Defining Measurement Plans
To define measurement plans, use the Measurement Plans component (QS_MFDS_PLAN). This topic discusses how to define measurement plans.
|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Usage |
|---|---|---|
|
QS_MFDS_PLAN |
Create and edit measurement plan characteristics. Define a group of characteristics for analyzing quality data. Specify the unit of measure, specification, acceptance limits, and the control procedures and charts for monitoring the characteristics. Define formulas to calculate sample values for characteristics that cannot be measured directly. |
|
|
QS_MFDS_CALC_PNL |
Create or edit characteristic formulas. |
|
|
QS_MFDS_PLAN_TXT |
Add operator instructions. |
Use the Measurement Plans - Characteristics page (QS_MFDS_PLAN) to create and edit measurement plan characteristics.
Define a group of characteristics for analyzing quality data. Specify the unit of measure, specification, acceptance limits, and the control procedures and charts for monitoring the characteristics. Define formulas to calculate sample values for characteristics that cannot be measured directly.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Measurement Plans - Characteristics page: General tab. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
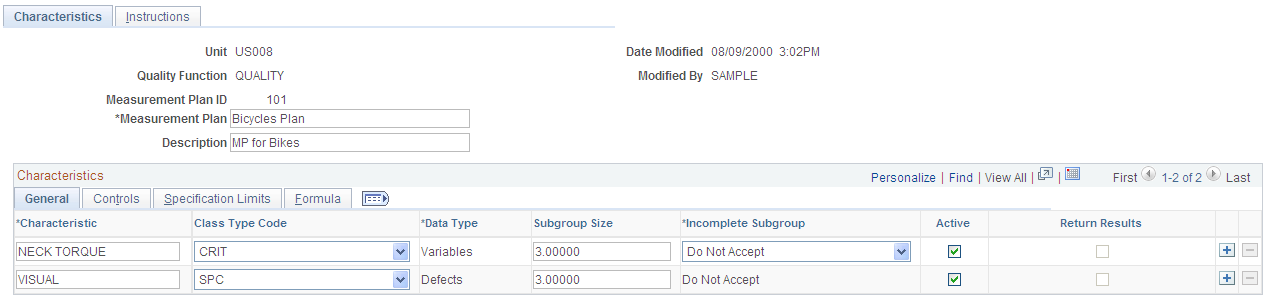
Note: Do not use special characters, such as dashes and percent signs, in characteristic names.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Class Type Code (classification type code) |
Select the classification code that you want to use for inspection requirements. |
Data Type |
Select the data type for this characteristic. Values are: Variables: Quantitative or physically measurable (or derived) properties, such as size, mass, or time. Defects: Qualitative or observed data on defect types—such as scratches and blemishes—and associated counts. Defectives: Counts the number of units that are defective using a pass-or-fail criteria. |
Subgroup Size |
Enter the size of the sample taken during each inspection cycle. A 0 indicates that the subgroup size may vary, and the size is entered at the time of inspection. Size ranges are:
|
Incomplete Subgroup |
Select to determine how the system responds when insufficient data exists to satisfy the subgroup size that is defined. This field is applicable to the variables data types only. Average: The system completes incomplete subgroups using the average of the sample values that have been collected. Do Not Accept: The system analyzes the subgroup only after the subgroup size is reached. |
Active |
Select to enable data collection for the characteristic. |
Return Results |
Select to have the system return subgroup results to integrated applications. This option also enables applications that call Quality data to capture information from the Quality session and use it for additional processing. In practice, the most significant results are usually pass-or-fail counts. Quality returns results for a single defectives type characteristic. Indicate the characteristic for which the system returns results. |
Controls
Select the Controls tab.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Control Chart |
Select the control chart that the system uses to monitor process variability. The standard system-supplied charts include: c Chart np Chart p Chart u Chart X and Moving Range Xbar and Range Xbar and Sigma Any custom charts that you define are also available for selection. Control chart selections depend on the characteristic data type. |
Graphic Preferences |
Select the default analysis content and graphic presentation for a characteristic during data entry or review. Graph preferences are configured using the Graph and Display Preferences component. |
Control Procedure |
Select the control procedure that the system uses to assess process control. |
Specification Limits
Select the Specification Limits tab.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
LSL (lower specification limit) and USL (upper specification limit) |
Enter the limits for product or dimensional adherence. They are typically manufacturing and assembly tolerances or customer-specified targets. Leave either field blank to accommodate unilateral specifications. |
LAL (lower acceptance level) and UAL (upper acceptance level) |
Enter the absolute minimum and maximum values accepted during manual data entry operations. This reduces the entry of spurious data. You can leave either or both fields blank. |
Formula
Select the Formula tab.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Factor 1 and Factor 2 |
Enter constant values that are imported into optional, derived characteristic formulas. |
Formula |
Specify a formula that the system uses to derive sample values for the characteristic. Enter the formula or click the Formula Definition button to access the Formula Definition page. Note: During data entry, the system calculates sample values of characteristics with defined formulas. These cannot be edited. |
Use the Formula Definition page (QS_MFDS_CALC_PNL) to create or edit characteristic formulas.
Navigation:
Click the Enter Formula button on the Formula tab of the Measurement Plans - Characteristics page.
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Formula Definition page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
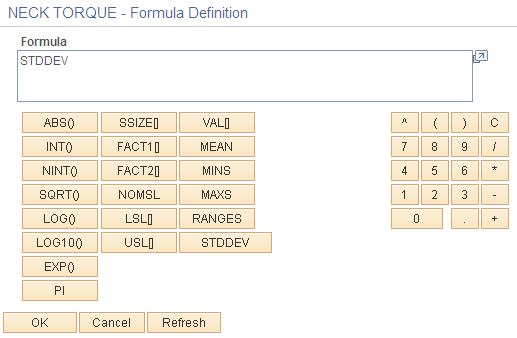
Equation component buttons are grouped according to these types of functions (from left to right):
Basic or standard mathematical functions.
Configuration parameters.
Simple statistics.
Sample value.
You can define a characteristic formula by entering values in the Formula field or by:
Clicking an equation component button.
Using the keypad area to insert numbers, mathematical operators, parentheses, and decimal points.
Examples of Characteristics
|
Type of Calculation |
Formula |
|---|---|
|
Multiply two characteristics. |
(VAL[Length]*VAL[Width]) |
|
Calculate the deviation from the nominal of the specification. |
(MEAN[Length]–NOMS[Length]) Note: Requires bilateral specifications. |
|
Round the value of length to hundredths. |
(NINT(VAL[Length]*100)/100) |
|
Calculate Cpk for the current subgroup of length. |
(MINS((USL[Length]–MEAN[Length] /(3*STDEV[Length])) ((MEAN[Length]–LSL[Length]) / (3*STDEV[Length]))) Note: Recommended usage should include the length characteristic with n>7 (at least 3) and an Xbar and sigma chart. Cpk characteristic should be n=1 with an X and Moving Range chart. |
Note: When defining formulas with algebraic calculations, enclose the formula in parentheses, for example, (VAL[Length] * VAL[Width]).
Equation Construction Functions
|
Function |
Description |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
ABS( ) |
Absolute value of the quantity specified in parentheses. |
ABS(VAL[Length]) Note: Computes absolute value of the reading entered for length. |
|
EXP( ) |
Exponential function. Returns e raised to the power of the specified value. |
EXP(2) |
|
FACT1 |
Factor 1 from the Specifications page. |
FACT[1] |
|
FACT2 |
Factor 2 from the Specifications page. |
FACT[2] |
|
INT( ) |
Integer portion. |
INT(VAL[Length]) Note: Computes integer portion of the reading entered for length. |
|
LOG( ) |
Natural log function. |
LOG(Length) |
|
LOG10( ) |
Log based 10 function. |
LOG10(Length) |
|
LSL |
Lower specification limit of the current characteristic. |
LSL |
|
MAXS (maximum) |
Maximum value in subgroup of readings entered for a characteristic. |
MAXIMUM[Length] Note: Computes maximum value in the subgroup of readings entered for length. |
|
MEAN |
Mean of subgroup of readings entered for a characteristic. |
MEAN[Length] Note: Computes mean of the subgroup of readings entered for length. |
|
MINS (minimum) |
Minimum value in subgroup of readings entered for a characteristic. |
MINIMUM[Length] Note: Computes minimum value in the subgroup of readings entered for length. |
|
NINT( ) |
Nearest integer. |
NINT(VAL[Length]) Note: Computes nearest integer to the reading entered for length. |
|
NOMSL |
The center point between the nominal specification lower limit and the nominal specification upper limit (LSL, USL). |
NOMSL[Length] |
|
PI |
π (3.14159) |
(VAL[Diameter]) * PI Note: Multiplies the reading entered for diameter by 3.14159. |
|
RANGES |
Range of subgroup of readings entered for a characteristic. |
RANGE[Length] Note: Computes range of the subgroup of readings entered for length. |
|
SQRT( ) |
Square root. |
SQRT(VAL[Length]) Note: Computes square root of the reading entered for length. |
|
SSIZE |
Subgroup size of the current characteristic. |
SSIZE |
|
STDDEV |
Standard deviation of subgroup of readings entered for a characteristic. |
STDDEV[Length] Note: Computes standard deviation of the subgroup of readings entered for length. |
|
USL |
Upper specification limit of the current characteristic. |
USL |
|
VAL |
Reference to the current sample for the characteristic. |
VAL[Length] * VAL[Width] Note: The equation processor works from sample 1 to sample n within the current subgroup and attempts to reference the characteristics that make up the derived one. |
Use the Measurement Plans - Instructions page (QS_MFDS_PLAN_TXT) to add operator instructions.
Navigation:
Enter the text for the instructions. The text corresponds to the entire measurement plan.