2.19.4 Equipment Identity Register
Figure 2-74 EIR solution architecture.

EIR is a DSR Application on DA MP and STP MP. Screening supported for IMEI Individual or Range (with possible IMSI mapping), TAC (provisioned as IMEI range), SVN, IMSI range, Status override possible with IMSI association. EIR only provides the device status information.
The UDR NO provides the functionality of the Equipment Identity Register (EIR) database to the DSR. The database stores white, gray, and black lists of IMEI numbers.
- Supports an internal query interface towards DA-MP and STP MP for vEIR.
- Provides options of provisioning GUI as well as Bulk provisioning.
- Provides FTP and SFTP based provisioning. Provisioning interfaces supported are REST/SOAP/XML/LDAP.
Data Types that are supported at EIR data base:
IMEI
- 100M Individual entries.
- 10M IMEI range/TAC.
- 1 IMEI up to 10 IMSI.
- SVN supported
- IMSI Range (1000)
- To support whitelisting special subscribers.
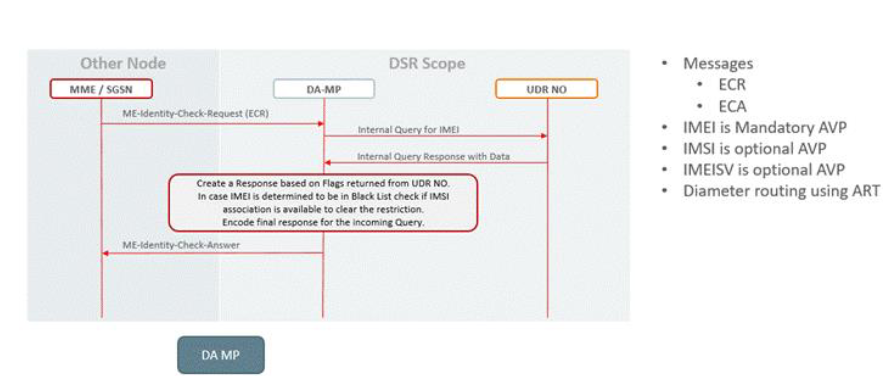
Figure 2-75 SS7 EIR call flow
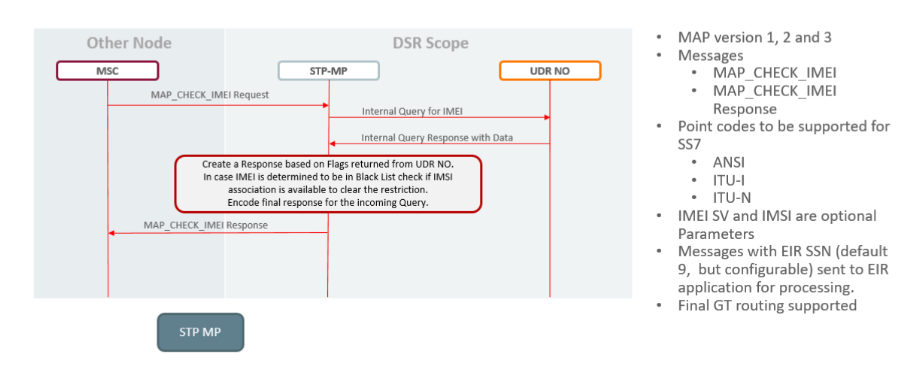
Figure 2-76 S13 EIR Call Flow
EIR leverages DSR architecture for Measurements and Alarms, Backup and restore, OAM and Congestion Control.
ANSI ITU Conversion
- Cross domain(ANSI/ITU) signaling can be MTP routed or GT routed.
- Cross domain conversion combination supported across domains are:
- ANSI, ITU-I(S) ,ITU-N(S)
- ITU-N24, ITU-I(S)
- Based on message type, ANSI/ITU Conversion supports UDT, XUDT, UDTS and XUDTS messages.
- The feature provides SCCP management (SCMG) across network type boundaries.
- This feature also provide support of China Point Code SCCP conversions to ITU-International.
- Without the GT Modification feature, VSTP performs the following translations on a per GTA basis: DPC and DPCSSN.
- Below table describes the fields modified within the Called party portion of the SCCP data of a MSU.
- The GTT Modification feature allows modification of all the fields of SCCP layer.
- The GTT Modification feature is activated by default that is no special activation process is required.
- The GTT Modification allows users to configure the Called Party / Calling Party modification data corresponding to each Global Title Address entry.
Table 2-19 Global Title Address entry
| XLAT | Fields Modified | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DPC | OPC | DPC | RI | |
| DPCSSN | OPC | DPC | RI | SSN |
MTP Screening
- MTP Screening feature provides a first level of security check for VSTP.
- The MTP Screening feature examines the contents of a Message Signaling Unit (MSU) attempting to enter the VSTP against predefined criteria in the VSTP database to determine if the MSU should be allowed to enter.
- When a message comes on a linkset, the associated screen set will be looked up. Based on the NSFI and rule group name associated with screen set, the rule in the corresponding rule group will be looked up.
- If rule lookup is successful, then message will go for further screening level based on NSFI and the next screen rule group name associated with it.
- If rule lookup does not find a match, then:
- In case of BLKOPC/BLKDPC rule type, default rule for that rule group will be looked up and based on NSFI and next screen rule group name associated with default rule further screening performed.
- In case of OPC/SIO/DPC/AFTDSTN rule type, FAIL NSFI will be performed.
- The final result of MTP screening should always be either FAIL or
STOP.
- n case of FAIL, the message will be discarded.
- In case of STOP, the message will go for further processing in VSTP.
Multiple PC
- This feature proposes to start support for Secondary Point Codes and increase the number of supported Capability point codes.
- Multiple Point Code (MPC) feature shall allow the vSTP to add the support of Secondary Point Codes (SPCs) in addition to the true point codes used by the vSTP in any of the three domains ANSI, ITUN/ITUN-Spare (14-bit or 24-bit) and ITUI/ITUI-Spare.
- This is a different concept from capability point codes. The provisioning and routing will use secondary point codes as if they were the actual point code of the vSTP. SPCs are supported for any type of link (A, B, C, D, so on).
- In addition to the one True Point Code (TPC) already supported for each of the ANSI, ITU-N (14-bit or 24-bit) and ITU-Idomains, the vSTP support a pool of Secondary Point Codes (SPC), each of which may be assigned as either ANSI,ITUI/ITUI-Spare, 14-bit ITUN/ITUN-Spare, or 24-bit ITUN.
- In addition to the SPCs this feature also recommends increasing the number of CPCs supported by the vSTP.
- Currently only 1 CPC is supported. This number shall be increased to 100. The increase CPC would allow the vSTP to support more applications on the same node and allow route-on-gt functionality for routing to various application.
- MPC feature creates the framework to allow provisioning and usage of SPCs in vSTP. This change shall primary affect the provisioning and routing algorithms. In addition to the SPC’s the CPC shall also be increased.
TUI-Spare/ITUN-Spare
- The vSTP to fully support ITU National Spare and ITU International Spare by providing a new PC sub type named Spare.
- ITUN_S and ITUI_S indicates a Spare point code. Spare point codes only apply to ITU-I and ITU-N point code types.
Figure 2-77 ITUI-Spare/ITUN-Spare
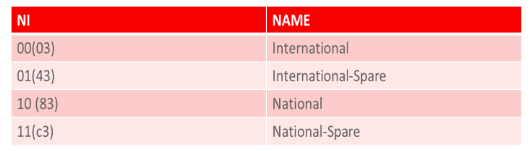
- The subservice field contains the network indicator and two spare bits. The network indicator is used by signaling message handling function.
- The vSTP currently provides full supportfor four types of point codes (PC) – ANSI, ITU-National (NI=10binary ), ITU-National 24-bit, andITU-International (NI=00 binary ). ITU NationalSpare PCs (NI=11 binary ) and ITU International Spare(NI= 01 binary) PCs can be primarily supported.
- If the Spare PC feature is enabled then vSTP will validate the NI value of incoming message on designated linkset . If NI value matches then link will be mark available otherwise message will be discarded.
Loop Detection
- The Loop Detection Feature design is both simple and flexible by using a Loopset table consisting of up to 12 pointcodes (OPCs) and comparing only the OPC of an MSU on a per GTT Translation basis requires the GTT translation to have a loopset provisioned.
- No assumptions/rules are imposed, everything is provisional whether concurring or opposite direction defines a ”Loop”,whether Customer using Capability Point Codes or True or Secondary Point Codes, which node is Adjacent and which is not, which node is mate and which is not.
- Will detect looping on “multi-hop” translations and “single-hop” ones.
- Allows provisioning “Loops” for each Global Title Translation (GTA record).
- Allows provisioning/re-using same Point Codes in different LoopSets.
- Allows re-using same LoopSets for different Global Title Translations (GTA records).
- Allows provisioning “Loops” for each GTT Action record.
- Allows re-using same LoopSets for different GTT Action records.
IDP Query
- Message flow for INPQ Solution on vSTP.
- MSC will send INPQ request to vSTP-MP over SS7 links.
- vSTP-MP will decode and verify the INPQ Message.
- vSTP-MP will decode and verify the INPQ Message.
- Check whether INPQ message has valid request (the requestedInfo parameter must be MNP Requested Info and/or Location Information).
- Decode the MSISDN parameter from the Subscriber Identity parameter.
- Condition the MSISDN to the international format.
- vSTP-MP will query the UDR NOAM for conditional MSISDN DB.
- UDR NOAM will look up MSISDN DB and will send response to the vSTP-MP.
- Determine whether the lookup is considered to be successful based on provisioned options. If yes, use entity information to encode INPQ ACK response and route the response to the originator. If no, send INPQ NACK response with appropriate error code.
Map based Routing
TOBR (TCAP Opcode Based Routing).
- If the message/package type is NOT one of those mentioned in the list above slide, VSTP will treat it as an unknown message type and will not proceed with the decoding.
- As part of TOBR feature, VSTP will attempt to decode TCAP portion of all UDT/UDTS/Unsegmented XUDT/Unsegmented XUDTS queries coming to SCCP layer for GTT.
- If decoding fails, the message will still undergo GTT using some default values for the TCAP data th at denote their absence in the message.
- ACN will be used for all supported ITU TCAP messages except ABORT. No attempt to retrieve ACN will be made for Abort messages. All other supported messages may have a Dialog portion containing Dialogue Request / Unidirectional Dialogue/ Dialogue Response PDU, from which the ACN will be retrieved. If no Dialog portion is detected, then ACN is assumed to be NONE.
- TOBR will attempt to find Operation Code (Opcode) in all supported ITU TCAP messages except ABORT. These messages must contain Invoke or Return Result (Last or Not Last) as the first component. If not, Opcode is assumed to be NONE.
- TOBR will attempt to find Operation Family and Specifier in all supported ANSI TCAP messages (except ABORT) containing an INVOKE component. For all other messages, Family and Opcode are assumed to be NONE.
- When GTT mode is “FLOBR CDPA”, CDPA fields in the MSU shall be used for GTT selector search and GTT set shall be taken from “CDPA GTT SET Name” configured in the selector entry.
- When GTT mode is “FLOBR CGPA”, CGPA fields in the MSU shall be used for GTT selector search and GTT set shall be taken from “CGPA GTT SET Name” configured in the selector entry.
- When GTT hierarchy is “FLOBR CDPA and FLOBR CGPA”, GTT selectors shall be searched as defined in 1. If no selector match is found or CDPA GTTSET is not provisioned, GTT selectors shall be searched as defined in 2.
- When GTT hierarchy is “FLOBR CGPA and FLOBR CDPA”, GTT selectors shall be searched as defined in 2. If no selector match is found or CGPA GTTSET is not provisioned, GTT selectors shall be searched as defined in 1.
- If GTT selectors are not found as specified in 1, 2, 3 or 4 then VSTP will consider this as translation failure.
- With FLOBR, the user can provision a fallback option for each translation that
tells us how to route an MSU under the following conditions:
- Routing when subsequent search failed in FLOBR.
- Routing when same GTT set name is referred more than once.
- Limiting the number of database searches to 7 for FLOBR.
- Under the above conditions:
- When fallback option in last matched translation is set to “No”, the GTT will fail and MSU shall be discarded.
- When fallback option in last matched translation is set to “Yes”, the GTT will be performed based on that matched entry.
MBR (MAP Based Routing)
MBR provides VSTP with the ability to route messages based on their 'MAP Components'. This can be done by adding5 new GTT set types. These new GTT set types will be linked by OPCODE set type or any of them.
- IMSI
- MSISDN
- VLRNB
- SMRPOA
- SMRPDA
The GTT Sets of the types mentioned above are allowed to be provisioned ONLY in GTA entries from a GTT Set of the type OPCODE or any of the other GTT Set types supported by this feature.
Only TCAP Package Types BEGIN, CONTINUE & END are going to be supported for MAP based routing, so “optsn”with one of the MAP GTT Set types (listed above) are allowed to be provisioned only for TOBR GTA entries that have“pkgtype” as BGN or CNT or END.