2.18.4 Equipment Identity Register
Figure 2-71 EIR solution architecture.
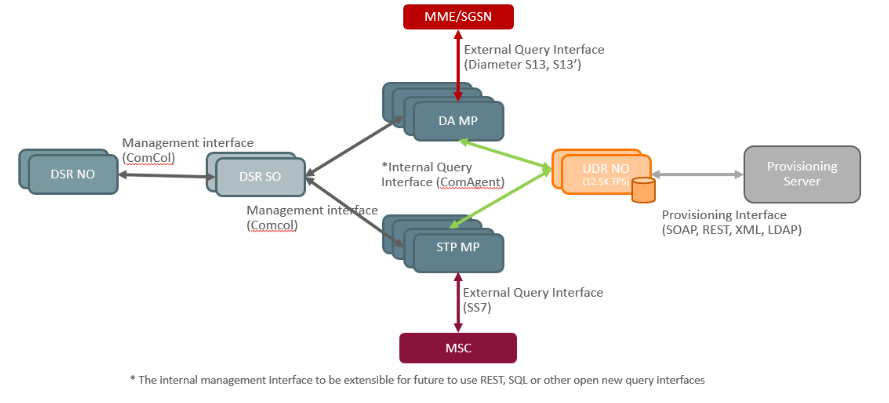
EIR is a DSR Application on DA MP and STP MP. Screening supported for IMEI Individual or Range (with possible IMSI mapping), TAC (provisioned as IMEI range), SVN, IMSI range, Status override possible with IMSI association. EIR only provides the device status information.
The UDR NO provides the functionality of the Equipment Identity Register (EIR) database to the DSR. The database stores white, gray, and black lists of IMEI numbers.
- Supports an internal query interface towards DA-MP and STP MP for vEIR.
- Provides options of provisioning GUI as well as Bulk provisioning.
- Provides FTP and SFTP based provisioning. Provisioning interfaces supported are REST/SOAP/XML/LDAP.
Data Types that are supported at EIR data base:
IMEI
- 100M Individual entries.
- 10M IMEI range/TAC.
- 1 IMEI up to 10 IMSI.
- SVN supported
- IMSI Range (1000)
- To support whitelisting special subscribers.
Figure 2-72 SS7 EIR call flow
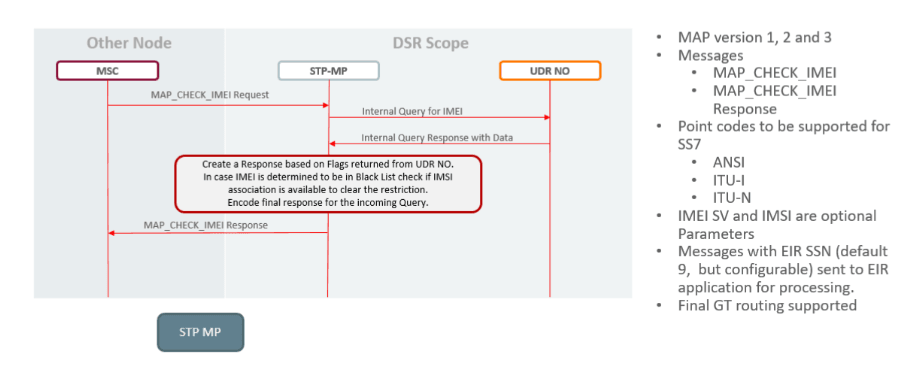
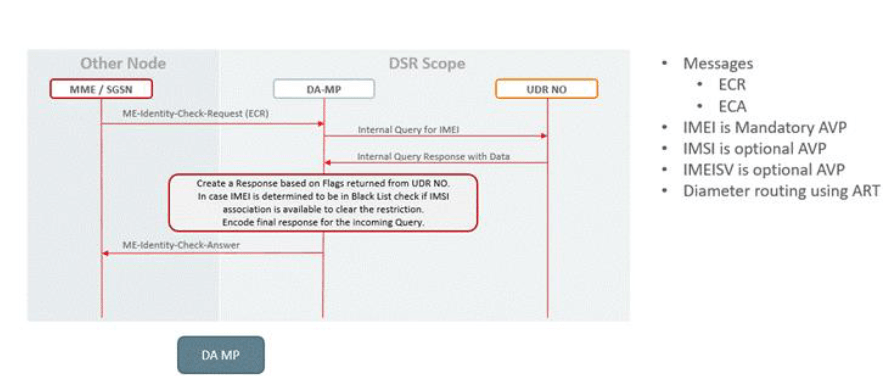
Figure 2-73 S13 EIR Call Flow
EIR leverages DSR architecture for Measurements and Alarms, Backup and restore, OAM and Congestion Control.