Setting Up Case and Email Auditing
To choose actions to audit, use the Audit - Setup (RC_COMP_AUDIT) component.
This topic discusses how to set up case auditing.
|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Usage |
|---|---|---|
|
RC_COMP_AUDIT |
Choose which actions (add, change, and delete) to audit. |
Use the Audit - Setup page (RC_COMP_AUDIT) to choose which actions (add, change, and delete) to audit.
Navigation
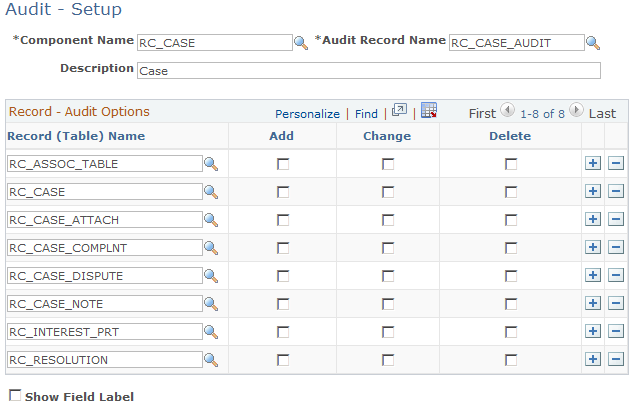
Image: Audit - Setup page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Audit - Setup page.
|
Field or Control |
Definition |
|---|---|
| Component Name |
Enter the object name of the component. PeopleSoft delivers entries for RC_CASE (the Case component) and RB_EM_IB (Search Inbound Emails component). Although you configure auditing at the component level, the processing occurs at the record level. Therefore, when multiple components are based on the same record, the system captures data changes regardless of which component the user was in when making the change. For example, the auditing that you establish for the RC_CASE component is also valid for the self-service case components, which are based on the same records. |
| Audit Record Name |
Enter the record where the system stores information about data changes. The structure of this record determines which fields get audited. |
Record - Audit Options
The fields in the Record - Audit Options region enable you to select which actions (add, change, and delete) to capture for each record that you audit. The selections apply to all audited fields in the specified record. You cannot set any field-level auditing options; all fields in a record must use the same auditing rules. To set field-level auditing options, you must redefine the audit record using PeopleSoft Application Designer.
When you activate auditing on the Audit Setup page, you turn on auditing only for the fields that are included in the audit record (RC_CASE_AUDIT or RB_INEM_AUDIT—the record that stores the audit trail data.
All auditing is based on differences between the field values at the time that the component is opened and at the time that the component is saved. If a user saves several times while working in a component, each save triggers auditing activity.
|
Field or Control |
Definition |
|---|---|
| Record (Table) Name |
Enter the record that is associated with the audited component. For example, the Case component includes data from several records. |
| Add |
Select to have the system capture the change every time a value is added to a field that is audited. A value is considered as added in two situations:
|
| Change |
Select to have the system capture the change every time the value of an audited field is updated. A value is considered updated when a new non-null value is different from the previous non-null value. |
| Delete |
Select to have the system capture the change every time the value of an audited field is deleted. A value is considered deleted when a null value replaces a non-null value. |
| Show Field Label |
Select to have the runtime audit page display the field labels rather than the field's object name. For example, if you're auditing the RC_PRIORITY field, selecting this option causes the audit page to refer to this field as Priority rather than RC_PRIORITY. If this check box is clear, the audit page displays field values. If the audited field has translate values, the translate long value appears. |