Configurations for SASL Authentication
Siebel CRM-Kafka integration supports the following SASL authentication mechanisms:
-
SASL/PLAIN
-
SASL/SCRAM-SHA-256
-
SASL/SCRAM-SHA-512
-
OAUTHBEARER
Configuring SASL/PLAIN
Changes in Kafka broker:
-
Create a new java Authentication and Authorization Service (JAAS) file called
kafka-server-jaas.confwith contents like the one below. You need to add the Kafka server users in this file.KafkaServer { org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username="admin" password="admin-secret" user_admin="admin-secret" user_alice="alice-secret" user_siebel="siebel-secret"; }; Pass the above mentioned jaas file as JVM parameter in Kafka broker as follows:
-Djava.security.auth.login.config=<pathto kafka_server_jaas.conf>For example, in a Windows Kafka environment, it can be done as follows. For configuration for other platforms, please check Kafka official reference documentation.
set KAFKA_OPTS=-Djava.security.auth.login.config=kafka-server-jaas.conf-
Update the
server.propertiesfile of the Kafka broker as follows:listeners=SASL_SSL://serverurl.oraclevcn.com:9095 security.inter.broker.protocol=SASL_SSL sasl.mechanism.inter.broker.protocol=PLAIN sasl.enabled.mechanisms=PLAINand also add (for SSL configurations)
ssl.keystore.location=C:\\DebugBuild\\certs\\siebelkeystore.jks ssl.keystore.password=siebel ssl.truststore.location=C:\\DebugBuild\\certs\\siebeltruststore.jks ssl.truststore.password=siebel ssl.key.password=siebel ssl.client.auth=required
Changes in AI sidecar for SASL/PLAIN:
-
Generate the encrypted password for the passwords setup in the Kafka-server-jaas.conf file (shown above) by using the EncryptString jar file in
<AI server>\webapps\siebel\WEB-INF\lib. -
Update the following properties in application interface.properties:
SecureAIToKafkaCommunication=true KafkaServers=<Kafka host name>:<Kafka port number> KafkaAuthenticationEnabled=true KafkaAuthenticationMechanism=PLAIN KafkaAuthenticationUser=<SASL user name created in the Kafka-server-jaas.conf file on Kafka server> KafkaAuthenticationPassword=<Encrypted password for the above user from the kafka-server-jaas.conf file> KafkaKeyStoreType=JKS KafkaKeyStoreName=<Key Store location e.g. Z:\\siebel\\applicationcontainer_external\\siebelcerts\\siebelkeystore.jks> KafkaKeyStorePassword=<Encrypted Key Store Password> KafkaTrustStoreType=JKS KafkaTrustStoreName=< Encrypted Trust Store location for example, in Windows, Z:\\siebel\\applicationcontainer_external\\siebelcerts\\siebelkeystore.jks> KafkaTrustStorePassword=<Trust Store Password> KafkaPassword=<Encrypted Kafka user password>
Configuring SASL/SCRAM-SHA-256 or SASL/SCRAM-SHA-512
Suggested configuration changes in Kafka server (broker):
For more information, refer to Kafka Official Documentation. Use the following guidance:
-
To encrypt the passwords, use the
EncryptStringutility from the folder <Application External>\webapps\siebel\WEB-INF\libTo encrypt the password, run:
java -jar EncryptString.jar <password>and use the resulting encrypted string. -
All properties beginning with Kafka are used for sidecar AI-Kafka communication.
Make the following changes in Kafka broker:
-
Create new users in Kafka by following the official Apache Kafka documentation.
In Windows:
kafka-configs.bat --alter --add-config "SCRAM-SHA-256=[iterations=8192,password=admin- secret],SCRAM-SHA-512=[password=admin-secret]" --entity-type users --entity-name admin --bootstrap-server localhost:9092or
kafka-configs.bat --zookeeper localhost:2181 --alter --add-config "SCRAM-SHA- 256=[iterations=8192,password=admin-secret],SCRAM-SHA-512=[password=admin-secret]" --entity-type users --entity-name admin -
Create a file called
kafka_server_jaas.confwith the following contents:KafkaServer { org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username="admin" password="admin-secret"; }; -
Pass the JAAS config file location as JVM parameter to each Kafka broker:
-Djava.security.auth.login.config=/path to kafka_server_jaas.conf -
Configure SASL port and SASL mechanisms in server.properties:
listeners=SASL_SSL://<fully qualified server name>:<port number, for example 9093> security.inter.broker.protocol=SASL_SSL sasl.mechanism.inter.broker.protocol=SCRAM-SHA-256 (or SCRAM-SHA-512) sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule require d username=admin password=admin-secret; sasl.enabled.mechanisms=SCRAM-SHA-256 (or SCRAM-SHA-512) -
Configure SSL support configuration in server.properties:
ssl.keystore.location=<A keystore location> ssl.keystore.password=<keystore password> ssl.truststore.location=<truststore location> ssl.truststore.password=<truststore password> ssl.key.password=<necessary password> ssl.client.auth=required
Corresponding configurations in applicationinterface.properties file of AI sidecars:
SecureAIToKafkaCommunication=true
KafkaServers=<Kafka host name>:<Kafka port number>
KafkaAuthenticationEnabled=true
KafkaAuthenticationMechanism=SCRAM-SHA-256 (or SCRAM-SHA-512)
KafkaAuthenticationUser=<SASL user name created in step 1 on Kafka server>
KafkaAuthenticationPassword=<Encrypted password for the above user created in step 1>.
KafkaKeyStoreType=JKS
KafkaKeyStoreName=<Key Store location>
KafkaKeyStorePassword=<Key Store Password>
KafkaTrustStoreType=JKS
KafkaTrustStoreName=<Trust Store location>
KafkaTrustStorePassword=<Trust Store Password>
KafkaPassword=<Kafka user password>
…
….other properties for Siebel-Kafka integration….
….other properties for AI not related to Siebel-Kafka Integration…
…Configuring SASL/OAUTHBEARER
In an Event Publication and Subscription setup, SASL/OAUTHBEARER is used to ensure secure and protected data exchange between Siebel CRM and Kafka. It enables Kafka clients (producers and consumers running in the sidecar AI) and brokers to authenticate with Kafka brokers using secure tokens issued by an OAuth 2.0 authorization server, such as Oracle IDCS, and so on.
A sample information exchange flow for SASL/OAUTHBEARER authentication is shown in the following diagram.
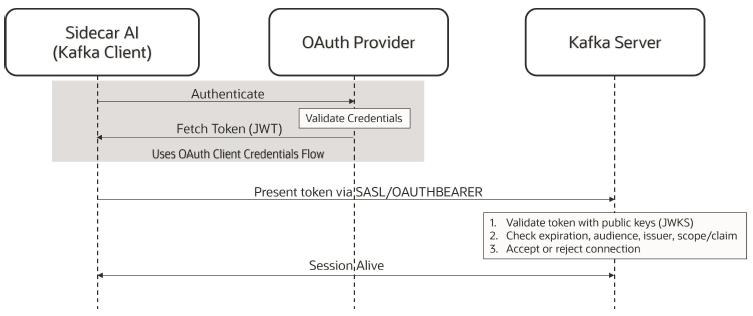
In this case, when a producer (Kafka client) running in the Sidecar AI wants to publish messages to Kafka, the following happens:
- The producer fetches a token from the OAuth 2.0 server.
- The producer connects to the Kafka Server (or broker) using the SASL/OAUTHBEARER mechanism and includes the token.
- The Kafka Server validates the token with JWKS keys and verifies other authentication/authorization parameters.
- Once validated, the Kafka Server initiates the secure event exchange with the producer over a session.
To configure Kafka with OAuth 2.0 authentication:
- Retrieve the following information from the OAuth 2.0 server:
Data Description Sample data from the OAuth 2.0 server (Oracle IDCS)
Client ID Unique identifier assigned to the client that is registered with an OAuth 2.0 server. 915cf6zzzz25413zzzzzz0897c754zzzz Client secret Password used to access protected resources. xxxxxx-7eaf18zz-88x5-455x-8235-e846xxxx1111 Scope Defines the level of access a client application has to a resource. All Token URL URL that will be used to request an access token from the OAuth 2.0 server. https:// xxxx.xxx.xxxx.xxx.com.com:443/oauth2/v1/token JWKS URL Endpoint URL that gives the list of the public keys used to verify the signature of JSON Web Tokens (JWT). https://xxxx.xxx.xxxx.xxx.com:443/admin/v1/SigningCert/jwk Audience Refers to the intended recipient of the access token. abc Issuer Refers to the authorization server that created and signed the access token. https://identity.oraclecloud.com/ - Configure the Kafka broker to use OAuth 2.0 in the server.properties file. For more information, see Changes in Kafka broker.
- Configure the sidecar AI to use OAuth 2.0 in the
applicationinterface.propertiesfile. For more information, see Changes in Sidecar AI.
Changes in Kafka broker:
To configure SASL/OAUTHBEARER with Event Publication and Subscription for Kafka broker:
- Get the OAuth 2.0 server certificate. For
example:
openssl s_client -showcerts -connect <OAuthServer:Port>Note: The steps to generate the OAuth 2.0 certificate depends on the OAuth 2.0 server you are using. Please contact your OAuth 2.0 administrator to get the certificate. - Generate a truststore (JKS) file from the
certificate.
"C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_60\bin\keytool.exe" -importcert -trustcacerts -alias kafka-oauth-cert -file oauth2Cert2.pem -keystore oauth2-openssl-truststore.jks -storepass changeit - Configure the JVM parameters using the truststore file and its password. For
example, on Windows you can configure the JVM parameters by executing the
following command at the command prompt where the Kafka server will be
started:
set KAFKA_OPTS=-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=oauth2-openssl-truststore.jks -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=changeit - Update the OAuth2.0 properties in the
server.propertiesfile. Below is the sample of theserver.propertiesfile configured:Note: You must update the values of the properties in the server.properties file based on your environment set up.For SASL_PLAINTEXT:
advertised.listeners=SASL_PLAINTEXT://<fully qualified server name>:<port number, for example 9093> listeners=SASL_PLAINTEXT://<fully qualified server name>:<port number, for example 9093> sasl.enabled.mechanisms=OAUTHBEARER listener.name.sasl_plaintext.sasl.enabled.mechanisms=OAUTHBEARER listener.name.sasl_plaintext.oauthbearer.sasl.server.callback.handler.class=org. apache.kafka.common.security.oauthbearer.OAuthBearerValidatorCallbackHandler listener.name.sasl_plaintext.oauthbearer.sasl.login.callback.handler.class=org. apache.kafka.common.security.oauthbearer.secured.OAuthBearerLoginCallbackHandler listener.name.sasl_plaintext.oauthbearer.sasl.jaas.config=org. apache.kafka.common.security.oauthbearer.OAuthBearerLoginModule required clientId=<OAuth Client ID> clientSecret=<OAuth Client Secret> scope='xxxall'; listener.name.sasl_plaintext.sasl.oauthbearer.token.endpoint.url=https://<OAuth server name>:443/oauth2/v1/token listener.name.sasl_plaintext.sasl.oauthbearer.jwks.endpoint.url=https://<OAuth server name>:443/admin/v1/SigningCert/jwk listener.name.sasl_plaintext.sasl.oauthbearer.expected.audience=<recipient of the access token> listener.name.sasl_plaintext.sasl.oauthbearer.expected.issuer=<server that issued the access token> inter.broker.listener.name = SASL_PLAINTEXT sasl.mechanism.inter.broker.protocol=OAUTHBEARERFor SASL_SSL:
advertised.listeners=SASL_SSL:// <fully qualified server name>:<port number, for example 9095> listeners=SASL_SSL:// <fully qualified server name>:<port number, for example 9095> sasl.enabled.mechanisms=OAUTHBEARER listener.name.sasl_ssl.sasl.enabled.mechanisms=OAUTHBEARER listener.name.sasl_ssl.oauthbearer.sasl.server.callback.handler.class=org. apache.kafka.common.security.oauthbearer.OAuthBearerValidatorCallbackHandler listener.name.sasl_ssl.oauthbearer.sasl.login.callback.handler.class=org. apache.kafka.common.security.oauthbearer.secured.OAuthBearerLoginCallbackHandler listener.name.sasl_ssl.oauthbearer.sasl.jaas.config=org. apache.kafka.common.security.oauthbearer.OAuthBearerLoginModule required clientId=<OAuth Client ID> clientSecret=<OAuth Client Secret> scope='xxxall'; listener.name.sasl_ssl.sasl.oauthbearer.token.endpoint.url=https://<OAuth server name>:443/oauth2/v1/token listener.name.sasl_ssl.sasl.oauthbearer.jwks.endpoint.url=https://<OAuth server name>:443/admin/v1/SigningCert/jwk listener.name.sasl_ssl.sasl.oauthbearer.expected.audience=abc listener.name.sasl_ssl.sasl.oauthbearer.expected.issuer=<server that issued the access token> inter.broker.listener.name = SASL_SSL sasl.mechanism.inter.broker.protocol=OAUTHBEARER ssl.keystore.location==<keystore location> ssl.keystore.password=<keystore password> ssl.truststore.location==<truststore location> ssl.truststore.password==<truststore password> ssl.key.password==<user password> ssl.client.auth=required
Changes in Sidecar AI:
Configure SASL/OAUTHBEARER for sidecar AI
in the in the applicationinterface.properties file. Here is a
sample of the configured applicationinterface.properties
file:
For SASL_PLAINTEXT:
KafkaServers=<Kafka host name>:<Kafka port number>
SecureAIToKafkaCommunication=false
KafkaAuthenticationEnabled=true
KafkaAuthenticationMechanism=OAUTHBEARER
KafkaOauthClientID=<OAuth client ID>
KafkaOauthClientSecret=<OAuth client secret>
KafkaOauthScope=xxxall
KafkaOauthEndPointURL=<OAuth server name>:443/oauth2/v1/token
KafkaOauthTrustStore=<Complete path of the OAuth truststore JKS file>
KafkaOauthTrustStorePassword=<OAuth truststore password>
For SASL_SSL:
KafkaServers=<kafka host name>:<kafka port number>
SecureAIToKafkaCommunication=true
KafkaAuthenticationEnabled=true
KafkaAuthenticationMechanism=OAUTHBEARER
KafkaOauthClientID=<OAuth client ID>
KafkaOauthScope=xxxall
KafkaOauthEndPointURL=<OAuth server name>:443/oauth2/v1/token
KafkaOauthTrustStore==<Complete path of the OAuth truststore JKS file>
KafkaOauthTrustStorePassword=<OAuth truststore password>
KafkaKeyStoreType=JKS
KafkaKeyStoreName=<keystore location>
KafkaTrustStoreType=JKS
KafkaTrustStoreName=<truststore location>
KafkaPassword=<kafka user password >
For the parameter details, see the
applicationinterface.properties parameter table. You must
contact the OAuth 2.0 server administrator to get the values of the
parameters.
- An authentication error, it implies that the JWKS URL is not accessible.
- JWKS data in JSON format, it implies that the JWKS URL is accessible.
If your OAuth 2.0 authorization server is Oracle IDCS, you can configure access by Kafka brokers as follows:
- Log in to the IDCS Administration Console.
- Go to .
- Under Access signing certificate, select Configure client access.
OAuth token expiration management:
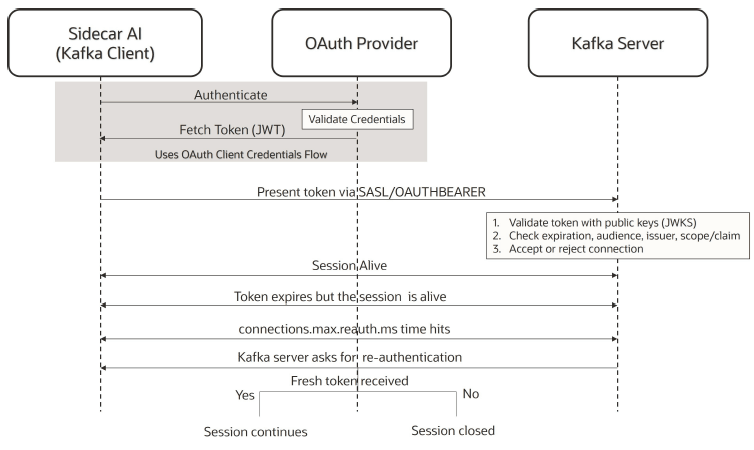
By default, Kafka disables reauthentication to avoid unnecessary system load.
Once a token is authenticated, Kafka does not re-authenticate it based on the
token’s expiration time. Instead, you can control how frequently the token is
re-authenticated through the Kafka broker connections.max.reauth.ms
parameter. You must set the value of this property carefully to prevent
potential abuse or system overload by managing how often re-authentication should
happen.