Genesysでのエージェント可用性の切替えの設定
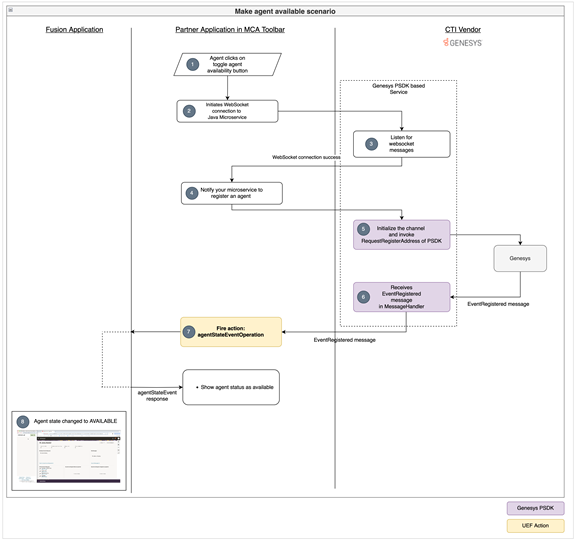
次のフロー図は、メディア・ツールバー・アプリケーションで「エージェント可用性」ボタンを切り替えることで、エージェントが使用可能にマークされると実行される操作の順序を示しています:
概要
メディア・ツールバー・アプリケーションの「エージェント可用性」ボタンをクリックすることで、エージェントが使用可能にマークされた後に実行される操作の順序の概要を次に示します:
- エージェントは、メディア・ツールバーのエージェントの可用性の切り替えボタンをクリックします。
- メディア・ツールバー・アプリケーションは、Javaマイクロサービスへのwebソケット接続を開始します。
- マイクロサービスは接続を受け入れ、webソケット・メッセージをリスニングします。
- メディア・ツールバー・アプリケーションからwebソケット接続が成功した場合は、エージェントを登録するようマイクロサービスに通知します。
- マイクロサービスがこの通知を受信した場合、マイクロサービスは次のことを行う必要があります:
com.genesyslab.platform.voice.protocol.tserver.requests.dn.RequestRegisterAddressリクエストを使用して、使用するエージェントのDNを登録com.genesyslab.platform.voice.protocol.tserver.requests.agent.RequestAgentLogin.RequestAgentLoginリクエストを使用してエージェントにサインイン- ログインが成功すると、EventRegisteredイベントがマイクロサービスから起動されます。
RequestRegisterAddressリクエストが成功すると、EventRegisteredメッセージがGenesysからマイクロサービスを介してメディア・ツールバー・アプリケーションに伝播されます。- メディア・ツールバー・アプリケーションで
EventRegisteredイベントを受信すると、agentStateEventUEF操作が起動され、エージェントの状態が使用可能になります。 - 最後に、Fusionアプリケーションはアクションを識別し、エージェントの状態もFusionで使用可能になります。
エージェントがメディア・ツールバーの「Agent Availability」ボタンを切り替えます
最初に、エージェントがメディア・ツールバーの「Agent Availability」ボタンをクリックして使用可能になります。
メディア・ツールバー・アプリケーションは、Javaマイクロサービスへのwebソケット接続を開始
マイクロサービスは、webソケットを介してイベントをパブリッシュします。 このwebソケットは、最初のステップとしてメディア・ツールバー・アプリケーションで初期化する必要があります。 これは、エージェントがアプリケーションの「エージェント可用性」ボタンを選択したときに実行できます。 次に例を示します。
次の例に示すように、マイクロサービス・エンドポイントURLを保持するために、vendorHandler.tsファイルに静的変数を定義します:
export class VendorHandler implements ICtiVendorHandler {
private static REST_ENDPOINT_URL: string = 'http://localhost:8087/genesys/events';
private static WS_ENDPOINT_URL: string = 'ws://localhost:8087/genesysWs';
}次の例に示すように、vendorHandler.tsファイルのmakeAgentAvailable関数からwebソケットを初期化できます:
public async makeAgentAvailable(): Promise<void> {
let webSocket: WebSocket = new WebSocket(`${VendorHandler.WS_ENDPOINT_URL}`);
webSocket.onopen = this.webSocketOnOpenHandler.bind(this);
webSocket.onmessage = this.webSocketOnMessage.bind(this);
webSocket.onclose = this.webSocketCloseHandler.bind(this);
webSocket.onerror = this.webSocketErrorHandler.bind(this);
}webSocketOnOpenHandler, webSocketCloseHandler, webSocketErrorHandlerおよびwebSocketOnMessage関数を次のように定義します:
public async webSocketOnOpenHandler(): Promise<void> {
console.log("WebSocket opened");
}
public webSocketErrorHandler(error): void {
console.log("WebSocket error", error);
}
public webSocketCloseHandler(event: Event): void {
console.log("WebSocket is closed", event);
}
public webSocketOnMessage(event: MessageEvent): void {
// webSocketOnMessage function acts as the listener for events published from the Java Microservice.
const jsonMessage = JSON.parse(event.data);
console.log(jsonMessage);
if (jsonMessage.eventName === "EventRegistered") {
// Genesys notifies that the agent is ready through the Java microservice
} else if (jsonMessage.eventName === "EventRinging") {
// Show incoming call notification
} else if (jsonMessage.eventName === "EventEstablished") {
// Genesys notifies that the call is accepted
} else if (jsonMessage.eventName === "EventReleased") {
// Genesys notifies that the call is disconnected
}
console.log("Message is received");
}webSocketOnMessage関数は、Javaマイクロサービスから公開されたイベントのリスナーとして機能します。
マイクロサービスは接続を受け入れ、webソケット・メッセージをリスニングし、エージェントを登録するようマイクロサービスに通知
メディア・ツールバー・アプリケーションからwebソケット接続に成功したら、エージェントを登録するためにマイクロサービスに通知する必要があります。 これは、webSocketOnOpenHandler関数から実行できます。 次に示すようにwebSocketOnOpenHandlerファンクションを更新して、REST APIコールを起動してエージェントを登録するようにマイクロサービスに通知します:
public async webSocketOnOpenHandler(): Promise<void> {
console.log("WebSocket opened");
const headers: Headers = (new Headers()) as Headers;
headers.set('Content-type', 'application/json');
const message: any = {
"type": "initialize"
};
const request: Request = new Request(`${VendorHandler.REST_ENDPOINT_URL}`, {
method: 'POST',
headers: headers,
body: JSON.stringify(message)
}) as Request;
await fetch(request);
}マイクロサービスは、PSDKを介してエージェントを登録するリクエストを作成し、エージェントが登録されていることを通知
マイクロサービスは、リクエストの作成にPSDKを使用します。 エージェントの登録リクエストが成功すると、GenesysサーバーはEventRegisteredイベントで応答し、マイクロサービスを介してメディア・ツールバー・アプリケーションに伝播します。
マイクロサービスはEventRegisteredメッセージを受信
DNの登録リクエストが成功すると、GenesysサーバーはEventRegisteredメッセージで応答します。このメッセージは、マイクロサービスを介してメディア・ツールバー・アプリケーションに伝播されます。
メディア・ツールバー・アプリケーションからagentStateEventを起動
EventRegisteredイベントがwebソケットを介して受信されると、次の例に示すように、integrationEventsHandler.tsファイルで起動されるmakeAgentAvailable関数が次のようになります:
public webSocketOnMessage(event: MessageEvent): void {
const jsonMessage = JSON.parse(event.data);
console.log(jsonMessage);
if (jsonMessage.eventName === "EventRegistered") {
// Genesys notifies that the agent is ready
this.integrationEventsHandler.makeAgentAvailable();
} else if (jsonMessage.eventName === "EventRinging") {
// Show incoming call notification
} else if (jsonMessage.eventName === "EventEstablished") {
// Genesys notifies that the call is accepted
} else if (jsonMessage.eventName === "EventReleased") {
// Genesys notifies that the call is disconnected
}
console.log("Message is received");
}エージェントの状態はFusionアプリケーションで有効です
エージェントの状態は、Fusionアプリケーションで有効と表示されます。
完全なコード
エージェント・ステータスを使用可能にするためのvendorHandler.tsファイルの完全なコードを次に示します。
import { ICtiVendorHandler } from './ICtiVendorHandler';
import { IntegrationEventsHandler } from '../integrationEventsHandler';
export class VendorHandler implements ICtiVendorHandler {
private static REST_ENDPOINT_URL: string = 'http://localhost:8087/genesys/events';
private static WS_ENDPOINT_URL: string = 'ws://localhost:8087/genesysWs';
private integrationEventsHandler: IntegrationEventsHandler;
constructor(integrationEventsHandler: IntegrationEventsHandler) {
this.integrationEventsHandler = integrationEventsHandler;
}
public async webSocketOnOpenHandler(): Promise<void> {
console.log("WebSocket opened");
const headers: Headers = (new Headers()) as Headers;
headers.set('Content-type', 'application/json');
const message: any = {
"type": "initialize"
};
const request: Request = new Request(`${VendorHandler.REST_ENDPOINT_URL}`, {
method: 'POST',
headers: headers,
body: JSON.stringify(message)
}) as Request;
await fetch(request);
}
public webSocketErrorHandler(error: any): void {
console.log("WebSocket error", error);
}
public webSocketCloseHandler(event: Event): void {
console.log("WebSocket is closed", event);
}
public webSocketOnMessage(event: MessageEvent): void {
const jsonMessage = JSON.parse(event.data);
console.log(jsonMessage);
if (jsonMessage.eventName === "EventRegistered") {
// Genesys notifies that the agent is ready
this.integrationEventsHandler.makeAgentAvailable();
} else if (jsonMessage.eventName === "EventRinging") {
// Show incoming call notification
} else if (jsonMessage.eventName === "EventEstablished") {
// Genesys notifies that the call is accepted
} else if (jsonMessage.eventName === "EventReleased") {
// Genesys notifies that the call is disconnected
}
console.log("Message is received");
}
public async makeAgentAvailable(): Promise<void> {
let webSocket: WebSocket = new WebSocket(`${VendorHandler.WS_ENDPOINT_URL}`);
webSocket.onopen = this.webSocketOnOpenHandler.bind(this);
webSocket.onmessage = this.webSocketOnMessage.bind(this);
webSocket.onclose = this.webSocketCloseHandler.bind(this);
webSocket.onerror = this.webSocketErrorHandler.bind(this);
}
public async makeAgentUnavailable(): Promise<void> {
// TODO: call the vendor specific api to make the agent available
}
public async makeOutboundCall(phoneNumber: string, eventId: string): Promise<void> {
// TODO: call the vendor specific api to make the make an outbound call
}
public async acceptCall(): Promise<void> {
// TODO: call the vendor specific api to accept a call
}
public async rejectCall(): Promise<void> {
// TODO: call the vendor specific api to reject a call
}
public async hangupCall(): Promise<void> {
// TODO: call the vendor specific api to hangup a call
}
}進捗の確認
Fusionアプリケーションにサインインし、メディア・ツールバーを開きます。 メディア・ツールバー・アプリケーションから「エージェント可用性」ボタンをクリックします。 Fusionアプリケーションのボタンの色が変わり、電話アイコンのステータスが「使用可能」に変更されることがわかります。