defined Tables screen. The same is configurable and you add/update account parameters. |
Description |
View the attribute description maintained in GL ATTRIBUTES User Defined Table. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.6.1.3 Transaction Definition
The Transaction Definition screen enables you to define GL transactions and to associate the Debit and Credit segments for each GL Transaction.
In GL Transactions sub screen, the Transaction Code column contains GL transactions defined by the client team. The Segments section contains a Debt and Credit section. These are both detail segments.
To setup Transaction Definition
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > General Ledger > General Ledger > Transaction Definition.
- In the GL Transactions section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Transaction Code |
Specify unique GL transaction code. |
Description |
Specify description for the GL transaction. |
Product Type |
Specify the product type. |
Backdated Txn |
Specify the back dated transactions. |
Product |
Specify the product. |
Status |
Specify the status. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the transaction. |
Attribute 5 |
Specify the header attribute 5. |
Attribute 6 |
Specify the header attribute 6. |
Attribute 7 |
Specify the header attribute 7. |
Attribute 8 |
Specify the header attribute 8. |
Attribute 9 |
Specify the header attribute 9. |
Attribute 10 |
Specify the header attribute 10. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- In the Segments section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Sort Seq |
Specify the sort sequence (optional). |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the segment. |
Debit section |
|
Debit ACC # |
Select the segment value from the drop-down list. |
Branch |
Select the segment value from the drop-down list. |
Segment #3 |
Select the segment value from the drop-down list. |
Segment #4 |
Select the segment value from the drop-down list. |
Segment #5 |
Select the segment value from the drop-down list. |
Segment #6 |
Select the segment value from the drop-down list. |
Segment #7 |
Select the segment value from the drop-down list. |
Segment #8 |
Select the segment value from the drop-down list. |
Segment #9 |
Select the segment value from the drop-down list. |
Segment #10 |
Select the segment value from the drop-down list. |
Credit section |
|
Credit ACC # |
Select the segment value from the drop-down list. |
Branch |
Select the segment value from the drop-down list. |
Segment #3 |
Select the segment value from the drop-down list. |
Segment #4 |
Select the segment value from the drop-down list. |
Segment #5 |
Select the segment value from the drop-down list. |
Segment #6 |
Select the segment value from the drop-down list. |
Segment #7 |
Select the segment value from the drop-down list. |
Segment #8 |
Select the segment value from the drop-down list. |
Segment #9 |
Select the segment value from the drop-down list. |
Segment #10 |
Select the segment value from the drop-down list. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
As mentioned in the Attributes Definitions screen section, the system can support up to 10 header segments.
Each transaction can be mapped to one or more GL accounts using the segment mapping section. A segment number can be a natural account or can be a derived segment. In case of a natural account, you need to select the segment value (from the list of predefined segments).
Entering DERIVED in the Segment Number field instructs the system to look for the derived value from the segments defined in the Segments Definition section on the Translation Definition screen.
Let’s take an example:
Company: ABC Bank
Transaction Code: adv
Description: Advance
Product Type: Funding Transaction
Branch: CB-001
Segment #1: 200000
Segment #2: DERIVED
Let’s assume segment #2 is derived from the branch where the account belongs. While calculating the account number, the system interprets segment #2 as follows:
The system will look for a segment value for segment #2 for the account in question using the branch of the account (CB-001). It will use the segment value it finds, say HQ. This will be segment value for segment #2.
IMPORTANT: The derived segment logic can be used for all segments except for the one designated as the natural account segment.
CAUTION: Please note that the logic for calculation of the derived segments is customized for each client. You will need to contact Oracle Financial Services Software inc. in case you want to change the logic or add new derived segments.
“Best Match Feature” for General Ledger (GL) Transactions
The system provides the functionality wherein for each monetary transaction, you can generate entries in the General Ledger (GL) based on the setup. For a single transaction (for example, a late charge), the system allows GL entries to be generated based on different criteria regarding the loan account (for example, product type, product, status, and so on). A late charge entry for one product type can differ from a late charge entry for a different product type.
For example,
Assume you have set up the following four late charge fee GL transactions based on product and status.
GL Transactions section
Transaction Code |
Description |
PRODUCT |
STATUS |
flc_a |
late charge |
loan auto |
|
flc_aa |
late charge |
loan auto |
active |
flc_b |
late charge |
loan atv |
|
flc_bb |
late charge |
loan atv |
active |
For a late fee for an ACTIVE account for a LOAN AUTO, Oracle Financial Services Lending and Leasing will process the GL Transaction FLC_AA. However, if the late fee is for a CHARGED OFF account for a LOAN ATV, Oracle Financial Services Lending and Leasing will process the GL Transaction FLC_B.
3.6.1.4 Transaction Links
The system enables you to map the various transactions to your General Ledger transaction types with the Transaction Links screen. The list of transactions available in the Transaction Code will be derived from the transactions setup on the Transaction Definition screen.
To setup the Transaction Links
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > General Ledger > General Ledger > Transaction Links.
- In the Transaction Links section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below::
Field: |
Do this: |
Transaction Code |
Specify the transaction code. |
Description |
Select the transaction description from the drop-down list. |
GL Transaction Code |
Specify the corresponding GL transaction code. |
Description |
Select the GL transaction description from the drop-down list. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
You can have more than one transaction mapped to a user-defined GL transaction. In that case, the system summarizes all the transactions to the GL transaction. For example, the system uses separate transaction codes for fees, such as LATE_FEE and SERVICING_FEE. If a client site would rather have all fees go into one debt and one credit account, they would define a GL transaction and link all transactions to that defined transaction.
You could also have one transaction linked to more than one GL transaction. The system will use the setup on the header segments to identify the correct GL transaction setup to use.
For example, if the FLC (Late Charge) transaction is mapped to the CHG_LC and CHGR_LC transactions, then the system will look at the header segment definitions to identify the correct GL transaction. Let’s say the header segment used is Account status and that CHG_LC is used for “active” accounts and CHGR_LC is used for “charged off” accounts. In this case, the system will identify the correct GL transaction depending on the account status.
3.7 Queues
When processing an account, various users might work on the accounts to complete different tasks.
The account processing workflow facilitates the movement of the account from one person to another with queues. Queues create a work section of accounts waiting for a particular and common task to be performed. The system’s powerful queuing module automates this otherwise manual process.
In the Queues setup screen, you can setup and manage workflow and work assignments on a daily basis to ensure that the appropriate queues are available for users at all times.
Any time an account’s status is changed, the system checks whether the account is in the right queue.
The system will sort queues based on an account’s status and condition. A condition is the state of an account at a particular time, such as a delinquent, which determines the action a user needs to take.
Queues in the system are distinguished to two types of queues:
- Origination Queues
- Customer Service Queues.
Customer service queues
In the Customer Service screen, queues create a work list of accounts waiting for a particular and common task to be performed, such as collecting on a delinquency. The system’s powerful queuing module automates this otherwise manual process. The Queue Setup form allows you to manage workflow and work assignments and ensure that all accounts are in the queues of the appropriate users at all times.
Customer Service queues distribute and route accounts that require some particular action to be performed to specific users or departments. The system sorts customer service queues based on an account’s status and condition.
Accounts become available for queue assignment when an account receives a condition. Conditions can be applied automatically by the system or manually by users. For example, during nightly processing, the system recognizes an account as delinquent and automatically assigns it a condition of DELQ (“Delinquent”). The users can manually change an account’s condition using combination of Action and Result field entries on the Servicing > Servicing > Customer Service > Customer Service > Customer Service > Call Activities.
These Action and Result field entry combinations are set up on Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Queues > Call Actions Results.
The system associates an account with one or more queues based on multiple parameters, including user-defined criteria and the follow-up date. For example, customer service queues might be configured so accounts are parsed to users according to:
- Due date changes
- Deferment requests
- Title and insurance follow-up dates
Collections queues are included in the Customer Service queue. These queues focus on:
- General collections
- Bankruptcy
- Foreclosure
- Repossession
- Deficiency
Customer Service queues can be built online or in a nightly batch job. Within each queue, the order of the accounts can be sorted based on user-defined criteria.
Note
- Although, the system allows you to define your own selection criteria in creating queues, the system’s performance depends on how the selection criterion is defined. The application highly recommends that you get approval from your database administrator before using any queue selection criteria. Also, avoid using user-defined tables and columns in the selection criteria.
- You can use these same methods for creating and closing queues in the case of repossession, foreclosure and deficiency.
The Call Actions Results screen allows you to define the contents of the Action and Result fields on the Customer Service screen’s Add Call Activities section. The system uses this information to allow users to manually change the condition of an account, and thus assign or remove the account to a queue.
Depending on how you set up call action result codes on the Call Actions screen, conditions and queues are created or closed. You can also restrict the use of certain call activities based on responsibility.
The lookup type ACC_CONDITION_CD defines which account conditions can be created. The application’s queuing engine determines, if queues need to be created based on the information in the Lookups sub screen for this lookup type.
The following table displays the possible combinations of condition and queue.

- Condition: Open, Queue: Open
- In this state, both the account condition and queue are created or opened at the same time.
- The system’s transaction-processing engine automatically creates DELQ, TIP, SCHGOFF conditions and queues; therefore, you need not setup any call action result with these conditions.
- CHGOFF is an account status, so no queues are created. To follow-up on charged-off accounts, create DEFICIENCY condition with this option.
- BKRP (Bankruptcy), REPO (Repossession), FORC (Foreclosure) account conditions and queues can be opened with this option. Also, account level indicators (for reporting purpose) are set.
Note
- An account is moved to the condition, when a Call activity is posted; however, the Queue is moved only when you click Update queue manually or in the EOD batch.
- Accounts are automatically moved based on the system parameter set up.
- Condition: Open, Queue: NA
- In this state, only the account condition is created or opened.
- This option should be used only if queuing is not necessary on this account condition.
- Condition: NA, Queue: Close
- In this state, the queue associated to the account condition is closed.
- This is a bankruptcy condition and delinquency follow-up is not necessary. In such case, DELQ queue can be closed while the condition is still open.
- DELQ, TIP, SCHGOFF queues can be closed by using this option.
- Condition: Close, Queue: Close
- In this state, both the account condition and queue are closed.
- The system’s transaction-processing engine automatically closes DELQ, TIP, SCHGOFF conditions and queues; therefore, don’t setup any call action result with these conditions.
- BKRP (Bankruptcy), REPO (Repossession), FORC (Foreclosure) account conditions and queues can be closed with this option. Also, account level indicators (for reporting purposes) are set.
Note
Condition will be removed from the Summary conditions section.
Navigating to Queues screen
- On the Oracle Financial Services Lending and Leasing home screen, click Setup > Setup > Queues.
- The system displays the Queue Setup screen. You can setup queues related to:
- Customer Service
- Call Action Results
3.7.1 Criteria Based Condition
OFSLL supports various conditions on an Account with the ability for users to open and close required account conditions. A condition can either be posted ‘automatically’ by the system (like updating DELQ delinquency condition on account) or ‘manually’ through a transaction or call activity.
The Criteria Based Condition screen facilitates to automate the manual process of opening or closing conditions on account by defining criteria which helps to categorize specific accounts and post conditions on to those accounts in bulk.
For example,
- You can define specific conditions to Send Letters, Post Transaction and so on if Account Maturity date is less than 90 days from current system date.
- You can post a condition to allow Extension transactions on an account if 50% of financed amount is received.
- When there is a natural calamity, you can post a condition to allow Extension transactions on Accounts belonging to that particular zip code.
However, note that the following conditions are controlled only by the system and cannot be defined to process automatically.
- DELINQUENT
- SCHEDULE FOR CHARGEOFF
- PAYOFF/TERMINATION IN PROGRESS
- NON ACCRUAL
- BANKRUPTCY
- DEFICIENCY
- REPOSSESSION
- FORECLOSURE
In the Criteria Based Condition screen, you can setup Criteria Definitions and define Actions to Open or Close a condition on account. This in-turn is processed during the execution of automated batch job QCCPRC_BJ_100_01 (CRITERIA BASED CONDITION POSTING) in SET-QCS batch job set and while executing the batch job QCCPRC_BJ_100_02 in SET_QRT batch job set.
At account level once the condition is opened/closed, system posts a comment with the Criteria definition details.
3.7.1.1 Criteria Definition
In this section, you can define Criteria definition which can perform specific action on the Accounts.
To Setup Criteria Definition
You can either define new Criteria Definition or specify a new name in the New Criteria field and click Create Copy to create a copy of selected criteria with header and child tab details.
- Click Setup > Administration > User > Queues > Criteria Based Condition tab.
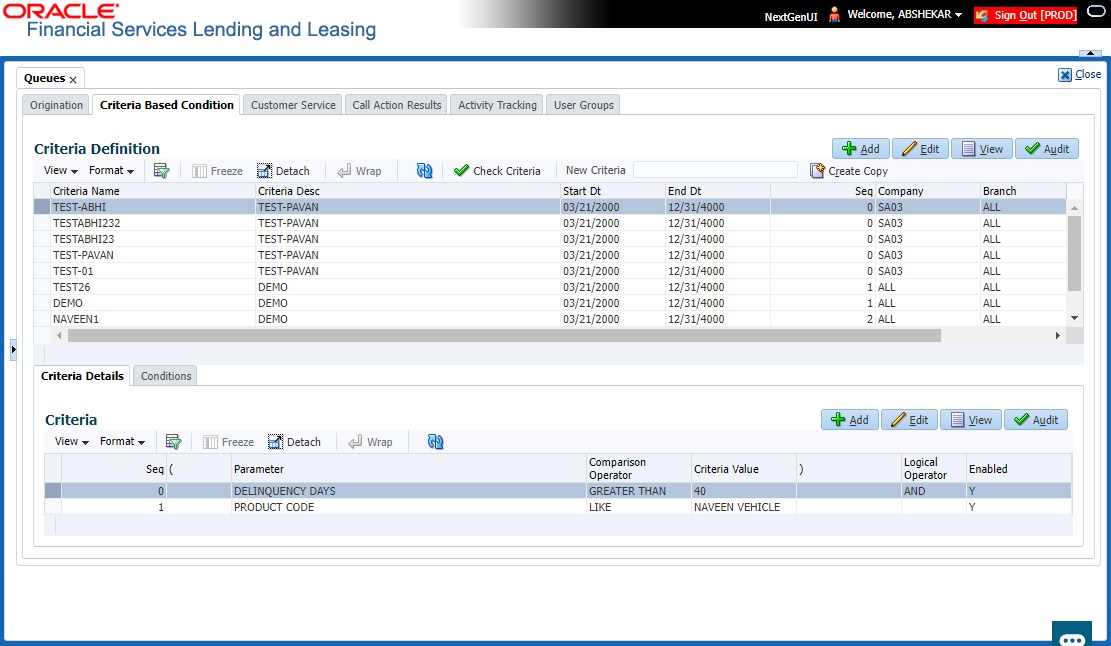
- In the Criteria Definition section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Name |
Specify an unique Criteria definition code. |
Description |
Specify the description of the criteria. |
Start Dt |
Select the start date from when the Criteria is to be considered for execution using the adjoining calendar. |
End Dt |
Select the end date till when the Criteria is to be considered for execution using the adjoining calendar. |
Company |
Select the company from the drop-down list. |
Branch |
Select the branch drop-down list. |
Seq |
Specify the sequence for criteria execution. When there are multiple conditions to be posted on account, the same is processed based on the sequence defined here. However, there cannot be more than one enabled Criteria with same sequence and this condition is auto validated by the system. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the Criteria Definition. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.7.1.2 Criteria Details
The Criteria Details section helps you to define the account selection criteria.
- Click the Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Queues > Criteria Based Condition tab.
- Select the required Criteria definition.
- In the Criteria section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
Note
Although system allows to define customized selection criteria, the execution of additional selection criteria requires additional processing at server level and can have significant performance impact delaying the EOD processing/web services. Hence it is recommended to have careful consideration while defining the additional selection criteria (like using user-defined tables and columns) and/or get approval from your database administrator before using any selection criteria.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Seq |
Specify sequence numbers. |
( |
Specify left bracket. |
Parameter |
Select the parameter from the drop-down list. |
Comparison Operator |
Select comparison operator from the drop-down list. |
Criteria Value |
Specify criteria value. |
) |
Specify right bracket. |
Logical Expression |
Specify logical operator from the drop-down list. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the selection criteria. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.7.1.3 Conditions
The Condition section determines whether the Condition in the selected Criteria Definition is to be opened or closed on the matching accounts.
- Click the Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Queues > Criteria Based Condition tab.
- Select the required Criteria definition, define Criteria and click Conditions tab.
- In the Condition section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Condition |
Select the Condition from the drop-down list. This list is populated based on lookup code ACC_CONDITION_CD which consists of all the matching conditions associated with the selected Criteria Definition. Note that, some of the conditions like Delinquency, Scheduled for Charge-Off and so on (listed above) are automatically opened/closed by system and is not available in this list for selection. |
Action |
Select the action as Open / Close by clicking on the adjacent radio button. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the Condition. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.7.2 Customer Service Tab
The Customer Service section allows you to set up the customer service queues. The screen includes a Hard Assigned box. When selected, the system assigns an equal amount of accounts to each individual user working on a that queue. Also, an account that is hard assigned will remain assigned to the individual who opens that account until that person is no longer working that queue
Customer Service command buttons
The Customer Service screen contains following three command buttons:
Command button: |
Function: |
Update Queue |
Queues can be updated whenever selection criteria has been updated. They may also be updated manually, if the nightly batch fails. |
Un-Assigned |
Depends on location of the cursor when you choose this button. Customer Service - “Un-assigns” all accounts in this queue. Responsibilities and Users > Responsibilities - “Un-assigns” all accounts in this queue. Responsibilities and Users > User - “Un-assigns” all accounts assigned to the specific user. Unassigned accounts may now be selected by updating the queue and re-assigned. |
Check Criteria |
Reviews the selection criteria for errors. The system will not allow you to enable a queue with invalid selection criteria. |
To set up the Customer Service queues
You can either define new Customer Service Queue Definition or specify a new name in the New Queue field and click Create Copy to create a copy of selected Queue Definition with header and child tab details. The new Queue Definition created this way will be in disabled state by default.
- On the Queue Setup screen, click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Queues > Customer Service. Queues are further filtered based on the following criteria:
- Selection Criteria
- Sort
- Responsibilities and Users
- Data node assignments
- Group Assignment
- In the Queue Definition section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
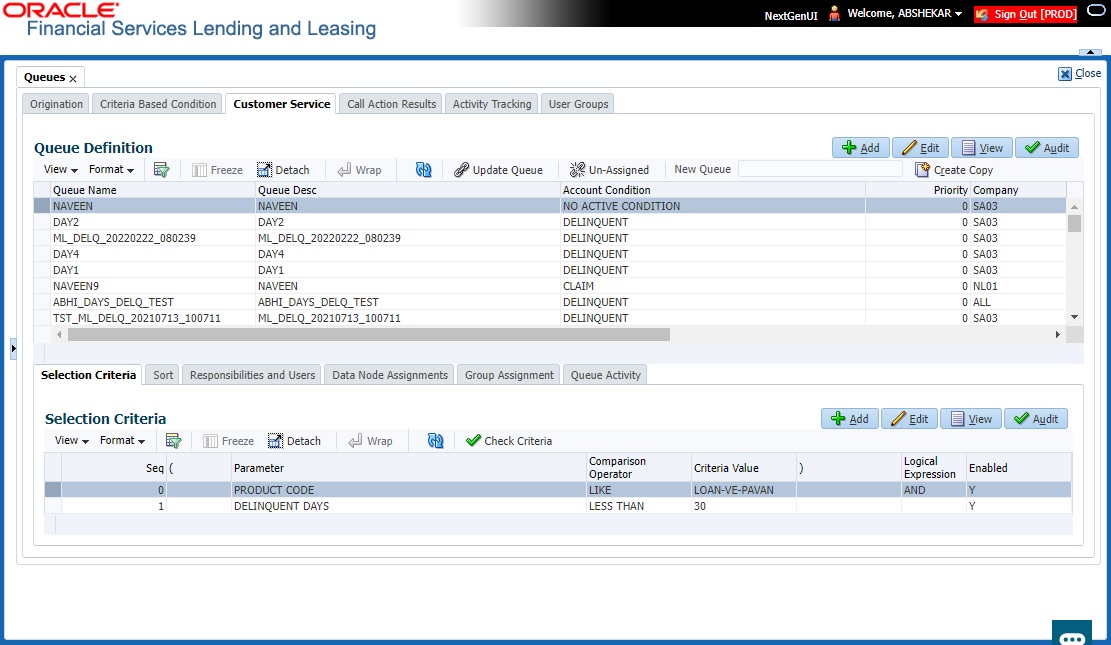
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Queue Name |
Specify queue name. |
Queue Desc |
Specify queue description. |
Account Condition |
Select account condition from the drop-down list. |
Priority |
Specify the priority. |
Company |
Select the company from the drop-down list. |
Branch |
Select the branch from the drop-down list. |
Hard Assigned |
Check this box to assign an equal amount of accounts to each individual user working on a that queue. Also, an account that is hard assigned remains assigned to the individual who opens that account until that person is longer working that queue. |
Group Follow-up Ind |
Check this box to enable the bank to indicate whether the accounts belonging to the same customer have to be followed-up in groups. |
Near Real-Time |
Check this box to select the queues for the near real time refresh. You can specify the time interval and frequency to run this queue. When a batch is run, it picks only customer service queues marked as “Real Time” queues for re-assignment. |
Dialer Extract |
Check this box to indicate if the accounts satisfying the selection criteria should be extracted from the batch process or not. If the user is hard-assigned, then user gets identified by the dialer system as ‘Permission to call” user. The extract will also have data pertaining to customer time zone and privacy opt out indicator. |
Enabled |
Check this box to activate the queue. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- Click the Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Queues > Customer Service > Selection Criteria.
- In the Selection Criteria section, you can define the account selection criteria with the following fields. Perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
Note
Although system allows to define customized selection criteria, the execution of additional selection criteria requires additional processing at server level and can have significant performance impact delaying the EOD processing/web services. Hence it is recommended to have careful consideration while defining the additional selection criteria (like using user-defined tables and columns) and/or get approval from your database administrator before using any selection criteria.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Seq |
Specify sequence numbers. |
( |
Specify left bracket. |
Parameter |
Select the parameter from the drop-down list. |
Comparison Operator |
Select comparison operator from the drop-down list. |
Criteria Value |
Specify criteria value. |
) |
Specify right bracket. |
Logical Expression |
Specify logical operator from the drop-down list. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the selection criteria. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- Click the Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Queues > Customer Service > Sort.
- In the Sort section, you can define the order to sort the account selection criteria with the following fields. Perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Seq |
Specify sequence number. |
AssAgpCode |
Select sort field from the drop-down list. |
Order |
Select sort order from the drop-down list. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Queues > Customer Service > Responsibilities and Users.
- In the Responsibilities section, you can define the responsibilities that are authorized to work on the queue. Perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Responsibility |
Select the responsibility from the drop-down list. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the responsibility. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- In the Users section, you can define the users who are authorized to work on the queue. Also, you can hard assign the queues to the user. Perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
Note
The system allows the work queue list to be sorted by user-defined criteria.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Name |
Select user name from the drop-down list. |
# Assigned |
Specify number of accounts assigned. |
Hard Assigned |
Check this box to hard assign. (For more information, see the following section in this chapter, Using the Hard Assigned Feature). |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Queues > Customer Service > Data Node Assignments. You can enable the administrator to configure the User interface nodes that should be made available for the applications that are being processed in that particular origination queue.
- In the Data Node Assignments section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below::
Field: |
Do this: |
Node |
Specify the node. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the record. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- Click Load Queue Nodes on the Node Assignments sub screen to display the respective UI nodes in the origination module.
- Click Setup > Administration > User > Queues > Origination > Group Assignment. In the Group Assignment sub tab, you can add user groups to Customer Servicing Queue and also if required, you can un-assign users from the user group.
Note
Modification of user details (adding or disabling users) within a user group which is added to Group Assignment will implicitly be updated in Responsibilities and Users tab also.
- In the User Group section, Click Add. You can also perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Group Name |
Select the user group name from the drop-down list. The list displays the pre-defined user groups available in the system. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the user group. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- (Optional) Click 'Un-Assigned' button to un-assign all the users of the group in the queue.
Note the following:
- If the queue is 'Hard Assigned', then it implies that all users in the user group(s) attached to that queue are not 'Hard Assigned'. Hence all those Users should have to be explicitly marked as hard assigned in the queue added through user group.
- User added directly to the queue should be disabled manually. For common users present at Queue and User Group, you need to manually maintain the data in sync.
- Following table indicates various combinations for enabling and disabling Users and User Group(s) from Queue and User group(s).
Entity
Added in Queue
Added in User Groups
Enabling and Disabling options
User
Yes
No
User should be disabled /enabled only in that particular Queue.
No
Yes
User should be disabled / enabled in all the Queues where the user group is attached.
User Group
Yes
No
User group should be disabled /enabled only in that particular Queue.
No
Yes
User group should be disabled / enabled in all the Queues where the user group is attached.
Group Follow-up
The system enables lending institution to conduct “one time only” follow-up activity on the Customer Service screen, if the customer has multiple accounts in various conditions or in various queues. This avoids unnecessary confusions that arise when more than one user is performing collection tasks on multiple accounts belonging to the same customer.
You can follow-up on multiple accounts in the same condition at the same time using the group follow-up functionality. The system locks the accounts in the low priority queues and displays the same in the high priority queues. You can perform the follow-up activity on all the accounts when the account in the high priority queue becomes due for follow-up.
For example,
Suppose a customer holds three accounts, one that’s 30 days delinquent and in the 0_30_DAYs_DEL queue, one that’s 60 days delinquent and in the 30_60_DAYs_DEL queue and one that’s 90 days delinquent and in the 90+_DAYs_DEL.
a) If each of the queues Group Followup Ind is unchecked on the Customer Service screen, then no group follow-up will be performed.
b) If each of the queues Group Followup Ind is checked on the Customer Service screen, while updating the follow-up date for the low priority days queue, then the system will use the 90 days follow-up date
c) If the Group Followup Ind is checked on Customer Service screen for the 0_30_DAYs_DEL and 30_60_DAYs_DEL queues and note the 90+_DAYs_DEL queue, and the customer has accounts in each of the queue, then the system will use the follow-up date of 60 days for the low priority account.
Using the Hard Assigned feature
The system’s “Hard Assigned” queues feature allows companies to evenly distribute accounts between users. The following example explains how it works:
Let’s say there are 40 unassigned accounts in a queue. Three users are assigned to the queue, Hard Assigned is checked for two.
When you select Update Queue on the Customer Service screen (or Oracle Financial Services Lending and Leasing processes the CUSTOMER SERVICE QUEUE PROCESSING nightly batch) each of the two Hard Assigned users receives 20 accounts, while the one that isn’t marked as Hard Assigned receives zero.
If users already have accounts assigned to them, the system attempts to balance the workload when assigning new accounts. For example, let’s say there are three users in a queue. The first has 15 accounts, the second has ten and the third has five. If there are ten new accounts, the system would give the third user the first 5 accounts, thus bringing that user's total to ten. The system splits the next five between the second and third, bringing their totals to 13 and 12, respectively.
Note
The system randomly assigns these accounts.
To set up a user as Hard Assigned feature
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Queues > Customer Service > Responsibilities and Users.
- In the Responsibilities section, select the level responsibility of the users you want to hard assign in the queue.
- In the Users section, check the Hard Assigned check box for each user you want to hard assign.
- On Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Queues > Customer Service, click Update Queue to distribute the applications in the queue to the hard assigned users.
The system displays an Information section with the message as “Queue creation submitted in background”.
- Choose OK beneath the Error Message section box containing the words NO ERROR.
The system distributes and hard assigns the accounts in the queue to the selected users in the Users section.
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
To remove a user
- In the Responsibilities section, select the responsibility of the user you want to remove.
- In the Users section, select the user you want to work with.
- If you don’t want that user to be hard assigned any longer, uncheck the Hard Assigned check box.
- If you don’t want that user to be assigned to that queue any longer, uncheck the Enabled check box.
- The system updates the number of accounts assigned to a user only after:
- Running the nightly batch job
- Clicking the Update Queue button.
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
Queue Activity
The queue Activity sub tab allows you to add specific activities which are defined in Queues > Activity Tracking tab for the selected queue in ‘Queue Definition’ section. These activities can be tracked for updates in Customer Service > Queue Assignment tab.
- In the Queue Activity Definition section, Click ‘Add’. You can also perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter. A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field:
Do this:
Activity Code
Select the Activity Code from the drop-down list. The list displays only those activities which are Enabled in Queues > Activity Tracking tab.
In case the same ‘Activity’ is disabled in Queues > Activity Tracking tab after adding it here, the same needs to be manually disabled.
Enabled
Check this box to enable the selected activity.
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.7.3 Call Action Results tab
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Queues > Call Action Results. The screen contains two sections:
- Call Actions
- Call Results
- In the Call Actions section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
You can either define new Call Action details or specify a new action code in the New Action field and click Create Copy to create a copy of selected call action with details.
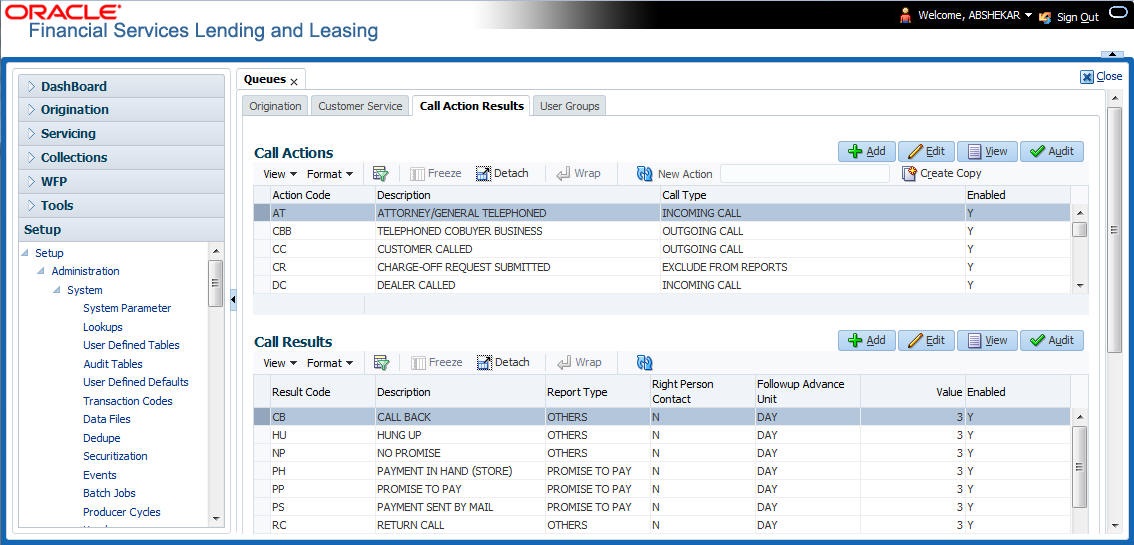
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Action Code |
Specify the action type code. |
Description |
Specify the description for the call action type. |
Call Type |
Select the call type from the drop-down list. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the call action. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- In the Call Results section, you can define call action result codes and corresponding descriptions. Perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- A brief description of the fields is given below:
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Result Code |
Specify the result type code for the specified call action type. |
Description |
Specify the description for the result type. |
Report Type |
Select the report type for the result type, from the drop-down list. |
Right Person Contact |
Check this box to indicate that result type is a right person contact. |
Follow-up Advance Unit |
Select the unit for advancing the follow-up date/time from the drop-down list. |
Value |
Specify the value for the follow-up advance unit. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the result. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
Queues are further filtered based on the following criteria:
- Conditions
- Responsibilities
The Conditions section determines whether the selected action/result will cause the listed conditions to be opened or closed. It also determines whether the queue will be opened or closed.
- In the Conditions section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Condition |
Select the account condition to be open/close for the action from the drop-down list. |
Condition |
Select ‘Open’ to open the listed condition, ‘Close’ to open the listed condition, or ‘NA’, if the condition is not applicable. |
Queue |
Select ‘Open’ to open the listed Queue, ‘Close’ to open the Queue, or ‘NA’, if the Queue is not applicable. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the account condition. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- In the Responsibilities section, define the responsibilities that are authorized to use the call action result combination.Perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Responsibility |
Select the responsibility that can perform the action result from the drop-down list. |
Allowed |
Select ’Yes’ if access is allowed. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the responsibility. |
Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.7.4 Activity Tracking
The Activity Tracking tab in Queues screen allows you to define 36 different activities at any given time. You can define unique Action and Result for each activity and also set the activity expiry duration beyond which new actions can be defined for the same activity.
The Activity defined in this tab is used in User > Queues > Customer Service > Queue Activity tab to define activities for selected ‘Queue Definition’ which in-turn is used in Customer Service > Queue Assignments tab to track the updates from call activity results.
![]()
- In the Activity Definition section, Click ‘Add’. You can also perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter. A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field:
Do this:
Activity Code
Select the activity code from the drop-down list. The list displays pre-defined activity codes which are enabled as part of ‘QUEUE_ACTIVITY_TYPE_CD’ lookup code maintained in the system.
Description
View the description of activity code.
Action
Select the Action for the activity from the drop-down list. The list displays all the customer service call actions available in the system.
Result
Select the appropriate Result for the action from the drop-down list. The list is sorted with results based on the action selected.
Activity Expiry Days
Specify the number of days after which the activity has to expire (i.e. status set ‘N’). An activity code in ‘N’ status can be used to associate new action for tracking.
Enabled
Check this box to enable the activity.
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.7.5 User Groups Tab
The User Groups tab in Queues is a centralized repository which allows you to define user groups, add and remove users from user groups.
The User Groups tab consists of User Group Definition section listing the defined User Groups and User section below listing the associated users of the selected User Group.
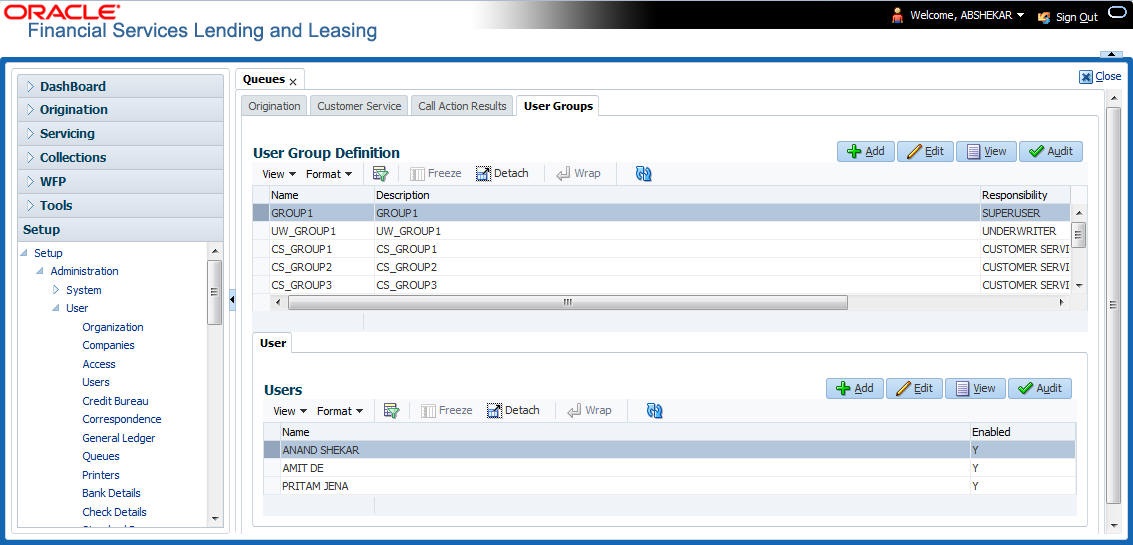
To define a User Group
- On the Oracle Financial Services Lending and Leasing home screen, click Setup > Administration > User > Queues > User Groups.
- In the User Groups section, Click Add. You can also perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Name |
Specify user group name. |
Description |
Specify an appropriate user group description. The same is used while referring this User Group on other screens. |
Responsibility |
Select the responsibility of the user group from the drop-down list. You can later add only those ‘Users’ who have the selected responsibility into the user group. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the user group. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
To add Users to User Group
- On the Oracle Financial Services Lending and Leasing home screen, click Setup > Administration > User > Queues > User Groups.
- In the User Groups section, select the required User Group.
- In the Users section, Click Add. You can also perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Name |
Select the user from the drop-down list, The list displays the available users based on the responsibility defined for the user group. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the user. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.8 Printers
The Printers screen allows you to set up an unlimited number of network printers and fax devices to be used with the system server. The system uses the information on this screen while selecting a printer, when the printing process involves a batch job or uses a job scheduler. Examples include printing reports and correspondence.
The printers and fax devices can be set up at each organization, division, or department to promote efficient printing of documents, and reports. The system uses this information during product setup and on the Letters screen in the Batch Printer field.
Special printer names
The following printer names are predefined and have specific functions within the system:
Name |
Description |
UNDEFINED |
Indicates that the document to be printed is to be previewed in your browser instead of actually printing the document. |
archive |
Instead of sending an item to the printer, the system generates a PDF document and saves it in the archive directory on your server. |
For Loan origination correspondences that can be faxed, the system e-mails the document as a PDF attachment to the consumer for direct Loans or to the producer in the case of in-direct Loans. |
|
fax |
For Loans origination correspondences that can be faxed, the system generates a PDF document and will send to the fax server defined in System Parameters. |
Additionally, you may set up composite entries in the Printer Name field to perform two or more functions at the same time. This can be done by defining a printer name with the following format:
Printer name = <Printer_Name1> + <Printer_Name2>
For example, if a printer named jet4050 was previously defined, as were the special printer names listed above, then the following additional printers could be defined:
Name |
Description |
jet4050+archive |
Prints the document with the jet4050 printer and archives the document. |
fax+archive |
Faxes and archives the document. |
email+archive+jet4050 |
E-mails, archives, and prints the document with the jet4050 printer. |
To set up the Printers
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Printers. The system displays the Printers screen
- In the Printers section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
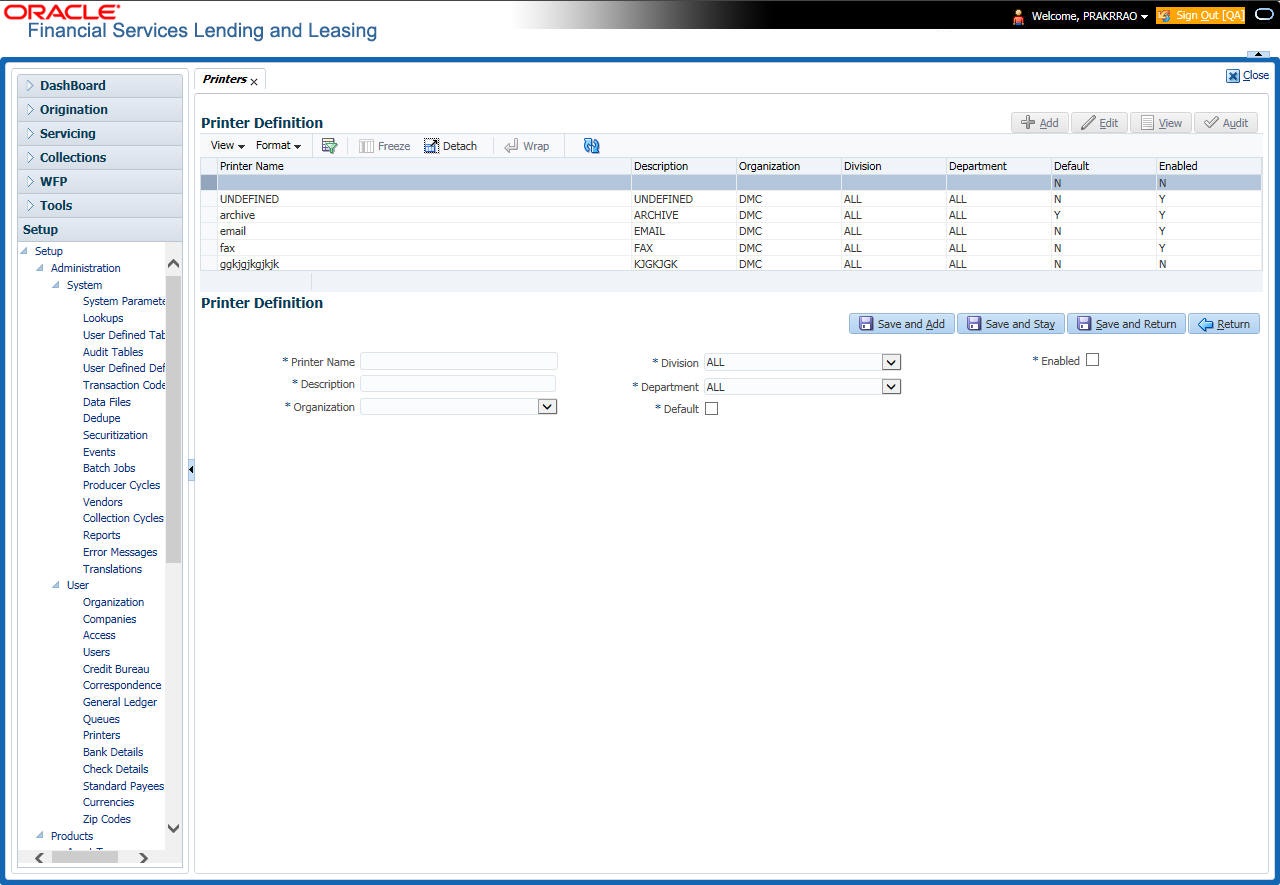
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Printer Name |
Specify the printer name. The name of the printer as defined by the server. For a UNIX server, the name might be jet4050, while to access the same printer from a Windows server the name would be: \\servername\jet4050. |
Description |
Specify the description for the printer. |
Organization |
Select the organization to which the printer belongs, from the drop-down list. |
Division |
Select the division to which the printer belongs, from the drop-down list. The division will be displayed based on the organization selected. |
Department |
Select the department to which the printer belongs, from the drop-down list. The department will be displayed based on the division selected. IMPORTANT: When you select a printer to use, the system searches for a best match using the following attributes: 1 Organization 2 Division 3 Department Hence, Oracle recommends creating a version of each edit, where ALL is the value in these fields. It is also recommended that, you define a default printer for an Organization, Division and Department. |
Default |
Check this box to set the printer as a default printer. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the printer and that the printer is active. Note: Never disable the UNDEFINED printer. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.9 Intelligent Segmentation
OFSLL is equipped to leverage the Machine Learning (ML) feature of Oracle Database to suggest and create Customer Servicing Queues by analysing the current system data. Using this functionality, system automatically identifies the possible Queue/Segmentation for Account data using the Machine Learning Algorithm thereby creating an Intelligent Segmentation.
This helps to automate the manual process of queue creation which is otherwise done by identifying different segments of Accounts and assigning day to day Customer Service Activities. Further queue processing workflow continues as detailed in ‘Queues’ section.
3.9.1 Machine Learning for Queue Creation
The Intelligent Segmentation screen in OFSLL is based on the Oracle JavaScript Extension Toolkit (Oracle JET) framework. This facilitates to identify different clusters of data and create queues.
In order to access the Intelligent Segmentation screen from the User Interface menu link, you need to enable the system parameter FLL_SET_JET_INTELLIGENTSEG_URL (JET INTELLIGENT SEGMENTATION URL). For more details on installing and deploying this feature in OFSLL, refer to Installation Manual.
In this screen, you do the following:

- Identify Cluster of Data for a given Account Condition.
- View hierarchy of cluster and list of accounts falling into different levels of cluster.
- Create a queue by selecting Cluster
3.9.2 Machine Learning Data visualization
The data generated by the system is represented in the following view formats.
3.9.2.1 Cluster view
3.9.2.2 Segment View
3.9.2.3 Insights View
3.9.2.4 Selection Criteria Attributes
Clicking on any of the data segment system displays dynamic record details (Attribute Name and Attribute Value) along with the option to create queue.
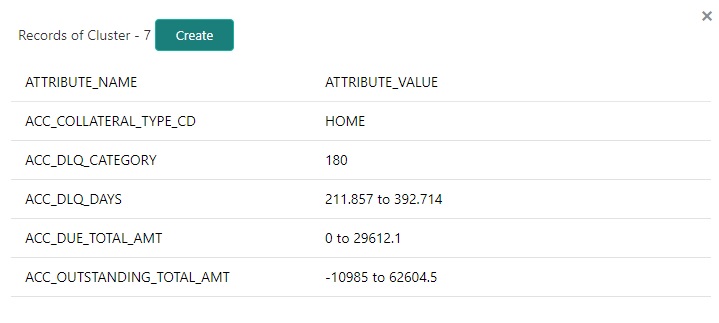
3.9.3 View Machine Learning Generated Queue
To view ML based queue
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Intelligent Segmentation. The following screen is displayed:
- Select the following option:
Field:
Do this:
Company
Select the company from the drop-down list. The list is populated only with those Company Definitions to which you have been provisioned access.
Branch
Select the branch within the company from the drop-down list. This may be ALL or a specific branch. This must be ALL, if you have selected ‘ALL’ in the Company field.
Account Conditions
Select the required account conditions. There are various Account Conditions which are either posted ‘automatically’ by the system (like updating DELQ delinquency condition on account) or ‘manually’ through a transaction or call activity.
- Click ‘Submit’. System generates different data segments based on above selected combination using a background job process. By default, the data is represented in clusters and can be viewed on other view formats as detailed in ‘Machine Learning Data visualization’ section.
3.9.4 Create ML Based Queue
On generating the data segments in the Intelligent Segmentation screen, you can further drill down to each cluster and view details with different selection criteria. However, the details of each record is based on the data maintained in the system.
Button |
Action |
Create |
Clicking on this option creates a Queue in OFSLL and the selection criteria of the Queue is populated with the Cluster Attributes. The queue sequence is based on Queue name/Description and is displayed as a confirmation message in the format ‘Queue ML <Account Condition > <Date YYYYMMDD > <Time HHMMSS> created successfully’.
The newly created queue is available in Setup > Administration > User > Queues screen. |
Note that following with ML generated Queues:
- All Queues are created in ‘Disabled’ status with Selection Criteria ‘Enabled’.
- Priority is defaulted to 0.
- Company/Branch is defaulted to selected combination.
- Hard Assigned/Group Follow-up/Near Real-Time/Dialler actions are marked as disabled.
3.10 Bank Details
The Banks screen defines the banks, a company/branch uses for processing Automatic Clearing House (ACH) and lock box payments.
Note
This is “behind the scenes” information that the system uses for payments and does not appear on any other forms.
To set up the Banks
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Bank Details link. The system displays the Bank Details screen.
- In the Banks Definition section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Code |
Specify the bank code (ID used internally by Oracle Financial Services Lending and Leasing to represent the bank). |
Name |
Specify the name for the bank. |
Short Name |
Specify the short name for the bank (ID displayed to represent the bank. This may be included in any output files). |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable and indicate this as an active bank |
Account # |
Specify the account number used for banking transactions with the bank. Note: If the organizational parameter UIX_HIDE_RESTRICTED_DATA is set to Y, this appears as a masked number; for example, XXXXX1234. |
Routing # |
Specify the routing number of the bank. |
BIC |
Select the Business Identifier Code from the drop-down list. The list displays the BIC codes defined in the system. |
IBAN |
Specify the IBAN (International Bank Account Number). IBAN is used for identifying bank accounts across national borders with a minimal of risk of propagating transcription errors. Ensure that value entered satisfies the check-digit validation based on modulo 97. On save, system automatically validates the IBAN number length based on country code, characters, white spaces, and checksum. Validation is also done during posting non-monetary transaction (ACH Maintenance). You can maintain the IBAN length and other details required as per the country code in the user defined table (Setup > Administration > System > User Defined Tables). Note: IBAN for 'NL' country code (IBAN_FORMAT_NL) is defined by default with length of IBAN as 18. |
Country |
Select the country where the bank is located, from the drop-down list. |
City |
Specify the city where the bank is located. |
State |
Select the state where the bank is located, from the drop-down list. |
Address Line 1 |
Specify the address line 1 for the bank. |
Address Line 2 |
Specify the address line 2 for the bank. |
Zip |
Specify the zip code where the bank is located, from the drop-down list. |
Extn |
Specify the extension of the zip code where the bank is located. |
Creditor Id |
Specify the creditor identification details. |
Phone 1 |
Specify the primary phone number of the bank. |
Extn 1 |
Specify the phone extension for the primary phone number. |
Phone 2 |
Specify the alternate phone number for the bank. |
Extn 2 |
Specify the phone extension for the alternate phone number. |
Fax 1 |
Specify the primary fax number for the bank. |
Fax 2 |
Specify the alternate fax number for the bank. |
ACH Format |
Select the ACH format accepted by this bank from the drop-down list. The list displays the following options: - NACHA Format - SEPA Format |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Bank Details > ACH.
- On the ACH Definition sub screen, you can create ACH files for the bank listed in the Banks section. Perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Company |
Select the portfolio company from the drop-down list. |
Branch |
Select the portfolio branch from the drop-down list. |
ACH Identifier |
Specify the lock box ID provided by the bank. This field is used in the ACH files to identify the bank. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the ACH and indicate this as an active ACH identifier. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Bank Details > Lock Box.
- On the Lock Box sub screen, you can create lock box files for the bank listed in the Banks screen. Perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Lock Box Identifier |
Specify the lock box ID provided by bank. This field is used in the lock box files to identify the bank. |
Company |
Select the portfolio company from the drop-down list. |
Branch |
Select the portfolio branch from the drop-down list. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the lock box. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.11 Standard Payees
The Standard Payees screen defines the third parties that are frequent payees for checks issued within your organization. These payees are then available on the Consumer Lending screen’s Advance Entry screen. When you select the Payee # in the Advance Allocation section, the system completes the remaining fields in this screen with information from the Standard Payees screen.
Note
The Payee # field on the Advance Payment forms is a non-validated field. This allows you to select an entry or enter one of your own.
To set up the Standard Payees
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Standard Payee. The system displays the Standard Payees screen.
- In the Payee Definition section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Payee # |
Specify the payee number (Identifier for the payee). |
Name |
Specify the payee name. |
Pmt Mode |
Select the payment method for the payee from the drop-down list. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enabled the payee. |
Country |
Select the country where the payee is located from the drop-down list. |
City |
Specify the city where the payee is located. |
State |
Select the state where the payee is located from the drop-down list. |
Address Line 1 |
Specify the address line 1 for the payee (optional). |
Address Line 2 |
Specify the address line 2 for the payee (optional). |
Zip |
Select the zip code where the payee is located from the drop-down list. |
Extn |
Specify the extension of the zip code where the payee is located. |
Phone 1 |
Specify the primary phone number for the payee. |
Phone 2 |
Specify the alternate phone number for the payee. |
Bank Name |
Specify the payee ACH bank name used by the standard payee. |
Routing # |
Specify the payee ACH bank routing number of bank used by the standard payee. |
Account Type |
Select the payee type of ACH bank account maintained by the Standard Payee from the drop-down list. |
ACH Account # |
Specify the payee ACH bank account number. |
Company |
Select the company from the drop-down list. The list is populated with Company definitions based on the Country selected. |
Branch |
Select the branch drop-down list. The list is populated with Company branch based on the Country selected. |
BIC |
Select the Business Identifier Code from the drop-down list. The list displays the BIC codes defined in the system. |
IBAN |
Specify the IBAN (International Bank Account Number). IBAN is used for identifying bank accounts across national borders with a minimal of risk of propagating transcription errors. Ensure that value entered satisfies the check-digit validation based on modulo 97. On save, system automatically validates the IBAN number length based on country code, characters, white spaces, and checksum. Validation is also done during posting non-monetary transaction (ACH Maintenance). You can maintain the IBAN length and other details required as per the country code in the user defined table (Setup > Administration > System > User Defined Tables). Note: IBAN for 'NL' country code (IBAN_FORMAT_NL) is defined by default with length of IBAN as 18. |
Start Dt |
Specify the payment mode start date, the date the current payment method was implemented (defaults on Pmt Mode change). you can also select from the adjoining calendar icon. |
Comment |
Specify a comment for this advance allocations. This is the default comment to include with payments to this Payee. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.12 Check Details
The Check Details screen allows you to set up check details.
To setup the Check Details
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Check Details. The system displays the Check Details screen.
- In the Check Definition section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
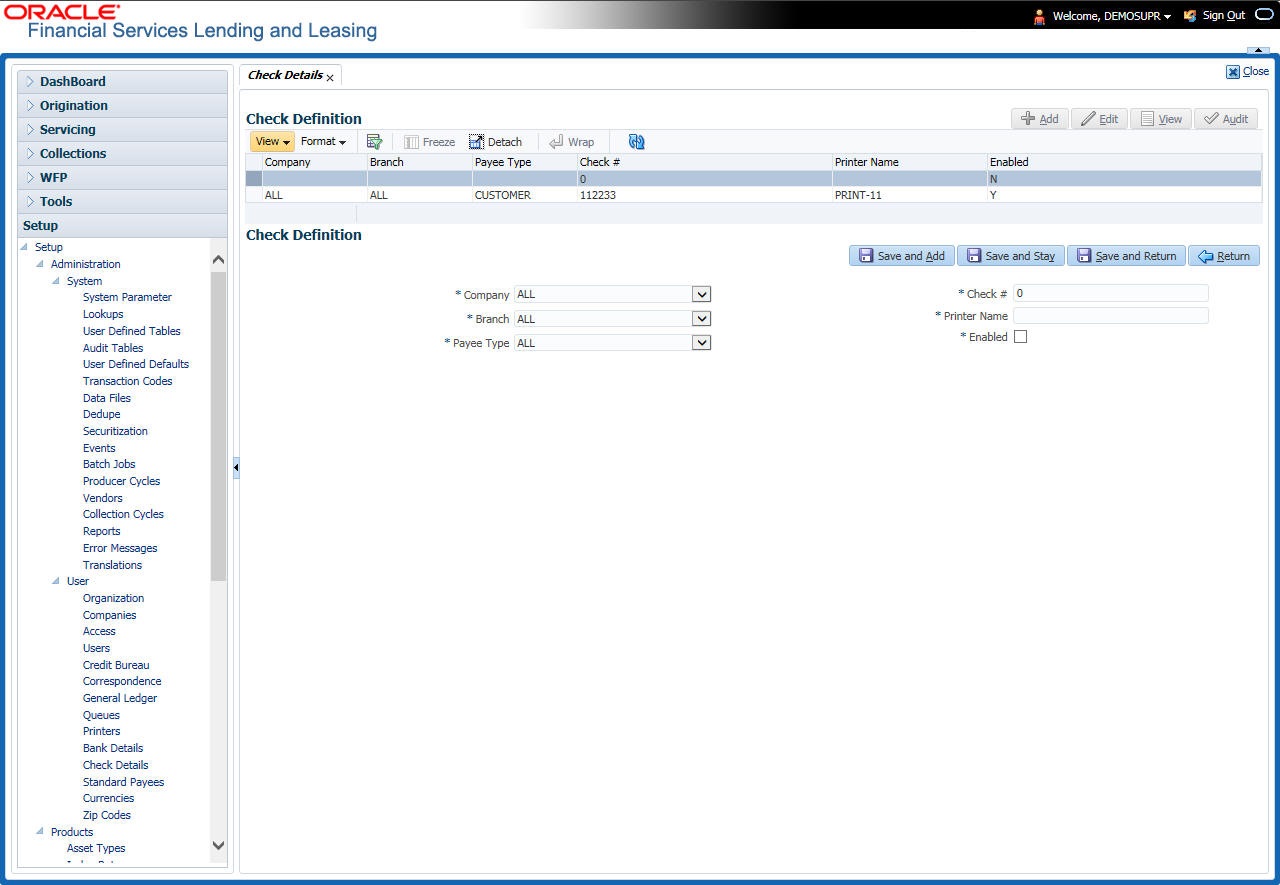
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Company |
Select the company from the drop-down list. |
Branch |
Select the branch from the drop-down list. |
Payee Type |
Select the payee type from the drop-down list. |
Check # |
Specify the check number (required). |
Printer Name |
Specify the printer name (required). |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the check details entry. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.13 Currencies
The Currencies link allows you to set up currency details.
Navigating to currencies
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Currencies. The system displays the Currencies screen. In this screen, you can set up:
- Currency Definition
- Currency Pair Definition
3.13.1 Currency Definition
The Currency Definition screen allows you to set up currency details.
To set up the currency definition information
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Currencies > Currency. The system opens the Currency Definition tab by default.
- In the Currency section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
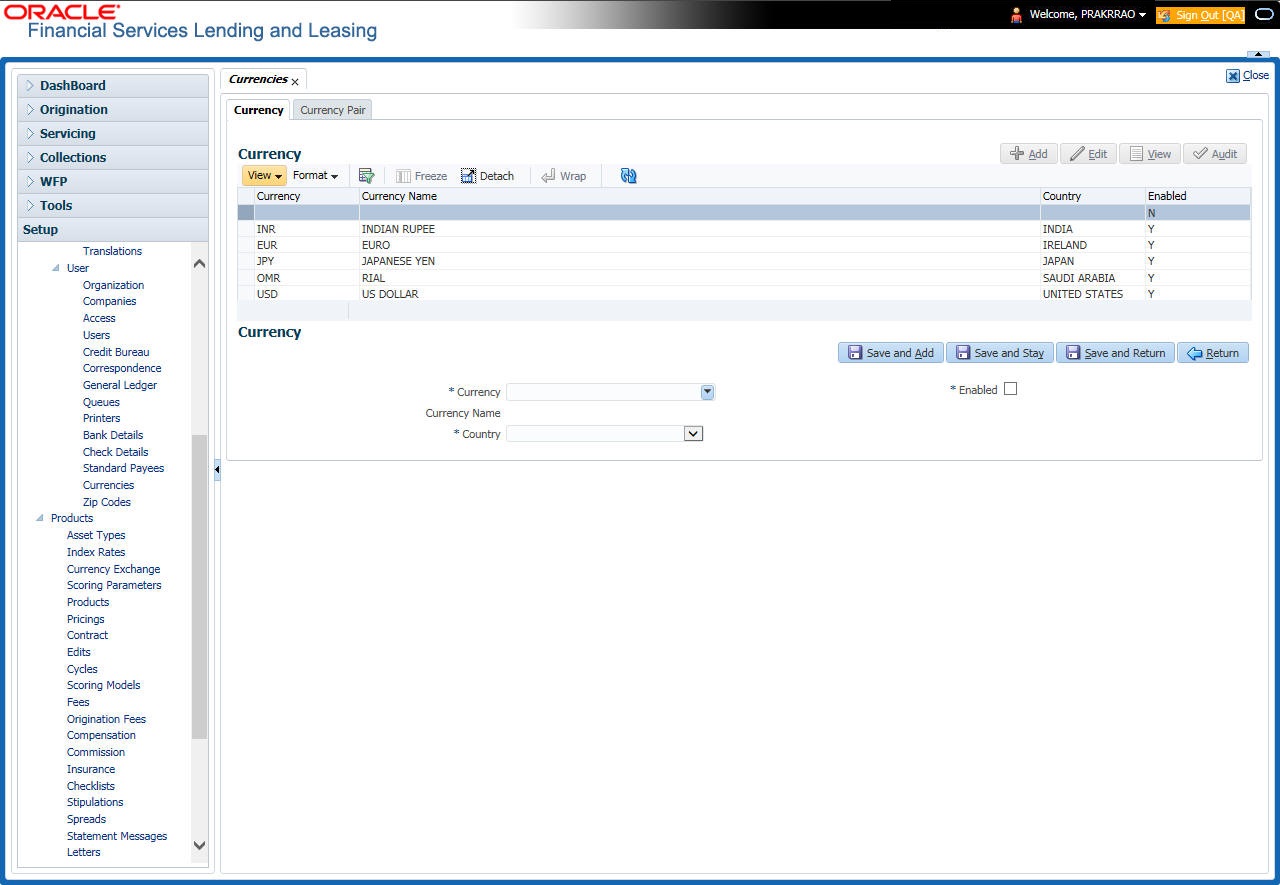
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Currency |
Select the currency you want to define, from the drop-down list. |
Currency Name |
The system displays the currency name based on the currency selected. |
Country |
Select the country for which the currency is defined, from the drop-down list. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the currency entry. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.13.2 Currency Pair link
The Currency Pair Definition link allows you to set up currency pair details.
To set up the currency pair definition information:
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Currencies > Currency Pair. The system displays the Currency Pair Definition screen
- In the Currency Pair Definition section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
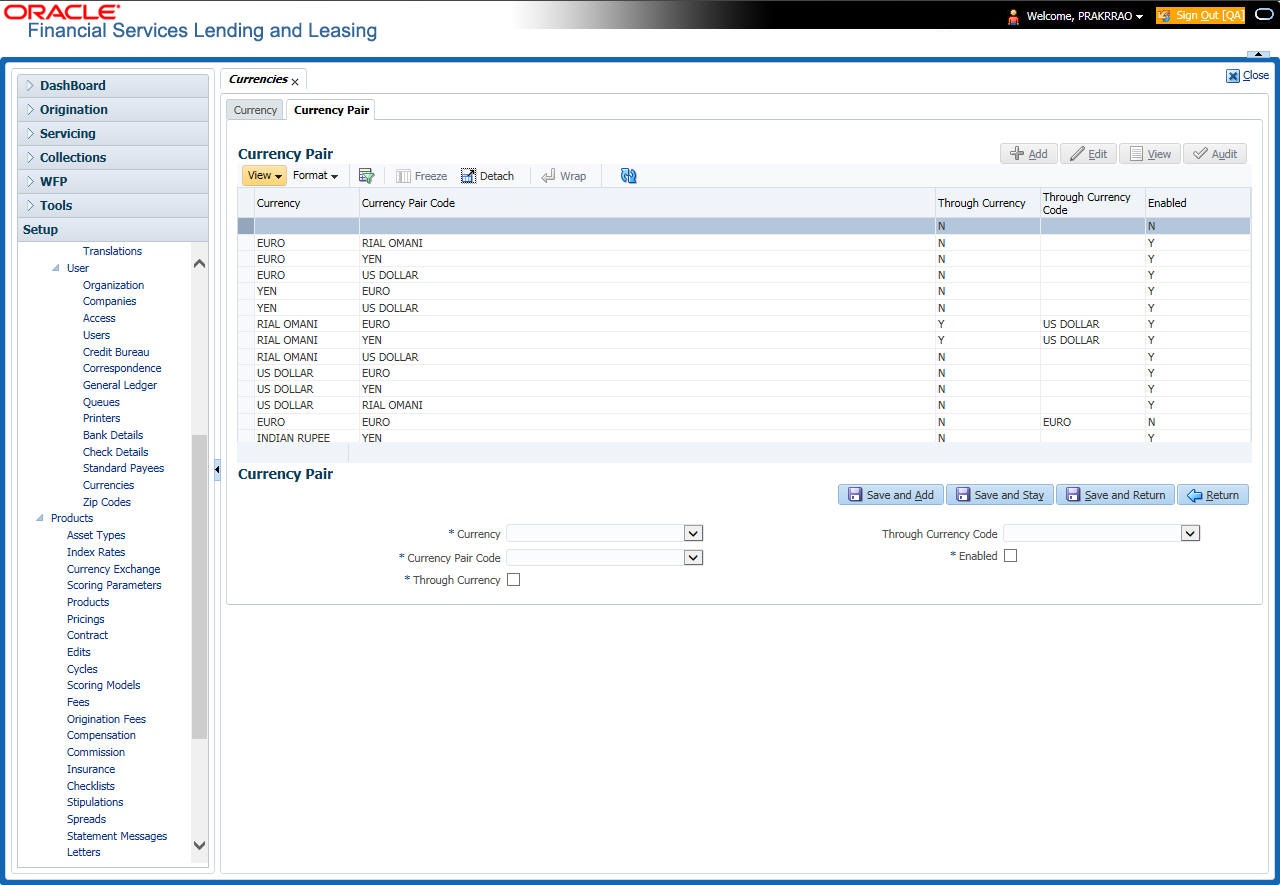
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
View this: |
Currency Code |
Select the currency code from the drop-down list. |
Currency Pair Code |
Select the currency pair code from the drop-down list. |
Through Currency |
Check this box to set the selected currency as a through currency. |
Through Currency Code |
Select the through currency code from the drop-down list. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the currency pair entry. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.14 Zip Codes
The Zip Codes screen allows you to set up zip code details.
To set up the zip codes information
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > ZipCodes. The system displays the Zip Codes screen
- In the Zip Codes section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
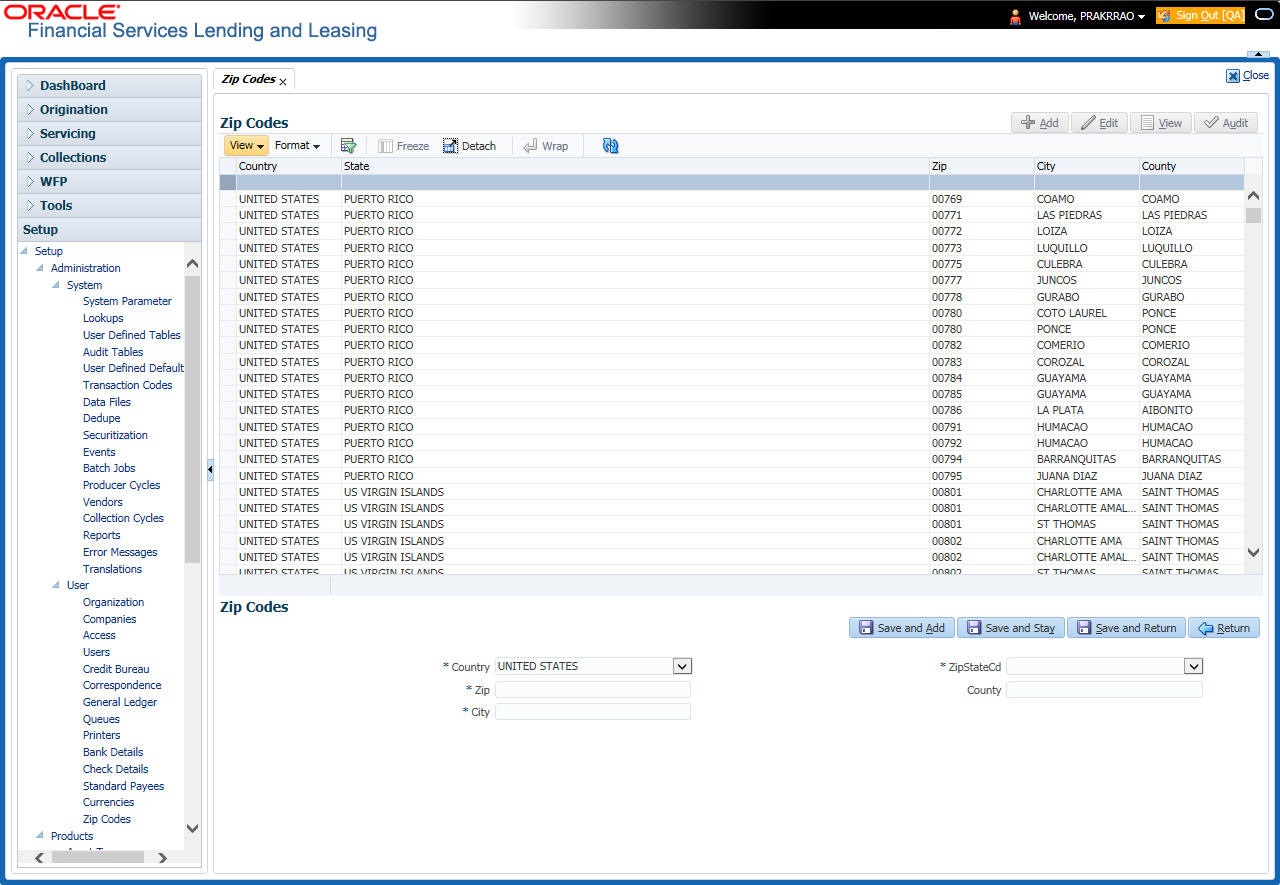
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
View this: |
Country |
Select the country from the drop-down list. |
State |
Select the state from the drop-down list. |
Zip Code |
Specify the zip code (required). |
City |
Specify the city. |
County |
Specify the county. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
3.15 Payment Hierarchy
The Payment Hierarchy screen facilitates to define hierarchy definition along with payment appropriation, excess payment handling, account selection criteria and sort order. These details are required by the system to allocate payments to the matching accounts of a customer, when customer based payments are being processed in ‘Payment Entry’ screen.
Below is an illustration on how payment hierarchy is used to post customer based payments.
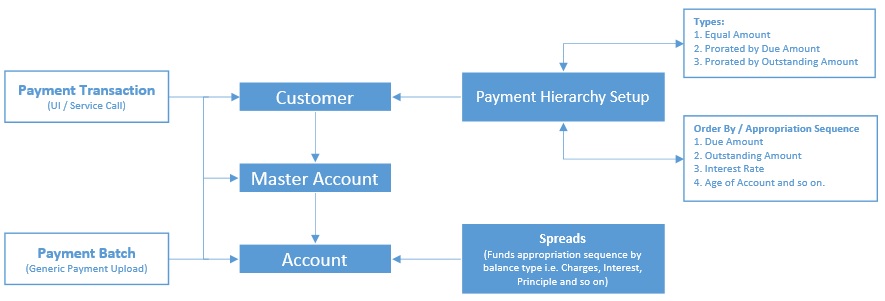
Any Payment transaction generated in the system either from UI / Web Service Call or through a Payment Batch (Generic Payment Upload) can be directly posted to an Account or at Customer level.
- If payment is posted directly to an Account, the funds are allocated based on the defined spread with funds appropriation sequence of balance type i.e. Charges, Interest, Principle and so on.
- If payment is posted at Customer level having two accounts and if the payment amount is less than the due, then appropriation sequence is required. Else, one of the account can have a short fall with payment allocation.
In such case, the Payment Hierarchy determines the sequence of payment as to which account is to be appropriated first and which is to be appropriate next. This is based on 'order by clause' and ‘appropriation sequence’ defined.
Also the Balance Type determines the distribution type as one of the following:
- Equally to all the accounts
- Prorated by Due amount (i.e. highest due or lowest due first)
- Prorated by Outstanding Amount.
Once the account is narrowed down and payment amount is decided, then based on spread the payment is appropriated. This gives additional flexibility for defining payment modes at the master account level.
If Payment Hierarchy is not defined while funding an application or needs correction, the same can be done by posting ‘MASTER ACCOUNT PAYMENT HIERARCHY MAINTENANCE’ non-monetary transaction in Servicing > Maintenance > Transaction Batch Information section. At Customer level, Payment hierarchy can be updated by posting CUSTOMER MAINTENANCE transaction.
3.15.1 Payment Appropriation Methods
While creating Hierarchy definition in the Payment Hierarchy screen, you can use any of the following payment appropriation methods available in Hierarchy Type field. On selecting the specific Hierarchy definition at Application or Account level, the defined method is used to allocate payments to corresponding accounts.
However in all the methods, the payment criteria is also used for identifying the due accounts and careful consideration is required while defining the same.
Method |
Description |
EQUAL AMOUNT |
To allocate payment equally to all the accounts picked. This is traditional method of payment allocation in which the total payment amount received is divided and adjusted equally to all customer linked accounts. |
DUE AMOUNT RATIO |
To allocate payment based on the ratio of amount due on all accounts. In this method, the due accounts are identified based on the defined selection criteria and the payment appropriation is done on the ratio of amount due on each account using the below formula.  Following is an illustration on payment allocation: 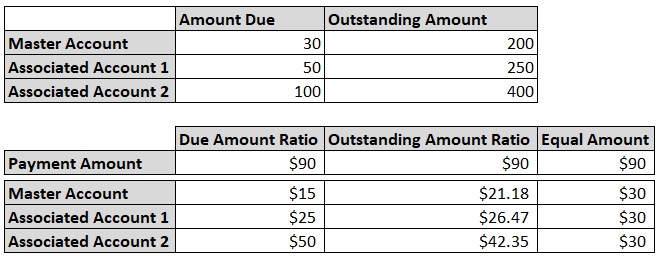 |
OUTSTANDING BALANCE RATIO |
To allocate payment based on the ratio of total outstanding due on all accounts. Similar to above, even in this method the due accounts are identified based on the defined selection criteria and the payment appropriation is done on the ratio of outstanding amount due on each account using the below formula. 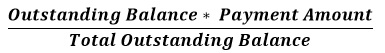 This method can be selected if the received payment amount is equal to total outstanding due on all linked accounts indicated in Customer Service > Transaction History > Balances screen. |
ACCOUNT COLUMN BASED |
To allocate payment based on hierarchy order. In this method, the due accounts are identified based on the defined selection criteria and the payment appropriation is done as per the sequence of due accounts defined either in ascending/descending order. |
During payment appropriation, system allocates the payment amount only up to the total of resulted accounts and remaining amount (if any) are processed based on the excess payment method value.
While onboarding accounts through web services, system considers the value of system parameter PMT_HIERARCHY_CODE to default the payment allocation in Customer/Business Details screen after account activation.
Also while onboarding if the Payment Hierarchy is not passed as part of the request (Applicant/Application), then system parameter value is considered.
3.15.2 Excess Payment Appropriation
During or after payment appropriation, there can be a residual amount pending for allocation. For example, $0.01 remains when $100 is equally paid to 3 accounts. In such case the residual amount is transferred to last account in the hierarchy sequence. However, note that system performs this residual payment allocation only once.
In other case where there in an excess payment received which is more than account dues, the same can be processed for payment allocation using any of the following ‘Excess Handling Method’ while defining the Hierarchy Definition.
Method |
Description |
SUSPENSE |
To post the excess amount as suspense on Customer or Master account. |
HIERARCHY BASED |
To allocate the excess payment based on any of the Hierarchy Definitions maintained in the system. |
Based on the selection, system re-allocates the excess amount to corresponding accounts.
To set up payment hierarchy
- Click Setup > Setup > Administration > User > Payment Hierarchy.
- In the Hierarchy Definition section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
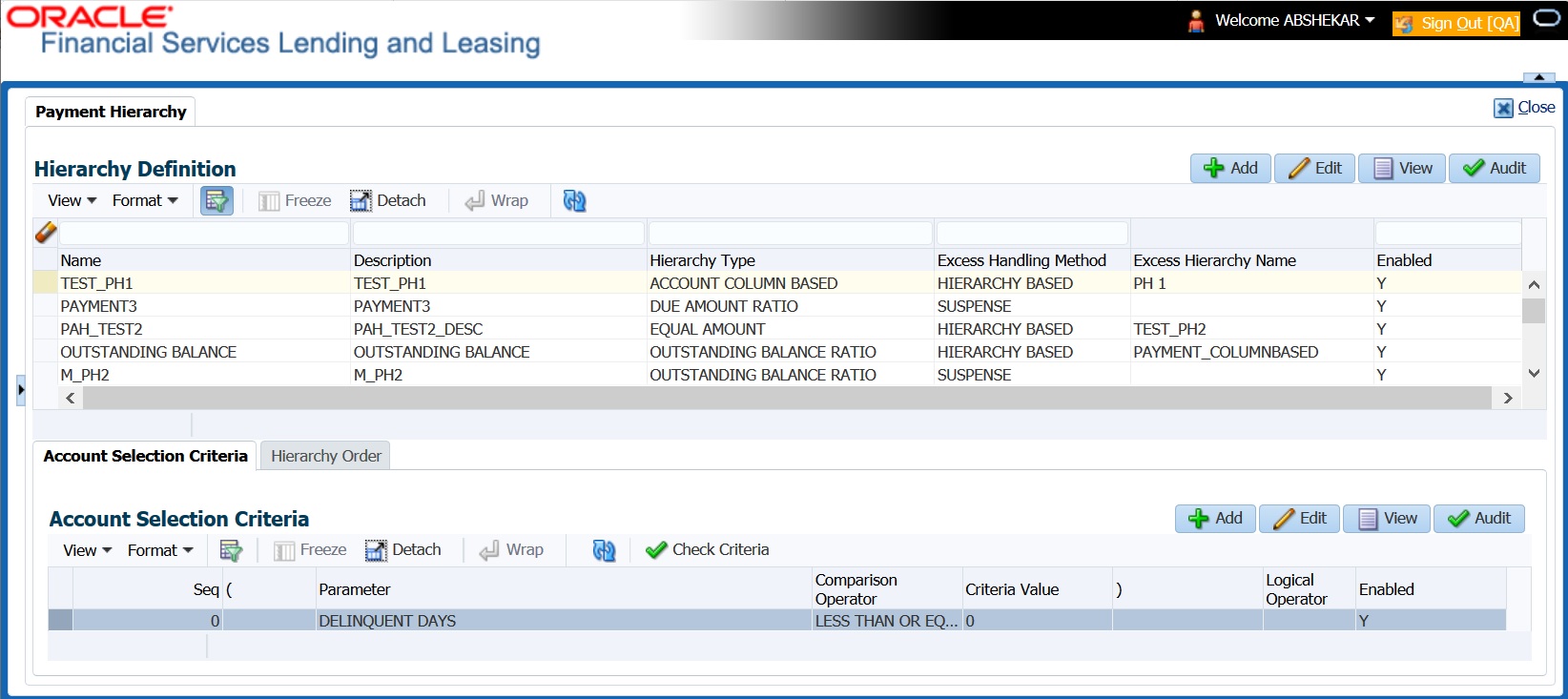
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
View this: |
Name |
Specify an unique name for the hierarchy definition. |
Description |
Specify the description for the hierarchy definition. |
Hierarchy Type |
Select one of the following type of payment allocation method from the drop-down list. The list is populated based on the PMT_HIERARCHY_TYPE_CD lookup. - EQUAL AMOUNT - DUE AMOUNT RATIO - OUTSTANDING BALANCE RATIO - ACCOUNT COLUMN BASED For more information on the above methods, refer to ‘Payment Appropriation Methods’ section. You can define multiple Hierarchy definitions with same Hierarchy type. |
Excess Handling Method |
Select one of the following type of excess payment allocation method to be used with payment hierarchy definition from the drop-down list. The list is populated based on PMT_HIERARCHY_EXCESS_METHOD_CD lookup. - SUSPENSE - HIERARCHY BASED For more information on the above methods, refer to ‘Excess Payment Appropriation’ section. |
Excess Hierarchy Name |
This field is enabled and is mandatory if the Excess Handling Method is selected as ‘Hierarchy Based’. Select the Hierarchy Definition from the drop-down list. This list is populated with all the pre-defined and enabled hierarchy definitions maintained in the system. For more information on the above methods, refer to ‘Excess Payment Appropriation’ section. |
Enabled |
By default this check box is enabled for new hierarchy definition. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
Account Selection Criteria
This sub tab facilitates to define the account selection criteria that is used to identify due account for payment allocation. Atleast one valid account selection criteria is required for all the Hierarchy Types.
- In the Account Selection Criteria section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter.
Note
Although system allows to define customized selection criteria, the execution of additional selection criteria requires additional processing at server level and can have significant performance impact delaying the EOD processing/web services. Hence it is recommended to have careful consideration while defining the additional selection criteria (like using user-defined tables and columns) and/or get approval from your database administrator before using any selection criteria.
A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field: |
Do this: |
Seq |
Specify sequence numbers. |
( |
Specify left bracket. |
Parameter |
Select the parameter from the drop-down list. The list is populated based on the values maintained in CUSTOMER PAYMENT HIERARCHY ORDER PARAMETERS user defined table. |
Comparison Operator |
Select comparison operator from the drop-down list. |
Criteria Value |
Specify criteria value. |
) |
Specify right bracket. |
Logical Expression |
Select logical operator from the drop-down list. |
Enabled |
Check this box to enable the selection criteria. |
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.
- You can click ‘Check Criteria’ for system to validate the query and display the results.
Hierarchy Order
This sub tab facilitates you to define hierarchy order that is used to sort the due account for payment allocation. This sub tab is enabled only for ‘ACCOUNT COLUMN BASED’ Hierarchy type.
- In the Hierarchy Order section, perform any of the Basic Operations mentioned in Navigation chapter. A brief description of the fields is given below:
Field:
Do this:
Seq
Specify sequence number.
Sort Field
Select sort field from the drop-down list. The list is populated based on values maintained in CUSTOMER PAYMENT HIERARCHY ORDER PARAMETERS user defined table.
Order
Select sort order as either Ascending or Descending from the drop-down list.
- Perform any of the Basic Actions mentioned in Navigation chapter.