Event Management Business Process
The event management business process consists of four process steps:
Plan.
Invite and Register.
Execute and Convert.
Analyze.
Image: Event Management business process
The following diagram shows the event management business process, detailing the steps that occur during the planning phase, the invite and register phase, the execute and convert phase, and the analysis phase. The people and functions who perform each task are shown.
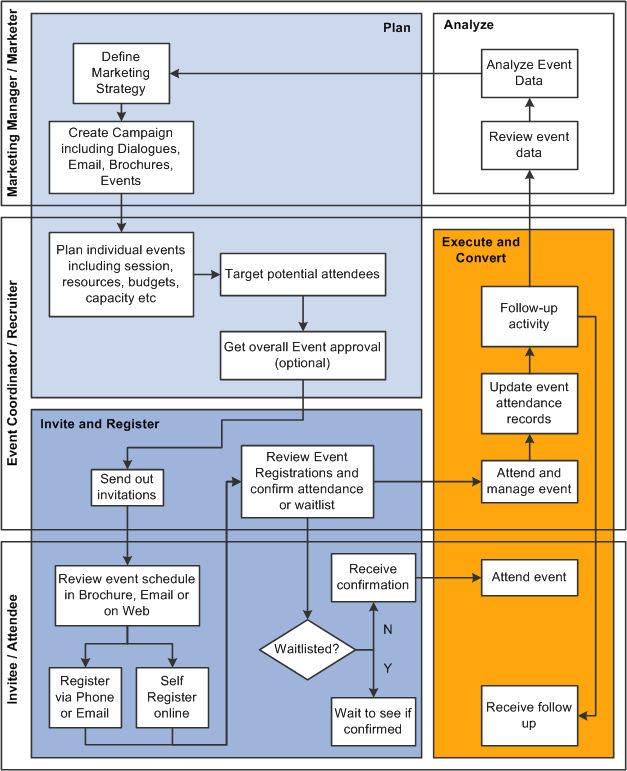
The PeopleSoft Event Management documentation is organized according to these business process steps.
Plan
In the Plan step, marketing managers and marketers formulate a plan to address the business opportunities and challenges that includes events. They determine the goals, collaborates with all the people and organizations that would be involved with the planning and execution of the event, and set up and manage the resources necessary to implement the event. These include setting budgets, obtaining approvals, defining event agendas, and organizing venues.
Begin by establishing the event basics like the event name; important dates like start, end and RSVP date; venue and capacity; event owner and whether the event is private or public.
An event can be a part of a larger marketing campaign. For example, a university's undergraduate student recruiting campaign might include web advertisements, multiple open house events, and postcards. Event Management provides the ability to link the event to a marketing campaign, specifically a roll up program, so that the high level budgets, costs, and metrics can be rolled up from all related programs and events and be viewed for the overall campaign.
Additionally, marketers can link any number of events that are related to this event (for example, if an open house is repeated on different days in different locations). They can display the related events as part of the self-registration process so that participants can sign up for similar events if they are not able to register for their first choice.
The marketer can define financial data for the event including budgets, planned and actual costs and event registration fees, including date based pricing such as early bird pricing. During the online self-registration process, the current price for the event is determined in real time.
After they have defined the high level detail for an event (budget, venue, and so on), marketers can submit it for approval prior to defining the rest of the event details. They do this by setting the event status to In Review. Doing this triggers an email or worklist entry to the event approver, who reviews the event and then sets the status to Approved. Additional data that can be set up at the event level includes resources (such as projectors and speakers), tasks, costs, notes, and metrics.
Marketers can also define multiple sessions for events along with a capacity and number attended for each session. They can define specific costs, metrics, notes, team members, and resources at the session level, allowing for more detailed tracking of popular sessions.
Further, they can target events to a specific list of participants. Event Management provides the ability to segment prospect, customer, and employee data to build the right audience for the event. Marketers can build the participant list both from audiences and by manually adding participants. The system automatically deduplicates the participants so that the event invitation is not sent to the same person twice.
Invite and Register
In the Invite and Register step, the event coordinator sends out the invitations using both inbound and outbound channels (such as phone, email, direct mail, call center, website, and fax). The Registration process step provides event coordinators and invitees the methods to capture registration information.
When sending the event invitation using email or the web, event coordinators can direct the recipient to an online registration page where he can register, decline, be waitlisted, or sign up for a future event. The online responses automatically update the registration status for the recipient within PeopleSoft Event Management, and the response date and time are updated to help determine whom to remove from the waitlist when space becomes available. In conjunction with Online Marketing, reminders can be sent to invitees using SMS and email.
During the registration process, Event Management determines the event price in real time and can take credit card payments (for event registration or donations) and display the payment transaction history.
Event coordinators can display related events as part of the self-registration process so that participants can sign up for similar events if they are not able to register for this particular event or if the capacity for this event is exceeded. As the responses are updated automatically, the coordinator can view in real time all the participants and their current response status for the event, as well as participant counts.
Note: In order to invite participants using email or to perform online registration, you must license PeopleSoft Online Marketing.
Execute and Convert
The Execute/Convert step provides event coordinators the ability to capture attendance and no-show information, self-service check-in (requires Online Marketing), and reports and lists of attendees for each event session.
After the event actually takes place, the attended or no-show field can be updated and any new prospects and leads can be added to the system. Event coordinators can convert event success to action, leveraging event participant lists for the automated creation of leads and and follow-up communications, as well as leveraging integrated surveying tools of Online Marketing to survey invitees and attendees to identify future event interest and improve events for the future.
Analyze
The Analyze and Measure step reports on the effectiveness of the event planning and execution process. Event Management provides a number of different metrics to help event coordinators analyze how successful the event was in terms of revenue (for a fundraising event), leads and opportunities generated (for a recruiting event), attendance rates (for a seminar), and more.