24 Extended Web Services Quality of Service /Diameter
This chapter describes the Oracle Communications Services Gatekeeper Extended Web Services Quality of Service (QoS)/Diameter communication service in detail.
See Services Gatekeeper Application Developer's Guide for information on the QoS RESTful interface.
Understanding the EWS Quality of Service/Diameter Communication Service
The Services Gatekeeper Extended Web Services Quality of Service (QoS)/Diameter communication service provides applications with a RESTful interface that allows them to control the quality of a subscriber connection. Among the connection quality aspects that the QoS feature can control include limiting and boosting subscriber connection bandwidth, as well as tuning connection latency. The QoS RESTful interface allows the application to initiate the following operations:
-
Apply a QoS policy
-
Apply a QoS policy based upon a pre-defined template
-
Modify an existing QoS policy
-
Remove an existing QoS policy
-
Register and unregister for QoS-related events
-
Query a QoS policy
While the Services Gatekeeper QoS feature enables an application to control QoS, actually executing the applied QoS policy and applying quality changes to a subscriber connection requires a separate Policy and Charging Rule Function (PCRF), such as Oracle Communications Policy Controller, working in conjunction with a Policy and Charging Enforcement Function (PCEF), solutions which are provided by various third parties.
Note:
Services Gatekeeper applies a QoS plan to a subscriber ID and a framed IP address. Applying QoS plans to individual data streams for a particular subscriber ID is not supported.Using Degraded Mode
This communication service offers a degraded mode feature to multi-tier Services Gatekeeper implementations that use databases on standalone systems. Degraded mode allows your implementation to continue processing traffic using Oracle coherence storage in the event that the database becomes unavailable for any reason. Processing time is not degraded, however this is intended as a short-term solution. Your coherence memory is limited and can fill up depending on your request rate and the size of your coherence memory. Once the coherence memory is full, your implementation will no longer process requests.
To use this feature you must configure your Oracle Coherence settings; see "Configuring Coherence to Use Degraded Mode" for details.
An Example End to End QoS Solution
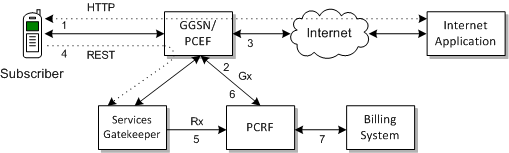
While Services Gatekeeper can apply and remove QoS plans, it provides no capability for actually enforcing QoS changes; instead it works in conjunction with PCRF and PCEF servers. Figure 24-1 illustrates a typical end to end QoS solution:
In Figure 24-1:
-
A subscriber's mobile device is registered with the Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN) or the PCEF.
-
The GGSN or PCEF requests a default QoS plan from the PCRF.
-
Once the QoS plan is returned from the PCRF, the GGSN or PCEF executes that plan and connects the subscriber's device to the Internet.
-
A subscriber application sends a RESTful request to Services Gatekeeper for a change in QoS.
-
Services Gatekeeper sends the QoS request to the PCRF using the Rx protocol.
-
The PCRF pushes the new QoS plan to the PCEF using the Gx protocol, and the PCEF executes that plan.
-
The PCRF interfaces with BRM or another billing management system to charge the subscriber appropriately.
Application Interfaces
For information about the RESTful-based interface for the Extended Web Services Quality of Service (QoS)/Diameter communication service, see the discussion of QoS interfaces in the Services Gatekeeper Application Developer's Guide, another document in this set.
Events and Statistics
The Extended Web Services Quality of Service (QoS)/Diameter communication service generates Event Data Records (EDRs) and alarms, to assist system administrators and developers in monitoring the service.
For general information, see "Events, Alarms, and Charging".
Event Data Records
Table 24-1 lists IDs of the EDRs created by the Extended Web Services Quality of Service (QoS)/Diameter communication service.
Table 24-1 EDRs Generated Quality of Service/Diameter Communication Service
| EDR ID | Method Called |
|---|---|
|
91801 |
ApplyQoSFeatureResponse and applyQoSFeature |
|
91802 |
QoSStatus and getQoSStatus |
|
91803 |
ActualProperties and modifyQoSFeature |
|
91804 |
removeQoSFeature |
|
91805 |
QoSFeatureExpiration |
|
91806 |
startQoSNotification |
|
91807 |
stopQoSNotification |
|
91808 |
sendInitAAR |
|
91809 |
sendModifyAAR |
|
91810 |
sendSTR |
|
91811 |
handleRxRAR |
|
91812 |
applicationQoSNotification_NotifyQoSEvent |
|
91813 |
Application Tier: ApplyQoSFeatureResponse and applyQoSFeature |
|
91814 |
Application Tier: QoSStatus and getQoSStatus |
|
91815 |
Application Tier: ActualProperties and modifyQoSFeature |
|
91816 |
Application Tier: removeQoSFeature |
|
91817 |
Application Tier: startQoSNotification |
|
91818 |
Application Tier: stopQoSNotification |
|
91819 |
applyTemplateBasedQoS |
|
91820 |
modifyTemplateBasedQoS |
|
91821 |
Application Tier: applyTemplateBasedQos |
Specifications for the EWS Quality of Service/Diameter Communication Service
Table 24-2 lists the technical specifications for the Extended Web Services Quality of Service (QoS)/Diameter communication service.
Table 24-2 Elements of the Extended Web Services Quality of Service/ Diameter Communication Service
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
|
Managed object in Administration Console |
To access this object, select domain_name, then OCSG, AdminServer, Communication Services, and then Plugin_qos_diametern in that oder. Here, n is the number of the particular plug-in instance. |
|
MBean |
Domain=com.bea.wlcp.wlng Deployment Name=wlng_nt_qos#6.0.0.0 InstanceName=Plugin_qos_diametern where n is the number of the particular plug-in instance Type=oracle.ocsg.plugin.qos.diameter.management.QoSMBean |
|
Network protocol plug-in service ID |
Plugin_qos_diameter |
|
Network protocol plug-in instance ID |
Plugin_qos_diamtern where n is the number of the particular plug-in instance |
|
Supported address scheme |
tel |
|
Application-facing interface |
RESTful |
|
Network-facing interface |
Diameter Rx |
|
Service type |
QoS RESTful management interface |
|
Deployment artifacts |
wlng_at_qos_rest.ear, wlng_nt_qos_rest.ear, com.bea.wlcp.wlng.plugin.qos.diameter.store_6.0.0.0.jar, and RestfulQoSClient.jar (PTE) |
Managing the EWS Quality of Service/Diameter Communication Service
This section describes properties and workflows for the Extended Web Services Quality of Service (QoS)/Diameter communication service plug-in instance.
General Configuration Workflow
The following procedure provides an outline to configure the Extended Web Services Quality of Service (QoS)/Diameter plug-in using the Administration Console or an MBean browser.
-
Select wlng, then PluginManager, and then createPluginInstance.
-
Set PluginServiceId to Plugin_qos_diameter and PluginInstanceId to Plugin_qos_diametern where n is an integer that is not already in use by an existing QoS plug-in instance.
-
Select wlng then PluginManager then addRoute.
-
Set PluginInstanceId to the id you configured in step 2 and enter an appropriate value for AddressExpression depending upon your Services Gatekeeper configuration.
-
Select the MBean wlng_nt_qos#6.0.0.0 and select the plug-in instance you created in step 2.
-
Select wlng_nt_qos#6.0.0.0 then select the plug-in you created in step 2. Expand QoSMBean and configure the plug-in instance attributes:
Note:
DestinationHostandDestinationPortshould be the correct values for your PCRF. -
Ensure that your PCRF is listening on the DestinationPort configured for the QoS plug-in.
Configuring Coherence to Use Degraded Mode
Degraded mode uses coherence storage for processing in the even that an external database is unavailable. You need to configure the coherence storage cache settings from write-through to use both write-behind and refresh-ahead, and specify the database tables to use for processing.
See "Using Degraded Mode" for a discussion on when to use this option.
See "Caching Data Sources" in Developing Applications with Oracle Coherence for a discussion of the write-through, write-behind, and refresh-ahead options. See ”Managing and Configuring the Storage Service” in Services Gatekeeper System Administrator's Guide for instructions on how to change this setting in Services Gatekeeper.
To configure degraded mode:
-
Open the Gatekeeper_home/modules/com.bea.wlcp.wlng.storage.tc_6.0.0.0.jar/gk-coherence-cache-config.xml file for editing.
-
Configure the coherence cache to use write-behind and refresh-ahead as shown in the example below. This example sets up a write-behind cache with a write-requeue-threshold of 10, a refresh-ahead factor of 0.5, and an expiry-delay of 20 seconds.
<distributed-scheme> <scheme-name>default-wlng-write-behind</scheme-name> <service-name>DistributedCache</service-name> <backing-map-scheme> <read-write-backing-map-scheme> <internal-cache-scheme> <local-scheme> <scheme-ref>default-rw-local-scheme</scheme-ref> </local-scheme> </internal-cache-scheme> <cachestore-scheme> <class-scheme> <scheme-ref>default-db-class-scheme</scheme-ref> </class-scheme> </cachestore-scheme> <read-only>false</read-only> <write-delay>20s</write-delay> <write-batch-factor>0.2</write-batch-factor> <write-requeue-threshold>10</write-requeue-threshold> <refresh-ahead-factor>0.5</refresh-ahead-factor> <expiry-delay>20s</expiry-delay> </read-write-backing-map-scheme> </backing-map-scheme> <autostart>true</autostart> </distributed-scheme> -
Save and close the file.
-
Open the domain_home/config/stora_schema/com.bea.wlcp.wlng.plugin.qos.diameter.store_5.1.0.0.jar/wlng-cachestore-config-extensions.xml file for writing.
-
Change the table type names for these database tables in the wlng-cachestore-config-extensions.xml file:
-
rest_qos_session_data
-
rest_qos_notification_corres
-
rest_qos_notification_register
-
rest_qos_template
You need to change the type_id of these tables from
wlng.db.wt towlng.db.wb. For example, changewlng.db.wt.plugin.qos.diameter.session_datatowlng.db.wb.plugin.qos.diameter.session_data.Example 24-1 shows these tables with the correct table names:
Example 24-1 Changing the rest_qos tables in wlng-cachestore-config-extensions.xml
- <store type_id="wlng.db.wb.plugin.qos.diameter.session_data" db_table_name="rest_qos_session_data"> - <identifier> <classes key-class="java.lang.String" value-class="oracle.ocsg.plugin.qos.diameter.store.AFSessionData" /> </identifier> </store> - <query name="com.bea.wlcp.wlng.plugin.qos.diameter.SessionDataQuery"> - <sql> - <![CDATA[ SELECT * FROM rest_qos_session_data WHERE sessionId = ? ]]> </sql> <filter-class>oracle.ocsg.plugin.qos.diameter.store.FilterImpl</filter-class> </query> - <query name="com.bea.wlcp.wlng.plugin.qos.diameter.SessionDataQueryByNodeId"> - <sql> - <![CDATA[ SELECT * FROM rest_qos_session_data WHERE nodeid = ? ]]> </sql> <filter-class>oracle.ocsg.plugin.qos.diameter.store.FilterImpl</filter-class> </query> - <db_table name="rest_qos_notification_corres" desc="qos notification correlator"> <key_column name="correlator" data_type="VARCHAR(255)" desc="correlator" /> <bucket_column name="correlatorData" desc="correlator data" /> </db_table> - <store type_id="wlng.db.wb.plugin.qos.diameter.notification.correlator" db_table_name="rest_qos_notification_corres"> - <identifier> <classes key-class="java.lang.String" value-class="oracle.ocsg.plugin.qos.diameter.store.CorrelatorData" /> </identifier> </store> - <query name="com.bea.wlcp.wlng.plugin.qos.diameter.CorrelatorQuery"> - <sql> - <![CDATA[ SELECT * FROM rest_qos_notification_corres ]]> </sql> <filter-class>oracle.ocsg.plugin.qos.diameter.store.FilterImpl</filter-class> </query> - <db_table name="rest_qos_notification_register" desc=""> - <multi_key_column name="endUserId" data_type="VARCHAR(255)" desc=""> - <methods> <get_method name="getEndUserId" /> <set_method name="setEndUserId" /> </methods> </multi_key_column> - <multi_key_column name="eventCriteria" data_type="INT" desc=""> - <methods> <get_method name="getEvent" /> <set_method name="setEvent" /> </methods> </multi_key_column> <bucket_column name="qoSRegisterData" desc="The register data of the qos notification" /> - <value_column name="correlator" data_type="VARCHAR(255)" desc="correlator from client(parlayRest)"> - <methods> <get_method name="getCorrelator" /> <set_method name="setCorrelator" /> </methods> </value_column> - <value_column name="endpoint" data_type="VARCHAR(255)" desc="end point"> - <methods> <get_method name="getEndPoint" /> <set_method name="setEndPoint" /> </methods> </value_column> </db_table> - <store type_id="wlng.db.wb.plugin.qos.diameter.qos_register_data" db_table_name="rest_qos_notification_register"> - <identifier> <classes key-class="oracle.ocsg.plugin.qos.diameter.store.QoSEventRegistrationKey" value-class="oracle.ocsg.plugin.qos.diameter.store.QoSEventRegistration" /> </identifier> </store> - <query name="com.bea.wlcp.wlng.plugin.qos.diameter.NotificationRegisterQueryByCorrelator"> - <sql> - <![CDATA[ SELECT * FROM rest_qos_notification_register WHERE correlator = ? ]]> </sql> <filter-class>oracle.ocsg.plugin.qos.diameter.store.FilterImpl</filter-class> </query> - <db_table name="rest_qos_template" desc=""> - <multi_key_column name="pluginInstanceId" data_type="VARCHAR(255)" desc=""> - <methods> <get_method name="getPluginId" /> <set_method name="setPluginId" /> </methods> </multi_key_column> - <multi_key_column name="matchRule" data_type="VARCHAR(255)" desc=""> - <methods> <get_method name="getMatchRule" /> <set_method name="setMatchRule" /> </methods> </multi_key_column> <bucket_column name="qoSTemplateData" desc="The template data of the apply qos request" /> - <value_column name="content" data_type="BLOB" desc="template configuration in xml style"> - <methods> <get_method name="getContent" /> <set_method name="setContent" /> </methods> </value_column> </db_table>
-
-
Save and close the file.
-
If the domain is running, stop and restart it.
Managing Extended Web Services Quality of Service Templates
Using the Administration Console or an MBean browser such as the Platform Test Environment, you can perform the following operations on QoS templates:
The creation of QoS templates and the usage of the QoS RESTful interface is covered in detail in the Services Gatekeeper Application Developer's Guidee, another document in this document set.
Load a QoS Template
For more information creating QoS templates, see the discussion on template-based apply QoS in Services Gatekeeper Application Developer's Guide, another document in this document set. Once you have created a QoS template, to load it, do the following.
-
Select the MBean wlng_nt_qos#6.0.0.0 and select the plug-in instance you wish to configure.
-
Expand QoSMBean and select loadQoSRequestTemplate.
-
In the MatchRule text box, enter a regular expression that matches the subscriber identifiers you want associated with the QoS template.
-
In the Content text box, paste in the contents of a valid QoS template.
-
Execute the MBean operation.
The QoS template is loaded and available for use. See "Operation: loadQoSRequestTemplate" for more details.
Retrieve an Existing QoS Template
To retrieve an existing QoS template, do the following.
-
Select the MBean wlng_nt_qos#6.0.0.0 and select the plug-in instance you wish to configure.
-
Expand QoSMBean and select retrieveQoSRequestTemplate.
-
In the MatchRule text box, enter a regular expression that matches the subscriber identifiers you have associated with a QoS template. If you are not sure which MatchRules are defined, you can use the listQoSRequestTemplateMatchRules operation.
-
Execute the MBean operation.
The QoS template is returned in the Output text box. See "Operation: retrieveQoSRequestTemplate" for more details.
List Match Rules for a QoS Template
To list match rules for a QoS template, do the following.
-
Select the MBean wlng_nt_qos#6.0.0.0 and select the plug-in instance you wish to configure.
-
Expand QoSMBean and select listQoSRequestTemplateMatchRules.
-
Execute the MBean operation.
The MatchRules configured for the plug-in are returned in the Output text box. See "Operation: listQoSRequestTemplateMatchRule" for more details.
Delete a QoS Template
To delete a QoS template, do the following.
-
Select the MBean wlng_nt_qos#6.0.0.0 and select the plug-in instance you wish to configure using the Administration Console or an MBean browser.
-
Expand QoSMBean and select deleteQoSRequestTemplate.
-
In the MatchRule text box, enter a regular expression that matches the subscriber identifiers associated with the QoS template you want to delete.
-
Execute the MBean operation.
The QoS template is deleted. See "Operation: deleteQoSRequestTemplate" for more details.
Reference: Attributes and Operations for EWS Quality of Service/ Diameter
This section describes the attributes and operations for the configuration and maintenance of the Extended Web Services Quality of Service (QoS)/Diameter communication service:
Attribute: DestinationHost
Scope: Shared
Unit: Not applicable
Format: String
The host name of the PCRF diameter server.
Valid values are either a host name or a regular expression matching a host name. The default value is host.destination.com.
Attribute: DestinationPort
Scope: Shared
Unit: Not applicable
Format: Integer
Port number of the PCRF diameter server.
Valid values are 0–65535. The default value is 3588.
Attribute: DestinationRealm
Scope: Shared
Unit: Not applicable
Format: String
Diameter destination realm used for requests.
Valid values are either a realm or a regular expression matching a realm. The default value is destination.com.
Attribute: OriginHost
Scope: Local
Unit: Not applicable
Format: String
Host name of the machine running the QoS plug-in.
Valid values are either a host name or a regular expression matching a host name. The default value is host.origin.com.
Attribute: OriginPort
Scope: Local
Unit: Not applicable
Format: Integer
Port number of the machine running the QoS plug-in.
Valid values are 0–65535. A value of 0 indicates a random port and should be used when upgrading the plug-in. The default value is 0.
Attribute: OriginRealm
Scope: Local
Unit: Not applicable
Format: String
Diameter originating realm used for requests.
Valid values are either a realm or a regular expression matching a realm. The default value is origin.com.
Attribute: Connected
Scope: Local
Unit: Not applicable
Format: Boolean
Boolean value indicating whether the plug-in is connected.
Valid values are true or false. The default value false.
Operation: connect
Scope: Local
Connects the QoS plug-in to the PCRF diameter server. If the plug-in is already connected, it will first be disconnected and then reconnected using the current parameters.
Signature:
connect()
Operation: disconnect
Scope: Local
Disconnects the QoS plug-in from the PCRF diameter server. If the plug-in is not currently connected, no action is taken.
Signature:
disconnect()
Operation: loadQoSRequestTemplate
Scope: Shared
This operation loads a QoS template for use with the template-based QoS interfaces.
The MatchRule parameter is a regular expression that determines to which subscriber IDs the QoS template will apply. For example a MatchRule value of tel:1234* will match any subscriber whose ID begins with tel:1234.
The Content parameter takes a template formatted according to the XSD found in the xsd subdirectory in the plugin_qos_diameter.jar file which itself is contained within the wlng_nt_qos.ear archive located in Middleware_Home/ocsg_6.0/applications directory.
For more information on QoS templates, see the discussion on template-based apply QoS in Services Gatekeeper Application Developer's Guide.
Signature:
loadQoSRequestTemplate(MatchRule: String, Content: XML)
Table 24-3 lists the parameters that the loadQoSRequestTemplate operation accepts.
Operation: retrieveQoSRequestTemplate
Scope: Local
This operation retrieves a QoS template associated with a particular subscriber ID or a range of subscriber IDs defined by the MatchRule parameter.
The MatchRule parameter is a regular expression that determines to which subscriber IDs the QoS template is applied. For example a MatchRule value of tel:1234* will match any subscriber whose ID begins with tel:1234.
Signature:
retrieveQoSRequestTemplate(MatchRule: String)
Table 24-4 lists the parameters that the retrieveQoSRequestTemplate operation accepts.
Operation: listQoSRequestTemplateMatchRule
Scope: Local
This operation lists all of the match rules that have been defined for the plug-in.
Signature:
listQoSRequestTemplateMatchRule()
Operation: deleteQoSRequestTemplate
Scope: Shared
This operation deletes a QoS template associated with a particular subscriber ID or a range of subscriber IDs defined by the MatchRule parameter.
The MatchRule parameter is a regular expression that determines to which subscriber IDs the QoS template is applied. For example a MatchRule value of tel:1234* will match any subscriber whose ID begins with tel:1234.
Signature:
deleteQoSRequestTemplate(MatchRule: String)
Table 24-5 lists the operations that the deleteQoSRequestTemplate operation accepts.