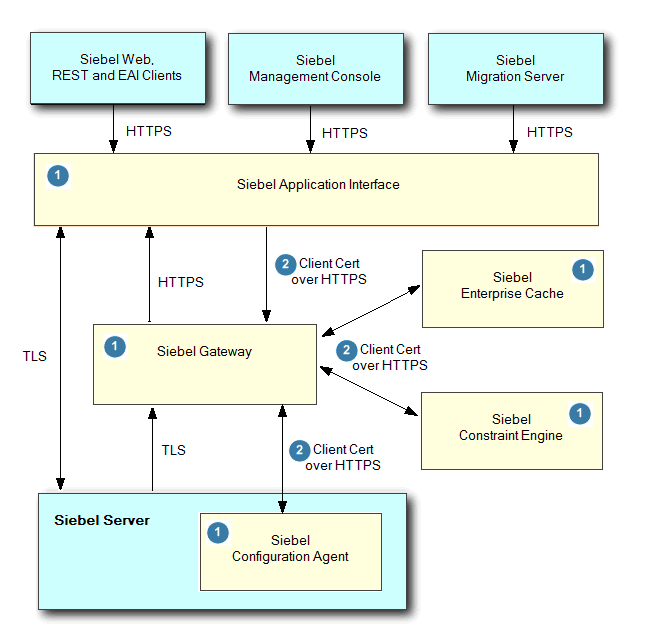
Certificate Requirements for Communications
Siebel installer for Siebel Business Applications enforces HTTPS during installation, as follows:
Siebel Web Clients, Siebel Management Console and the Siebel Migration server all communicate with the Siebel Application Interface over HTTPS.
All communication between Siebel services (Siebel Application Interface, Siebel Gateway, and Siebel Configuration Agent) are enforced over HTTPS by Siebel installer.
Siebel Application Interface is an external interface accessing Siebel services. All other Siebel services are internal services and they are protected by client certificate based authentication.
Any Siebel service-to-service access is over HTTPS with client certificate based authentication (for example, two-way SSL). Client certificates are used for service-to-service authentication.
The following figure illustrates the certificate requirements for communications as follows:
Siebel Application Interface, Siebel Gateway, and Siebel Configuration Agent are hosted in application containers (Apache Tomcat).
For information on configuring application containers, see Siebel Installation Guide. For information on starting and stopping application containers, see Siebel System Administration Guide.
During Siebel installation (of the aforementioned components), the installer prompts you to specify valid keystore and truststore files, as follows:
Keystore Name. Specify a file (such as a JKS file) you have generated that will serve as the keystore. For example, import the client or server certificate into the keystore using the Java Keytool utility.
Truststore Name. Specify a file (such as a JKS file) you have generated that will serve as the truststore. For example, import the Certificate Authority (CA) certificate into truststore using the Java Keytool utility.
Since Siebel internal nodes are configured for client certificate based authentication, make sure that you use the correct client identity in the CN and Subject Alternate Name (SAN) fields. You can create certificates with the exact FQDN or IP address, or with a wildcard in the FQDN. For example, if you replace
host.domain.subdomain.comwith*.domain.subdomain.com, then this eliminates the need to create separate client certificates for each machine.Note: It is recommended that you use certificates provided by a Certificate Authority (CA) rather than self-signed certificates. For production environments, you must create a certificate request and get it signed either by your internal CA (for employee-only environments) or an external CA (for customer, consumer, or partner environments). Self-signed certificates are suitable for development environments, for example, where you can provide instructions to users to import the self-signed certificate, since clients will not trust such a certificate unless it is manually installed into the certificate store.For more information, see About Generating Keystore and Truststore Files and Modifying Keystore and Truststore Files.
Password. Specify the password for the specified keystore and truststore files.
Confirm Password. Confirm the password for the specified keystore and truststore files.
Note: The Siebel Gateway requires that client connections from the Siebel Application Interface be authenticated using a client certificate (mutual authentication). As such, the SSL certificate on the Application Interface must be valid for use as a client certificate as well as a server certificate. When requesting the certificate, ensure that it will include both the"clientAuth"and"serverAuth"Extended Attributes. These are typically included in certificates issued by commercial Certificate Authorities, but may or may not be included by default in certificates issued by an internal CA.
For more information about certificate files, see About Importing Certificates into Keystore and Truststore and About Installing Certificate Files.