Aggregationsregel für Berichtssummen zuweisen
In diesem Thema werden Methoden beschrieben, wie Sie die Aggregationsregel für Berichtssummen explizit zuweisen können, um die Performance zu verbessern. Das ist speziell für technische Entwickler gedacht, die Berichte mit Oracle Analytics schreiben.
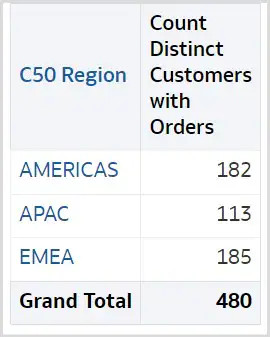
Die folgende Abbildung zeigt ein Beispiel, in dem der Bericht für Jahr, Monat und Kundenregion definiert ist, mit der Metrik Count Distinct of Customers with Orders (Anzahl eindeutige Kunden mit Bestellungen).
Die logische Abfrage sieht folgendermaßen aus:
SELECT
0 s_0,
"A - Sample Sales"."Cust Regions"."C50 Region" s_1,
"A - Sample Sales"."Counts"."32 # of Cust with Orders (Cnt Distinct)" s_2,
REPORT_AGGREGATE("A - Sample Sales"."Counts"."32 # of Cust with Orders (Cnt Distinct)" BY ) s_3
FROM "A - Sample Sales"
WHERE
("Time"."T02 Per Name Month" = '2011 / 11')
ORDER BY 2 ASC NULLS LAST
FETCH FIRST 500001 ROWS ONLYDie generierte physische Abfrage sieht folgendermaßen aus:
WITH
SAWITH0 AS (select count(distinct T42433.Cust_Key) as c1,
T42430.Region as c2
from
BISAMPLE.SAMP_CUSTOMERS_D T42428 /* D60 Customers */ ,
BISAMPLE.SAMP_ADDRESSES_D T42430 /* D62 Customers Addresses */ ,
BISAMPLE.SAMP_TIME_MTH_D T42405 /* D02 Time Month Grain */ ,
BISAMPLE.SAMP_REVENUE_F T42433 /* F10 Billed Rev */
where ( T42405.Mth_Key = T42433.Bill_Mth_Key and T42405.Per_Name_Month = '2011 / 11' and T42428.Cust_Key = T42433.Cust_Key and T42428.Address_Key = T42430.Address_Key )
group by T42430.Region),
SAWITH1 AS (select count(distinct T42433.Cust_Key) as c1
from
BISAMPLE.SAMP_TIME_MTH_D T42405 /* D02 Time Month Grain */ ,
BISAMPLE.SAMP_REVENUE_F T42433 /* F10 Billed Rev */
where ( T42405.Per_Name_Month = '2011 / 11' and T42405.Mth_Key = T42433.Bill_Mth_Key ) )
select D1.c1 as c1, D1.c2 as c2, D1.c3 as c3, D1.c4 as c4 from ( select D1.c1 as c1,
D1.c2 as c2,
D1.c3 as c3,
D1.c4 as c4
from
(select 0 as c1,
D1.c2 as c2,
D1.c1 as c3,
D2.c1 as c4,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY D1.c2 ORDER BY D1.c2 ASC) as c5
from
SAWITH0 D1,
SAWITH1 D2
) D1
where ( D1.c5 = 1 )
order by c2 ) D1 where rownum <= 500001
Der Gesamtwert 480 ist die Summe der Werte der einzelnen Bestandteile: 182 + 113 + 185. Die Summe wird mit dem folgenden logischen Abfrageausdruck berechnet: "REPORT_AGGREGATE("A - Sample Sales"."Counts"."32 # of Cust with Orders (Cnt Distinct)" BY ) s_3".
Wenn Sie REPORT_AGGREGATE verwenden, wird die Summe unabhängig von den Werten der einzelnen Bestandteile berechnet. Für dieses Berichtsdesign kann die korrekte Summe aber aus den einzelnen Bestandteilen für diesen Bericht berechnet werden.
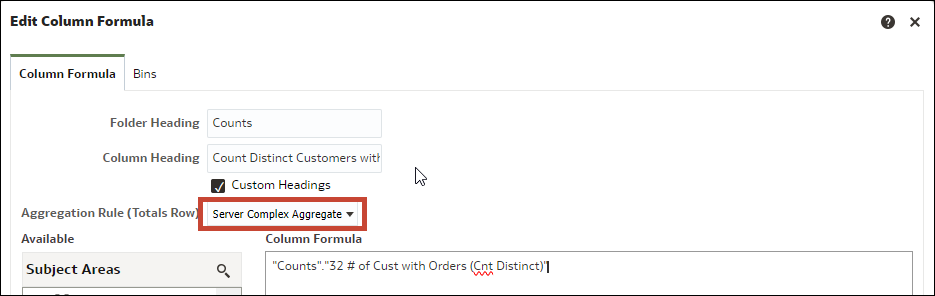
Wenn Sie die Spaltenformel bearbeiten, um Aggregationsregel (Summenzeile) von Serverkomplexaggregat in Summe zu ändern, werden die logische und die physische SQL-Abfrage geändert.
Die folgende Abbildung zeigt die ursprüngliche Aggregation.
Die folgende Abbildung zeigt die geänderte Aggregation.
Die geänderte logische SQL-Abfrage enthält jetzt REPORT_SUM.
SELECT
0 s_0,
"A - Sample Sales"."Cust Regions"."C50 Region" s_1,"A - Sample Sales"."Counts"."32 # of Cust with Orders (Cnt Distinct)" s_2,
REPORT_SUM("A - Sample Sales"."Counts"."32 # of Cust with Orders (Cnt Distinct)" BY ) s_3
FROM "A - Sample Sales"
WHERE
("Time"."T02 Per Name Month" = '2011 / 11')
ORDER BY 2 ASC NULLS LAST
FETCH FIRST 500001 ROWS ONLYDie folgende physische Abfrage wird generiert:
WITH
SAWITH0 AS (select count(distinct T42433.Cust_Key) as c1,
T42430.Region as c2
from
BISAMPLE.SAMP_CUSTOMERS_D T42428 /* D60 Customers */ ,
BISAMPLE.SAMP_ADDRESSES_D T42430 /* D62 Customers Addresses */ ,
BISAMPLE.SAMP_TIME_MTH_D T42405 /* D02 Time Month Grain */ ,
BISAMPLE.SAMP_REVENUE_F T42433 /* F10 Billed Rev */
where ( T42405.Mth_Key = T42433.Bill_Mth_Key and T42405.Per_Name_Month = '2011 / 11' and T42428.Cust_Key = T42433.Cust_Key and T42428.Address_Key = T42430.Address_Key )
group by T42430.Region),
SAWITH1 AS (select 0 as c1,
D1.c2 as c2,
D1.c1 as c3
from
SAWITH0 D1)
select D1.c1 as c1, D1.c2 as c2, D1.c3 as c3, D1.c4 as c4 from ( select D1.c1 as c1,
D1.c2 as c2,
D1.c3 as c3,
sum(D1.c3) over () as c4
from
SAWITH1 D1
order by c2 ) D1 where rownum <= 500001
Die gleiche Option zum expliziten Festlegen der Aggregation ist in Arbeitsmappen verfügbar. Siehe Numerische Werte von Visualisierungen formatieren. Ändern Sie in diesem Beispiel für die Spalte "Count Distinct Customers with Orders" die Aggregationsmethode in Summe.
Prüfen Sie, ob die beste Aggregationsregel für Ihre Berichte verwendet wird. Verwenden Sie eine explizite Aggregationsregeln, wenn das Berichtsdesign das zulässt.
Weitere Informationen zu Berichten finden Sie unter Analysen erstellen