Configure
This topic explains the required steps to configure connectivity between the AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) and the ODB Network for Oracle Database@AWS.
Required Permissions
Table 1-1 Required Permissions to Configure Connectivity
| Task | Cloud | Persona | Permissions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Configure connectivity between the AWS VPC and the ODB Network for Oracle Database@AWS | AWS |
To create route rule in App VPC's route table, the following EC2 IAM permissions are required.
For connectivity:
To create outbound endpoint in Route 53, the following Route 53 Resolver IAM permissions are required.
EC2 IAM:
To configure security rules in security group, EC2 IAM permissions are required.
|
Before you start to configure the connectivity between the AWS VPC and the ODB network for Oracle Database@AWS, you must download the latest AWS CLI . For more information, see Installing or updating to the latest version of the AWS CLI.
- Use the latest AWS CLI and run the following command:
aws --version - Make sure that you are using AWS CLI version
2.27.47or higher. For example, you will see the following output after running the previous command:aws-cli/2.27.47 Python/3.13.5 Darwin/24.5.0 source/x86_64 - Run the following command to confirm that you have access to the
--odb-network-arnparameter:aws ec2 create-route help - Verify that
[--odb-network-arn <value>]parameter appears in the help SYNOPSIS for thecreate-routeAPI:create-route [--destination-prefix-list-id <value>] [--vpc-endpoint-id <value>] [--transit-gateway-id <value>] [--local-gateway-id <value>] [--carrier-gateway-id <value>] [--core-network-arn <value>] [--odb-network-arn <value>]
Configuring Routing
This section outlines the creation of a route rule in the route table for enabling traffic to be routed to the Oracle Database@AWS through the ODB network. You must create an identical route rule in all route tables associated with the subnets from which you intend to access Oracle Database.
Create Route Rule Targeting the ODB Network
- If your operating system is Linux, use the following script to configure environment variable for the AWS CLI.
$ export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLEKEY $ export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLESECRETKEY $ export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION=<region-code> - If your operating system is Windows, use the following script to configure environment variable for the AWS CLI.
$ set AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLEKEY $ set AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLESECRETKEY $ set AWS_DEFAULT_REGION=<region-code> - Navigate to VPC dashboard and select Your VPCs from the Virtual private cloud in AWS console.
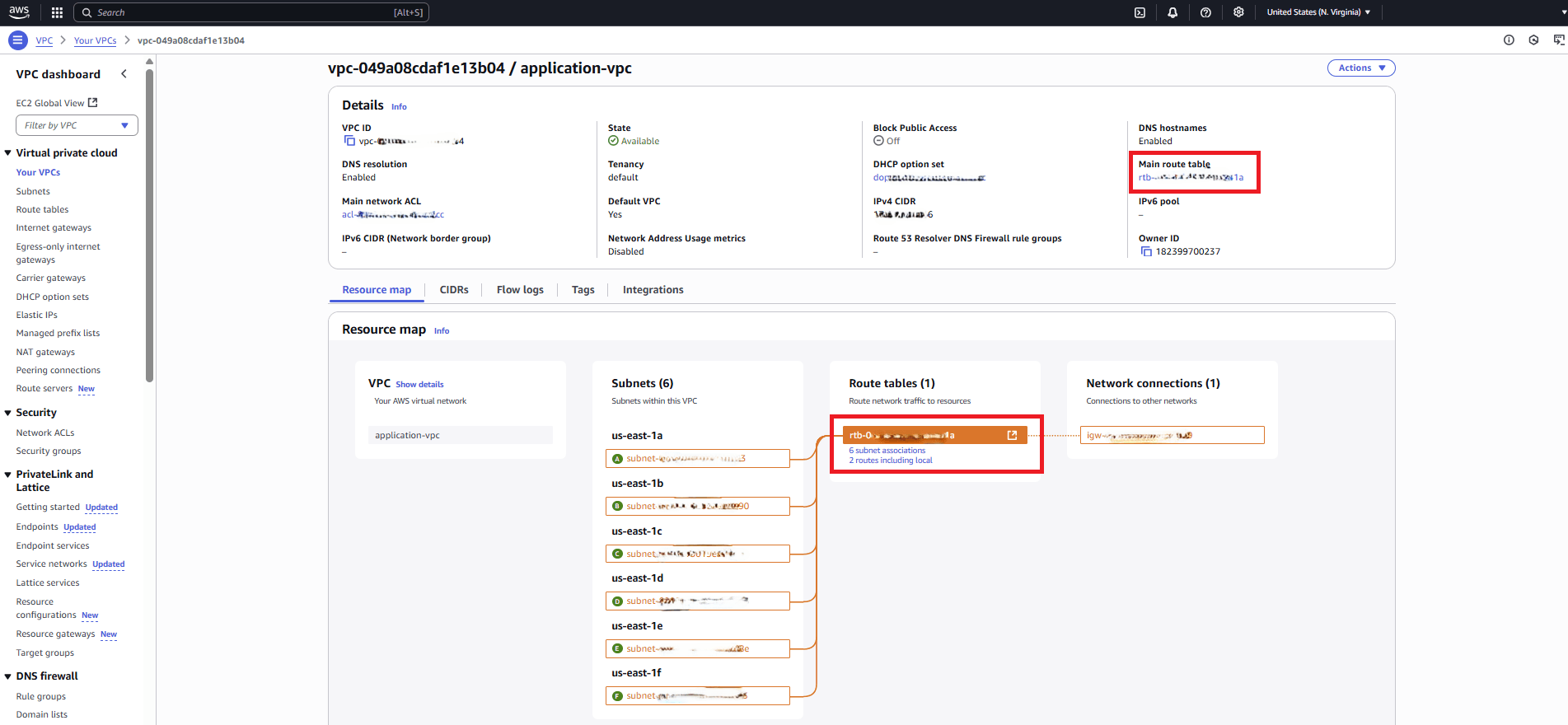
- Select the Resource map tab, and then select the route table that is associated with the subnet.
- From Oracle Database@AWS dashboard, select ODB networks, and then select your ODB network that you are using.
- Select the Summary tab to view details of ODB network ARN and Client subnet CIDR range.
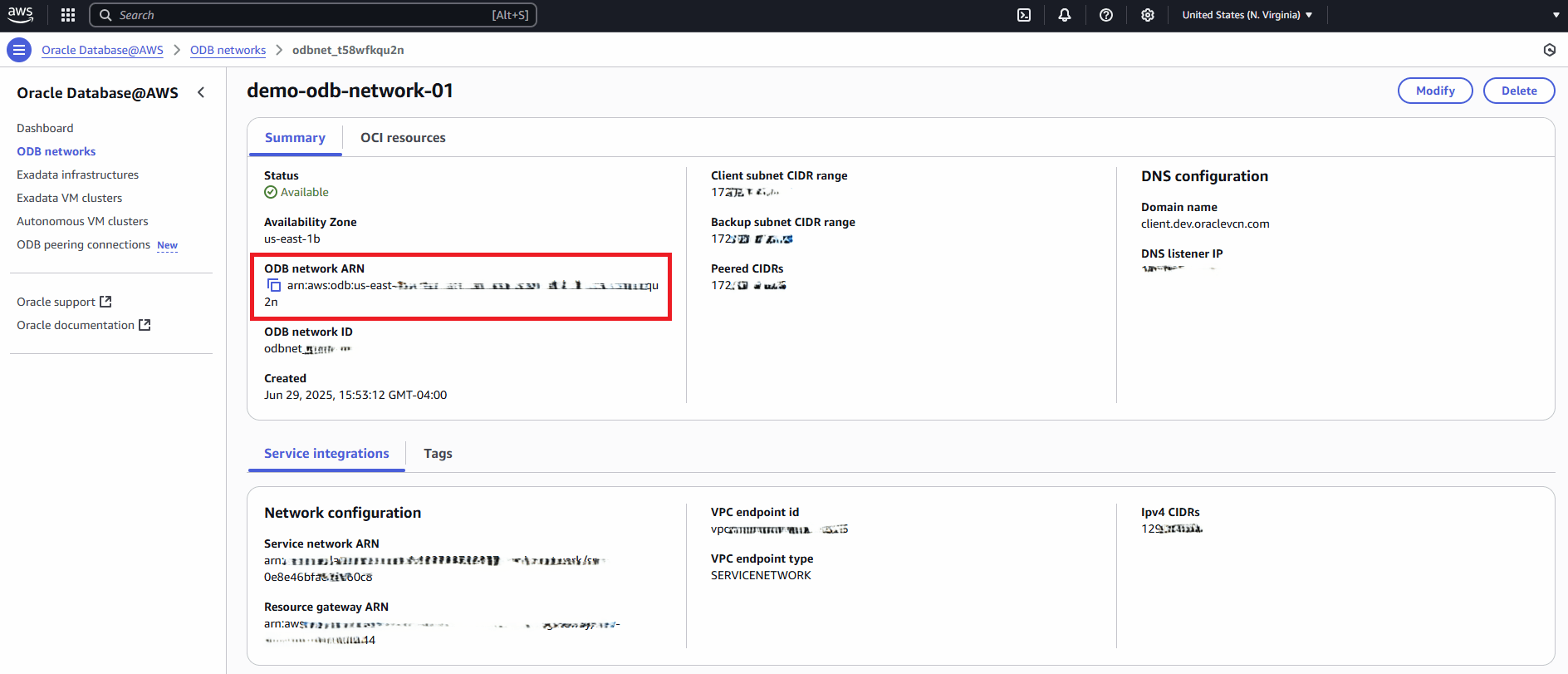
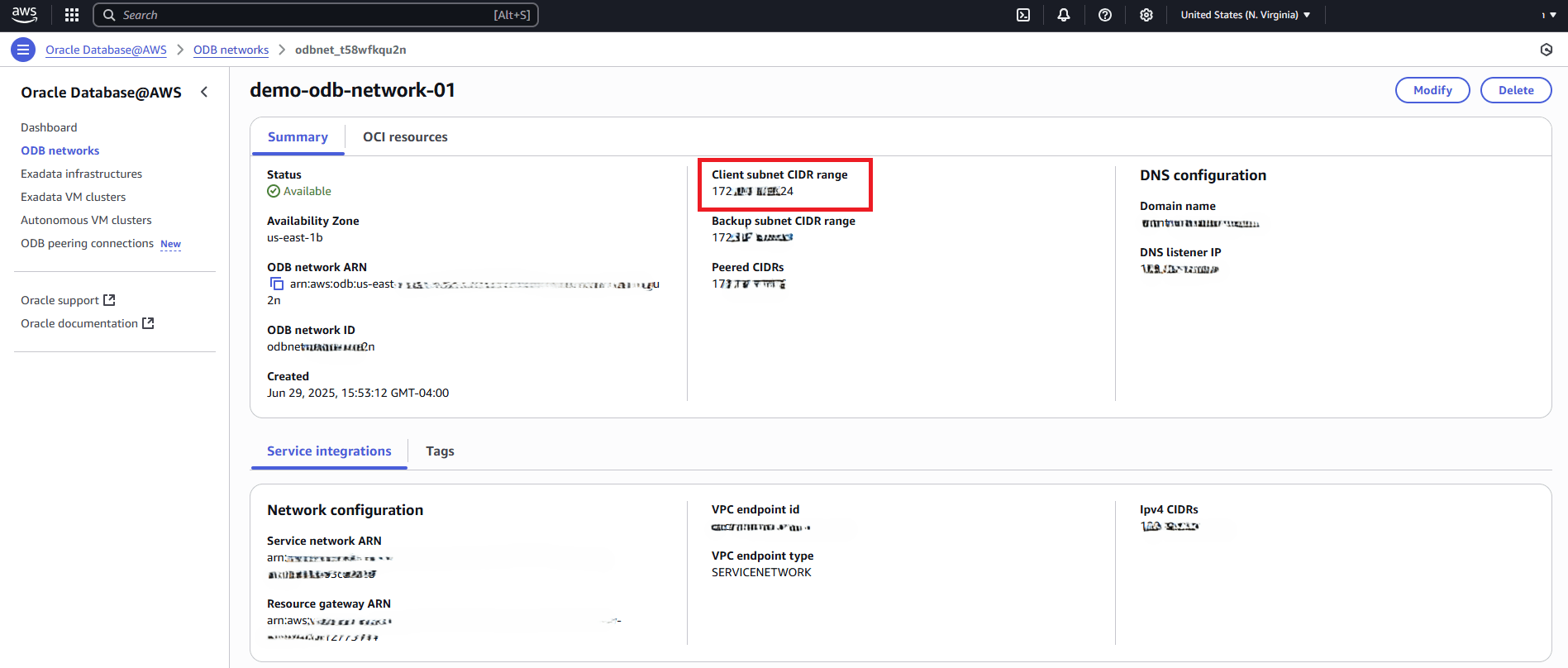
- Use the latest AWS CLI to run the following command. This command will create a new route in the application VPC's route table. This route directs application traffic route for the client subnet CIDR through the ODB network.
Note
If your operating system is Windows, include the caret symbol^at the beginning of the command before running it. If your operating system is Linux, include the slash symbol/at the beginning of the command before running it.aws ec2 create-route --destination-cidr-block <OCI_CLIENT_SUBNET_CIDR> --route-table-id <ROUTE_TABLE_ID> --odb-network-arn <ODB_NETWORK_ARN> --region <REGION>
Configure DNS Resolution
This topic explains the required steps to configure DNS resolution.
When the ODB network is created, two private resolver endpoints are deployed in the corresponding VCN. One endpoint serves as a listening address and the other as a forwarding address. However, DNS resolution is not enabled by default. You can enable DNS resolution from AWS to OCI or from OCI to AWS by following the configuration detailed below.
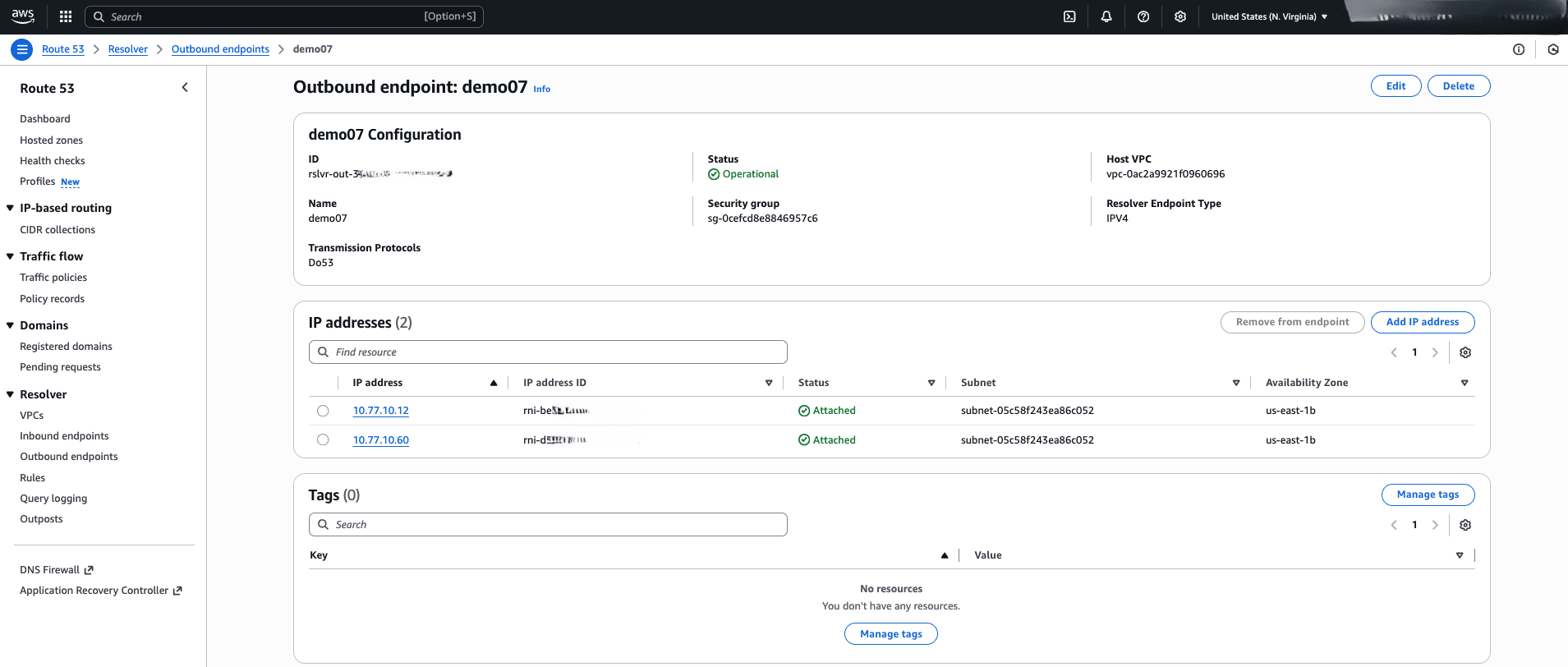
To resolve the Oracle Database FQDN from an AWS VPC, you need to configure a Route 53 outbound endpoint and create a resolver rule to forward domain name DNS queries to the ODB network listening endpoint. You must obtain your DNS listener IP and Domain name information from your ODB network.
 Route 53 Outbound Endpoint Configuration
Route 53 Outbound Endpoint Configuration- From the AWS console, navigate to Route 53.
- From the left menu, expand the Resolver section, and then select Outbound endpoints.
- Select the Create outbound endpoint button, and then complete the following substeps:
- Enter a descriptive name in the Endpoint name field. The endpoint name can have up to 64 characters consisting of a-z, A-Z, 0-9, space, underscore (_), and hyphen (-).
- From the dropdown list, select the VPC to use for resolving DNS queries (typically the VPC where your EC2 application is running).
- From the Security group for this endpoint dropdown list, select an existing security group.
- From the dropdown list, select Endpoint Type and Protocols for this endpoint such as Endpoint type (IPv4) and the protocols (Do53).
- From the IP Addresses section, select at least two IP addresses for the outbound endpoint. It is recommended to select two different Availability Zones and Subnets. The default option Use an IPv4 address that is selected automatically is selected from the IPv4 address section.
- From the Tags section, you can add tags to outbound endpoints to organize and identify them.
Note
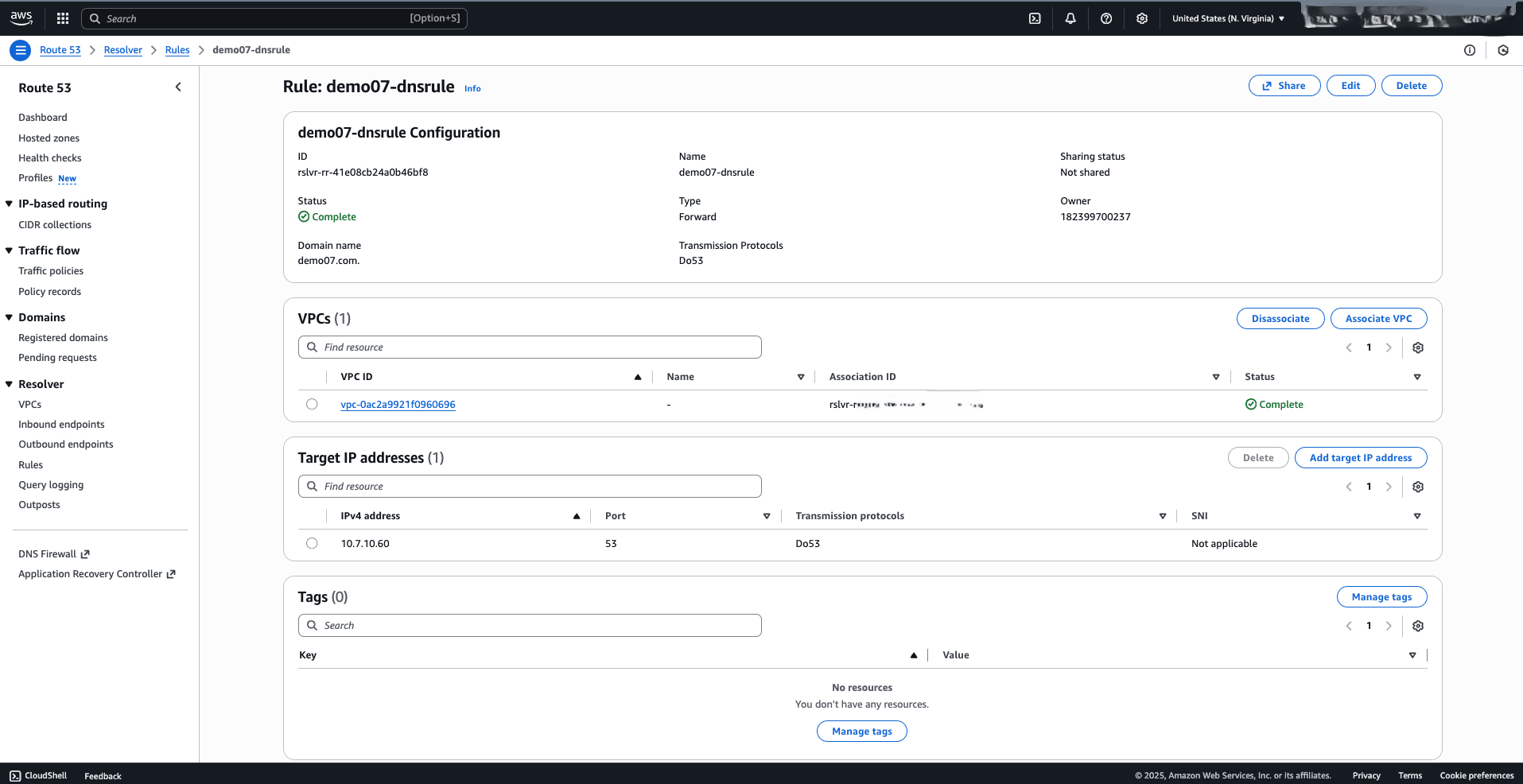
Create a security group dedicated to Route 53 endpoints, allowing TCP and UDP traffic on port 53 from anywhere.Route 53 Resolver Rule Configuration- From the AWS console, navigate to Route 53.
- From the left menu, expand the Resolver section, and then select Rules.
- Select the Create rule button, and then complete the following substeps:
- Enter a descriptive name in the Name field. The rule name can have up to 64 characters consisting of a-z, A-Z, 0-9, space, underscore (_), and hyphen (-).
- From the Rule type dropdown list, select the Forward option.
- In the Domain name field, specify the domain name. For example, the default domain name which is
oraclevcn.com, or the custom domain name defined during the ODB network creation. - From the VPCs that use this rule dropdown list, you can associate the rule with the VPC which you want to forward DNS queries to your network.
- From the Outbound endpoint dropdown list, select the outbound endpoint that you previously created.
- From the Tags section, you can add tags to rules to organize and identify them.
Test the DNS Resolution- From the AWS console, navigate to EC2.
- From the left menu, expand the Instances section, and then select your instance checkbox from the list.
- Select the Connect button at the top to connect to the instance.
- For example, you can select the Virtual machine DNS name, and then in a Linux instance, execute the following command:
nslookup hostname
- To resolve AWS domain names from Oracle Database, you need to configure a Route 53 inbound endpoint and create a resolver rule to forward domain name DNS queries from OCI to AWS.Note
The Route 53 private hosted zone is linked to your application or transit VPC.
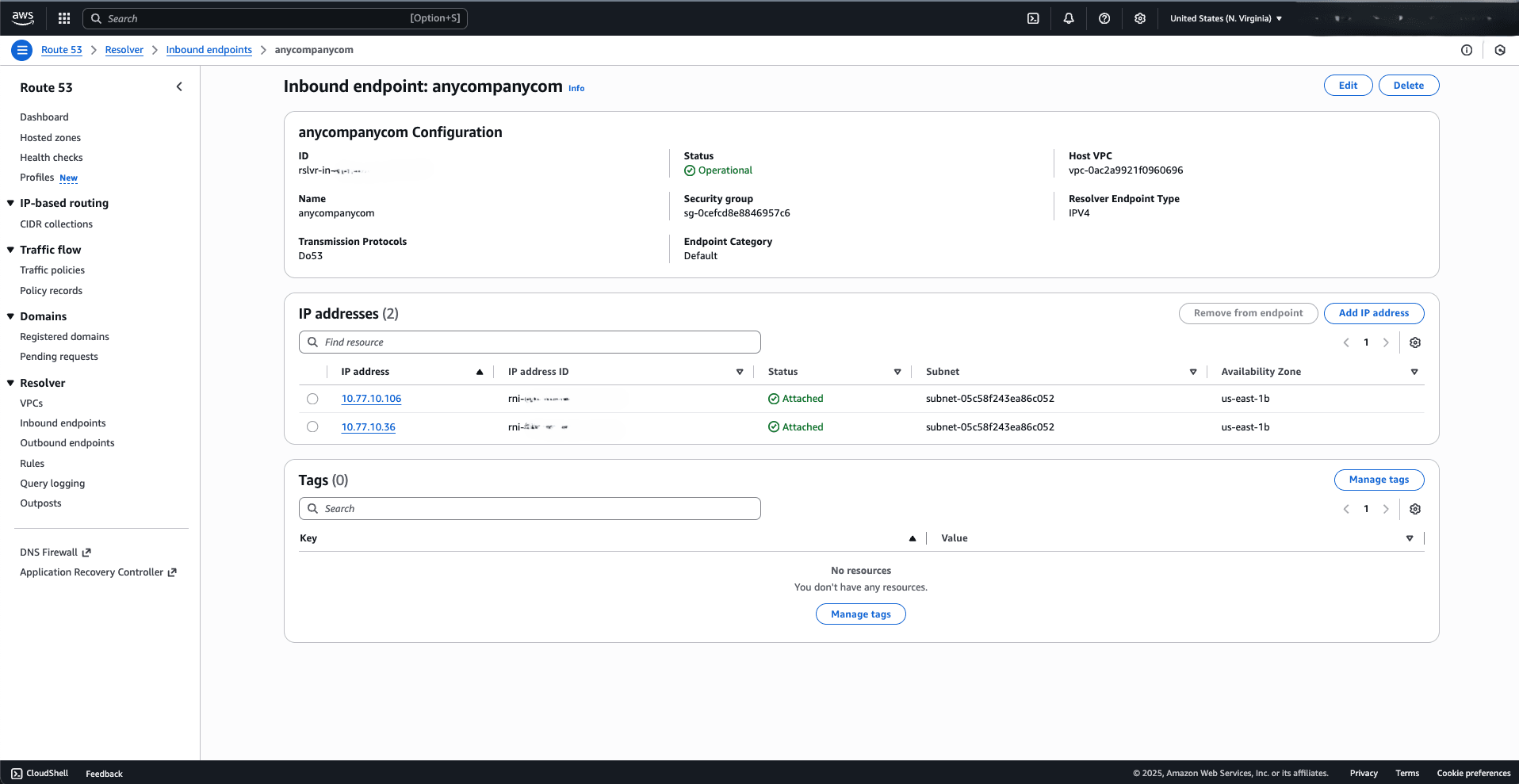
Route 53 Inbound Endpoint Configuration- From the AWS console, navigate to Route 53.
- From the left menu, expand the Resolver section, and then select Inbound endpoints.
- Select the Create inbound endpoint button, and then complete the following substeps:
- Enter a descriptive name in the Endpoint name field. The endpoint name can have up to 64 characters consisting of a-z, A-Z, 0-9, space, underscore (_), and hyphen (-).
- From the Endpoint Category dropdown list, select the Default option.
- From the dropdown list, select the VPC to associate with the Route 53 private host zone to resolve.
- From the Security group for this endpoint dropdown list, select an existing security group.
- From the dropdown list, select Endpoint Type and Protocols for this endpoint such as Endpoint type (IPv4) and the protocols (Do53).
- From the IP Addresses section, select at least two IP addresses for the outbound endpoint. It is recommended to select two different Availability Zones and Subnets. The default option Use an IPv4 address that is selected automatically is selected from the IPv4 address section.
- From the Tags section, you can add tags to outbound endpoints to organize and identify them.
OCI Private Resolver Configuration- From the Oracle Database@AWS dashboard, select ODB networks and then select your ODB network from the list.
- Select the OCI resources tab, and then select the VCN ID link which will redirect you to the OCI console.
- From the Virtual Cloud Networks section, select the Security tab to create the Security Group to allow traffic.
- Select the Create Network Security Group button and then complete following substeps:
- Enter a descriptive name in the Name field for your network security group.
- From the dropdown list, select your compartment where you want to create your network security group.
- From the Tags section, you can add tags to your resources to organize and identify them.
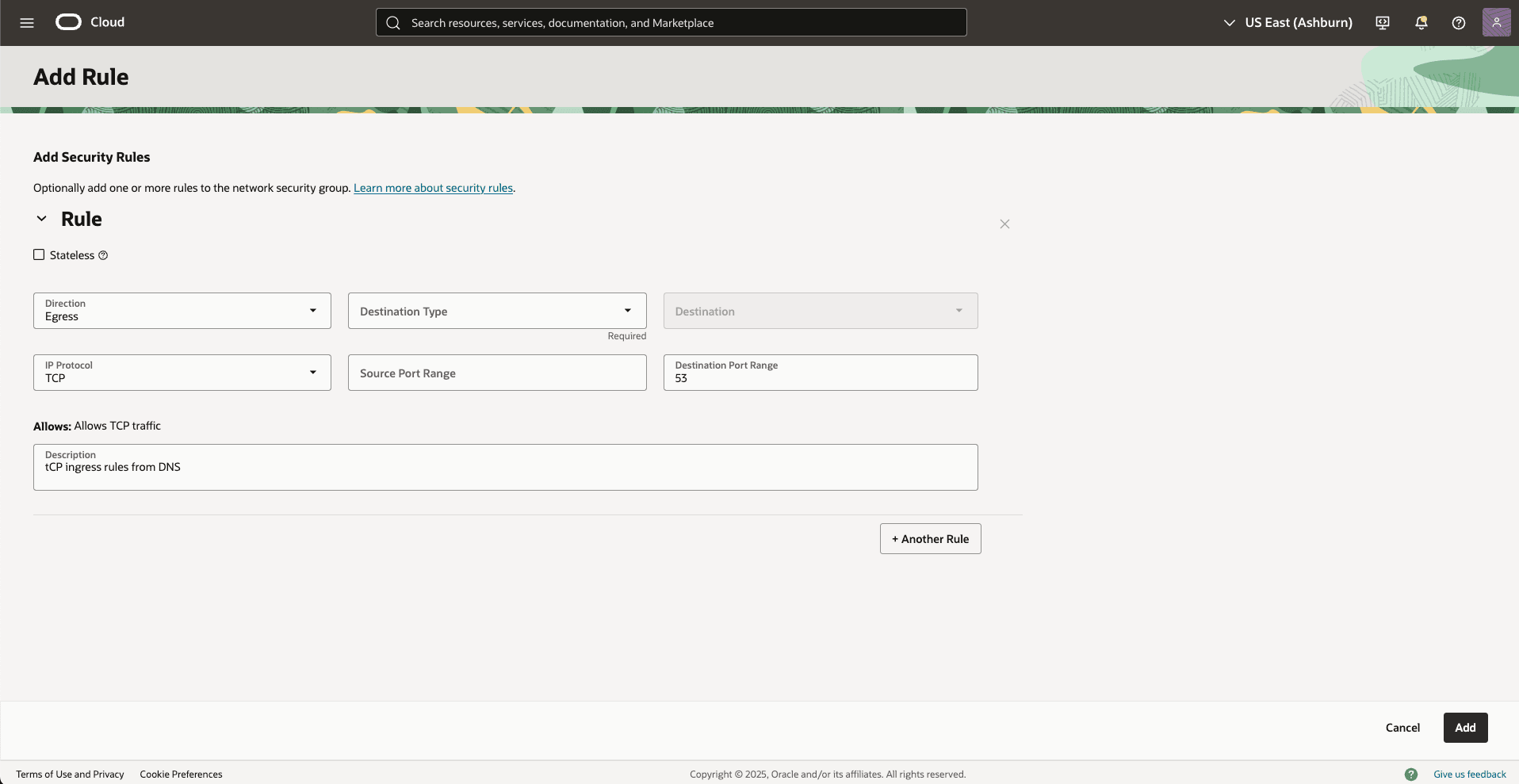
- From the Add Security Rules section, select Egress as Direction and select CIDR as Source Type. From the Source dropdown list, select the IP address of your AWS Inbound endpoint. Select the TCP option from the IP Protocol dropdown list. Enter 53 in the Destination Port Range field. Repeat with UDP.
- In the Allow field, enter a description that can have up to 255 characters.
- Select the Create button to apply the changes.
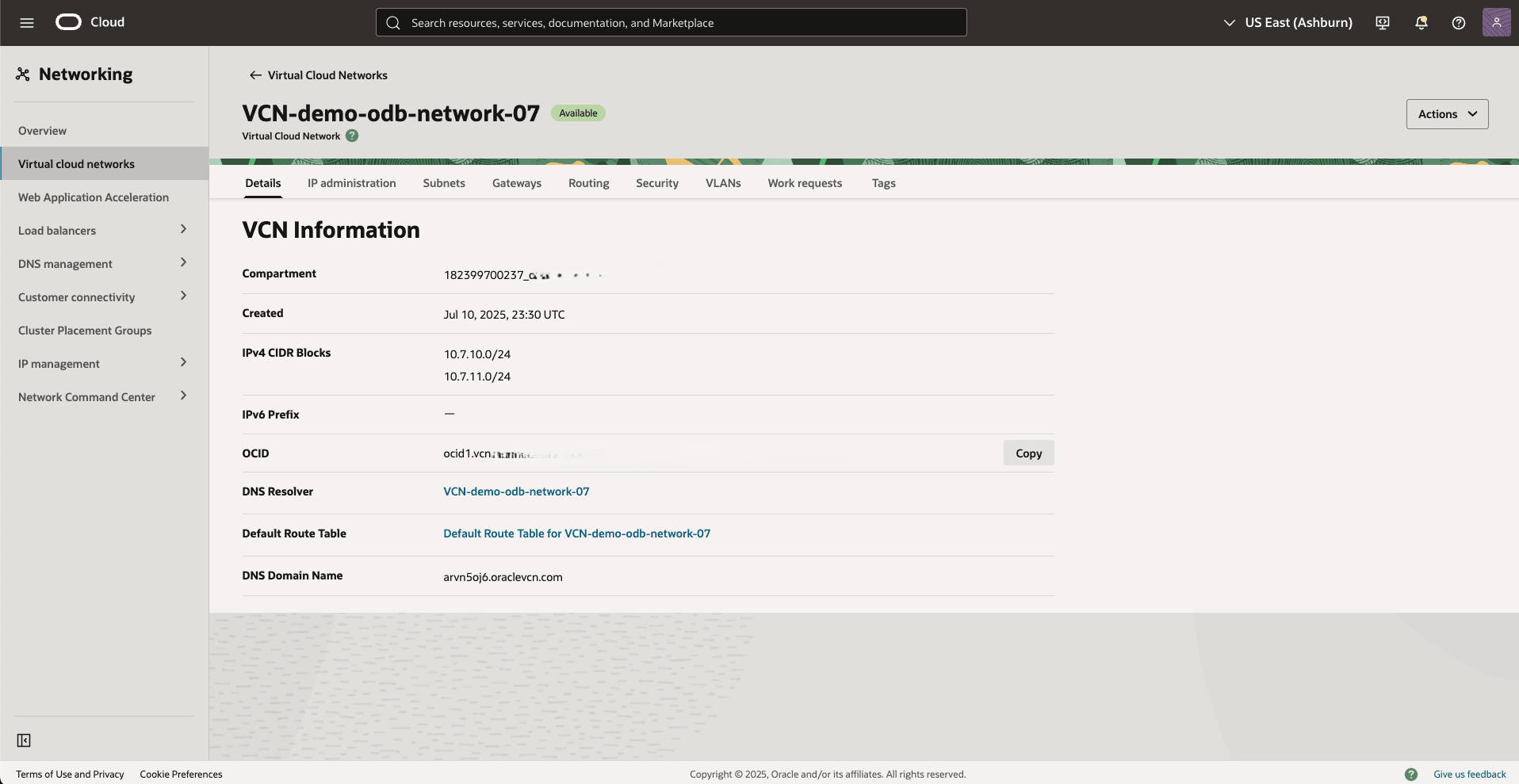
- Navigate back to Virtual Cloud Networks and then select the Details tab.
- From the Details section, select the DNS Resolver link.
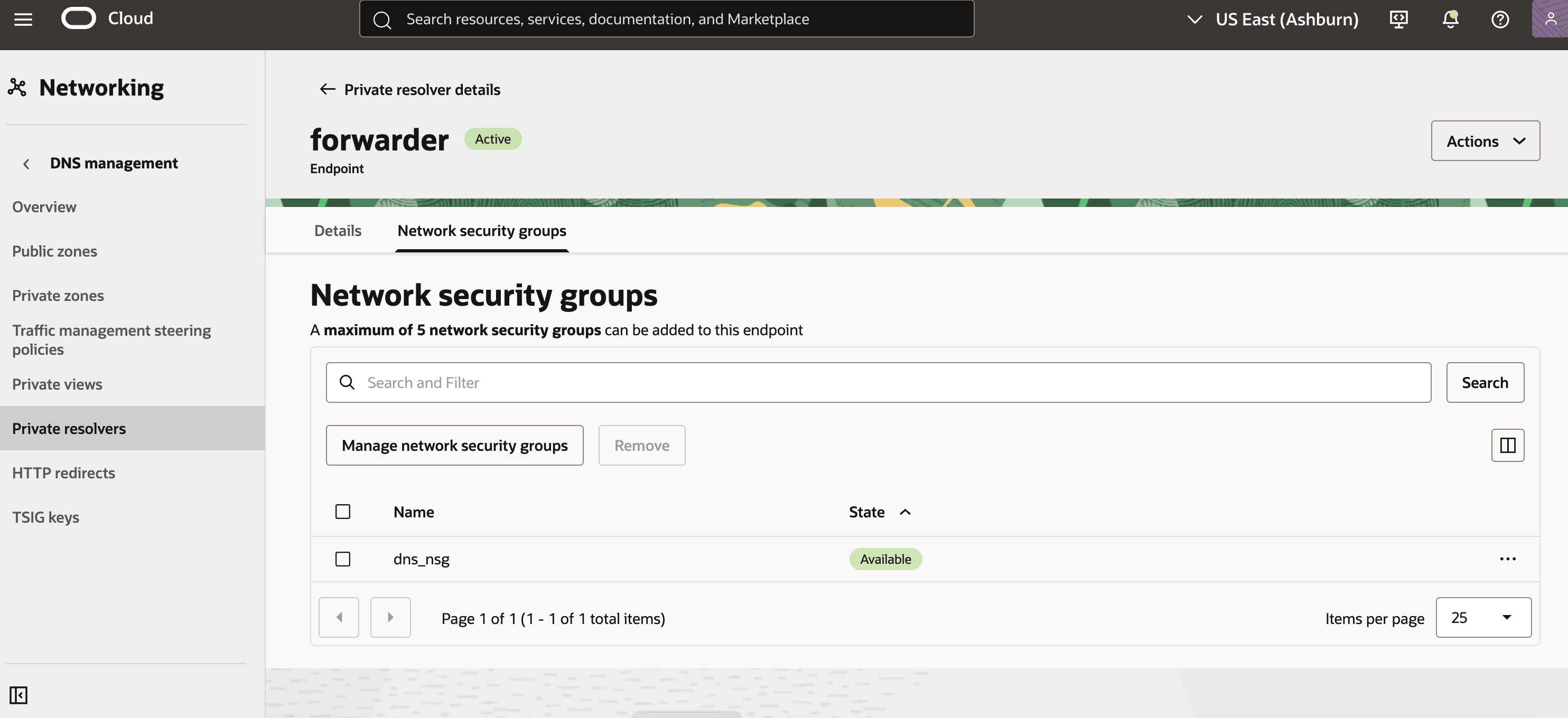
- From the Private resolvers page, select the Endpoints tab and then select the forwarder endpoint to add the Security Group that you created previously.
- Select the Network security groups tab.
- Select the Manage network security groups button.
- From the dropdown list, select your Network security group compartment and Network security group.
- Select the Save changes button to apply the changes.
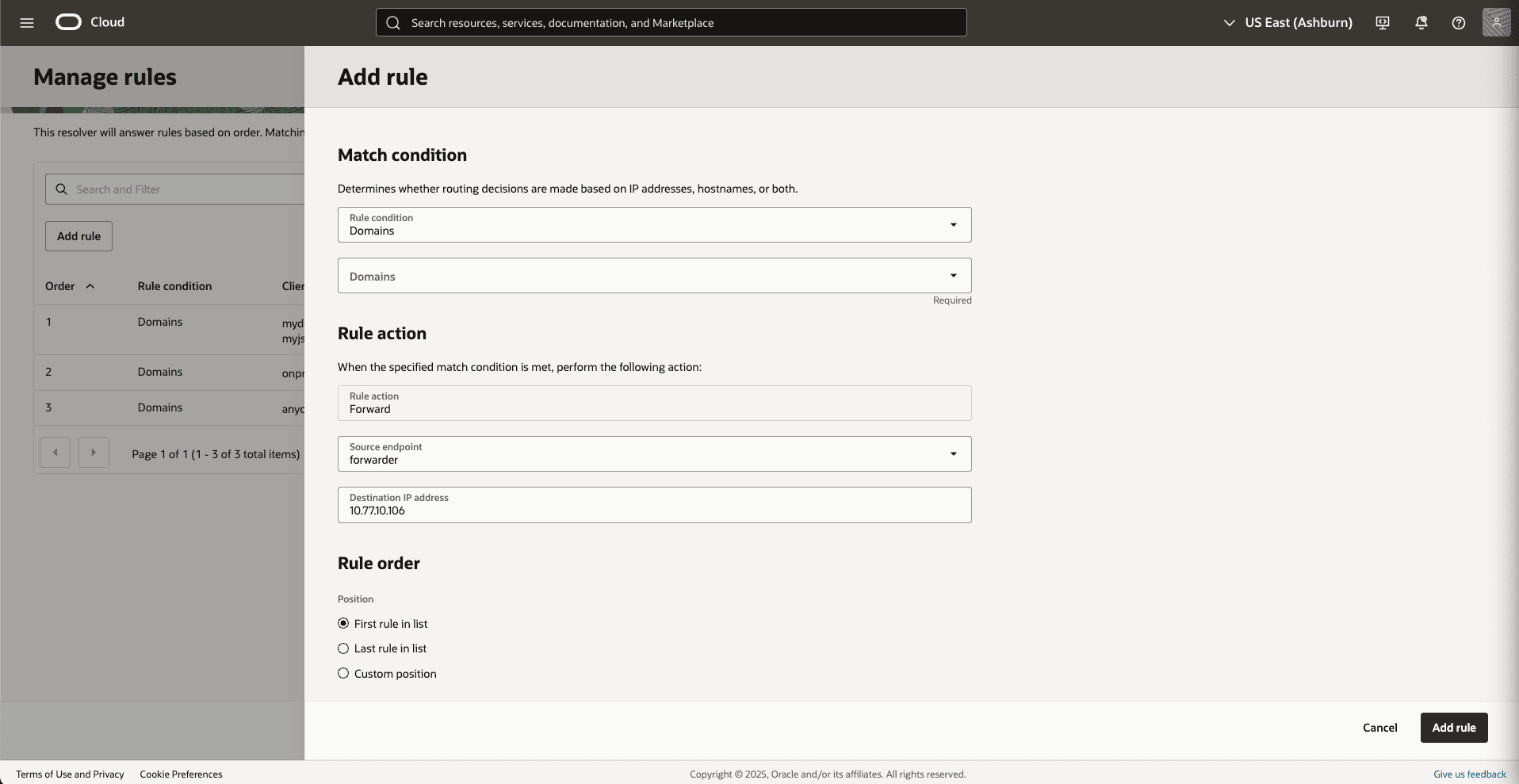
- From the Private resolvers page, select the Rules tab to create a rule to forward the DNS query to AWS Inbound enpoint. Select the Manage rules button, and then complete the following substeps:
- Select the Add rule button.
- From the Match condition section, select the Domains option as Rule condition.
- From the Domains dropdown list, select the Route 53 private zone domain.
- The Rule action field is selected as Forward by default.
- From the Source endpoint dropdown list, select the forwarder endpoint.
- In the Destination IP address field, enter the Route 53 Inbound endpoint IP address.
- Choose your Rule order.
- Select the Add rule button to save the changes.
Test the DNS Resolution- From the VM Cluster node , perform a DNS resolution by executing the following command:
nslookup hostname
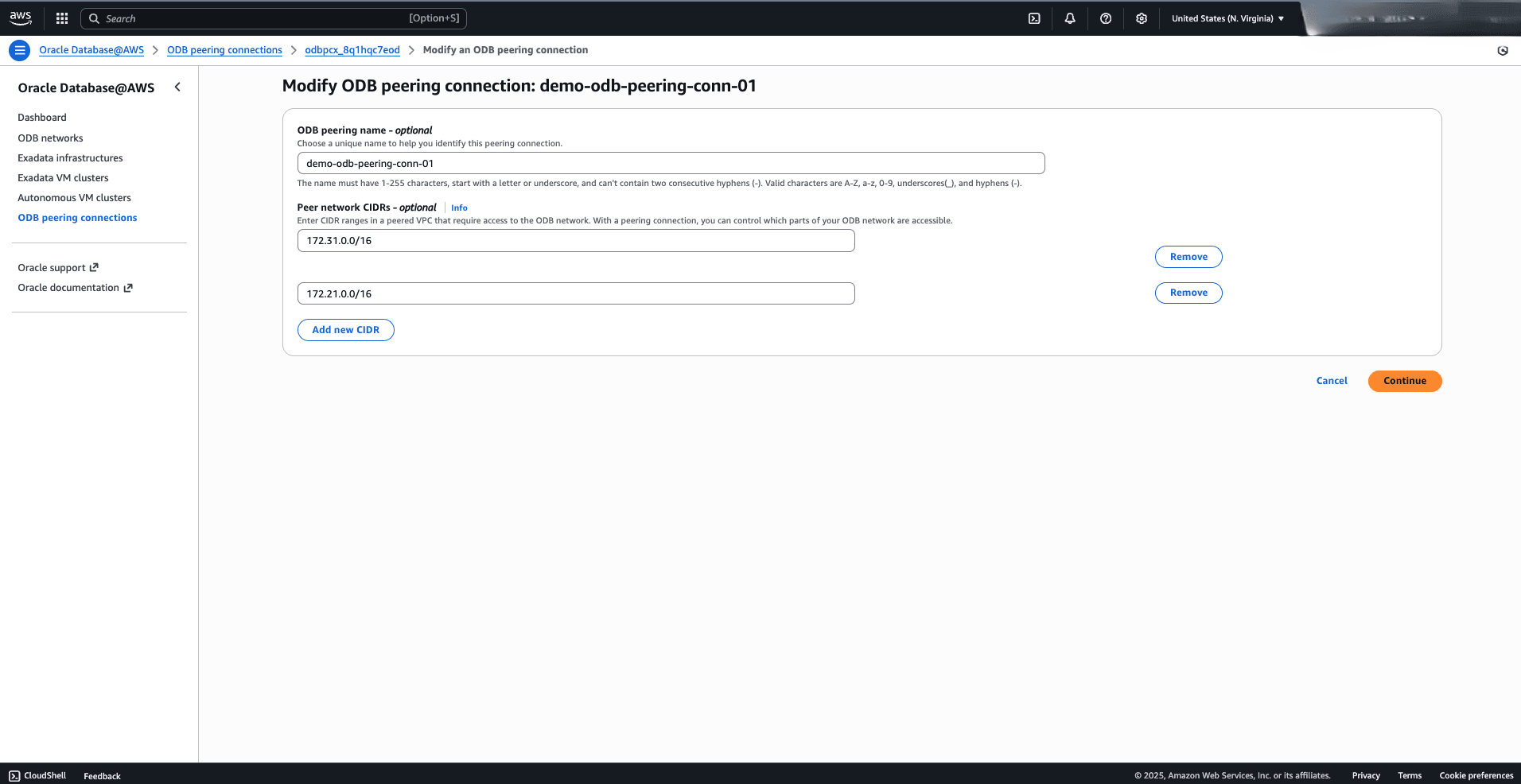
Allow CIDR to ODB Network
This topic explains the steps required to allow network access to the ODB Network.
To allow network access to the ODB Network for example, from on-premises environments or an AWS subnet, you must update the ODB peering connections to include the peer network CIDR blocks. For more information, follow the Modify ODB Peering Connections steps.