Invoking the External REST Service Endpoint Using Proxy Business Service at Runtime
This topic describes the steps involved when invoking an external REST service endpoint as a business service from a Siebel application or workflow.
-
Obtain the OpenAPI compliant JSON file. This step requires that you obtain the external JSON file or URL, and import it into Web Tools using the WSDL/JSON wizard. This creates the proxy business service, integration objects and Web service.
For more information, see Creating an Outbound REST Service Based on an OpenAPI Compliant JSON File.
-
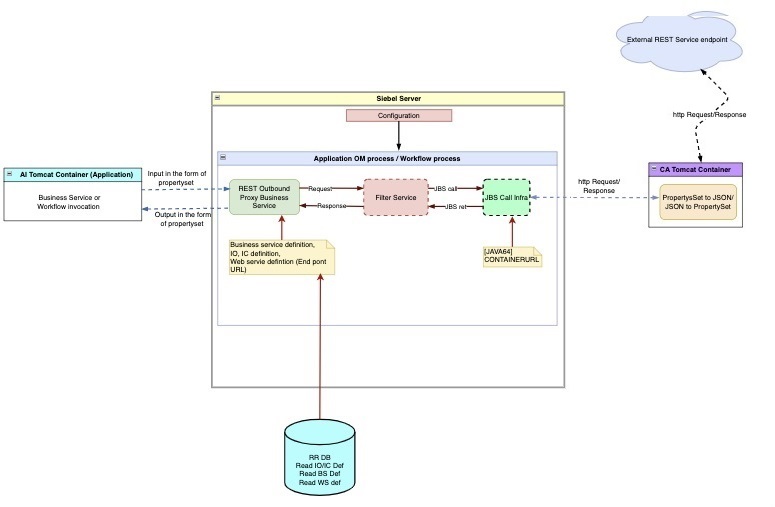
Prepare the input property set. This step requires that you prepare your input property set for input to the proxy business service. This depends on the definition of the proxy business service in Web Tools. Inputs can be simple, such as strings, or integers, or they can be complex types such as integration objects.
-
Set up the Filter Service (Request Filter and Response Filter). In this step, you can use the Filter Service to:
- Customize the Request/Response headers
- Add security parameters for different authentication mechanisms
- Specify a different Filter Business Service for each Service Method
- Specify a different Filter Business Service for Request and Response
You can make these changes in Application Administration > Web Services > Outbound REST Services UI. Following is a bare bones example of two methods: UpdateInput and UpdateOutput:
function Service_PreInvokeMethod (MethodName, Inputs, Outputs) { if(MethodName == "UpdateInput") { Inputs.SetProperty("REQFILTER","Request Filter working"); } if(MethodName == "UpdateOutput") { Outputs.SetProperty("RESPFILTER","Response Filter working"); } return (CancelOperation); } - Application or script or workflow invokes the proxy business service. In this
step, the proxy business service is invoked just like any other business service and
does the following:
-
It uses the Business Service definition to validate the inputs.
-
It uses the Web Service definition to obtain the endpoint URL and other details.
-
-
Proxy business service calls the Config Agent (CA) Tomcat. In this step, the proxy business service makes a Java Business Service call to the Config Agent (CA) Tomcat attached to the Siebel server. This executes the Java Business Service. The address of the CA Tomcat is obtained from the 64-bit Java subsystem attached to the Object Manager, passing the property set input obtained from the user.
The Java Business Service does the following:
- It converts the property set to JSON payload.
- It makes an HTTP call to external end point URL, obtaining the response, and then converting the JSON response back to a property set, and finally returning to the Proxy Business Service
-
Proxy business service converts the property set to output. In this step, on receiving the property set response from Java Business Service, the proxy business service converts it back to the output arguments according to its method’s out parameters.