Setting Up a Duration Option
To set up a calculation method, use the Duration (DURATION_OPTIONS) component.
|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Usage |
|---|---|---|
|
PA_AGECALC_PERIOD |
Choose a calculation method and set parameters associated with the method. |
|
|
PA_AGECALC_PARMS |
Set up a raw date to decimal date conversion method. |
Use the Calculation Options page (PA_AGECALC_PERIOD) to choose a calculation method and set parameters associated with the method.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Calculation Options page.
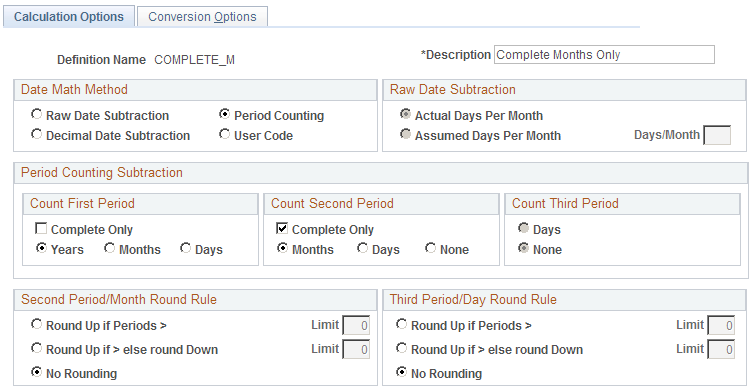
Date Math Method
Select one of the following date math methods:
Raw Date Subtraction
Also select options in the Raw Date Subtraction, Second Period/Month Round Rule, and Third Period/Day Round Rule group boxes.
Period Counting
Also select options in the Period Counting Subtraction, Second Period/Month Round Rule, and Third Period/Day Round Rule group boxes.
Decimal Date Subtraction
User Code
Raw Date Subtraction
Convert months to days in order to perform subtractions when the earlier date has fewer days than the later date. For example:
1990/11/06- 1977/12/13Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Actual Days Per Month |
The number of days depends on the month. In the example, the tenth month (October) is the most recent full month that you can convert to days. October has 31 days, so 90/11/06 becomes 90/10/37. |
Assumed Days Per Month |
Enter a fixed number of days in the Days/Month field. The system uses this number for every month. |
Period Counting
If you choose the period counting method, you need to indicate the period or periods to count. You can count either one type of period, such as years, or you can count successively shorter periods, such as years and then months.
You can define up to three types of counting periods: years, months, and days. You can use any combination of these periods, but you must use them in order: from longest to shortest.
Although you may not want to express shorter units in the final count, you may still want to count them for rounding purposes. For example, if you are only going to count years, but you are going to round by months, you also need to count months.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Count First Period |
Select the longest period. |
Count Second Period |
Select the next longest period, or select None if you do not use the second period. |
Count Third Period |
Select the third longest period, or select None if you do not use the third period. |
Complete Only |
When you select this option, the system does not count any shorter periods. If you do not use all three counting periods, select this check box in the shortest period that you do count. |
Second Period/Month Round Rule and Third Period/Day Round Rule
If you use raw date subtraction or period counting (both based on raw dates), you can choose to round the dates before calculating a duration. You specify the rounding options in the Second Period/Month Round Rule and Third Period/Day Round Rule group boxes.
You use these group boxes as follows:
For raw date subtraction, you specify the month round rule in the Second Period/Month Round Rule group box and the day round rule in the Third Period/Day Round Rule group box.
For period counting, you specify the second period in the Second Period/Month Round Rule group box and the third period in the Third Period/Day Round Rule group box.
For example, to round days to months when using raw date subtraction, use the day round rule. To round days to months when using period counting, first check which period counts days. If the second period counts days, use the second period rounding rule, even though the label is Month Round Rule.
Use the options in these group boxes as follows:
To round up only, select Round Up if Periods > and enter the threshold in the Limit field. For example, you could round days up to a full month after 25 days.
To round up or down, choose Round Up if Periods > … Else Round Down and enter the number of periods in the Limit field.
If you do not want to round at all, select No Rounding
Note: These options round the dates that are the duration endpoints. That is, the dates are rounded before the system performs raw date subtraction or period counting. To round the duration itself, or to round the endpoints before performing decimal date subtraction, use the Month Conversion Rules and Year Conversion Rules on the Conversion Options page.
Use the Conversion Options page (PA_AGECALC_PARMS) to set up a raw date to decimal date conversion method.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Conversion Options page.
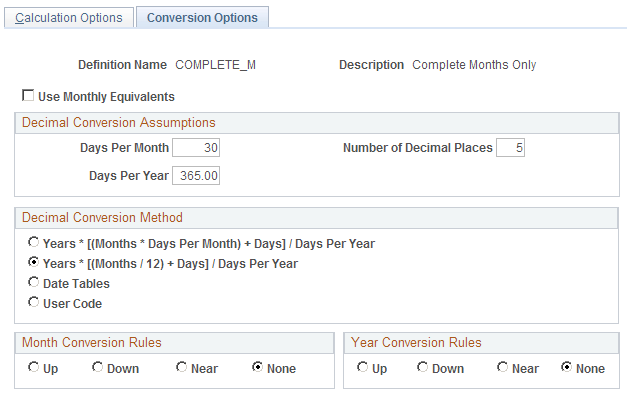
Unless your source dates are decimal dates, the system converts the raw dates or durations to decimal dates. If you use raw date subtraction or period counting, the system converts the duration after performing the date math. If you use decimal date subtraction, the system converts the endpoints before performing the subtraction.
When you convert raw dates and durations to decimal equivalents, you have to convert months and days to partial years. There are a number of ways to do this. Specify your conversion options in the Decimal Conversion Assumptions and Decimal Conversion Method group boxes.
Decimal Conversion Assumptions
Specify your assumptions about the number of days in a month and in a year. The system uses these values to convert dates to decimal values.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Days Per Month |
Specify a value if you select the decimal conversion method Yrs + ((Months * Days/Mth) + Days) / (Days/Yr). |
Days Per Year |
Specify a value if you select a decimal conversion method other than User Code. |
Number of Decimal Places |
Throughout the conversion process, decimals are rounded to the number of places you specify here. |
Decimal Conversion Method
Select one of the following options to indicate how to convert dates into decimal values:
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Yrs + [(Months * Days/Mth) + Days] / (Days/Yr) |
Convert the months to days, add these days to the specified days, then convert the total days to years to find the decimal portion of the duration. Add this to the years to get the total duration. In this case, you must specify the assumed days in Days Per Month and Days Per Year. |
Yrs + [(Months/12) + Days]/(Days/Yr) |
Convert the months to decimal years, then convert the days to decimal years. Add these together to find the decimal portion of the duration. Add this to the years to find the total duration. In this case, you must specify the assumed days in Days Per Year. The system knows there are twelve months per year; you do not need to enter this information. |
Date Tables |
Add the years plus the actual number of remaining days converted to years. The formula is: Years + (actual days / days per year) In this case, you have to specify the assumed days in Days Per Year. The number of actual days depends on the time being measured. For a duration from 4/15/1994 to 8/16/1998, the actual days are the days from 4/16/1998 to 8/16/1998. |
User Code |
Convert dates as specified in your own user code. |
Using Decimal Conversion Methods
This section provides examples of the decimal conversion methods. These examples convert the "raw" duration five years, six months and six days to a decimal value. The process is similar to that of converting a raw date to a decimal before performing decimal date subtraction.
For the examples, assume 30 days per month, 365 days per year, and four decimal places.
Years + [(Months * Days per Month) + Days ]/ (Days per Year)
Years + (months converted to days + days) converted to partial years Years = 5 Months converted to days = 6 * 30 = 180 Days = 6 Total days = (180 + 6) = 186 Total Days converted to partial years = 186 / 365 = 0.5096 Result: 5.5096Years + [ Months / 12 ] + [ Days/ Days per Year]
Years + months converted to partial years + days converted to partial years Years = 5 Months converted to partial years = 6 / 12 = .5000 Days converted to partial years = 6 / 365 = .0164 Result: 5.5164Date Tables: Years + (Actual Days)
To find the actual days value of six months and six days, you need to know which six months and six days they are. Assume this portion of the duration starts on January 1, 1992. This means the months are January through June, and the six days are then the first six days of July. Add 31 (January), 29 (February in a leap year), 31 (March), 30 (April), 31 (May), and 30 (June), and 6 (the remaining days) for a final value of 188. This is converted to years using the actual number of days in this year: 366 because of the leap year.
Years+ actual days converted to partial years [always using 365 days/year]Years = 5Actual days converted to partial years = 188 / 366 = .5137Result: 5.5137
Month Conversion Rules and Year Conversion Rules
If you use decimal date subtraction, the system uses the Month Conversion Rules and Year Conversion Rules settings to round the duration endpoints (which are decimal values) before the subtraction that determines the duration. You cannot further round the final result.
If you use raw date subtraction or period counting, the system uses the Month Conversion Rules and Year Conversion Rules settings to round the final duration result.
The settings work the same regardless of which value you're rounding. Select Up to round to the next month or year, Down to round to the previous month or year, or Near to round to the closer of the two rounded values. Select None to avoid rounding altogether.
Note: For decimal date subtraction, these rounding options operate on the decimal date endpoints before the system calculates the duration. For raw date subtraction or period counting, these rounding options operate on the duration itself. To round the endpoints for raw date or period counting methods, use the rounding rules on the Calculation Options page. You cannot round a duration produced by decimal date subtraction.
Using Monthly Equivalents
A duration produces a primary result, a decimal value representing the entire duration, and six secondary results (called results 2-7). The secondary results are:
|
Result Number |
Result |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
2 |
Round the duration to whole months. |
|
|
3 |
Round the duration to whole years. |
|
|
4 |
Express the total duration as whole months. |
6.25 (6 years, 3 months) becomes 75 months. Any remaining days are rounded. |
|
5 |
Disregard whole years. |
6.25 becomes just .25. |
|
6 |
Disregard whole years, and express the remainder as whole months. |
6 years, 3 months becomes just 3 months. |
|
7 |
Disregard whole years and express the remainder as days. |
5 years, 3 months becomes approximately 91 days (based on days per year assumption). |
In this table:
Results 2, 4, and 6 deal in whole months.
This means that any remaining days are rounded.
Results 3, 5, and 7 do not necessarily round days.
If you select the Use Monthly Equivalents check box on the Conversion Options page, these values are rounded according to the settings in the Month Conversion Rules and Year Conversion Rules group boxes on that page.
The Month Conversion Rules settings apply to the results that round days.
This is all three results if you use monthly equivalents.
You can round months and years up, down, or near, or you can choose not to round.
Note: If you do not use the secondary duration results, disregard the Use Monthly Equivalents field.
The following table provides examples of the seven results of a duration calculation. It shows the effect of selecting the Use Monthly Equivalents check box. The examples assume that both the monthly and yearly rounding options are set to Near and that there are 365 days per year.
|
Name |
Description |
Use Monthly Equivalents Selected? |
Example |
|---|---|---|---|
|
AGE |
Use decimal, including partial years. |
No (never rounded) |
65.497 years |
|
AGE2 |
Round AGE to the nearest whole month. |
No (always rounded) |
65.500 years |
|
AGE3 |
Round AGE or AGE2 to whole years. |
Yes Flag off: round AGE. Flag on: round AGE2. |
65 years
66 years |
|
AGE4 |
Express AGE2 in months. |
No (always rounded) |
65.500 * 12 = 786 months |
|
AGE5 |
Extract decimal from AGE or AGE2. |
Yes Flag off: AGE decimal. Flag on: AGE2 decimal. |
.497 years remainder
.500 years remainder |
|
AGE6 |
Extract decimal from AGE2 and express as months. |
No (always rounded) |
.500 * 12 = 6 months remainder |
|
AGE7 |
Express AGE5 as (whole) days. |
Flag off for AGE5 Flag on for AGE5 |
.497 * 365 = 181 days remainder .500 * 365 = 182 days remainder |
To reference the secondary results of a duration, add the appropriate numeric suffix to the duration name. These numbers correspond to the result numbers shown in the previous table—for example, AGE2 references result 2 for AGE.