Performing Vendor Managed Inventory Processes
|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Usage |
|---|---|---|
|
REPLEN_PARAM_VMI |
Define and calculate replenishment parameters for the Process VMI Replenishment process. |
|
|
IN_VMI_RPLN_RQST |
Create replenishment requests for VMI business units. |
|
|
RPLN_RQST_INVMI2 |
Review and delete replenishment requests for VMI business units. |
This section discusses VMI Processes, and which transactions cannot be performed.
VMI processes include:
The fulfillment process.
The receiving process.
The consumption process.
The return process.
The physical and cycle count process.
The EIP process.
The Fulfillment Process
The fulfillment process will process the sales order and the interunit MSR in the source inventory business unit as normal.
When a non-consigned item is reserved, the inventory business unit can send an order acknowledge message (855 EDI) to the customer. This message provides order information and can be used to receive non-consigned items. After the reservation process completes, the VMI manager can review shortages and backorders for consigned and non-consigned items.
When a sales order for a non-consigned item is shipped and depleted, the system performs these tasks:
An interunit ID is assigned to the demand line
A VMI shipment transaction (037) is written to the transaction table (TRANSACTION_INV) for the inventory business unit.
For non-consigned items, this shipment transaction represents the revenue recognition.
The interunit expected receipt EDI message can be sent to the customer, which contains the interunit ID.
When the Deplete On Hand Quantity process runs for the inventory business unit, the auto-putaway process can be initiated to update the item quantities in the VMI business unit.
The order management billing process (OMBILL) selects demand lines for invoicing and sends it to PeopleSoft Billing in order to create an invoice for the customer.
Note: Interunit orders that are created from sales order cannot be canceled by using the Cancel InterUnit Transfers page. Instead, you must receive the interunit order, then create a return material authorization against the order, and then receive the RMA.
When an interunit MSR for a consigned item is shipped and depleted, the system performs these tasks:
An interunit ID is assigned to the demand line.
An interunit transfer shipment transaction (031) is written to the transaction table (TRANSACTION_INV) for the inventory business unit.
PeopleSoft Cost Management credits the inventory account and debits the cost of goods sold account.
An interunit expected receipt EDI message can be sent to the customer, which contains the interunit ID.
When the Deplete On Hand Quantity process runs for the inventory business unit, the auto-putaway process can be initiated to update the item quantities in the VMI business unit.
Note: Items cannot be pegged in a VMI business unit.
The Receiving Process
The customer has the option of providing receipt confirmation for consigned goods.
If the customer provides receipt feedback, they use the interunit receipt IP. With this message, the customer provides lot, serial, and container information, if being used, for all items received.
If the customer does not provide receipt feedback, the auto-putaway process is initiated from the Deplete On-Hand Quantity process. When the auto-putaway process runs for the VMI business unit, an interunit transfer receipt transaction (022) is written to the transaction table (TRANSACTION_INV) for the VMI business unit. The Putaway process will allow items from an owned location (from the inventory business unit) to be placed into a non-owned location, if the destination business unit is a VMI business unit.
The Goods Consigned at Customer check box on the VMI Options page indicates whether a customer who is receiving non-consigned items will report lot IDs, serial IDs, and staged dates on consumption transactions. If you elect to not reports these inventory identifiers, the items are removed from inventory of a FIFO basis.
For lot controlled items, consumption occurs in the order of lot creation date.
For serial controlled items, consumption occurs in the order of serial ID.
For staged date controlled items, consumption occurs in the order of the date.
The Consumption Process
The customer communicates consumption one of two ways:
The customer sends the item balance message to update on-hand quantities in the VMI business unit. The item balance in the message is compared to the item balance in the VMI business unit.
If the item balance is higher than the VMI business unit balance, a User Adjustment (050) transaction is created.
If the item balance is lower than the VMI business unit balance, a VMI Consumption (038) transaction is created.
The customer sends a point of sale message or adjustment transaction to the VMI business unit, which creates a VMI Consumption (038) transaction.
All transactions are written to the transaction table (TRANSACTION_INV). The Create VMI Billing-Only Order process (IN_VMI_BILL) reads the transaction table and creates a billing-only sales order for all 038 transactions. A billing-only flag is located on the sales order header. The order management business unit is determined by associating it with the customer. The bill-only sales order creates an invoice in the billing business unit that is associated with the order management business unit, which is sent to the customer for the items consumed.
The quantity on-hand is reduced in the VMI business unit when the transaction is processed.
When a non-consigned item is consumed at the customer site, only the quantity on-hand in the VMI business unit is updated.
The Return Process
The customer can return consigned items and non-consigned items to the supplying inventory business unit.
If the item is non-consigned, the VMI manager creates a PeopleSoft Order Management return material authorization (RMA) from the VMI business unit, to track the return of the item. The VMI manager also performs an inventory adjustment, which creates a User Adjust (050) transaction in TRANSACTION_INV.
If the item is consigned, the VMI manager creates a PeopleSoft Inventory return material authorization (RMA) for an external customer in the source business unit, to track the shipment and depletion of the item. The customer sends an adjustment transaction message, with an adjust type of A (VMI Return), which creates an adjustment transaction that is not eligible for billing. The adjustment message initiates the Deplete On Hand Quantity process, which depletes the quantity for the VMI business unit. The source business unit can receive against the RMA.
The Physical and Cycle Counting Process
The VMI manager can perform physical and cycle counts at the customer site on a periodic basis for auditing purposes. The VMI manager can then perform the Physical or Cycle Count process on your enterprise system. Negative adjustments will use a VMI Consumption (038) transaction code. If a consigned item has a negative adjustment, the transaction will be eligible for the Create VMI Billing-Only Orders process.
The EIP Process
Inbound data is sent to your enterprise system, from the customer, in order to keep item quantities in sync. Outbound data is sent to the customer in order to notify the customer of expected receipts.
Asynchronous service operations in the PeopleSoft Integration Broker are used to receive item balance, point of sale, receipt, and adjustment information from VMI customers. Process the data by using the appropriate inventory transaction, which can be found from the SCM Integrations menu:
Quantity Adjustment (INPVIADJ) process.
InterUnit Receiving (INPJIURV) process.
VMI Quantity On Hand EIP (VMI_QOH_EIP) process.
If lot, serial, container, or staged date information is within the data and maintained in the VMI business unit, it is stored as received. When goods are not consigned in the inventory location, inventory decreases can be sent to the system without lot or serial number. The EIP process removes items from VMI inventory on a FIFO basis. If the FIFO logic is applied, the data is set to an error status if the transaction quantity is going to cause the inventory balance to be negative.
Note: When both receipt and balance information is received from a customer, procedures should be established to ensure that transactions are processed in the proper order.
Inventory Transactions That Cannot and Should Not be Performed
These transactions are not allowed with a VMI business unit:
Bin-to-bin transfers within a VMI business unit.
InterCompany and Inter general ledger express orders from a VMI business unit or to a VMI business unit.
A VMI business unit cannot be part of a distribution network.
A VMI business unit cannot be part of the procurement setup.
These transactions can be performed, but a warning is received:
Interunit transfers to a VMI business unit for non-consigned items.
The movement of non-consigned items is typically performed by creating a sales order. If items are moved using an interunit transfer, there is no automatic mechanism to bill for the items.
Express issue of items from a VMI business unit.
Movement of items in a VMI business unit represents movement from a customer's inventory. In the case of consigned items, this results in a depletion for which the customer may be billed.
To replenish VMI at the customer site, the VMI manager uses the VMI Replenishment component.
The VMI replenishment process creates a sales order in the order management business unit if the item is not consigned. The non-consigned item sales order has a source code of VMI. When the sales order is shipped, the VMI customer is billed for the items.
The replenishment process creates an interunit MSR in the inventory business unit if the item is consigned. When the interunit MSR is shipped, the VMI business unit is not billed for the items.
The VMI manager can review replenishment quantities and make adjustments prior to creating replenishment requisitions if needed.
The VMI manager has the option to run the Replenishment process and allow the system to immediately generate sales orders and MSRs. Or, the VMI manager can review replenishment requests, remove suggested requests, and then allow the system to generate sales orders and MSRs based on the adjustments.
Follow these steps to replenish VMI:
Run the Calculate VMI Replenishment Parameters process. (Optional)
Review replenishment parameters and make adjustments if necessary.
Run the VMI Replenishment process to create replenishment requests.
Review suggested replenishment requests. (Optional)
Process reviewed requests.
Continue the VMI Replenishment process.
Use the Calculate VMI Replenishment page (REPLEN_PARAM_VMI) to define and calculate replenishment parameters for the Process VMI Replenishment process.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Calculate VMI Replenishment process page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
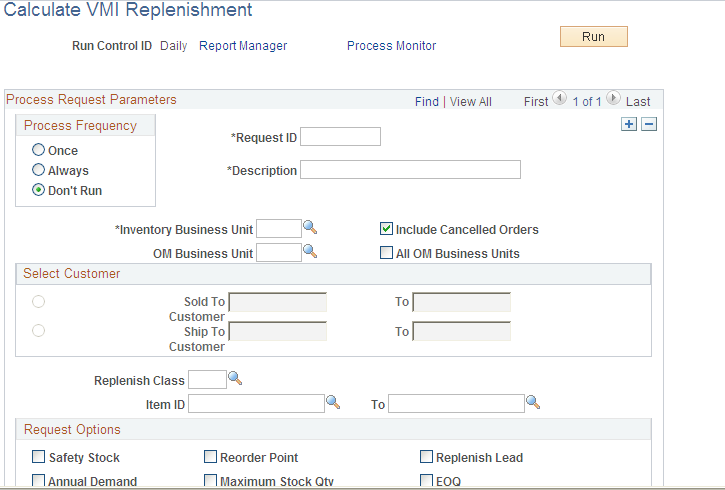
The Calculate VMI Replenishment Parameters process runs similar to the Calculate Replenishment Parameters process with these exceptions:
The replenishment lead-time is manually entered or can be calculated for the Calculate VMI Replenishment Parameters process.
When calculating EOQ for non-consigned items, if there is no cost for an item in the VMI business unit, the process will use the item cost in the source business unit.
It only updates the fields at the ship-to and item level.
Use the Process VMI Replenishment page (IN_VMI_RPLN_RQST) to create replenishment requests for VMI business units.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Process VMI Replenishment page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
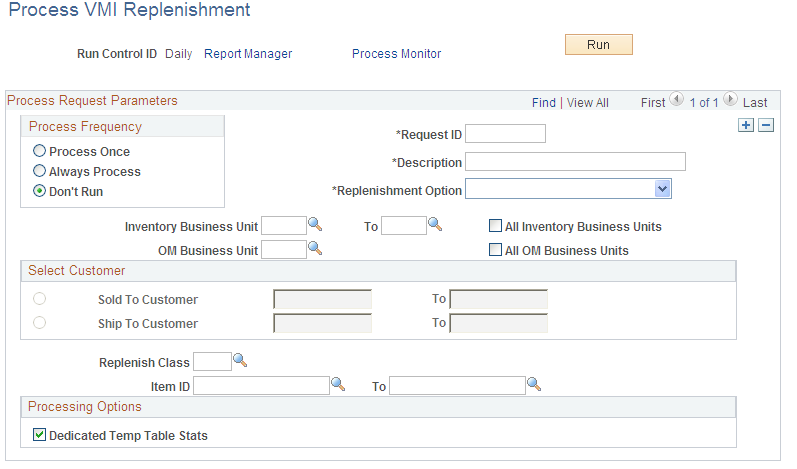
The VMI Replenishment (IN_VMI_RPLN) process runs similar to the Replenishment process with these exceptions:
On-hand quantity is determine at the location level in the VMI business unit.
On-order quantity is the sum of sales and interunit orders for the ship-to and item combination for the source business unit.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Replenishment Option |
Select a replenishment option: Select Create Replenishment Requests to create suggested replenishment requests. Select Create and Process Requests to create suggested replenishment requests and immediately pass the sales orders to PeopleSoft Order Management and the material stock requests to PeopleSoft Inventory. Select Process Reviewed Requests to pass reviewed sales orders to PeopleSoft Order Management and material stock requests to PeopleSoft Inventory. |
Dedicated Temp Table Stats |
Select to generate accurate table statistics for dedicated temporary tables. |
Use the VMI Replenishment Review page (RPLN_RQST_INVMI2) to review and delete replenishment requests for VMI business units.
Navigation:
The review replenishment requests page is used to review and delete suggested replenishment orders. Suggested orders that are not deleted, will be used to create MSRs and Sales Order after saving the page and then selecting the Process Reviewed Requests option on the Process VMI Replenishment page.