Installing Siebel Monthly Update in a Siebel CRM Environment Deployed using SCM
You can use the procedure in this topic to install latest monthly updates in a Siebel CRM environment deployed using SCM. These steps do not include repository upgrade steps, which are optional and identical to those relevant for on-premises Siebel CRM deployments.
kubectl get pods" may throw error.
Sourcing of virtual environment and k8sprofile can be done by running the following
commands:sudo podman exec -it cloudmanager bash
bash-4.4$ source /home/opc/venv/bin/activate
source /home/opc/siebel/<env_id>/k8sprofile-
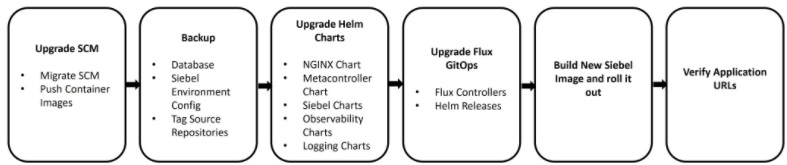
Back up the database
You must perform a backup of the database. Preferably, a full backup.
-
Upgrade SCM
You must upgrade your SCM instance to match the target Siebel CRM version to which you wish to upgrade. For more information, see Updating Siebel Cloud Manager with a New Container Image.
-
Back up the SCM files for the Siebel environment
You must back up the files in the current environment to ensure that you have a working version of the required set of files in case of any issues with the new upgrade or if you want to roll back to the previous version.
To create a backup, do the following:
- Create a backup
directory:
ssh -i <private_key> opc@<cm_instance> mkdir /home/opc/siebel/<ENV_ID>/<backup_dir_name> - Exec in to the SCM
container:
sudo podman exec -it cloudmanager bash - Copy the SCM Helm charts, SCM Git repositories, environment configurations
(for example, CGW and SES), Siebel server (for example, quantum) and AI
configurations (for example, quantum) to the backup directory
(
backup_dir_name):cd /home/opc/siebel/<env_id>/<backup_dir_name> cp -R /homsiebelsiebel/<ENV_ID>/<env_namespace>-helmcharts/ /homsiebelsiebel/<ENV_ID>/<env_namespace>-cloud-manager/ /homsiebelsiebel/<ENV_ID>/<env_namespace>-siebfs0/<ENV_NAMESPACE>/CGW/ /homsiebelsiebel/<ENV_ID>/<env_namespace>-siebfs0/<ENV_NAMESPACE>/SES/ /homsiebelsiebel/<ENV_ID>/<env_namespace>-siebfs0/<ENV_NAMESPACE>/edge/ /homsiebelsiebel/<ENV_ID>/<env_namespace>-siebfs0/<ENV_NAMESPACE>/quantum/ /homsiebelsiebel/<ENV_ID>/<backup_dir_name> exitThe variables in the example have the following values:
- <private_key>: The key used in SCM stack creation.
- <cm_instance>: The SCM instance IP address.
- <backup_dir_name>: The name of the backup directory.
- <env_id>: The six characters long environment ID.
- <env_namespace>: The name of the environment given in the payload.
- <ENV_NAMESPACE>: The name of the environment given in the payload, in uppercase.
- edge: Siebel CRM server name.
- quantum: The ai server name.
- Create a backup
directory:
-
Tag git repositories
- Create a tag in the SCM Gitrepository as
follows:
sudo podman exec -it cloudmanager bash cd /home/opc/siebel/<ENV_ID>/<env_namespace>-cloud-manager/ git pull git tag <tag_name> git –sh origin --tagsIn the example, <
tag_name> is the source Siebel CRM version. For example, 23.8. - Create a tag in the Helm charts Git repository as
follows:
sudo podman exec -it cloudmanager bash cd /home/opc/siebel/<ENV_ID>/<env_namespace>-helmcharts/ git pull git tag <tag_name> git push origin --tags exitIn the example, <
tag_name> is the source Siebel CRM version. For example, 23.8.
- Create a tag in the SCM Gitrepository as
follows:
-
Update SCM container images to the user registry
- Copy the SCM container images to the user registry using the SCM mirror API. For more information, see Mirroring Siebel Base Container Images.
- Verify the mirror API logs for all the images that are pushed; you will need the details of the pushed images in later stages of the upgrade process to verify image details.
-
Update secrets with user registry details
You must update the secret definition used to pull images from the user registry to the user registry credentials. To recreate the secret definition with the user registry credentials and update the secret named
ocirsecretused in flux project, do the following:- Delete existing secret definitions as
follows:
sudo podman exec -it cloudmanager bash source /home/opc/siebel/<ENV_ID>/k8sprofile kubectl delete secret -n <env_namespace> ocirsecret kubectl delete secret -n <env_namespace> customsecret - Go to the
secretsdirectory, create newocirsecretandcustomsecretdefinitions with the user registry details and write the secrets to YAML files as follows:cd /home/opc/siebel/<env_id>/<Cloud manager repository name>/flux-crm/infrastructure/secrets kubectl --dry-run=client -n <env_namespace> create secret docker-registry ocirsecret \ --docker-server=<registry_url> \ --docker-username=<registry_username>\ --docker-password=<registry_password> \ --docker-email=siebel@oracle.com \ -o yaml > ocir-siebeldev.yaml kubectl --dry-run=client -n <env_namespace> create secret docker-registry customsecret \ --docker-server=<registry_url> \ --docker-username=<registry_username>\ --docker-password=<registry_password> \ --docker-email=siebel@oracle.com \ -o yaml > customsecret.yaml - Apply the
ocirsecretandcustomsecretcreated in the namespace:kubectl apply -f ocir-siebeldev.yaml -n <env_namespace> kubectl apply -f customsecret.yaml -n <env_namespace> - Commit the changes to the remote Git
repository:
git add . git commit -m "updated secrets with user registry details" git pull git push - Reconcile flux to rollout the new secret created to the SCM
repository:
flux reconcile source git siebel-repo namespace-repo -n <env_namespace> flux reconcile kustomization infrastructure -n <env_namespace> - Verify the
ocirsecretandcustomsecretdefinitions:- Get the secret and observe the age of the secret to confirm that the
secret is updated:
kubectl -n <env_namepace> get secret ocirsecret kubectl -n <env_namepace> get secret customsecret - Verify that the secret is working by pulling a basic image from the
user registry using the new
ocirsecret, as follows:Note: Sinceocirsecretis updated in <env_namespace>, you must create the test image pod with the nametest_imagePull.yamlonly in <env_namespace>.- Go to the
siebeldirectory:cd /home/opc/siebel/ - Create a kubernetes YAML file with the name
test_imagePull.yamlthat uses the updated secret to pull the image from user registry. Create thetest_imagePull.yamlfile:vi test_ImagePull.yamlAdd the following details to the
test_ImagePull.yamlfile:apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: test-image-pod namespace: <env_namespace> spec: containers: - name: my-test-container image: <user_registry_url>/<registry_prefix>/busybox:latest command: ["sh", "-c", "echo 'Image pulled successfully!' && sleep 180"] imagePullSecrets: - name: ocirsecretIn the example above, <
env_namespace> is the secret's namespace.
- Go to the
- Apply
test_imagePull.yamlmanifest to verify the secret:kubectl apply -f test_imagePull.yaml -n <env_namespace> - Query the status of pod continuously until the status changes from
ContainerCreatingtoRunning:kubectl get pod test-image-pod -n <env_namespace> -w - Verify if the image has been pulled
successfully:
kubectl -n <env_namespace> logs po/test-image-pod - Clean up the test
pod:
kubectl delete -f test_imagePull.yaml -n <env_namespace>
- Get the secret and observe the age of the secret to confirm that the
secret is updated:
- Delete existing secret definitions as
follows:
-
Update Helm chart and Helm release
You must update the Helm chart repository (
/home/opc/siebel/<ENV_ID>/<env_namespace>-helmcharts/)to the latest version and Helm release (/home/opc/siebel/<ENV_ID>/<env_namespace>-cloud-manager) to point to user registry for the following:- Infrastructure (
ingress-nginx) - Metacontroller (
metacontroller) - Siebel Operator (
siebel-operator) - Siebel Gateway (
siebel-gateway) - Siebel Config (
siebel-config) - Siebel (
siebel) - Siebel Artifacts (
siebel-artifacts) - Siebel Observability (
siebel_observability) - Siebel Logging (
siebel-logging)
Note: For detailed steps to update the Helm chart repository and Helm release for the above, please contact Oracle Support. - Infrastructure (
-
Build and push the new Siebel Custom image for the target version
You must re-tag the copied Siebel base image to the user’s environment registry and push it to the user's environment registry.
- Re-tag the copied Siebel base image to the user's environment registry:
- Set the target Siebel
version:
sudo podman exec -it cloudmanager bash export target_version=<target_siebel_version> - Set the
source_base_imagevariable to the destination registry repository obtained from the mirror:export source_base_image="<user_registry_url>/<user_registry_prefix>/cm/siebel:$target_version-full" - Verify that the
source_base_imagevariable is set properly:echo $source_base_image export target_base_image="<user_registry_url>/<user_registry_namespace>/<env_namespace>/siebel:$target_version-full" - Verify that the
target_base_imagevariable is set properly:echo $target_base_image - Re-tag the target Siebel base image to the user's environment
registry:
podman tag $source_base_image $target_base_image
- Set the target Siebel
version:
- Log in to the docker registry to push the target Siebel base image to user's
registry:
podman login <user_region>.ocir.io podman push $target_base_image - Sync the local environment's Helm charts Git repository with the remote
repository for the custom artifacts
changes:
cd /home/opc/siebel/<ENV_ID>/<env_namespace>-helmcharts/ git clean -d -x -f git pull - Build a new custom image for the Siebel CRM web artifacts and push it to the
customer
registry:
cd /home/opc/siebel/<ENV_ID>/<env_namespace>-helmcharts/siebel-artifacts/build/ export target_image=<registry_url>/<registry_namespace>/<env_namespace>/siebel:$target_version.CUSTOM.1 podman build --build-arg BASE_IMAGE=${target_base_image} -t ${target_image} ./ -f dockerfile podman push $target_image exit
- Re-tag the copied Siebel base image to the user's environment registry:
-
Update the SCM repository files with the newly built target Siebel CRM Image
- Go to the
siebeldirectory:cd <git_url>/root/<Cloud manager repository name>/-/blob/master/ flux-crm/apps/base/siebel/ - Update the value of the
base_imageparameter insiebel-artifacts.yamlin SCM Git repository as follows:values: image: siebel: base_image: <user_registry_url>/<registry_prefix/object_namespace>/cm/siebel:$target_version-full registry: <user_registry_url> repository: <registry_prefix/object_namespace>/cm/siebel tag: <tag_id from mirror API response> - Commit the changes to the Git
repository:
git add . git commit -m "Updating new siebel base_image" git push - Update the version in Helm charts Git repository as follows:
- Go to the
siebel-artifactsdirectory:cd /home/opc/siebel/<ENV_ID>/<env_namespace>-helmcharts/siebel-artifacts/ - Open
Chart.yamland update version as follows:name: siebel-artifacts version: 0.1.1 appVersion: "25.5" - Commit the changes to the Git
repository:
git add . git commit -m "Updating new siebel base_image" git push
- Go to the
- Reconcile flux to fetch the latest state from the SCM repository and apply
the
same:
flux reconcile source git siebel-repo <env_namespace> -n <env_namespace> flux reconcile reconcile kustomization apps -n <env_namespace>
- Go to the
-
Check the status of the flux components after upgrade
flux get all -n <env_namespace> -
Monitor the successful completion of postinstalldb Kubernetes job
For more information, see Reviewing the PostInstallDBSetup Execution Status.
- The new image updates will trigger postinstalldb update through flux-crm sync up.
- Wait for the Kubernetes job completion.
- Manually verify the postinstalldb job reports and exit code from the logs.
- In case of errors, take corrective actions and rerun postinstalldb
Kubernetes job by updating the version in
chart.yamlfile as required for an incremental run.
For more information, see Making Incremental Changes.
sudo podman exec -it cloudmanager bash source /home/opc/siebel/<env_id>/k8sprofile kubectl -n <env_namespace> get pods -
Configuration instructions specific to a release
-
For any configuration instructions specific to a release, refer to Siebel Upgrade Guide and Siebel Release Notes.
-
Migrate the persistent volume content. Refer to the "Migrating Persistent Volume Content" section in the Deploying Siebel CRM Containers Guide.
-
-
Upgrade the repository
During the upgrade process if any new features require repository upgrade, then upgrade the repository. Refer to Using Siebel Tools Guide.
-
Troubleshoot any issues
-
In any of the above steps during the Siebel CRM new image rollout and flux sync-up, verify the Helm Release deployment status.
-
If HelmRelease is in failed state, rollback is required and increment the version in Chart.yaml for the helm upgrade.
To verify the helm release status:
kubectl get helmrelease -n <env_namespace>Note: In the command response, the value in the READY column should be "True" for all the helm releases.To verify the deployment status of helm charts:
helm ls -n <env_namespace>Note: In the command response, the value in the STATUS column should be "deployed" for all the helm charts.Rollback steps for Helm Charts
In case you notice any failure in the above two commands, find out the stable Helm chart revision and do a rollback of helm charts as follows:
-
To find out the previous stable REVISION deployed:
helm history siebel -n <env_namespace> -
Rollback to the previous stable REVISION identified by the previous command, that is, helm history:
helm rollback siebel -n <env_namespace> 1For example:
W0505 10:56:23.450209 3296 warnings.go:70] would violate PodSecurity "restricted:latest": allowPrivilegeEscalation != false (containers "persist-folders", "sai" must set securityContext.allowPrivilegeEscalation=false), unrestricted capabilities (containers "persist-folders", "sai" must set securityContext.capabilities.drop=["ALL"]), runAsNonRoot != true (pod or containers "persist-folders", "sai" must set securityContext.runAsNonRoot=true), seccompProfile (pod or containers "persist-folders", "sai" must set securityContext.seccompProfile.type to "RuntimeDefault" or "Localhost") W0505 10:56:23.511704 3296 warnings.go:70] would violate PodSecurity "restricted:latest": allowPrivilegeEscalation != false (containers "persist-fix", "ses" must set securityContext.allowPrivilegeEscalation=false), unrestricted capabilities (containers "persist-fix", "ses" must set securityContext.capabilities.drop=["ALL"]), runAsNonRoot != true (pod or containers "persist-fix", "ses" must set securityContext.runAsNonRoot=true), seccompProfile (pod or containers "persist-fix", "ses" must set securityContext.seccompProfile.type to "RuntimeDefault" or "Localhost") Rollback was a success! Happy Helming!
-
-
-
Verify the application URLs once the environment comes up.