3 Product Master Data Management Integration Option for Siebel CRM
This chapter describes the Oracle Application Integration Architecture (Oracle AIA) Product Master Data Management integration option for Siebel CRM.
About the Siebel CRM Option
The Siebel CRM option provides the following end-to-end process flows:
-
Synchronizing item catalog categories, which includes:
-
Relationships and structures
-
Attribute groups
-
Customer user-defined attributes (UDAs)
-
Transaction attributes
-
Hierarchies
See "About the Process Flow for Synchronizing Item Catalog Categories" for more information.
-
-
Synchronizing valuesets independently or as part of item catalog categories. See "About the Process Flow for Synchronizing Valuesets" for more information.
The Siebel CRM option also supports synchronizing items, price lists, and BOMs as described in "About the Process Flow for Synchronizing of Items and BOMs". This process flow also supports the following:
About the Process Flow for Synchronizing Item Catalog Categories
This process flow lets you use Oracle Product Hub to publish item catalog categories to participating applications.
You create or update item catalog categories as drafts, then release them to create working or active versions. At any given point, only one active released version of the item catalog category exists.
When you publish item catalog categories from Oracle Product Hub, the active released versions or the future-dated versions of the item catalog categories are published one at a time to the participating applications.
Publishing item catalog categories sends basic information, such as item catalog category ID, to the integration. The integration queries Oracle Product Hub for the complete details of the item catalog category and all the following associated entities:
-
Item catalog categories
-
Attribute groups
-
Seeded attributes and custom added attributes
-
Transaction attributes
-
Valuesets
-
Structures or relationships associated with item catalog category
When you publish a new item catalog category from Oracle Product Hub, the integration creates a workspace version of a product class in Siebel CRM. When you publish an updated item catalog category from Oracle Product Hub, the integration updates the existing product class. Updates can include updated associated entities.
Republishing a version of an item catalog category without any changes does not create a new version in Siebel CRM.
After the integration creates or updates the product class in Siebel CRM, it sends the status to Oracle Product Hub. Oracle Product Hub maintains a publication history for all the versions of item catalog category from each participating application.
The versions of item catalog category in Oracle Product Hub are associated with the effective start and end dates. You can only publish the active released version or future-dated versions from Oracle Product Hub, not draft versions.
You can revert to an earlier version of an item catalog category by creating a new version with effective dates. No impact occurs to the integration with the creation of this new version because the integration process handles this as new versions.
About Multi-Language Support for Item Catalog Categories
Item catalog category names are not translatable, but descriptions are. You can use up to 250 characters in the description to capture a language specific name. To capture language specific values, use the translatable validation type.
About Automatically Releasing Entities
By default, Oracle Product Hub activates the auto-release option. Siebel CRM releases the entity if the value is set or it must create the workspace version of the entity.
For more information about auto-release, see "Support for Controlling Auto-Release of Entities Published in the Same Batch".
About Synchronizing of Relationships and Structures
An item catalog category can be defined with relationship and structure that contains items and BOMs which have already been synchronized to the participating applications.
When the integration queries Oracle Product Hub for item catalog categories, Oracle Product Hub also provides the structures that are defined as relationships with the item catalog category. The item catalog category references only the latest version of the structure. The integration creates relationships for the product classes in Siebel CRM.
Oracle Product Hub also returns the component UDA associated with the relationship that stores context-specific values for the relationship within the item catalog category such as minimum, maximum, and default value. The integration uses this information to create relationships, add corresponding products, and set the context-specific values specified by the component UDA for the product class in Siebel CRM.
All types of BOMs can be added as the relationship for the item catalog categories.
The structure definition in Oracle Product Hub for item catalog categories supports two types of parent-child relationships:
-
Relationship of domain type as product: The product relationship represents another item that is related to the root item.
-
Relationship of domain type as class: The class relationship provides a list of items that can be treated as options. In Oracle Product Hub, these items are defined as BOM with BOM item type as option class, and the options are added as components of the BOM.
Note:
Domain type is a UDA associated with the item that identifies the type of relationship.For more information about telecommunications seeded library attributes and their corresponding valuesets, see the discussion of seeded item metadata libraries in Oracle Product Hub Implementation Guide.
This is an example of how various relationships under item catalog category are handled by the process integration. This is similar to the relationship handling of items in Option Class Support in Item Synchronization for Siebel CRM.
Table 3-1 is an example of how product and class type relationships are supported in Oracle Product Hub and how the process integration creates them in Siebel CRM:
Wireless Service item catalog category
Wireless Router (Item)
Bluetooth devices (Item with an option class type BOM and entity type of option group)
Samba Bluetooth Headset
B-Micro Bluetooth Headset
Table 3-1 Product and Class Types
| Wireless Router Class | Wireless Router |
|---|---|
|
Wireless Device Accessory |
Bluetooth devices |
|
Wireless Device Accessory |
Samba Bluetooth Headset |
|
Wireless Device Accessory |
B-Micro Bluetooth Headset |
Table 3-2 depicts the Oracle Product Hub definition of the relationship in the seeded attribute group Version Structure associated with the Wireless Service item catalog category. These attributes are component attributes values the values of which are set in context of the Wireless Service item catalog category.
| Relationship Name | Domain Type | Product | Class | Default Cardinality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Relationship1 |
Product |
Wireless Router |
1 |
NA |
|
Relationship2 |
Class |
Bluetooth devices |
Wireless device accessory |
1 |
For product relationships, the process integration creates a relationship of type product in Siebel CRM for the Wireless Service item catalog category. This relationship has an empty relationship domain in Siebel CRM.
For class relationships, the process integration creates a relationship of type class and adds all the components of the Bluetooth devices as the relationship domain. The product (Bluetooth devices) is not included as a part of the relationship in Siebel CRM.
This is an example of the support for relationship for product class in Siebel CRM:
Wireless Service item catalog category
Relationship1 Wireless Router
Relationship2 Wireless device accessory
Samba Bluetooth Headset
B-Micro Bluetooth Headset
Table 3-3 shows the structure attributes of the Wireless Service item catalog category in Siebel CRM.
Table 3-3 Structure Attributes
| Relationship Name | Domain Type | Product | Class | Default Cardinality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Relationship1 |
Product |
Wireless Router |
NA |
1 |
|
Relationship2 |
Class |
NA |
Wireless device accessory |
1 |
Table 3-4 shows the relationship domain and quantity.
| Relationship Domain | Quantity |
|---|---|
|
Samba Bluetooth Headset |
X |
|
B-Micro Bluetooth Headset |
X |
To update the relationship domain, more product components can be added to the product Bluetooth devices, and all the item catalog categories that have class relationship with Bluetooth devices must be synchronized to Siebel CRM for the relationship domain to be updated. Updating the Bluetooth devices and the synchronization is a prerequisite.
Any change in the relationship creates a new version of Wireless Service item catalog category in Oracle Product Hub. The process integration updates the corresponding Wireless Service item catalog category and the relationship in Siebel CRM.
About Synchronizing Attribute Groups
Every item catalog category is associated with zero or more attribute groups. Attribute groups are not defined within a context of the item catalog category and are reused across item catalog categories. Attribute groups are used to categorize user-defined attributes and operational attributes. The child item catalog category inherits the attribute groups of the parent item catalog category. The attribute groups are published when the associated item catalog categories are published. In the current release, Oracle Product Hub does not maintain the publication status of the attribute group in the publication history.
Whenever the integration queries Oracle Product Hub for the item catalog category, the attribute groups associated with the item catalog category are also returned. The attribute groups are represented at the canonical layer (specification group) as a part of classification scheme EBM. The attribute groups have reference attributes (specification).
None of the entities corresponds to attribute groups in Siebel CRM; therefore, they are ignored at the Siebel CRM connector service in the integration.
Note:
Oracle Product Hub provides a seeded telecommunications library that consists of a set of predefined attribute groups consisting of attributes that have predefined mapping to the fields of the item in the downstream application (Siebel CRM). Updates to these seeded attribute groups and the associated attributes are not supported by the Oracle Product Hub. In addition, the integration does not support addition or deletion of attributes within seeded attribute groups; however, you can define new attribute groups and attributes.New attribute groups with attributes can be defined. The integration differentiates between the customer-defined UDA and the seeded UDA and creates these as flex field attributes in Siebel CRM. Whenever customer-defined UDA is updated or new attributes are added, all the item catalog categories that are associated with the attribute groups have to be republished to the downstream applications.
Attribute groups can be of type multi-row. A multi-row attribute group is used to define characteristics that are record-based such as rules, pricelist lines, and so on. See the telecommunications seeded library attributes for definitions of multi-row seeded attribute groups.
When multi-row attribute groups are published, Oracle Product Hub provides the complete definition of these attribute groups with the records. The integration supports these multi-row attribute groups in the canonical model, but ignores them at the Siebel CRM connector. (The values for the multi-row attribute groups are defined during item definition and are set in the downstream applications during the item synchronization process.)
About Synchronizing Customer UDAs
The UDAs are defined within the context of the attribute group. These are not versioned entities. The UDAs are associated with valuesets. Context-specific values are set for every UDA within the attribute group. The child item catalog category inherits these UDAs from the parent item catalog category.
The static UDA, component UDA, and operational attributes are published with the attribute groups when the corresponding item catalog category is published.
Whenever integration queries Oracle Product Hub for item catalog category, the UDAs that are associated with the item catalog category through attribute groups are returned along with the item catalog category definition and other entities. The attributes that exist across the attribute groups are extracted and grouped under canonical models of the attribute.
Siebel CRM does not have attributes as separate entity. The static UDA and operational attributes that are defined within attribute groups are ignored in the Siebel CRM connector. These attributes have fixed mapping with the product fields in Siebel CRM and Oracle E-Business Suite respectively. The values for these fields are set during item synchronization.
Note:
UDAs are defined within the context of the attribute group. Any updates to the UDA results in the update of the attribute group. The item catalog category has to be republished for the updates on the UDA.All customer-defined UDAs are stored in the flexfield support provided by CRM; therefore, the you must ensure that you define unique attributes across custom attribute groups. The recommended approach is to prefix the corresponding attribute group name with XX for every customer-defined attribute. All the customer-defined attribute groups that are defined without a prefix are not mapped to any target application, but are available in the Oracle Application Integration Architecture (Oracle AIA) layer. You have to extend the connector services to map these attributes to the target applications.
The Oracle Product Hub does not track the publication status for attributes in the publication history for UDA.
About Synchronizing Transaction Attributes
Note the following:
-
The transaction attributes are defined within the context of the item catalog category in Oracle Product Hub. These are not versioned entities. The transaction attributes are associated with versioned valuesets in Oracle Product Hub. Context-specific values are set for every transaction attribute within the item catalog category. The child item catalog category inherits the transaction attributes and the valueset from the parent item catalog category.
-
Whenever the integration queries the Oracle Product Hub for item catalog category, the transaction attributes that are associated with the item catalog category are also returned. The integration process extracts all the transaction attributes and includes them in the specification section of the classification composition EBM. The process integration creates these as attributes of the product class in Siebel CRM and sets the corresponding context-specific values.
-
Any changes in the transaction attributes associated with the item catalog category (add, delete, or update the context specific values) updates the item catalog category and a new version is released in Oracle Product Hub. When an updated item catalog category is published, the integration updates the corresponding product class with the transaction attributes in Siebel CRM.
-
The static attributes and the transaction attributes both are grouped within the canonical model. The static attributes in the specification is ignored by the Siebel CRM connector and the transaction attributes are created as product class attributes.
-
Duplicate transaction attributes cannot be defined within an item catalog category. If a similar transaction attribute is defined in a parent item catalog category and the one of its child item catalog category in the hierarchy, the definition in the child hierarchy overrides the definition of the inherited transaction attribute.
-
If the inherited transaction attribute is updated in the child item catalog category, the transaction attribute does not remain an inherited attribute. It becomes a native attribute of the child item catalog category.
About Synchronizing Transaction Attributes without Valuesets
Transaction attributes are associated with valuesets and the values for the transaction attributes are selected from the list during order capture. For some transaction attributes, the values can be freeform text. For such transaction attributes, a valueset may not be associated in certain applications. For example, Oracle Product Hub.
In Oracle Product Hub, a transaction attribute is created in context of an item catalog category. The transaction attributes may or may not be associated with versionable valuesets. The following are the data types supported for the transaction attributes:
-
Char
-
Number
-
Datetime
-
Standard Datetime
-
Translatable Text
-
BOOL (Oracle Product Hub does not support the Boolean type. If the transaction attribute name has a BOOL suffix, it is treated as a Boolean data type.
-
INT (Oracle Product Hub does not support the Integer data type. If the transaction attribute name has an INT suffix, it is treated as an Integer data type)
For the transaction attributes of the first four data types associating the valueset is not mandatory but a valueset can be associated in Oracle Product Hub. However, for a transaction attribute of data type 'Translatable Text' a valueset cannot be associated. This is restricted with the validations in Oracle Product Hub.
During the Item Catalog Synchronization from Oracle Product Hub to Siebel CRM, if a transaction attribute has no valueset associated with it, then the process synchronization creates an attribute definition of Domain Type freeform by using the transaction attribute name and the datatype provided by Oracle Product Hub.
Subsequent updates to Item Catalog categories, for instance, the addition or deletion of transaction attributes or items in the structure will not affect the transaction attributes in Siebel CRM.
About Synchronizing Item Catalog Category Hierarchies
Note the following:
-
The publication framework for item catalog category provides flags that provide these publishing options for the product administrator in Oracle Product Hub:
-
Publish only the selected item catalog category.
-
Publish selected item catalog category and all its parents.
-
Publish selected item catalog category and all its children.
-
Publish selected item catalog category and all its parents and children.
-
-
In cases in which a single item catalog category is selected for publishing, if that item catalog category has a parent item catalog category that is not published, the parent item catalog category must be published to the downstream applications. If not, the process integration fails. You must publish the parent item catalog category and republish the child item catalog category. In this case, the child item catalog category references the parent item catalog category. The integration process associates the child item catalog category and its parent in Siebel CRM. Alternately, whenever a parent item catalog category is updated, the product administrator must publish the complete hierarchy associated with the item catalog category.
-
In cases in which the flag to publish the entire hierarchy (parents or children; or parents and children) is set, the integration process queries Oracle Product Hub for all the item catalog categories in the hierarchy. Oracle Product Hub returns the complete definition of all the item catalog categories in the hierarchy. The standard methodology to publish the entire hierarchy (parents and children) is recommended. The integration process creates the complete hierarchy of all the product classes in Siebel CRM.
-
Whenever an item catalog category is updated in Oracle Product Hub and published to downstream applications, the integration updates the existing product classes. In addition, the corresponding hierarchy is updated in Siebel CRM using the references to children or parent classes. The product classes are released to reflect the hierarchy in the active version.
-
The structure, transaction attributes, and the attribute groups of the parent item catalog category are passed to the child item catalog category. The inherited structure in the child item catalog category can be updated, for example, cardinality. Whenever an inherited structure is updated in the context of the child, the inheritance breaks and the structure becomes a native relationship of the child item catalog category. The behavior is the same for transaction attributes. The process integration updates the corresponding entities in the downstream applications.
About Associating Item Catalog Categories with Items
An item catalog category can be associated with the items. The items inherit the static attributes, transaction attributes, and structure associated with the item catalog category. An item can be associated with only one item catalog category.
-
When items are published in the publication framework, a reference to the item catalog category is published with the item.
-
The process integration creates the association of item and the item catalog category during the item synchronization process.
Synchronizing Item Catalog Category Implementation Flow
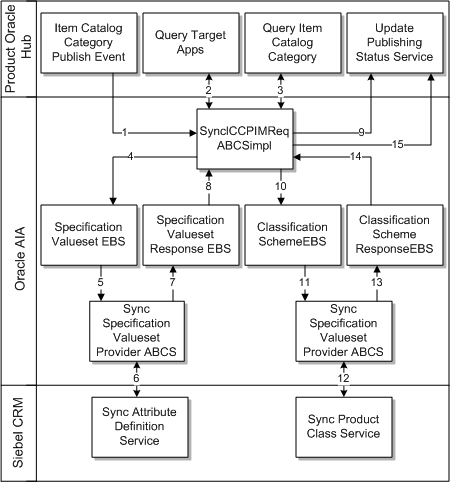
Figure 3-1 shows the high-level integration flow for the item catalog category synchronization.
These are the synchronization steps:
-
The product administrator in Oracle Product Hub publishes the item catalog category from the publication-framework user interface. The process publishes an event and provides basic information about item catalog category. The event consumer process invokes the requester ABCS for Oracle Product Hub.
-
The requester ABCS queries the target applications from Oracle Product Hub by calling the get target systems service.
-
Once the target systems are retrieved, the requester queries the item catalog category definition from Oracle Product Hub by calling the Oracle Product Hub Query item catalog category interface. The Oracle Product Hub Query item catalog category interface returns the complete information of the item catalog category together with the complete definitions of the associated entities (attribute groups, attributes, and valuesets). Valuesets are independent entities and can be associated with different attributes within the same or different attribute group in an item catalog category.
-
The Oracle Product Hub requester connector service transforms the response from the Oracle Product Hub query item catalog category interface into the SpecificationValuesetListEBM and ClassificationSchemeListEBM. The ClassificationSchemeListEBM has complete definitions of item catalog categories, attribute groups, attributes, and their associated valuesets. The connector service invokes an enterprise business service and provides the SpecificationValuesetListEBM as the input.
-
The specification valueset enterprise business service routes to the appropriate synchronize attribute definition Siebel CRM provider ABCS.
-
The attribute definition class Siebel CRM provider ABCS invokes the API provided by Siebel CRM to create the corresponding attribute definitions in Siebel CRM.
-
The Siebel CRM synchronize attribute definition returns to the caller with indication of success or failure.
-
Once the response is returned by the synchronize attribute definition API, the Siebel CRM connector service invokes a response EBS.
-
The specification valueset response EBS returns the response to the requester ABCS. The Oracle Product Hub requester ABCS transforms the valueset response EBM and invokes the Oracle Product Hub service to update the status. The Oracle Product Hub service updates the publication history for the valueset.
-
The Oracle Product Hub requester ABCS invokes the ClassificationSchemeEBS and provides ClassificationSchemeListEBM as input.
-
The ClassificationSchemeEBS routes to the appropriate synchronize product class Siebel CRM provider ABCS. It invokes the API provided by Siebel CRM to create product classes and their attributes. The product class also has structure or relationships associated. The relationships are created based on the relationship type. Siebel CRM API also synchronizes the product class names in multiple languages.
-
The synchronize product class API returns the status to the connector service.
-
The Siebel CRM connector service invokes a response EBS.
-
The ClassificationSchemeResponseEBS sends the status back to the requester ABCS.
-
The Oracle Product Hub requester ABCS transforms the classification scheme response EBM and invokes the Oracle Product Hub service to update the status. The Oracle Product Hub service updates the publication history for the item catalog category.
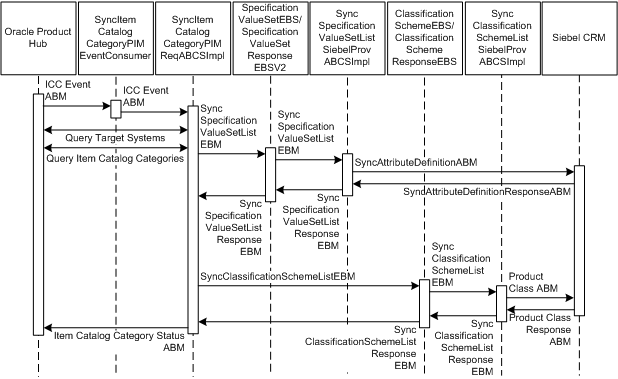
Figure 3-2 illustrates the services and their interaction.
The following are the sequence diagram steps and descriptions:
-
Oracle Product Hub item catalog category publish events are raised when the product administrator publishes the item catalog category from the Oracle Product Hub system.
-
SyncItemCatalogCategoryPIMEventConsumer listens to the business event and receives the WF_EVENT_T_msg event payload. SyncItemCatalogCategoryPIMEventConsumer routes to SyncItemCatalogCategoryPIMReqABCSImpl with complete event payload.
-
The Oracle Product Hub requester, SyncItemCatalogCategoryPIMReqABCSImpl, receives the event payload and calls the Oracle Product Hub publication service to get the list of target applications by passing the batch ID. It then constructs the query item catalog category Oracle Product Hub ABM, calls the Oracle Product Hub query item catalog category web service, and gets the complete item catalog category details.
It transforms the Query item catalog category response message to SyncSpecificationValueSetListEBM (only if valuesets are associated with T-Attr in Oracle Product Hub and the SyncValueSet flag is set to True in AIAConfigurationProperties.xml) and SyncClassificationSchemeListEBM.
If valuesets are associated with T-Attr and the valueset synchronize property is set to True in the AIAConfigurationProperties.xml, SyncItemCatalogCategoryPIMReqABCSImpl invokes SpecificationValueSetEBS, passing SyncSpecificationValueSetListEBM to synchronize valuesets in Siebel CRM and other participating applications.
Once the valueset synchronization is done successfully, it calls the classification scheme EBS passing SyncClassificationSchemeListEBM to synchronize the item catalog category.
It gets the item catalog category synchronization response, constructs the Oracle Product Hub publication service ABM, and calls the Oracle Product Hub publication web service.
This service takes the batch ID and gives the list of the target systems to which the synchronization should be done.
-
Oracle Product Hub Query item catalog category web service receives the batch ID, publishes parent hierarchy and child hierarchy flags, and returns the item catalog category details associated with that batch.
-
SpecificationValueSetEBS receives SyncSpecificationValueSetListEBM as an input and routes it to the SyncSpecificationValueSetListSiebelProvABCSImpl service to synchronize valuesets.
-
SyncSpecificationValueSetListSiebelProvABCSImpl receives SyncSpecificationValueSetListEBM. It transforms the EBM into the SyncAttributeDefinition ABM and calls the Siebel CRM valueset-synchronization Web service. Once synchronization is done, it gets the response from the Siebel CRM system, transforms SyncSpecificationValueSetEBM to SyncSpecificationValueSetResponseEBM, and invokes SpecificationValueSetResponseEBS.
-
Synchronize attribute definition Siebel CRM Web service synchronizes the attribute definition in Siebel CRM.
-
SpecificationValueSetResponseEBS receives SyncSpecificationValueSetListRespEBM as input and routes it to the SyncItemCatalogCategoryPIMReqABCSImpl service.
-
Once the valueset synchronization is done successfully in Siebel CRM, SyncItemCatalogCategoryPIMReqABCSImpl calls the ClassificationSchemeEBS passing SyncClassificationSchemeListEBM as its input and routes it to the SyncClassificationSchemeListSiebelProvABCSImpl service.
-
SyncClassificationListSiebelProvABCSImpl receives SyncClassificationSchemeListEBM. It transforms the EBM into a SWIClassImportUpsert_Input message and calls the Siebel CRM product-class synchronization web service to synchronize simple product class along with attributes or structures if associated.
It then populates the cross-reference with the corresponding Siebel CRM IDs. Once this is done, it checks for any associated hierarchy. If it exists, it makes another call to the same Siebel CRM Web service passing hierarchy information. Once synchronization is done, based on the workspace auto-release flag (Y), it calls the Siebel CRM product-class synchronization service again and passes the workspace auto-release flag. It then constructs the SyncClassificationSchemeListResponseEBM and passes it to ClassificationSchemeResponseEBS.
-
Synchronize product class Siebel CRM Web service synchronizes the product class in Siebel CRM and returns the response message.
Once the product class synchronization is done in Siebel CRM, SyncClassificationSchemeListSiebelProvABCSImpl calls the Siebel CRM product-class synchronization Web service again, passing workspace name, workspace refuse flag, and workspace auto-release flag to release the workspace.
-
ClassificationSchemeResponseEBS gets the SyncClassificationSchemeListResponse message and routes it to SyncItemCatalogCategoryPIMReqABCSImpl.
-
Once the Oracle Product Hub requester gets the item catalog category synchronization response message, it calls the Oracle Product Hub item catalog category publish status Web service to update the publication status in Oracle Product Hub. These are the possible status values:
-
Failed
-
Succeeded
-
Partial Fail (in case valueset fails)
-
About the Process Flow for Synchronizing Valuesets
The valuesets can be published independently or during the item catalog category publish from the Oracle Product Hub publication framework. The valuesets can be associated with the static UDA, customer UDA, and transaction attributes. For all the seeded valuesets of the telecommunications library, the integration provides DVMs. For all the valuesets that are associated with the transaction attributes, the integration with Siebel CRM creates the attribute definitions.
Valuesets associated with the customer-defined UDAs are handled as freeform values with the corresponding language codes. The MLS support for the valuesets depend on the validation type associated with the valueset. See "Multi-Language Support for Item Synchronization" for more information.
Synchronization of Valuesets as Part of Item Catalog Categories
Note the following:
-
Whenever the integration queries Oracle Product Hub for the item catalog category that is published, the valuesets that are associated with the attributes of the item catalog category are returned.
Note:
This includes the nonversionable valuesets that are associated with the UDA within the attribute groups and the versionable valuesets associated with the transaction attributes. In addition, if the same valueset is associated with more than one attribute, Oracle Product Hub returns a unique set (union) of valuesets associated with the item catalog category. -
The integration supports only the synchronize operation.
-
In cases in which a versioned valueset is republished to Siebel CRM, the updates on the attribute definition do not create a new version in Siebel CRM. Once the attribute definitions are created, they are associated with the corresponding attributes of the product classes in Siebel CRM.
-
Even though the canonical model consists of valuesets associated with the UDA and the transaction attributes, the Siebel CRM connector ignores all the valuesets that were associated with the UDA and creates attribute definitions for all the valuesets that were associated with the transaction attributes. The integration provides DVMs for all the valuesets that are associated with the seeded attributes of the telecommunications library.
-
Whenever an item catalog category is published, the publication framework extracts the version of all the valuesets that were associated when the item catalog category was released, implying that the version of the valueset that was associated with the item catalog category when the item catalog category was created might differ from the active released version of the valueset; therefore, publishing always picks up the version of the valueset that was associated when the item catalog category was released. The version in the downstream application is driven by the versions that are published. No one-one mapping exists between the versions of entities in Oracle Product Hub and the downstream applications. Oracle Product Hub provides validation to ensure that only the released version of the valueset can be associated with the attribute.
Synchronization of Valuesets Independently
Note the following:
-
The publication framework provides a separate user interface to search and to publish the valuesets. Multiple versions of the valueset exist in Oracle Product Hub, but at any point, only one active released version of a valueset exists. Only the active released version and the future-dated versions of the valuesets can be published. Oracle Product Hub enables you to publish one or more valuesets per publish process to the downstream participating applications. The publishing of valuesets is a manual process performed by the Oracle Product Hub product administrator.
-
The publish action invokes the integration process and provides basic information about valuesets. The integration queries Oracle Product Hub for the complete details of all the valuesets.
-
In cases in which a version valueset is republished to Siebel CRM, the updates on the attribute definition do not create a new version in Siebel CRM.
-
The versions of valuesets in Oracle Product Hub are associated with the effective start and end dates. Only the active released versions or future-dated versions are published.
-
Draft versions-versions that are not yet released-cannot be published from Oracle Product Hub.
-
Once the attribute definitions are successfully created in Siebel CRM for versionable valuesets of Oracle Product Hub, a status is propagated back to Oracle Product Hub. Oracle Product Hub maintains the publication history for all the versions of valuesets for each downstream application.
-
Oracle Product Hub supports these data types:
-
Char
-
Number
-
Standard Date
-
Standard Date time
-
BOOL (Oracle Product Hub does not support the Boolean type. If the valueset name has a BOOL suffix, it is treated as a Boolean type)
-
INT (Oracle Product Hub does not support the Integer type. If the valueset name has an INT suffix, it is treated as an Integer type)
-
-
Siebel CRM supports all of these data types as well as Boolean and Integer data types except Datetime.
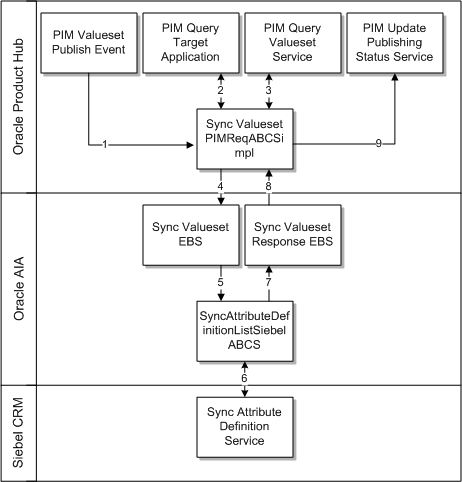
Figure 3-3 illustrates the valueset publish from Oracle Product Hub to Siebel CRM.
These are the steps depicted in the diagram.
-
The product administrator in Oracle Product Hub publishes one or more valuesets from the publication-framework user interface. The process publishes an event and provides basic information about the valuesets. The event consumer process invokes the requester ABCS for Oracle Product Hub
-
The requester ABCS queries the Oracle Product Hub valueset service.
-
The Oracle Product Hub valueset service returns a single payload with all the valuesets to the Oracle Product Hub requester ABCS.
-
The Oracle Product Hub requester ABCS extracts all the valuesets and transforms them into a single SpecificationValuesetListEBM. It invokes an enterprise business service with the synchronization operation and provides the SpecificationValuesetListEBM as input.
-
The enterprise business service routes to the appropriate provider ABCS.
-
The Siebel CRM provider ABCS transforms the incoming SpecificationListEBM into attribute definitions. The Siebel CRM provider ABCS invokes the Siebel CRM interfaces.
-
The Siebel CRM interface creates the corresponding attribute definitions. It checks the workspace auto-release flag: If it is Y, it calls Siebel CRM Web service to release workspace. If it is N, the workspace is not released. In case of D (default behavior), it reads release workspace from AIAConfigurationProperties.xml. The interface returns to the caller.
-
The Siebel CRM provider ABCS sends the status through a response EBS.
-
The response enterprise business service routes to the appropriate update valueset publish status Oracle Product Hub provider ABCS.
-
The update valueset publish status Oracle Product Hub provider ABCS invokes the Oracle Product Hub update status Web service and provides the valuesets and the corresponding statuses. The Oracle Product Hub update status service updates the publication history to reflect the status of publish.
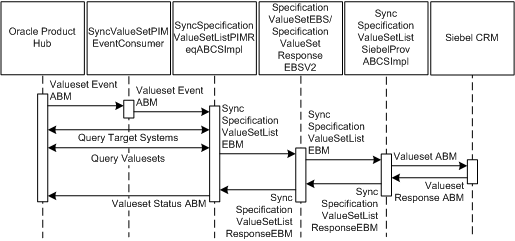
Figure 3-4 illustrates the services and their interactions:
The following are the sequence diagram steps and descriptions:
-
Oracle Product Hub valueset events are raised when the product administrator publishes the valuesets from the Oracle Product Hub system.
Valuesets can be published in batches.
-
There are two sub-steps in this step.
-
SyncValueSetPIMEventConsumer listens to the business event and receives the WF_EVENT_T_msg event payload for the valueset event. SyncValueSetPIMEventConsumer routes to SyncSpecificationValueSetListPIMReqABCSImpl with complete event payload.
-
The Oracle Product Hub requester ABC implementation service, SyncSpecificationValueSetListPIMReqABCSImpl, takes the batch ID from the WF_EVENT_T ABM payload, queries the get target systems service, and calls the Query valueset Oracle Product Hub service to get the response.
SyncSpecificationValueSetListPIMReqABCSImpl service also calls the query target application's Oracle Product Hub service and gets the response back. It counts the target applications from response, and based on the count it constructs the EBM for applications.
SyncSpecificationValueSetListPIMReqABCSImpl service transforms the Query valueset Oracle Product Hub service response ABM into QuerySpecificationValueSetList EBM and calls the SpecificationValueSetEBS Service.
-
-
SpecificationValueSetEBS Service gets SyncSpecificationValueSetList EBM as its input and routes it to the SyncSpecificationValueSetListSiebelProvABCSImpl service.
-
There are two sub-steps in this step.
-
SyncSpecificationValueSetListSiebelProvABCSImpl receives the SyncSpecificationValueSetList EBM message as input. SyncSpecificationValueSetListSiebelProvABCSImpl transforms the SyncSpecificationValueSetList EBM message into a Siebel CRM request ABM message and calls the synchronize attribute definition Siebel CRM Web service.
This service also filters the MLS mapping. A filter condition uses DVM to get the details on how many languages a provider system is supporting and another DVM is used for language code translation across applications. Only supported languages are synchronized to the provider system, for example, Siebel CRM.
Synchronize attribute definition Siebel CRM Web service returns the response to SyncSpecificationValueSetListSiebelProvABCSImpl service, which has the status detail.
-
SyncSpecificationValueSetListSiebelProvABCSImpl receives the response from synchronize attribute definition Siebel CRM Web service and transforms the Siebel CRM response ABM message into SyncSpecificationValueSetListResponseEBM and calls the SpecificationValueSetResponseEBS service.
The valueset synchronization is based on all or none basis. If Oracle Product Hub is sending a batch of 10 valuesets out of which five fail, this status is sent back to Oracle Product Hub that batch failed and the error that comes from the provider service is logged in error-handling framework.
-
-
SpecificationValueSetResponseEBS routes the SyncSpecificationValueSetListResponseEBM to SyncSpecificationValueSetListPIMReqABCSImpl.
-
SyncSpecificationValueSetListPIMReqABCSImpl service transforms the SyncSpecificationValueSetListResponseEBM message into a Oracle Product Hub valueset status-update Web-service input message and calls the Oracle Product Hub value set status-update Web service.
-
This Web service takes the input message from the SyncSpecificationValueSetListPIMReqABCSImpl service and updates the status in Oracle Product Hub as:
-
Success
-
Failed
-
About Other Supported Features
This section lists other features supported by the Siebel CRM option.
Multi-Event Product Synchronization from Oracle Product Hub to Siebel CRM
Products that have multiple charges and events are created as customizable products in Siebel CRM. Events are created as separate products and are added as child products of the main product. The component products represent the charges and events and have the billing type of event that is set in Siebel CRM. The item synchronization process from horizontal implementation supports both create and update of products in Siebel CRM.
To support create and update of pricelist, the process integration to Siebel CRM reuses the communications pricelist Siebel CRM-provider-connector services. The Oracle Product Hub requester item ABCS must create the corresponding item and pricelist line cross-references.
Support for Class Type Relationship in Product Synchronization for Siebel CRM
The item definition in Oracle Product Hub (for product) supports two types of parent-child relationships:
-
Relationship of domain type as product: The product relationship represents another item that is related to the root item.
-
Relationship of domain type as class: The class relationship provides a list of items that can be treated as options. In Oracle Product Hub, these items are defined as a BOM with BOM item type as option class. The options are added as components of the BOM. During the promotion definitions, the item that has a class relationship is reused across promotions and one or more items in the options are included or excluded based on the promotion modeling.
Note:
Domain type is a UDA associated with the item that identifies the type of relationship.For more information about Telco seeded library attributes and their corresponding valuesets, see the discussion of seeded item metadata libraries in Oracle Product Hub Implementation Guide.
Table 3-5 provides an example of how product and class type relationships are supported in Oracle Product Hub and how the process integration creates them in Siebel CRM.
Root item (item with a model type of BOM)
Wireless router (item)
Bluetooth devices (item with an option class type of BOM and entity type of option group)
Samba Bluetooth Headset
B-Micro Bluetooth Headset
Table 3-5 Example of How Product and Class Type Relationships are Supported in Oracle Product Hub
| Item Catalog Category | Item | Item Components |
|---|---|---|
|
Wireless Router Class |
Wireless Router |
NA |
|
Wireless Device Accessory |
Bluetooth devices |
NA |
|
Wireless Device Accessory |
NA |
Samba Bluetooth Headset |
|
Wireless Device Accessory |
NA |
B-Micro Bluetooth Headset |
Table 3-6 depicts the Oracle Product Hub definition of the relationship in the seeded attribute group: version structure associated with the root item. These attributes are component attributes for which values are set in context of the root item.
The type is expected to be set to Option Group. If the type is not set to Option Group, the class relationship is not set in Siebel CRM; instead, it is associated as a product.
Table 3-6 Oracle Product Hub Definitions
| Relationship Name | Domain Type | Product | Class | Default Cardinality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Relationship1 |
Product |
Wireless Router |
NA |
1 |
|
Relationship2 |
Class |
Bluetooth devices |
Wireless device accessory |
1 |
For product relationship, the process integration creates a relationship of type product in Siebel CRM for the root item. This relationship has an empty relationship domain in Siebel CRM.
For class relationship, the process integration creates a relationship of type class and adds all the components of the Bluetooth devices as the relationship domain. The product (Bluetooth devices) is not included as a part of the relationship in Siebel CRM.
Table 3-7 provides an example of the support for relationship for products in Siebel CRM.
Root Item
Relationship1 = Wireless Router
Relationship2 = Wireless Device Accessory
Samba Bluetooth Headset
B-Micro Bluetooth Headset
The structure attributes of the root item in Siebel CRM are:
Table 3-7 Attributes for Root Items in Siebel CRM
| Relationship Name | Domain Type | Product | Class | Default Cardinality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Relationship1 |
Product |
Wireless Router |
NA |
1 |
|
Relationship2 |
Class |
NA |
Wireless device accessory |
1 |
Table 3-8 shows the relationship domain and quantity.
| Relationship Domain | Quantity |
|---|---|
|
Samba Bluetooth Headset |
X |
|
B-Micro Bluetooth Headset |
X |
To update the relationship domain, you can add more product components to the product Bluetooth devices and all the items that have a class relationship with Bluetooth devices must be synchronized to Siebel CRM for the relationship domain to be updated. Updating the Bluetooth devices and synchronizing them is a prerequisite.
Siebel CRM has a relationship type attribute called domain type, and a DVM is created to map the domain type.
Any change in the relationship creates a new version of root item in Oracle Product Hub. The process integration updates the corresponding root item and the relationship in Siebel CRM.
Note:
A BOM item with the same item catalog category or a simple item cannot be added as a component of any root item more than once for any parent-child relationship in Oracle Product Hub.Support for Controlling Auto-Release of Entities Published in the Same Batch
The Product Master Data Management integration enables the product administrator to control the automatic release of all the entities within the project workspace in Siebel CRM at a more granular level than the Siebel CRM system parameter. This enables different behaviors with regard to entity auto-release based on the publishing style and the needs of the various product administrators.
Oracle Product Hub passes a flag to allow a more granular control at the batch level for the release of all the entities within the project workspace. This flag specifies whether the entities within the project workspace should be auto-released, should not be auto-released, or should use the default behavior set in Siebel CRM with regard to auto-release.
-
While Oracle Product Hub sets the flag at the batch level, Siebel CRM cannot use it at the batch level because within a batch, multiple Siebel CRM services are called for product and discounts, pricelist items, promotions, and structures. If the flag is set at service invocation level, inconsistencies may exist, for example, the service for product and discounts may succeed and all the product and discounts released in Siebel CRM, but the service for the associated structures may fail and the overall batch publishing would fail; however, the entities for product and discounts are released in Siebel CRM. Hence, the workspace cannot be released until all the entities in the batch that need to be synchronized are successfully synchronized.
-
Oracle Product Hub also passes a workspace name. The Siebel CRM ABCS uses the workspace name received from Oracle Product Hub as the product workspace name. The workspace name allows creating all the entities from the same batch within the same workspace.
-
Oracle Product Hub passes the batch auto-release flag and workspace name with each payload (item payload and BOM payload) at the header level. Values of these parameters are consistent in different payloads associated with the same batch ID.
-
The batch auto-release flag is set to one of these values:
-
Y - indicates that the batch is released automatically
-
N - indicates that the batch is released manually
-
D - indicates that the release of the batch should be controlled by the Siebel CRM system parameter. This is the default.
Oracle Product Hub always publishes the batch auto-release flag with a value of D.
-
-
Siebel CRM services for the creation of product and discounts, promotions, pricelist items, and structure take these at the header level:
-
Workspace name
-
Workspace reuse flag
-
Auto-release flag
If a workspace does not exist, Siebel CRM creates a new workspace; however, if it exists, the workspace reuse flag is set to Y and the workspace is reused. Otherwise, if the workspace exists and the workspace reuse flag is set to N, a new workspace is created the name of which is a concatenation of the value in the workspace name and a time stamp.
-
-
When the first Siebel CRM service within a batch is invoked, which typically is the service for the creation of products and discounts:
-
The value passed from Oracle Product Hub in the workspace name is used for the Siebel CRM workspace name.
-
The value passed in the batch auto-release flag is used for the Siebel CRM auto-release flag (upon DVM conversion), and the Siebel CRM workspace reuse flag is set to N.
-
-
When subsequent Siebel CRM services are invoked for the same batch:
-
The value passed in the batch name is used for the Siebel CRM workspace name.
-
The value passed in the batch auto-release flag is used for the Siebel CRM auto-release flag (upon DVM conversion), and the Siebel CRM workspace reuse flag is set to Y.
-
-
Finally, when all the Siebel CRM services pertinent to the same batch have been invoked and if the batch has succeeded, one more service for the creation of product and discounts is invoked with an empty sequence of products and discounts. It has these values for the header attributes:
-
The workspace name is the value passed in the batch name.
-
The Workspace reuse flag is Y.
-
The Auto-release flag is Y.
-
-
Within Siebel CRM, an unpublished workspace is not discarded, because administrators may want to access them for investigation. Periodic cleansing of unpublished workspaces is an administrator activity in Siebel CRM.
Note:
The auto-release flag is always passed as Default from Oracle Product Hub.Synchronization of Promotions from Oracle Product Hub to Siebel CRM
Promotions are defined as items in Oracle Product Hub with entity type as promotion. The process integration creates product promotions for every such item in Siebel CRM.
Promotions have model BOM as the structure. The model BOM can have one or more items that have model BOMs as structure or can have items that represent promotion level discounts. The process integration adds the corresponding customizable products as components of the promotions in Siebel CRM.
-
Promotions cannot have an option class BOM associated with the root item. The immediate components of the promotion can have a BOM of type option class. The items or components that are associated with BOMs of type option class are reused to create different promotions.
-
Promotions support n-level nesting of BOMs. The typical value for n is between 1 (one) and 6 (six).
-
In addition to the seeded UDA that is set for the item, these seeded user-defined attributes (UDAs) that are specific to items of entity type promotions are set during the promotion definition in Oracle Product Hub. See Sellable Product Information Library under Telco Seeded Library Attributes for more information.
-
Promotion: More Information
-
Charge Plan: Non Recurring Charge Details
-
Charge Plan: Recurring Charge Details
-
Charge Plan: Charges, Adjustment, Usage Plan Details
-
Commitment: Charges Credits
-
Product Promotions: Upgrade
-
-
The process integration to Siebel CRM sets the corresponding fields of the promotion in Siebel CRM.
-
Whenever a BOM is created for the promotion (root item) and the components are added, these seeded component UDAs are set during the promotion definition in Oracle Product Hub. See Component UDA for Item Synchronization under Telco Seeded Library Attributes.
-
Product Promotions: Components (Component UDA)
-
Product Promotions: Component Pricing (Component UDA)
-
Product Promotions: Pricing: Components: Adjustments (Component UDA)
-
-
Once the promotions and all the associated BOMs and their components are successfully synchronized to Siebel CRM, the status is updated in Oracle Product Hub publication history. Even if one of the components or child components of the BOM within the promotion fails, or is partially successful, the status on the promotion item is failed.
-
Adding, deleting, or updating the components that are directly associated with the promotions, or updating the fields of promotions such as promotion name, description, and so on, or updating the promotion-related information such as seeded and component UDA creates a new revision of the promotion in Oracle Product Hub. The new revision must be published to the downstream applications from the publication framework in Oracle Product Hub. For the deletion of components, the expectation is that the Oracle AIA configuration property synchronization flag be set to Y.
Populating Commitments on Sub-components: Level 3 Products
Whenever there are level 3 products in a product, structure and data for commitments need to be populated. Access the Product Promotion components structure UDA and populate the commitments such as Grace Period, Grace period, UOM, ApplyComponentCharge, Commitment, Prorated Plan and so on in the override column instead of the New Column.
For example, M113 Options is an Option Class or a Class Aggregate as it is an immediate component of a Promotion which has one default product, P113 Voice Unlimited Service. For this Product P113 Voice Unlimited Service, you need to populate the Default Cardinality field in the Override Value column.
Populating the Default Products in a Promotion Aggregate
If a Promotion has Aggregate (Product Class/Product Line) and they have some products in the hierarchy, then populate the 'Default Cardinality' value in the override column of Version structure UDA of the corresponding products.
For example, if you need to populate the commitments, do that in the same column in the Product Promotions Components UDA which is above the Version Structure. This is for products under both the Bundle as well as Aggregates.
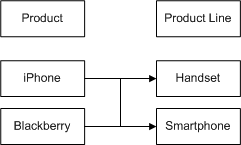
Component Exclusion in Context of Promotions
Whenever a promotion is defined in Oracle Product Hub, some of the components of the promotion or subcomponents under the root item can be excluded. See Figure 3-5 for an example of component exclusion.
Figure 3-5 An Example of Component Exclusions
Description of ''Figure 3-5 An Example of Component Exclusions''
Oracle Product Hub publishes the entire promotion definition with all the components, and wherever exclusions exist, it explicitly marks the exclusions by providing the path of exclusion from the root item (promotion).
The process integration to Siebel CRM handles the exclusions as follows:
-
Siebel CRM provides a contextual framework to control the promotion definition. In Siebel CRM, the complete promotion definition with components at all levels can be updated in context of the promotion without affecting the original definition of the customizable products that are included in the promotion definition. The integration identifies the components that are excluded, which is specified in the payload that is published from Oracle Product Hub. Siebel CRM does not remove or delete the components of customizable products in context of the promotions. This is a documented Siebel CRM limitation.
The process integration uses the cardinality associated with the components to exclude the components in context of the promotion.
The promotion definition in Oracle Product Hub can specify the exclusions in these ways:
-
Promotion definition can set the minimum cardinality and maximum cardinality of the component UDA to be 0 (zero).
-
Promotion definition can mark the exclusions of the components.
Note:
Siebel CRM provides the context-specific framework only in case of product promotions, not for customizable or component-type customizable products.Exclusions Within Option Class BOMs
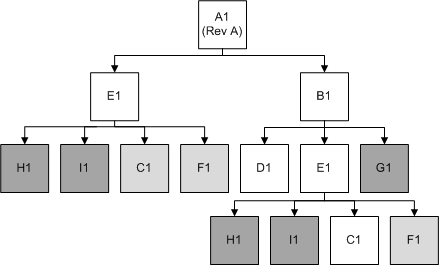
Table 3-9 explains the exclusions within option class BOMs.
Table 3-9 Exclusions Within Option Class BOMs
| Level | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
VoIP Limited Package |
|
1.1 |
VoIP Core Bundle |
|
1.1.1 |
VoIP Core Service |
|
1.1.1.1 |
VoIP Service Options |
|
1.1.1.1.1 |
Basic VoIP |
|
1.1.1.1.2 |
VoIP w/unlimited calls |
|
1.1.1.1.3 |
Fast Dialing |
|
1.1.1.2 |
VoIP Voicemail |
|
1.1.1.3 |
VoIP Caller ID |
|
1.1.1.4 |
VoIP Fax Service |
|
1.1.2 |
VoIP Adaptor |
|
1.1.3 |
VoIP Phone |
|
1.1.4 |
VoIP Laptop Phone |
|
1.2 |
VoIP Recurring Discount |
Case 1: Exclude components of item that represents promotions
The component items that are directly under the promotion are excluded by removal of the components.
These are the immediate components of the promotion VoIP Limited Package
-
VoIP Core Bundle
-
VoIP Recurring Discount
If any of these components have to be excluded, both the minimum and the maximum cardinality in the component UDA - Product Promotions: Components must be set to 0 (zero) in Oracle Product Hub and synchronized to Siebel CRM.
Case 2: Exclude components of items that represent bundles within the promotion
The component items that are not immediate children of the promotions but are subcomponents in the promotion definition are excluded by specifying the minimum and maximum cardinality as 0 (zero).
These are the subcomponents of the promotion VoIP Limited Package:
-
VoIP Core Service
-
VoIP Service Options
-
VoIP Voicemail
-
VoIP Caller ID
-
VoIP Fax Service
-
VoIP Adapter
-
VoIP Phone
-
VoIP Laptop Phone
The component items that are not immediate children of the promotions but are subcomponents in the promotion definition are excluded by right click on the component and exclude from current revision onwards in Product workbench of Oracle Product Hub. In Siebel CRM, the excluded component's Default quantity is blanked out.
Case 3: Exclude component of option class items
The components under an option class item have to be excluded in Oracle Product Hub by means of the exclusion method provided in the product workbench. Default cardinality in the component UDA - Version: Structure must be specified in Oracle Product Hub for all the items that are not excluded.
These are the components of the option class item VoIP Service Options:
-
Basic VoIP
-
VoIP with unlimited calls
-
Fast Dialing
If one of the components of the option class has to be made optional in context of the promotion, the default cardinality must override to 0 (zero).
Note:
If a component has to be excluded from the option class, right click on the Component and exclude from Current Revision onwards in the Product Workbench of Oracle Product Hub.If an override is not specified to any of the components, none of the components are excluded and the default quantity in the target application is set to 0 (zero), thus making all the components available as optional items as part of the same promotion.
Component Overrides in Context of Promotions
-
The promotions contain various levels of BOMs, where the model BOM is the root BOM. The components association with the BOMs within the context of the promotion can be overridden. For example, the minimum cardinality set at the immediate parent item can be overridden in context of the promotion.
-
This UDA is used to update the component association at every level of the BOM: Version: Structure (Component UDA).
-
The process integration sets the component overrides in context of promotions in Siebel CRM.
Transaction Attribute Value Exclusions in the Context of Promotions
-
A valueset is associated with every transaction attribute of the item. In Oracle Product Hub, a subset of values from the set of values of the valueset can be excluded for the transaction attribute of a component in context of the promotion. The metadata synchronization process synchronizes all the valuesets from Oracle Product Hub to Siebel CRM. See "About the Process Flow for Synchronizing Valuesets".
-
Whenever the items are added as components of the BOMs of parent items or added as components of BOMs that are included in the promotions, the product administrator in Oracle Product Hub can exclude a subset of values from the valueset associated with the transaction attribute in context of the BOM or the root item. During promotion synchronization to Siebel CRM, Oracle Product Hub provides the values that were excluded from the valueset. The component that is marked in green represents the excluded value. This is marked C in the diagram depicting components exclusion.
-
The process integration to Siebel CRM must set the values as exclusions for the corresponding attributes published from Oracle Product Hub in context of the promotion.
Promotion Based Discounts
The discounts on the components of the promotion are specified by means of these component UDAs:
-
Product Promotions: Component Pricing (Component UDA)
-
Product Promotions: Pricing: Components: Adjustments (Component UDA)
For more information about how to define promotion-based discounts in Oracle Product Hub, see the whitepaper ”Guidelines and Methodology to Define and Manage Entities in Oracle Product Hub for Oracle Product Master Data Management Integration” in article ID 1086492.1 on My Oracle Support.
Siebel CRM Interfaces
Siebel CRM interfaces used by the integration are:
Inbound Siebel CRM Web Services: Synchronize Items or BOMs
-
Service name: SWIProductIntegrationIO
-
Operation name: SWIProductImportUpsert
-
Request and response: SWIProductImportUpsert_Input, SWIProductImportUpsert_Output
-
Inbound Siebel CRM Web Services: Synchronize Pricelist
-
Service name: SWIISSPriceListItemIO
-
Operation name: SWIPriceListItemUpsert
-
Request and response: SWIISSPriceListItemIO.xsd
-
Inbound Siebel CRM Web Services: Synchronize Promotions
-
Service name: SWIPromotionIntegrationIO
-
Operation name: SWIPromotionUpsert
-
Request and response: SWIPromotionUpsert_Input, SWIPromotionUpsert_Output
-
Inbound Siebel CRM Web Services: Synchronize Attribute Definition
-
Service name: SWIAttributeIntegrationIO.wsdl
-
Operation name: SWIAttributeImportUpsert
-
Request and response: SWIAttributeIntegrationIO.xsd
-
Inbound Siebel CRM Web Services: Synchronize Product Class
-
Service name: SWIProductClassIntegrationIO.wsdl
-
Operation name: SWIClassImportUpsert
-
Request and response: SWIProductClassIntegrationIO.xsd
-
Inbound Siebel CRM Web Services: Synchronize Product Line
-
Service name - SWIProductLine.wsdl
-
Operation Name - SWIProductLine_Synchronize
-
Request and response - SWIProductLine.xsd
-
Outbound Siebel CRM Web Services
There are no outbound events from Siebel CRM for the Oracle Product Hub integration.
For more information about Siebel CRM web services, see CRM Web Services Reference.
Siebel CRM Integration Services
These are the integration services required for Siebel CRM to integrate with Oracle Product Hub:
-
SyncProductSiebelProvABCSImpl
-
SyncBillOfMaterialsListSiebelProvABCSImpl
-
SyncClassificationSchemeListSiebelProvABCSImpl
-
SyncSpecificationValueSetListSiebelProvABCSImpl
-
ProductOptimizedSyncPriceListListSiebelCommsProvABCSImpl
-
SyncItemCompositionListSiebelCommsProvABCSImpl
SyncProductSiebelProvABCSImpl
This single operation service accepts a SyncItemListEBM product message as a request. It does the following on receiving the ItemEBM based on the entity type specified with the item:
For type promotion, it transforms this message into a Siebel CRM promotion ABM and invokes the Siebel CRM promotion ABM. For the type as product or discount, it is assumed to be of type product.
For type as option_group it is assumed as Option Group. For discount_model it is assumed as Discount Model and for bundle it is assumed as Commercial Bundle. In case of non-promotion items-based on the entity type, the transformation conditionally transforms the corresponding elements required to support that entity.
This service transforms the message into Siebel CRM product ABM. It invokes the Siebel CRM product web service to synchronize with Siebel CRM.
SyncBillOfMaterialsListSiebelProvABCSImpl
This single operation service accepts a SyncBillOfMaterialsListEBM product message as a request and returns SyncBillOfMaterialsListResponseEBM message. The BillOfMaterialsEBS invokes SyncBillOfMaterialsListSiebelProvABCSImpl.
This service receives SyncBillOfMaterialsListEBM, transforms it into a Siebel CRM product ABM, and invokes the Siebel CRM product web service to synchronize the item structure with Siebel CRM.
When an item is defined as an option class in Oracle Product Hub, the provider services has two distinct behaviors:
-
Synchronize option class as a product with the option components as relationships with domain type of components.
-
Option class item can be established as a child with domain type of class. The service to establish the same as class is based on the values set for the component UDAs associated with the product. Domain type must be set to class, and the relationship name and class name must be same as item catalog category name that is pre-established in Siebel CRM as product class.
-
The components under the option class item in Oracle Product Hub are set as relationship domain for the class type relationship.
SyncClassificationSchemeListSiebelProvABCSImpl
This single operation service accepts a SyncClassificationListEBM product message as a request.
The responsibility of this service is to receive SyncClassificationListEBM, transform it to Siebel CRM product class ABM, and invoke the Siebel CRM product-class web service to synchronize it into Siebel CRM. Once the product class synchronization is done in Siebel CRM, it passes the response message to ClassificationResponseEBS.
SyncSpecificationValueSetListSiebelProvABCSImpl
This single operation service accepts a SyncSpecificationValueSetListEBM product message as a request.
The responsibility of this service is to receive SyncSpecificationValueSetListEBM, transform it to Siebel CRM attribute definition ABM, and invoke the Siebel CRM attribute-definition web service to synchronize it into Siebel CRM. Once the attribute synchronization is done in Siebel CRM, it passes the response message to specification valueset response EBS.
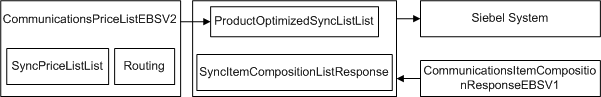
ProductOptimizedSyncPriceListListSiebelCommsProvABCSImpl
The ProductOptimizedSyncPriceListListSiebelCommsProvABCSImpl service transforms the PriceList EBM into a Siebel CRM pricelist message and then calls the Siebel CRM pricelist web service on operation InsertOrUpdate. The ProductOptimizedSyncPriceListListSiebelCommsProvABCSImpl transforms the PriceList EBM into a Siebel CRM product message and then calls the Siebel CRM product web service on operation Product_spcImport_spcUpdate. The Siebel CRM web service completes the request and returns a response message. ProductOptimizedSyncPriceListListSiebelCommsProvABCSImpl then transforms the Siebel CRM response message into the PriceList response EBM and sends it back to PriceListEBS.
Figure 3-6 ProductOptimizedSyncPriceListListSiebelCommsProvABCSimpl
Description of ''Figure 3-6 ProductOptimizedSyncPriceListListSiebelCommsProvABCSimpl''
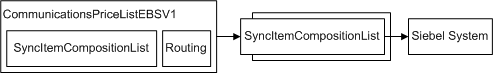
SyncItemCompositionListSiebelCommsProvABCSImpl
The SyncItemCompositionListSiebelCommsProvABCSImpl process accepts the SyncItemCompositionListEBM. It transforms SyncItemCompositionListEBM into the Siebel CRM product ABM. It then invokes the Siebel Product web service to create products and product structures in Siebel CRM.
Figure 3-7 SyncItemCompositionListSiebelCommsProvABCSImpl
Description of ''Figure 3-7 SyncItemCompositionListSiebelCommsProvABCSImpl''
Assumptions and Constraints for the Siebel CRM Option
The assumptions and constraints for the Siebel CRM option are:
-
The Item with BOM item type = "Option Class" and its component items must have the same item catalog category.
-
Changes to the seeded static attribute groups are not supported. If you want to introduce new static attributes, you must define new attribute groups and static attributes provided that the internal name of the custom static attribute have a prefix of 'XX_'. The integration creates these as flex attributes in Siebel CRM. If you introduce new valuesets in Oracle Product Hub for new UDA, the integration passes the information as free-form text.
-
The items and BOMs in the structure of an item catalog category must be published before the item catalog category is published.
-
The item catalog categories that are associated with the items must be synchronized to Siebel CRM before the items are published.
-
Every operating unit in Oracle Product Hub that has an associated order-entry item-validation organization needs to be defined as a business unit in Siebel CRM and the item validation organization defined as the inventory location associated with the business unit in Siebel CRM. This is required even if the operating unit and inventory organization role is associated with the same organization. For more information about establishing cross-references, see "Setting Up Cross-References". (This is applicable only if the Order to Cash: Siebel CRM - EBS integration is being planned or implemented with Product Master Data Management.)
-
The cross-references for inventory organization for item validation organization are set only for Siebel CRM and only those items from an item validation group that are associated with a single operating unit can be synchronized to Siebel CRM. (This is applicable if the Order to Cash: Siebel CRM - EBS integration is being planned or implemented with or without Product Master Data Management).
-
Oracle Product Hub produces multiple BOM revisions, but it can identify whether the component item of the BOM is part of the current revision or a future revision of the BOM so that Siebel CRM can filter out the item components that are not part of the current BOM structure. Siebel CRM has a limitation that it uses only the current BOM revision.
-
The integration supports multi-tier pricing between Oracle Product Hub and Siebel CRM and product prices with different effective dates. One Rate plan can have multiple pricing with different non-overlapping effective dates.
-
For Siebel CRM, these entities and associated subcomponents need to be setup manually in Oracle Product Hub:
-
Proration plans for items of entity type of promotion.
-
Compatibility rule matrix.
-
Volume discounts.
For Siebel CRM, these entities and associated subcomponents need to be enriched post synchronization:
-
Eligibility rules.
-
Configurator Rules
-
Sales Catalog
-
Volume discounts.
-
-
Once the products are successfully synchronized from Oracle Product Hub to Siebel CRM, they can also be updated to enrich the product definition.The existing products (subscription) that have references to pending quotes, orders, or assets in Siebel CRM or Oracle Communications Billing and Revenue Management (BRM) cannot be enabled as simple-service bundles. Similarly, the simple service bundles cannot be changed into subscription based billing products because by doing this, it impacts the existing asset cross-references. This is enforced by using the Siebel CRM validation only in the UI.
A mechanism or methodology must be defined for a product administrator in Oracle Product Hub to identify a given set of products that have pending quotes, orders, or assets in Siebel CRM (Order capture application). Once identified, the corresponding products must not be updated and synchronized to Siebel CRM unless the validation is added in the Siebel CRM application.
-
Pricelist:
-
A price list contains multiple product offerings and a product can appear in multiple price lists.
-
A Siebel CRM price list contains prices for all product offerings in one currency.
-
Changes to pricing either the current or future effectivity is done within the same price list
-
A single product definition is created for a specific asset (for example, handset) and separate one-time prices are defined in different price lists. For example, Consumer Price list and Business Price list. This helps in creating or using price lists for consumer, creating or using price list for business and associating single product definition of asset to each of the pricelist and define prices in price lists.
-
A single product definition is created for the monthly tariff and separate recurring prices are defined in different price lists. For example, Consumer Price list and Business Price list. This helps in creating or using Price list for consumer, creating or using price list for business and associating single product definition of asset to each of the pricelist and define prices in Price lists.
-
Publishing the product definition from Oracle Product Hub:
-
Synchronizes the product definition and the different pricing information in the consumer and business price lists in Siebel CRM. Future date effectivity prices must be added as new pricelist line items within the existing price list.
-
Synchronizes the product definition and the different pricing information for the consumer and business users as separate rate plans in BRM. For example, Consumer Pricelist and Business Pricelist. To track the relationship of rate plans with the pricelist, separate rate plans and rate plan selector definitions are created in BRM. Future date effectivity prices must be added as new rate tiers within the existing rate plan.
-
-
Multiple Price List Methodology
This section details the methodology of multiple price lists having Oracle Product Hub/BRM as its product master.
About Price Lists and Rate Plans
In Siebel CRM, a price list is a set of standard prices for products and services. You can use multiple price lists to offer separate prices for the same product and you can specify a default price list. The price list specifies a price, the currency for that price, and the frequency with which the price is charged.
For example, you can use separate price lists to charge business customers US$30 a month for internet service and to charge residential customers US$50 a month for the same service. In this example, the residential price list specifies that the price is 30, the currency is US dollars, and the frequency is monthly and the business price list specifies that the price is 50, the currency is US dollars, and the frequency is monthly.
You can use multiple price lists to offer different prices in different market segments (such as consumer or business customers, as in the previous example), different currencies, different sales channels (such as products purchased online or at a store), or different geographic locations.
Siebel CRM price lists map to rate plans in Oracle Product Hub/BRM. You create the price lists in Siebel CRM and set up the mapping between price lists and rate plans in the PRICELIST domain value map (DVM) before creating products in Oracle Product Hub/BRM.
While creating products in Oracle Product Hub/BRM, you define rate plans to specify what to charge for the products. You associate the rate plans with corresponding price lists configured in Siebel CRM so that the integration can determine where Siebel CRM tracks charges.
Note:
BRM also has a price list entity, but this is different from the Siebel CRM price list. When this document refers to price lists, it is referring to the Siebel CRM entity.Creating or Updating Rate Plans in Oracle Product Hub/BRM
The product master (Oracle Product Hub/BRM) stores the relationship between a rate plan and the pricelist. The integration uses this relationship to create or update pricing information in Siebel CRM.
-
In Oracle Product Hub/BRM, for multiple Rate Plans the Rate Plan Selector is used to define the relationship between a Rate Plan and the Pricelist.
-
To define price lists, you can either choose Standard pricing model or Billing pricing model. In Oracle Product Hub, the Rate Plan attribute group is used for Pricing Code Billing and Pricing:Simple Price List attribute group for Pricing Code Standard is used to define the relationship between a Rate Plan and the Pricelist.
-
When no pricelist is explicitly specified, the configured default pricelist is used.
Associating Rate Plans in Oracle Product Hub/BRM with Siebel CRM Price Lists
You associate rate plans in Oracle Product Hub/BRM with Siebel CRM price lists in Pricing Center using a rate plan selector.
To associate a rate plan with a price list using a rate plan selector:
-
In Pricing Center, follow the steps for defining rate plan selectors described in the Pricing Center Help.
-
When setting up columns for your rate plan selector, create a column called EVENT.PIN_FLD_USAGE_TYPE.
-
Add a row for each rate plan and corresponding price list that you intend to use.
-
In the EVENT.PIN_FLD_USAGE_TYPE column:
-
To associate a rate plan with a specific price list, enter the name of the price list exactly as it appears in the PRICELIST DVM.
If you enter a name that does not appear in the PRICELIST DVM, an error will occur when you synchronize the products to Siebel CRM.
-
To associate a rate plan with the default price list, enter * in the place of a price list name. The integration maps * to the default price list. See Table 3-11 for an example.
-
-
In the Rate Plan column, enter the name of the rate plans that correspond to the price lists that you entered in the EVENT.PIN_FLD_USAGE_TYPE column.
-
Finish defining the rate plan selector as described in the Pricing Center Help.
In this example:
-
Two products have been synchronized from BRM to Siebel CRM: Broadband and GSM.
-
A default price list has been set up in Siebel CRM, and entered into the AIAConfigurationProperties.xml file and the PRICELIST DVM, as described in "Setting Up Cross-References".
-
Four additional price lists have been set up in Siebel CRM and entered into the PRICELIST DVM: ConsumerPL, BusinessPL, NewYorkPL, and CaliforniaPL.
-
Five rate plans have been set up in Pricing Center: ConsumerRP, BusinessRP, NewYorkRP, CaliforniaRP, and StatesRP.
Table 3-10 shows the rate plan structure for the Broadband product. For this product, the product administrator uses two price lists to offer different prices for consumer and business customers.
Table 3-10 Example Rate Plan Structure for Broadband Products
| Rate Plan Name | Price List Associated with the Rate Plan | Tier | Start Date | End Date | Monthly Cycle Forward Fee |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ConsumerRP |
ConsumerPL |
1 |
01/01/2013 |
12/31/2013 |
$40 |
|
BusinessRP |
BusinessPL |
1 |
01/01/2013 |
12/31/2013 |
$30 |
Table 3-11 shows the rate plan structure for the GSM product. For this product, the pricing administrator uses the NewYorkPL and CaliforniaPL price lists to offer different prices for customers in New York and California and the default price list for customers in all other states. To make the integration use the default price list, the product administrator enters * for the price list associated with the StatesRP rate plan.
Table 3-11 Example Rate Plan Structure for GSM Products
| Rate Plan Name | Price List Associated with the Rate Plan | Tier | Start Date | End Date | Monthly Cycle Forward Fee |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
NewYorkRP |
NewYorkPL |
1 |
01/01/2013 |
12/31/2013 |
$45 |
|
CaliforniaRP |
CaliforniaPL |
1 |
01/01/2013 |
12/31/2013 |
$40 |
|
StatesRP |
- |
1 |
01/01/2013 |
12/31/2013 |
$35 |
In Siebel CRM, the Broadband product is mapped to price list line items under the ConsumerPL and BusinessPL price lists and the GSM product is mapped to price list line items under the NewYorkPL, CaliforniaPL, and default price lists.
Offering a Product in Multiple Currencies
To offer a product in multiple currencies:
-
In Siebel CRM, create price lists as described in "Setting Up Cross-References", and enter them in the PRICELIST DVM. Create a separate price list for each currency.
-
In Pricing Center, create rate plans that use the same currencies as the price lists in the PRICELIST DVM.
-
Define a rate plan selector for your product, associating the rate plans in the rate plan selector with the Siebel CRM price lists that use the corresponding currency. You must ensure that the currency in the rate plans matches the currency in the associated price lists. Currency matching is not validated by Siebel CRM or BRM.
-
Finish defining the rate plan selector and product as described in the Pricing Center Help.
-
Commit the product to the Oracle Product Hub/BRM database so that it is synchronized to Siebel CRM.
Example of Offering a Product in Multiple Currencies
To offer a product called Broadband in Canadian dollars and U.S. dollars, the BRM product administrator uses a separate rate plan associated with a separate price list for each currency while creating the product.
In this example:
-
A default price list has been set up in Siebel CRM and entered into the AIAConfigurationProperties.xml file and the PRICELIST DVM.
-
Two additional price lists have been set up in Siebel CRM and entered into the PRICELIST DVM: CanadaPL and USAPL. The currency for the CanadaPL price list is Canadian Dollars (CAD) and the currency for the USAPL price list is U.S. dollars (USD).
-
Two rate plans have been set up in Pricing Center: CanadaRP and USARP. The currency for the CanadaRP rate plan is Canadian dollars (CDN$) and the currency for the USARP rate plan is U.S. dollars (US$).
The product administrator uses the rate plan structure shown in Table 3-12 when creating the product.
Table 3-12 Offering the Broadband Product in Multiple Currencies
| Rate Plan Name | Price List Associated with the Rate Plan | Tier | Start Date | End Date | Monthly Cycle Forward Fee |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
CanadaRP |
CanadaPL |
1 |
01/01/2013 |
12/31/2013 |
CDN$30 |
|
USARP |
USAPL |
1 |
01/01/2013 |
12/31/2013 |
US$35 |
When the product administrator commits the Broadband product to the BRM database to synchronize it to Siebel CRM, the Broadband product is mapped to price list line items under the CanadaPL and USAPL price lists.
Managing Pricing in Rate Plans and Price Lists
After you have synchronized your products from Oracle Product Hub/BRM to Siebel CRM, you can manage the prices in the rate plans in Oracle Product Hub/BRM and resynchronize the products to Siebel CRM to update the price lists. You can manage prices by changing a product from using multiple price lists to using the single default price list.
Changing a Product from Multiple Price Lists to a Single Price List
To change a product in Oracle Product Hub/BRM that has already been synchronized to Siebel CRM from using multiple price lists to using the default price list:
-
If the one of the rate plans in the rate plan selector is associated with the default price list (uses * in the EVENT.PIN_FLD_USAGE_TYPE column):
-
In Pricing Center, set the duration end dates to the current day for all of the rate plans for the product associated with non-default price lists. Leave the rate plan associated with the default price list as is.
See the discussion of defining the duration of a rate in the Pricing Center Help for more information about setting the duration end date.
-
Commit the product to the Oracle Product Hub/BRM database so that the product is resynchronized to Siebel CRM.
-
-
If none of the rate plans in the rate plan selector are associated with the default price list:
-
In Pricing Center, set the duration end dates to the current day for all of the rate plans associated with the product.
See the discussion of defining the duration of a rate in the Pricing Center Help for more information about setting the duration end date.
-
Commit the product to the Oracle Product Hub/BRM database so that the product is resynchronized to Siebel CRM.
-
Under the Rate Plan Structure column for the product, select Single Rate Plan.
-
Commit the product to the Oracle Product Hub/BRM database so that the product is resynchronized to Siebel CRM. The integration automatically associates the single rate plan structure with the default Siebel CRM price list.
-
Examples of Changing a Product from Multiple Price Lists to a Single Price List
To change the GSM product with the rate plan structure shown in Table 3-11 from using multiple price lists to using a single price list (the default price list), the Oracle Product Hub/BRM product administrator uses Pricing Center to edit the rate plan selector. The product administrator does the following:
-
Changes the end dates of the NewYorkRP and CaliforniaRP rate plans to the current date. See Table 3-13.
Table 3-13 Setting the End Date for Rate Plans for the GSM Product
Rate Plan Name Price List Associated with the Rate Plan Tier Start Date End Date Monthly Cycle Forward Fee NewYorkRP
NewYorkPL
1
01/01/2013
01/31/2013
$45
CaliforniaRP
CaliforniaPL
1
01/01/2013
01/31/2013
$40
StatesRP
-
1
01/01/2013
01/31/2013
$35
-
Commits the product to the Oracle Product Hub/BRM database to resynchronize the product to Siebel CRM and update the effectivity dates for the price list line items.
Setting the end date for the rate plans not associated with the default price list means that the integration only uses the default price list and StatesRP rate plan for that product.
To change the Broadband with the rate plan structure shown in Table 3-11 from using multiple price lists to using a single price list (the default price list), the Oracle Product Hub/BRM product administrator uses Pricing Center to edit the rate plan selector. The product administrator does the following:
-
Changes the end dates of the ConsumerRP and Business RP rate plans to the current date. See Table 3-14.
-
Commits the product to the Oracle Product Hub/BRM database to resynchronize the product to Siebel CRM and update the effectivity dates for the price list line items.
-
Selects Single Rate Plan under the Rate Plan Structure column for the Broadband product.
-
Commits the product to the Oracle Product Hub/BRM database to resynchronize the product to Siebel CRM.
Changing the rate plan structure to Single Rate Plan means that no price list is associated with the rate plan in Oracle Product Hub/BRM. The integration automatically associates this rate plan structure with the default Siebel CRM price list and maps the Broadband product to price list line items under the default price list.
Support for Effectivity
The price lists effectivity period can be managed by changing the start and end dates on a rate plan. Any extensions can be possible by creating the same pricelist with new effective dates.
Similarly, the change in pricelist name can be achieved by setting the end date on incorrect Pricelist and recreating a new rate plan, map it to the new pricelist/tier group/rate data and balance impact.
Synchronizing Sponsorship Items from Oracle Product Hub to Siebel CRM
Sharing groups are groups of services that share benefits. Sponsorship items are used to model splitting the cost of service. For example, using sharing groups, a company can pay for some of its employees' mobile phone usage and offer a discounted rate for calls between employees.
One of the use case for Sharing groups is for Charge sharing. Sponsorship objects represent the charge share object that defines the rules for sharing the charges.In Oracle Product Hub, you need to define the Sponsorship object and then synchronize to Siebel CRM, Pricing Design Center and BRM. After synchronization sponsorship item to Siebel CRM, further modelling of Sharing Groups is required. This includes defining Promotion Group and including sponsorship item in the promotion group.After synchronizing sponsorship item to Pricing Design Center and BRM, further enrichment is required to define the charge sharing model. Oracle Product Hub supports definition of Sponsorship and discounts objects. However, promotions groups are not supported.
The Oracle AIA Master Data Management Product pre-built integration interfaces between Oracle Product Hub, Siebel CRM, and BRM to process sharing group requirements using a connector. It maps the sharing group product and discount offerings between Oracle Product Hub, Pricing Design Center and BRM and also creates or updates Oracle AIA cross-references.
Sharing Group Components
Each sharing group definition consists of associated components. You need to define these components in Oracle Product Hub and map to Siebel CRM, BRM, and Pricing Design Center. These components include:
-
Sponsorships
-
Discounts
-
Members
-
Promotion Groups
During run time, the owner of a sharing group needs to create the group at the owner account level. Members and services are added to the group by the owner. To avail the benefits of the sharing group, members need to subscribe to the sharing groups published by the owner.
Sponsorship
Sponsorships are defined in Oracle Product Hub as items and mapped to billing type items of chargeshare in Siebel CRM. Chargeshare model have to be predefined in BRM. Sponsorship items are used to define rewards in promotion groups in Siebel CRM.
After a sharing group request is published from Oracle Product Hub, Oracle AIA looks at the billing service type to determine the type of sharing group to create in BRM. When a service creation plus a promotion group creation request comes in, Oracle AIA first creates the service and then the sharing group in BRM. During the initiate billing phase, the Oracle AIA BRM provider provisions the promotion group line items after all services have been sent to billing.
Discounts
Discounts and chargeshares are created in BRM and special rating products created in Siebel CRM, added at design time as rewards to be shared by the group owner and members.
Discounts are created as items in Oracle Product Hub and synchronized to one or more Siebel CRM instances. The items and BOMs together with the seeded telecommunications library attributes are used to model various entities like products, discounts, bundles, promotions in Oracle Product Hub.
For more information on modeling the entities in Oracle Product Hub, see the whitepaper ”Guidelines and Methodology to Define and Manage entities in Oracle Product Hub for Oracle Product Master Data Management Integration 2.5" Note ID - 1086492.1 on My Oracle Support.
For more information about the functional and technical details of this process flow, see "BRM Interfaces" and "Synchronizing Discounts and Discount Models to Siebel CRM and BRM".
Membership
Member components are used to define items that represent members of a sharing group in Oracle Product Hub. Members are defined using the item type, Promotion Group Membership and maps to Product Type in Siebel CRM. Members can also be other accounts or assets. When synchronizing sharing groups, memberships are defined as service bundle or simple service bundle in Siebel CRM.
Promotion Groups
Your customers can share charges, discounts, and special rating profiles by purchasing promotion groups. You create promotion groups at design time in Siebel CRM. Each promotion group definition includes an owner membership product, a member membership product, and one or more reward products.
For more information on how to model sharing groups using Siebel CRM promotion groups, refer to the Oracle® Application Integration Architecture Oracle Communications Order to Cash Integration Pack Implementation Guide for Siebel CRM, Oracle Communications Order and Service Management, and Oracle Communications Billing and Revenue Management, Release 11.4, ”Creating Promotion Groups”.
To process sharing group discounts, the Oracle AIA Pre-built Integration Pack integration does the following:
-
Promotion group rewards with the billing service type of discount is purchased for the owner.
-
Promotion group rewards with the billing service type of special rating Friends and Family ERA is created for the owner.
-
Promotion group rewards with the billing service type of subscription is purchased for the owner.
You use APIs to create or update sponsorships in BRM when published from Oracle Product Hub to BRM.
Defining a Charge Sharing Group and Publishing to Siebel CRM
A charge sharing group allows the owner of the group to sponsor the charges of one or more members of the group. Members subscribe to the sharing group to avail sponsorship and discount benefits.
Charge sharing groups are used to determine how charges are shared among members. For example, an employer can sponsor the voice charges incurred by employees who are members of a charge sharing group.
This figure shows the high-level tasks to create a charge sharing group in Siebel CRM and how the integration is handled in Oracle AIA and BRM:
Figure 3-8 Creating a Charge Sharing Group in Siebel CRM
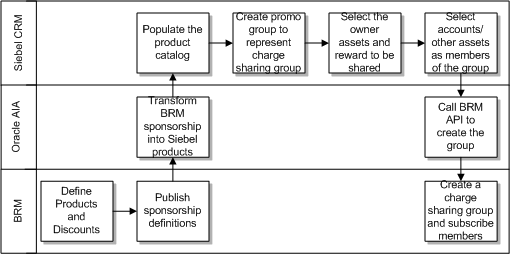
Description of ''Figure 3-8 Creating a Charge Sharing Group in Siebel CRM''
Here are the steps to define a charge sharing group in Oracle Product Hub and synchronize with Siebel CRM and BRM:
In Oracle Product Hub:
-
Define a sponsorship item type and specify the sponsorship attribute for chargeshare.
-
Map an event to the chargeshare model.
-
Create a Membership item type.
-
Create a Promotion Group item type.
-
Add one or more membership item to the promotion groups and define the cardinality of the membership products.
-
Add one or more products to each of the membership within the promotion groups.
-
Add one or more rewards products to the promotion groups and define the access control rules on the each of the membership within the promotion groups.
-
Define the promotion group validation rules such as the compatibility rules for promotion groups and membership in the context of the promotion groups.
-
Define the asset membership cardinality of the rewards products across promotion groups.
-
Associate the promotion groups, memberships and the rewards products to one of more pricelists.
-
Create or update the commitment terms and conditions for promotion groups and membership items.
-
Optionally, define pricing adjustments on the membership products, assets, and rewards in the promotion groups.
-
The promotion group, membership or rewards can be synchronized on their own or as part of the structure of the promotion group.
-
Publish and synchronize the following for promotion groups to Siebel CRM.
-
Publish and synchronize the Sponsorship Object from Oracle Product Hub to BRM/Pricing Design Center when Sponsorship object is published standalone or when it is published as part of the Promotion Group Structure.
-
Publish and synchronize the Membership Object from Oracle Product Hub to BRM/Pricing Design Center as billing product when there is a charge (recurring or onetime) for the member.
Oracle AIA synchronizes the sponsorship items from Oracle Product Hub to Siebel CRM. The product in Siebel CRM must indicate the billing type as sponsorship. Oracle AIA also synchronizes the sponsorship items from Oracle Product Hub to Pricing Design Center along with the charge share event map attributes and synchronizes the sponsorship items from BRM to Siebel CRM.
In Siebel CRM:
-
Map sponsorship item type to the billing type attribute in Siebel CRM.
In BRM:
-
Sync the sponsorship item to Siebel CRM using the billing item type.
-
Sync billing service type in BRM to these billing service types in Siebel CRM:
-
/account indicates that the charge sharing is at the account level.
-
/service/telco/gsm/telephony indicates charge sharing is for specific service.
-
Defining a Charge Discount Group and Publishing to Siebel CRM
Discount sharing group is a way to share a discount or resource, such as free minutes between multiple accounts or services. A member is charged for usage, discounting credits on the member's account and free minutes are deducted from the owner.
For example, Joe receives a 10,000 free minute discount. Joe wants to share the free minutes with his family members. Joe is the promotion group owner who is charged a recurring or one-time fee or both. In this plan, a discount in the promotion group fee is offered as a reward for using the sharing group.
In Siebel CRM:
-
Create a promotion group and assign Joe as the owner.
-
Add the members to the promotion group.
-
Specify the membership domain.
-
Define the rewards.
-
Map the promotion group reward billing service type, Discount to BRM
-
sharing group type, Discount Sharing Group.
In BRM:
-
Map the billing type in Siebel CRM to Subscription or Item. The billing item is charged to the promotion group owner at account or service level. The fee product billing service type should match the sharing group owner service type. In Siebel CRM, these products are added as rewards.
In this case, the reward for subscribing to the sharing group and paying the subscribing fee is 5GB data to be shared amongst the sharing group members.
When a service creation plus promotion group request comes in, Oracle AIA first creates the service and then sharing groups in BRM. During the billing phase, the Oracle AIA BRM provider processes the promotion group line items only after all services have been sent to billing.
Synchronizing Multiple Product Lines from Oracle Product Hub to Siebel CRM
You can now set up multiple product lines for a product in Oracle Product Hub (Oracle Product Hub) and then synchronize this relationship from Oracle Product Hub to Siebel CRM. For example, you can set up an iPhone to belong to two product lines: mobile handsets and smart phones.
Here are the high-level steps to set up and synchronize multiple product lines for a product from Oracle Product Hub to Siebel CRM:
In Oracle Product Hub:
-
Define product line object in Oracle Product Hub with these attributes:
-
Product Line (required)
-
Product Line Description
-
Zero or more Product Line Managers
-
-
Product line managers can be mastered in Siebel CRM and then setup in Oracle Product Hub as value sets as part of post installation steps.
-
Associate product lines to entities such as billing products and discounts, promotions, and bundles in Oracle Product Hub. Specify an effective date.
In Oracle AIA when you publish a product line in Oracle Product Hub, the Product Master Data Management integration synchronizes the product line definition and the product line relationships with Siebel CRM and creates or appropriate cross reference for the product lines.
Synchronizing Promotion Enhancements from Oracle Product Hub to Siebel CRM
Promotion aggregates allow you to group together products with common tariff plans. For example, you can group together handsets with common tariff plans.
Here are the high-level promotion aggregates integration steps between Oracle Product Hub and Siebel CRM:
In Oracle Product Hub:
-
Define a promotions product aggregate by product class.
-
Define one default product from a set of product options.
-
Specify one or more product line for a product offering.
-
Define promotion product aggregate by product line in Oracle Product Hub.
-
Specify a promotion adjustment by product line.
In Oracle AIA, synchronization occurs between a promotion and a product line or product class and promotion based aggregate pricing by product line or product class.
In Siebel CRM, web services are used to support integration of promotion aggregate definition and promotion pricing aggregate definition.
The Product Master Data Management Pre-built Integration Pack synchronizes the following promotion attributes from Oracle Product Hub to Siebel CRM:
-
Splitting and merging promotion definition
-
Promotions upgrade rules
-
Action attributes
-
Promotion upgrade attributes
-
Commitment attributes of promotion components
-
Commitment attributes of customizable product components
-
Relationships between a promotion and a product line or product class
-
Promotion based aggregate pricing by product line or product class
Integration Services
The synchronize product and price business flow uses the following BRM interfaces:
-
ProcessSalesOrderFulfillmentSiebelCommsReqABCSImpl
-
UpdateSalesOrderSiebelCommsProvABCSImpl
-
ProcessFulfillmentOrderBillingBRMCommsProvABCSImpl
-
ProcessFulfillmentOrderBillingBRMCommsAddSubProcess
-
ProcessFulfillmentOrderBillingBRMCommsUpdateSubProcess
-
ProcessFulfillmentOrderBillingBRMCommsDeleteSubProcess
Cross References
The cross references for working with sharing groups are as follows:
-
BUNDLEDPROMOTION_MEMBER_ID.xref: Used to maintain relationship between bundled promotion and its subcomponents.
-
PROMOTIONGROUP_MEMBER_ID.xref: Used to maintain the relationship between the promotion group and its members.
Assumptions and Constraints
The assumptions and constraints for working with the Oracle AIA Product Master Data Management pre-built integration connection between Oracle Product Hub, Siebel CRM, and BRM are as follows:
-
Oracle AIA creates a new sharing group in BRM for each type of promotion group reward. Promotion group rewards are shared by all promotion group members.
-
When synchronizing promotion group members to BRM, Oracle AIA directly associates them as SG members in BRM.
-
Promotion Group can have only one owner at any point of time.
-
When a promotion group ownership is changed on the Siebel CRM side, the system deletes the existing promotion group and adds new one.
-
Suspend or resume functions are not available for promotion groups.
-
If the promotion group owner is suspended, then all rewards are suspended for the promotion group members.
-
Although there is no corresponding information in Siebel CRM SalesOrderABM, Oracle AIA populates the promotion group information for the promotion group header order line.
-
The integration does not support initial load or batch load capability for item catalog categories. The recommended process is to publish the item catalog categories one at time because this is performed design time.