About Web Services and Web Single Sign-On Authentication
Siebel Web services support Web single sign-on (SSO) deployment scenarios in which third-party applications handle authentication, and then pass authentication information to the Siebel application. When the third-party application authenticates it, users do not have to explicitly log in to the Siebel application. The following illustrates a Web single SSO deployment scenario using Siebel Web services. For more information about Web SSO, see Siebel Security Guide.
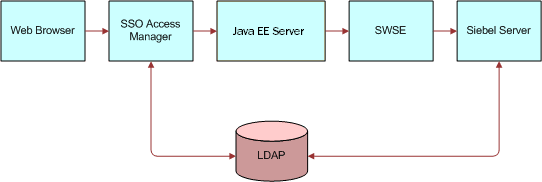
As shown in this figure, the components in an SSO scenario include the following:
-
SSO Access Manager. SSO Access Manager, configured in front of the Java EE server, challenges user login, authenticates user credentials with LDAP, and sets a security token in the browser (http header), which is forwarded to the Java EE server.
-
Java EE Server. This server extracts user credentials from the security token in the request. The Session Manager Login method takes the request as an argument and forwards it to the AI. The request contains the security token in the header.
-
Siebel Application Interface (replaced SWSE). AI extracts the user credentials from the security token and sends user credentials and the trust token to the Siebel Server.
-
Siebel Server. The Siebel Server validates user credentials with LDAP and validates the trust token with security settings.