Scenario: Using Sourcing Optimization and Constraints
Scenarios are examples of how to use some of the features within PeopleSoft Strategic Sourcing. These real-life examples describe some of the intended uses of these features, enabling you to understand how these features might be applied to your own organization.
Note: The real-life scenarios described within this documentation may not conform to the business rules and procedures within your organization. Do not construe these examples as consulting or implementation advice for your specific industry or your individual organization. You should adapt or disregard the information here based on the needs of your organization. Oracle does not guarantee that the information included here will work as intended within your environment.
This scenario demonstrates how you can use sourcing optimization and constraints. The objective is to demonstrate how the system can determine an ideal award based on bid information as well as business policies that are associated to the event. Our scenario will use this criteria:
Event US001-COMPUTERS – Computer Equipment Purchase has been setup in the demonstration environment to use as an optimization example. It's a four line event that also has one user defined line group as well as bidder-defined groups. Optimization will look at the line group pricing, cost or score and factor that into the award recommendation. Three event constraints associated with the event:
Credit Score – bidders with a credit score of 25 or less may receive a maximum of 25 percent of the total event award
Minority Owned Business – at least 15 percent of the total event award must be awarded to minority owned business bidders.
Past Experience – only 20 percent of the total event award may be awarded to bidders with a poor or below average rating.
In this scenario, East Bay Office has the best overall price and cost. However, East Bay has an unknown or poor past experience, and therefore may only receive a maximum of 25 percent of the entire award.
Optimization has already been run by score and cost so in this scenario, run optimization by price, and then compare all three optimization results.
Analyze the Event
Access the Analyze Event page (Strategic Sourcing, Maintain Events, Analyze Events).
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Analyze Events – Analyze Total page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.

On the Analyze Total page, there is a total bid amount (price), total bid cost (which includes cost contributions from bid factors) and the total event score.
There are 4 bids on this event. East Bay has a poor or unknown experience. As there is a business constraint that limits the amount that can be awarded to poor or unknown bidders to 20 percent of the total award; therefore East Bay can only receive a maximum of 20 percent of the total award.
East Bay has the lowest total price and lowest total cost. So, on optimization by cost or price, even though East Bay has the lowest price and cost, they will only receive 20 percent of the award. This is within the 20% maximum award objective. On this event, Midtown had the best cost and score but East Bay had the lowest price. This was used by optimization to determine the ideal award.
Reviewing Constraints
Click the Review Constraints link on the Award Details page.
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Analyze Events – Review Constraints page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.

This page shows the business policies and constraints associated with the event. You can associate constraints to the overall event as well as individual lines.
Click the Get Progress to Date button to calculate the progress against the defined constraints. This will show the amount and percent awarded for each constraint to date.
Notice that $233,730 has been awarded to minority bidders so far. Likewise, also see $233,730 has been awarded to Poor/Unknown bidders. The minority award percentage is 25% which exceeds the minimum requirement of 20%.
Recommending Awards
Click the Recommend Award link from the Go To menu.
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Request Parameters page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
Now, run optimization by price and compare the results to the cost and score optimization runs.
Enter a recommendation name (you can enter any name). You have the option to run optimization for a selected line, but in this example, run optimization for the entire event. Select what to base the optimization on – price, cost, or score. Select price, since optimization has already been run by cost and score. Click the Solve button and wait for the system to return a message that optimization has completed.
When optimization runs, it factors several things in determining an award:
Lowest total price, lowest total cost, or highest total score - Depending on how optimization was run (price, cost, score).
Minimum/maximum bid quantities – A bidder cannot be awarded more quantity than they bid.
Will take price breaks into consideration.
Business constraints – factors in business policies and constraints when determining the award.
Optimization uses the constraint priority to determine the award. Higher priority constraints are met first. If a mandatory constraint cannot be met, the system will alert the user that a mandatory constraint was violated. For example, if a mandatory constraint requires 20 percent of business to be awarded to minority bidders, but no minority bidders bid on the event, optimization will still produce an award recommendation, but the system will alert the user that a mandatory constraint was violated. Once optimization completes, a message displays at the bottom of the page. Click the Return button.
Reviewing Award Recommendations
Select the Review Optimization link in the Go To drop-down list on the Analyze Events page.
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Review Award Recommendation page (1 of 3). You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.

This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Review Award Recommendation page (2 of 3). You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.

This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Review Award Recommendation page (3 of 3). You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.

Click the View All link on the Award Recommendation Results page to see the award recommendations by price, cost, and score. In this example, the total award cost varies based on the optimization type. The cost is lowest based on optimizing by price and highest based on score. Notice that the award amounts to each bidder vary by the optimization run.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Total Award Cost |
This is the total amount of the recommended award. |
Total Awarded Price |
This is the award amount to each bidder. The sum of the bidder award price equals the total award cost. |
Reviewing the Award Constraint Summary
Click the Review Award Constraint Summary link on the Review Award Recommendation page.
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Review Award Constraint Summary page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.

Click the Calculate button for the CREDITSCORE constraint. This will calculate how much the constraint is costing the organization. The system will re-run optimization without this constraint and then compare the total award amount to the total award amount with the constraint applied to determine a cost. Notice that $5,466 could be saved if this constraint was not required.
You can see the Recommended Result compared to the Progress to Date which shows the amount and percent.
Reviewing Award by Bidders
Access the Award Recommendation Results page by clicking the Office Depot bidder link from the Review Award Recommendation page.
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Award Recommendation Results page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.

The award recommendation results shows the recommended award quantity and price for each bidder
Reviewing Recommendations by Line
Access the Review Recommendation by Line page by clicking the View Recommendations by Line link from the Analyze Events pages.
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Review Recommendations by Line page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
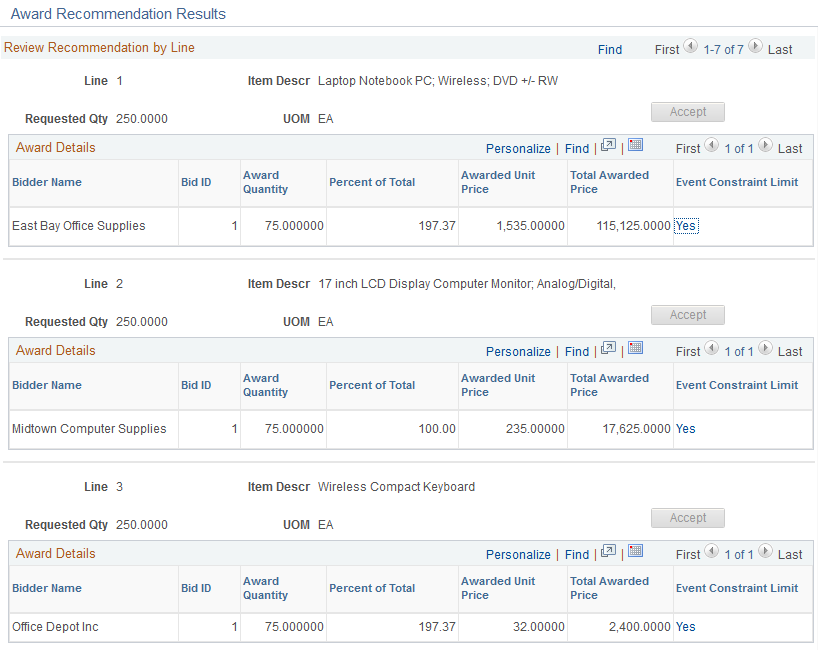
The Review Recommendation by Line page shows the recommended award by line item. The Event Constraint limit indicates whether one or more constraints impacted the recommended award.
Viewing the Award Details
Access the Award Details page after clicking the Accept Recommendation button on the Review Award Recommendation page and then clicking the Save button.
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Award Details page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.

You can post the awards for each bidder.
Viewing Updated Awards
Click the Review Constraints link from the Award Details page.
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Review Constraints page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.

Click the Get Progress to Date button to view the updated award amount and percent.