Using Search Pages to Retrieve Data
This section discusses how to:
Enter and save search criteria.
Use wildcard characters to find information.
Retrieve historical data.
Use autocomplete to suggest valid values.
This section discusses how to:
Enter search criteria.
Use operators.
Save search criteria.
Entering Search Criteria
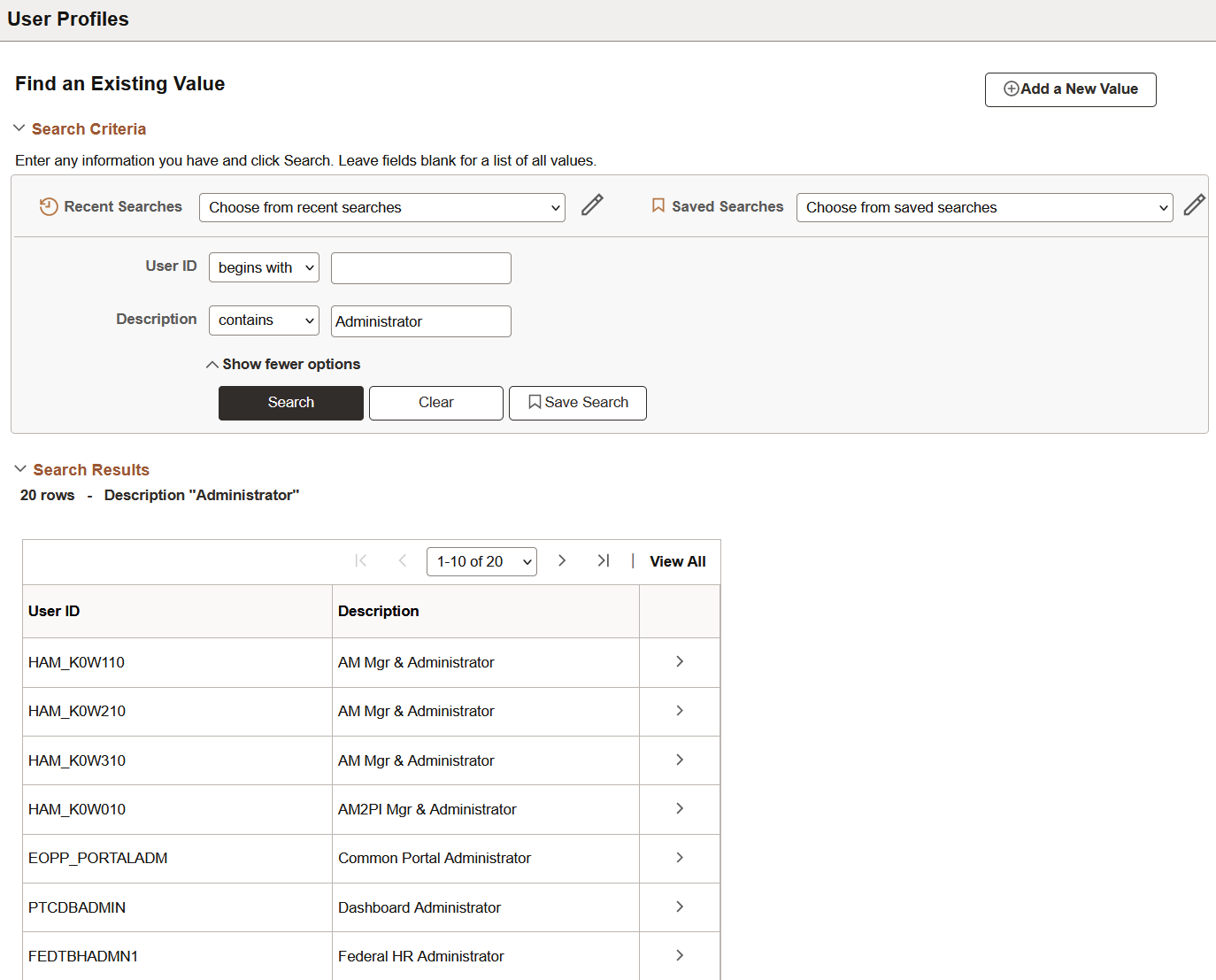
When specifying search criteria, you can enter a full or partial value for any key field. Based on what you enter, the system queries the search record, presents a list of possible matches or, if only one match exists, displays the page that you requested. Often, however, you do not have all of the information that you need. For example, you may want to find all administrator user profiles. If you enter the word Administrator in the Description field and the search criterion for that field is set to contains, then the system narrows the search by displaying all profiles that contain Administrator in the description. With this information, you might be able to determine which user profiles you want based on the results in the Search Results grid. Click any link in the row of the profile to access that profile in the Search Results grid.
This example illustrates specifying search criteria on an advanced search page.
When browsing through a large number of search results, use the browser scroll bar to view all listings on the current page. If not all results appear at one time, you can click the Show Next Rows button (the right arrow) in the grid header to view the next set of rows, and you can click the Show Previous Rows button (the left arrow) to see previous sets of rows. You can also click the First and Last links to display the first and last sets of rows of search results. In addition, you might be able to click a View All or View n button to view all records at one time or to view a designated number of records. (The application developer configures the value of n.)
When you select a value and access a page, notice that the key fields from the row that you selected on the search page appear as the display-only fields in the upper section of the page, usually just below the page tab.
Using Operators
When performing an advanced search, you can use a variety of operators to narrow your searches. For example, you can hunt for customers by a particular first letter, by values that are less than or greater than a specified amount, and so on. You can use the following operators:
|
Operator |
Field Use |
|---|---|
|
begins with |
Character fields. |
|
contains |
Character fields. |
|
= |
All field types. |
|
not= |
All field types. |
|
< |
All field types. |
|
<= |
All field types. |
|
> |
All field types. |
|
>= |
All field types. |
|
between |
All field types. |
|
in |
All field types. |
Note: If you use the in operator to search for multiple items, separated by commas, and you enter a space after the comma, the search automatically strips out that space. (For example, if you search for 1000, 1001, the search assumes that you are searching for 1000,1001. If you actually do want to search for a character string that contains a space, include that string within double quotes, like this: 1000," 1001".
You can use an operator for more than one field to make your search even more specific. For example, you could narrow your search for courses with the word orientation in the name by selecting the "=" operator for the Internal/External field and selecting Internal from the drop-down list box, as shown in the previous example. This search will find only courses that meet both criteria: internal courses that include the word orientation.
Saving Search Criteria
If you are conducting an advanced search, you can click the Save Search button to name and save the specifics of your search. If you have saved one or more searches, you can use the Choose from saved searches drop-down list box to select a saved search. After you save a search, you can use that saved search in other search pages that use the same search record. You can use the pencil icon to display the Manage Saved Searches dialog box where you can rename or delete your saved searches.
This example illustrates the Permission Lists Advanced Search page showing the PTools saved search.
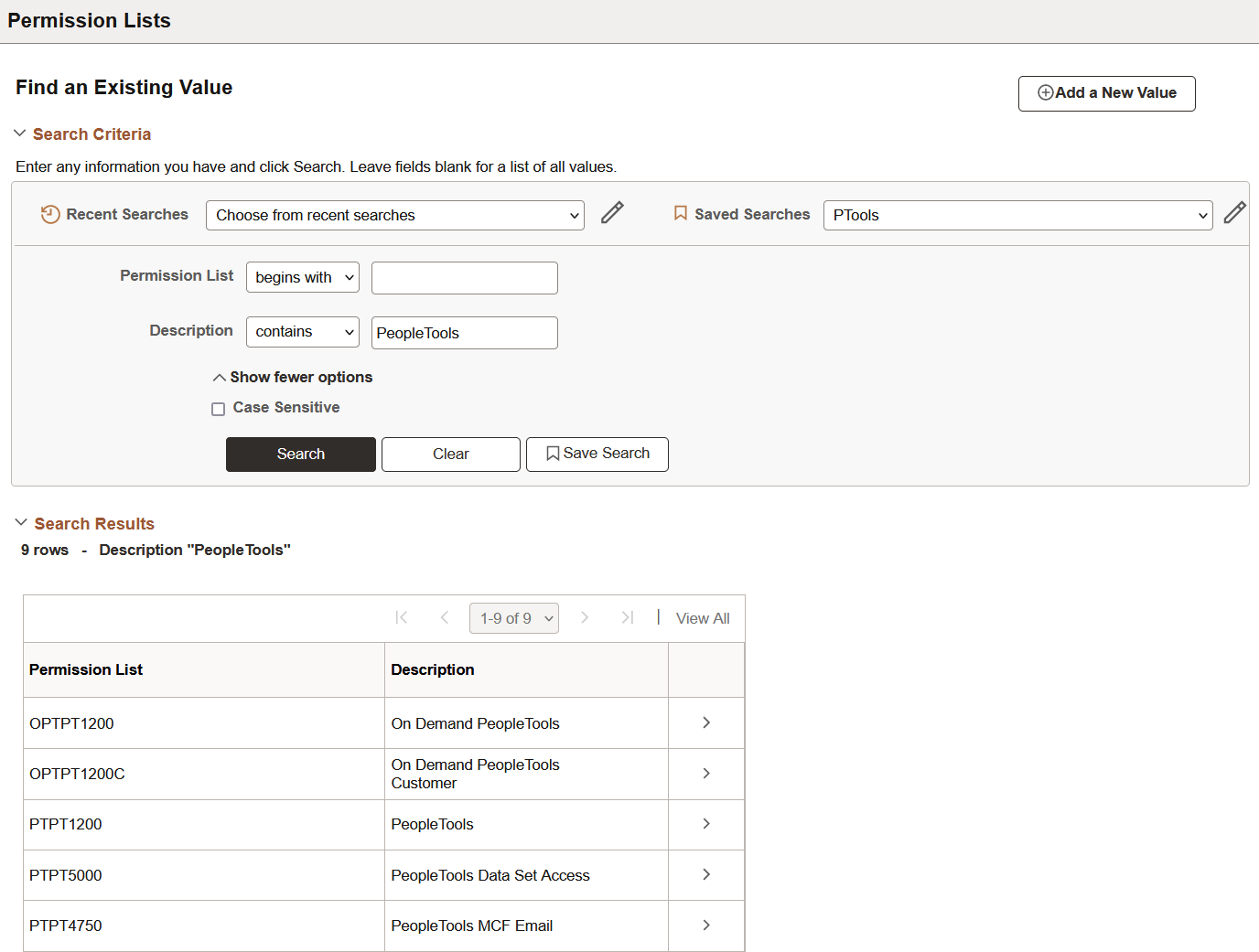
Note: The applications stores saved searches by user ID.
PeopleSoft applications support three wildcard characters to help you search for data in character fields. You can use these wildcard characters to find the information that you need. The % and _ wildcard characters work in all autocomplete fields. On search pages and look up pages, wildcard characters only work with the begins with and contains operators.
Note: Certain applications support wildcard characters that are specific only to that application. See your application-specific product documentation for details.
The supported standard wildcard characters are:
|
Wildcard |
Search Action |
|---|---|
|
% (percent symbol) |
Match one or more characters. |
|
_ (underscore) |
Match any single character. |
|
\ (backslash) |
Escape character; do not treat the next character as a wildcard. |
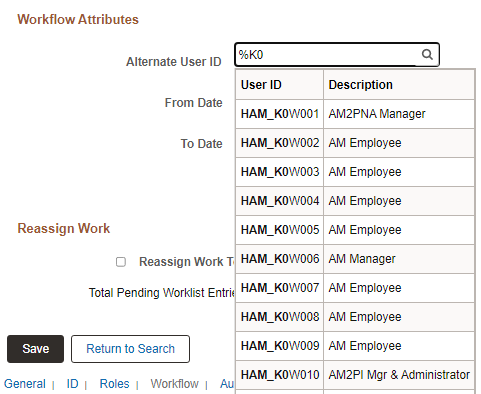
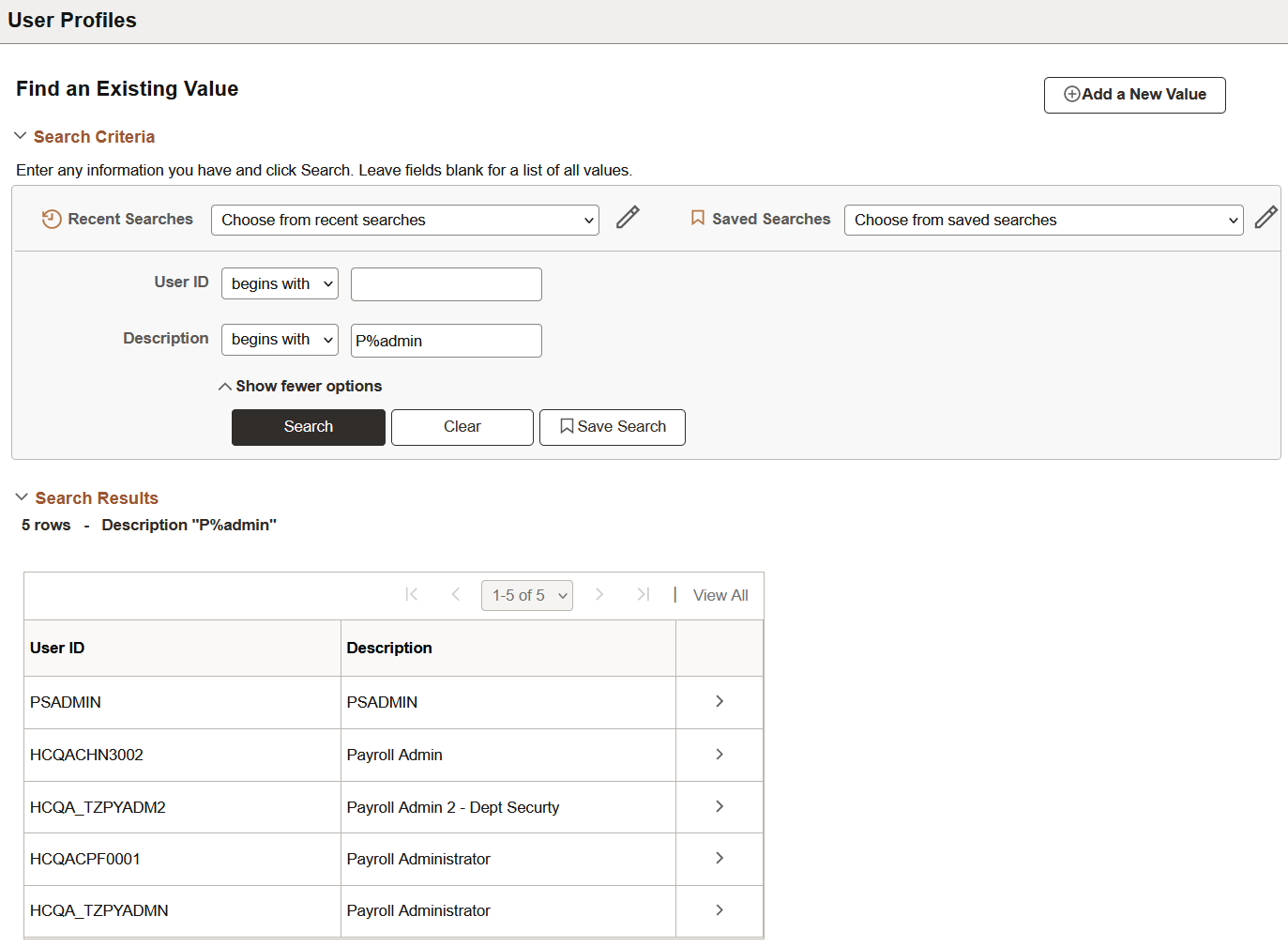
For example, if you enter P%admin in the Description field for the User Profile, then the system returns a list of User Profiles that begin with P and contain 'admin' as you can see in this example:
This example illustrates using wildcard characters on a search page.
The presence of action mode fields on the search page indicate that the component uses PeopleSoft effective date logic.
This example shows the Include History and Correct History options on a search page.
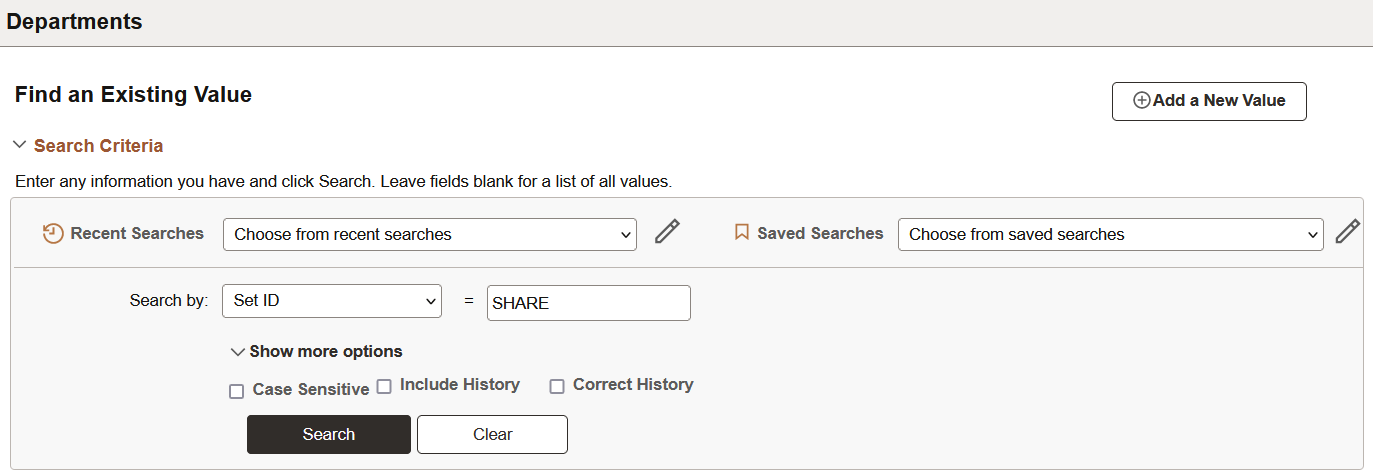
If you have the appropriate permissions for see and modify history records, then these two options can appear on a search page:
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Include History |
Select to retrieve history records when the system processes the search. |
Correct History |
Select to retrieve and be able to correct history records when the system processes the search. |
Detailed information about PeopleSoft effective date logic is available in the next topic in this documentation.
Autocomplete (sometimes referred to as “type ahead”) provides a list of suggestions that match the data you enter in edit and prompt fields. Autocomplete lists can appear for two types of fields:
Edit fields on search pages.
Prompt fields.
Autocomplete fields support the use of the % and _ wildcard characters.
Edit Fields on Search Pages
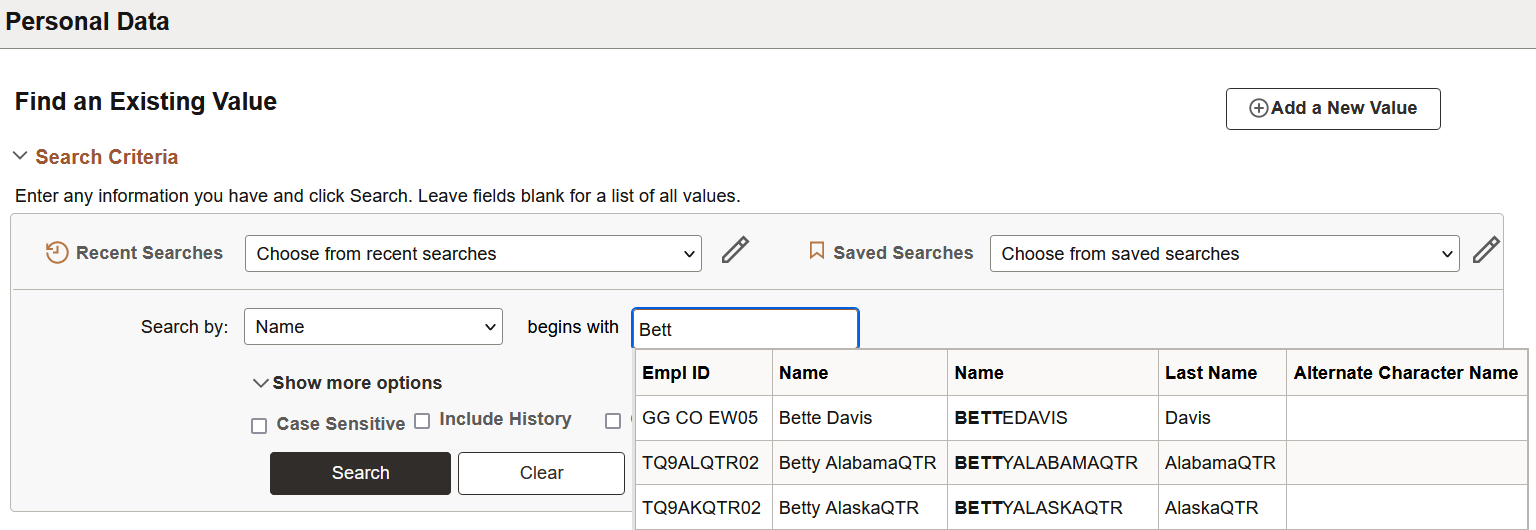
When a search record field is autocomplete-enabled, as you type a letter into the field, and then pause, the autocomplete list appears and shows you values that match the letters you have entered to this point. The system returns the maximum number of allowed values, but it shows you a subset in the autocomplete window. An administrator sets the list limit, the list limit default is 50.
This example illustrates an autocomplete list.
Prompt Fields
All prompt fields are autocomplete capable. When you enter data in a prompt field, the autocomplete results can vary slightly because you can configure the list to display up to five additional columns to assist in choosing the correct value.
This example shows an autocomplete list for the Role Name field.
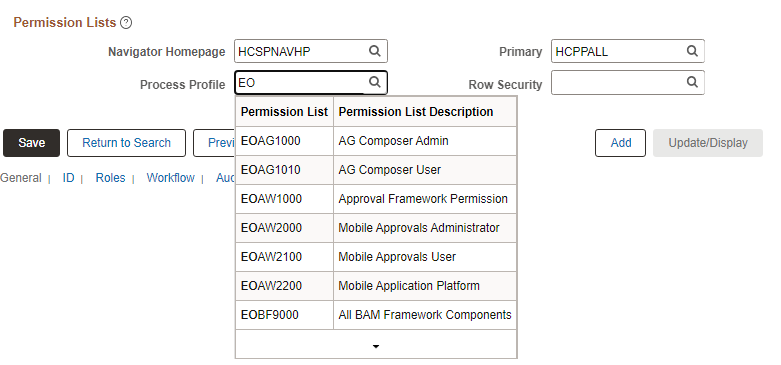
The following example illustrates autocomplete on a prompt field. Both the % and _ wildcard characters were used to generate this autocomplete list.