Setting Up Aging
|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Usage |
|---|---|---|
|
AGING_TABLE |
Define aging IDs that describe how the system ages open items. |
To set up aging, use the Aging component (AGING_TABLE).
Aging IDs define how the Aging process and aging reports age open items. They also enable you to define unique rules for aging deduction, disputed, collection, and doubtful items, and items paid by drafts with an accepted or remitted status.
Note: For readability, the phrase “items paid by drafts with an accepted or remitted status” may be shortened in this topic to “items paid by drafts”; however, please note that the system ages only items paid by drafts with an accepted or remitted status.
When you age deduction, disputed, collection, and doubtful items as well as items paid by drafts, you choose to do one of the following:
Age them like normal open items and place them in a category based on the age of the item.
Define a separate category for either all disputed, deduction, collection, or doubtful items, or items paid by drafts, regardless of their age, or create a separate category for each type of item.
This categorization is useful when you do not want these item types aged in a date range, but you want to see the total aged amount for these types of items separately.
You can also set up separate categories based on the dispute or deduction reason, or the collection code.
Exclude deduction, dispute, collection, or doubtful items, or items paid by drafts, from aging.
You have two options:
Exclude all deduction, disputed, collection, or doubtful items, or items paid by drafts with an accepted or remitted status, aged using the aging ID or any combination of these item types.
For example, you can exclude deduction and disputed items, but age collection items normally.
Exclude deduction and disputed items by their reason or collection items by their collection codes.
For example, you can exclude authorized deductions that are associated with a product discount, but age the remaining deductions normally or in a deduction category.
The Aging process uses the aging ID assigned to the bill to customer first, then defined at the business unit level to age items. The aging reports use the aging ID that you enter on the run control page to age the items on the reports. The following describes in detail how the system processes the items and how the aging ID is obtained:
During the aging process, the system processes all open items from the business unit entered on the run control page.
The system checks for an aging ID defined at the customer level for each SetID/customer ID that has open items entered in the business unit on the run control page. If there is a customer-level aging ID, items of this business unit/SetID/customer ID combination will be processed by this aging ID.
If this SetID/customer ID does not have an aging ID, then the system uses the aging ID defined at the business unit level.
See the General Information - Bill To Options Page for information about setting up the customer-level aging ID. See the Receivables Options - General 1 Page for information about setting up the business unit–level aging ID.
Use the Aging page (AGING_TABLE) to define aging IDs that describe how the system ages open items.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Aging page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
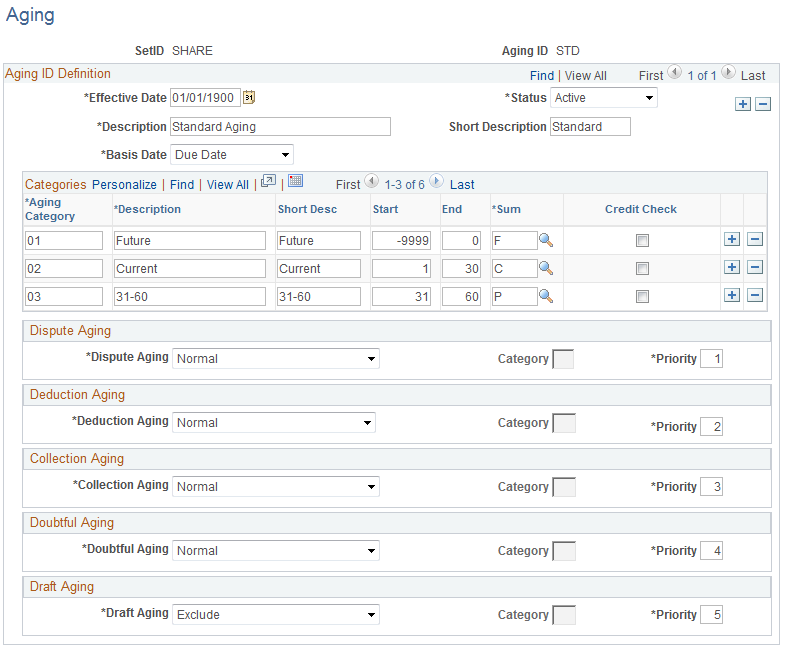
When you run the aging reports or view aging information on inquiry pages, the system uses the aging categories that you define to determine in which bucket to place an item. Each category represents an age range for the items. For example, suppose that you run an aging report using the 30–60 aging ID, as shown in the Aging page. You use an as of date of March 1. If you created an item on January 15, the system puts the item in the 31–60 category, which indicates the item is between 31 and 60 days old. If you defined unique categories for deduction, disputed, or collection items, the system places items flagged as deductions, in dispute, or in collection in the appropriate category.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Basis Date |
Select the type of date for aging open items. Values are: As of Date: A user-defined date for aging items. Acctg Date (accounting date): The accounting date for the item. Item Date: Usually the invoice date, but it may differ by implementation. Due Date: The due date assigned to the item. |
Aging Category and Description |
Enter an ID for the category and the description that you use to identify the categories on the reports and inquiry pages. |
Start and End |
Enter the number of days that define the beginning and ending of the category. Use –9999 as the start day for one category and 9999 as the end day for one category. The start date for each category must always be one day greater than the last end day for the previous category with one exception. If you are defining a separate category for disputed, deduction, or collection items, the start and end days is always 9999. |
Sum (summarization) |
Select a value that links the aging category to one of these summarization categories: Current Due, Past Due, Future Due, or Other. |
Credit Check |
Select if the aging category should be considered in the credit checking performed by PeopleSoft Order Management. Upon running the aging process, the system stores the aging total of selected categories with credit check both by business unit and customer ID, and by business unit, customer ID, and subcustomer. |
Dispute Aging and Category |
Specify how the system ages disputed items. Values are: Categorize: Select if you have created a unique category for disputed items and enter the category ID in the Category field. You can use the same category ID for all types of items or create a unique category for the different types of items. Exclude: Select if you do not want to age all disputed items. Normal: Select to age items normally by the basis date. Vary by Disp Status: Select to age disputed items based on the aging method for their dispute reason on the Dispute Reason page. |
Deduction Aging and Category |
Specify how the system ages deduction items. Values are: Categorize: Select if you have created a unique category for deduction items and enter the category ID in the Category field. You can use the same category ID for all types of items or create a unique category for the different types of items. Exclude: Select if you do not want to age all deduction items. Normal: Select to age items normally by the basis date. Vary by Ded Status: Select to age deduction items based on the aging method for their deduction reason on the Deduction Reason page. |
Collection Aging and Category |
Specify how the system ages collection items. Values are: Categorize: Select if you have created a unique category for collection items and enter the category ID in the Category field. You can use the same category ID for all types of items or create a unique category for the different types of items. Exclude: Select if you do not want to age all collection items. Normal: Select to age items normally by the basis date. Vary by Coll Status: Select to age collection items based on the aging method for their collection code on the Collection Code page. |
Doubtful Aging and Category |
Specify how the system ages doubtful items. Values are: Categorize: Select if you have created a unique category for doubtful items and enter the category ID in the Category field. You can use the same category ID for all types of items or create a unique category for the different types of items. Exclude: Select if you do not want to age all doubtful items. Normal: Select to age items normally by the basis date. |
Draft Aging and Category |
Specify how the system ages draft items. The system includes closed items paid by draft with a Draft Status of Accepted or Remitted in the aging process and aging reports because, although these items are closed, the company has not received funds for them yet while the draft is accepted or remitted. Values are: Categorize: Select if you have created a unique category for draft items and enter the category ID in the Category field. You can use the same category ID for all types of items or create a unique category for the different types of items. Exclude: Select if you do not want to age draft items. This is the default value. Normal: Select to age items normally by the basis date. Draft items will be categorized in the regular categories based on their age. |
Priority |
Enter a number to indicate which rule to use for an item that is marked with more than one dispute, deduction, collection, doubtful, or draft flag. An item can be aged based on only one of the reason codes. For example, if an item is a disputed item and in collection, the priority number indicates whether the system should use the disputed aging rule or the collection aging rule. |
The aging methods for individual dispute reasons, deduction reasons, and collections codes are to age normally, use a specific category, or be excluded from aging.
Note: Use the Entry Type page to place all items for an entry type in a specific aging category.