Migrate to Exadata Database
Oracle AI Database Migration Using Amazon S3 File Gateway
Amazon S3 File Gateway provides a streamlined, scalable solution for backing up Oracle AI Database to the cloud. By leveraging Oracle AI Database’s durable and cost-efficient storage, you can achieve reliable data protection while benefiting from local caching for fast access. With support for Network File System (NFS) and Server Message Block (SMB) protocols, you can integrate into existing backup workflows, ensuring compatibility across different environments. Whether managing on-premises or cloud databases, Amazon S3 File Gateway enables you to implement unified backup strategies that reduce complexity and eliminate additional licensing costs by using AWS and Oracle tools.
This topic explains how to scale Oracle AI Database backups to Amazon S3 using multiple Amazon S3 File Gateways. It also covers large-scale backup strategies, optimal configurations, and enhanced performance monitoring techniques. With these capabilities, you can achieve a robust and cost-effective approach to data immutability and scalability, making this solution ideal for enterprises seeking secure and efficient backup solutions across hybrid infrastructures.
Key Considerations for Migration
Selecting the optimal Amazon S3 File Gateway configuration depends on workload size, performance requirements, and storage needs.- Cache Disk Sizing
- You can use multiple local disks, which improves write performance by enabling parallel access.
- You must ensure the cache disk is large enough to accommodate the active working set.
- Network Performance
- A network bandwidth of 10 GB or greater is recommended for high-throughput workloads.
- Avoid using ephemeral storage for gateways running on Amazon EC2.
- Protocol Selection
- NFS is recommended for the Linux-based workloads.
- SMB is suitable for the Windows environments.
- Gateway Scaling
- When handling hundreds of terabytes, deploying multiple gateways enhances scalability.
- Each gateway should be configured according to the number of files per directory, with a recommended limit of 10,000 files per directory.
- Performance Optimization
- You must use Amazon EBS General Purpose SSDs for cache disks to maximize IOPS.
- You must ensure that the root EBS volume is at least 150
GiBfor optimal starting performance.
Architecture Overview
This approach demonstrates the scalability of Oracle AI Database backups using multiple Amazon S3 File Gateways. By leveraging Amazon S3 File Gateway, you can handle very large databases totaling hundreds of terabytes.
The architecture diagram below illustrates how Amazon S3 File Gateways write backup data to Amazon S3 from source Oracle AI Databases running on an on-premises data center, as well as from a target Oracle Exadata Database system running Oracle Database@AWS.
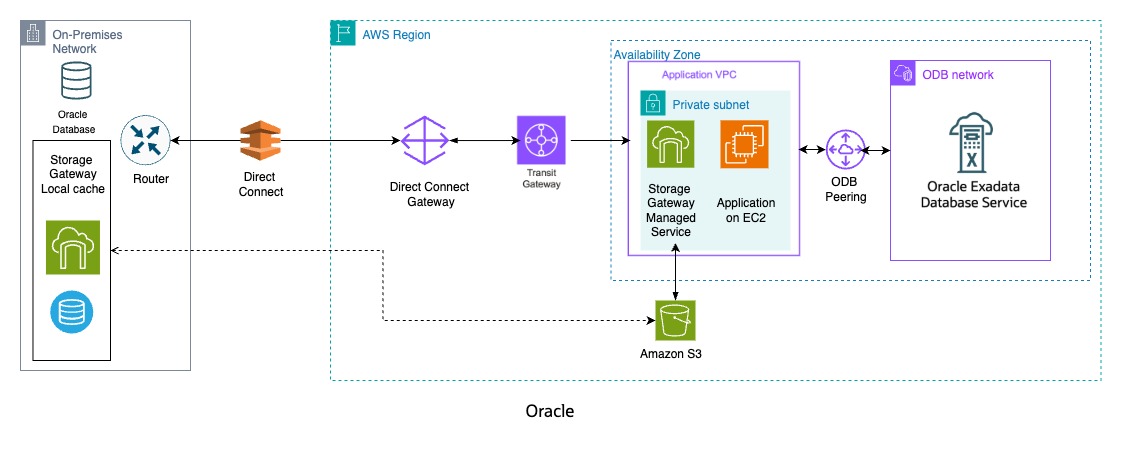
Solution Overview
For the use case, we focus on a standalone scenario where both Oracle AI Databases are running in AWS. The source Oracle AI Database runs on Amazon EC2, while the target Oracle Exadata Database runs on AWS. The solution below details the steps for creating an Amazon S3 Storage Gateway and using it to migrate Oracle AI Database from EC2 to Oracle AI Database on Exadata. The following diagram illustrates the architecture of our solution.
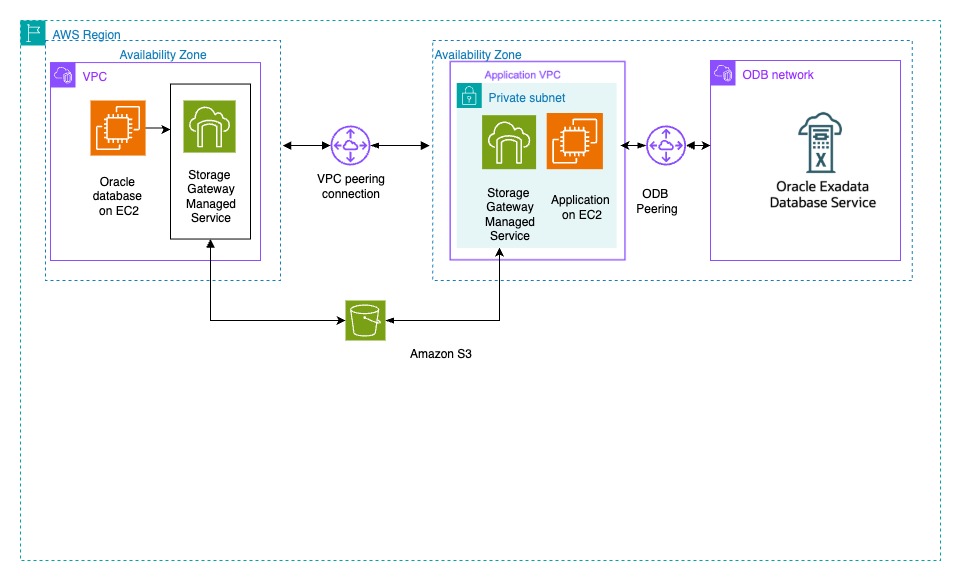
Prerequisites
The following prerequisites are required to migrate to Exadata Database using Amazon S3 File Gateway.- Source database running on compatible Oracle AI Database such as Exadata Database, RAC or database instance.
- Target Exadata Database as part of Oracle Database@AWS
- S3 bucket shared across the 2 VPC’s.
- To use an Amazon S3 File Gateway across two different VPCs, you need to establish a private connection between the gateway and the S3 buckets within the other VPC. This typically involves setting up a VPC Endpoint for S3 within the gateway's VPC and then using VPC Peering or a Transit Gateway to connect the two VPCs.
- Modify the S3 bucket policy to allow access from both endpoint IDs.
Backup an On-Prem Oracle AI Database from an EC2 Instance Using Amazon S3 File Gateway: This topic explains the process of using Amazon S3 File Gateway to back up an Oracle AI Database hosted on an EC2 instance. The same approach is applicable for on-premises environments, covering both Storage Gateway and local databases. These are the steps implement the backup solution:- Provision an Amazon S3 File Gateway
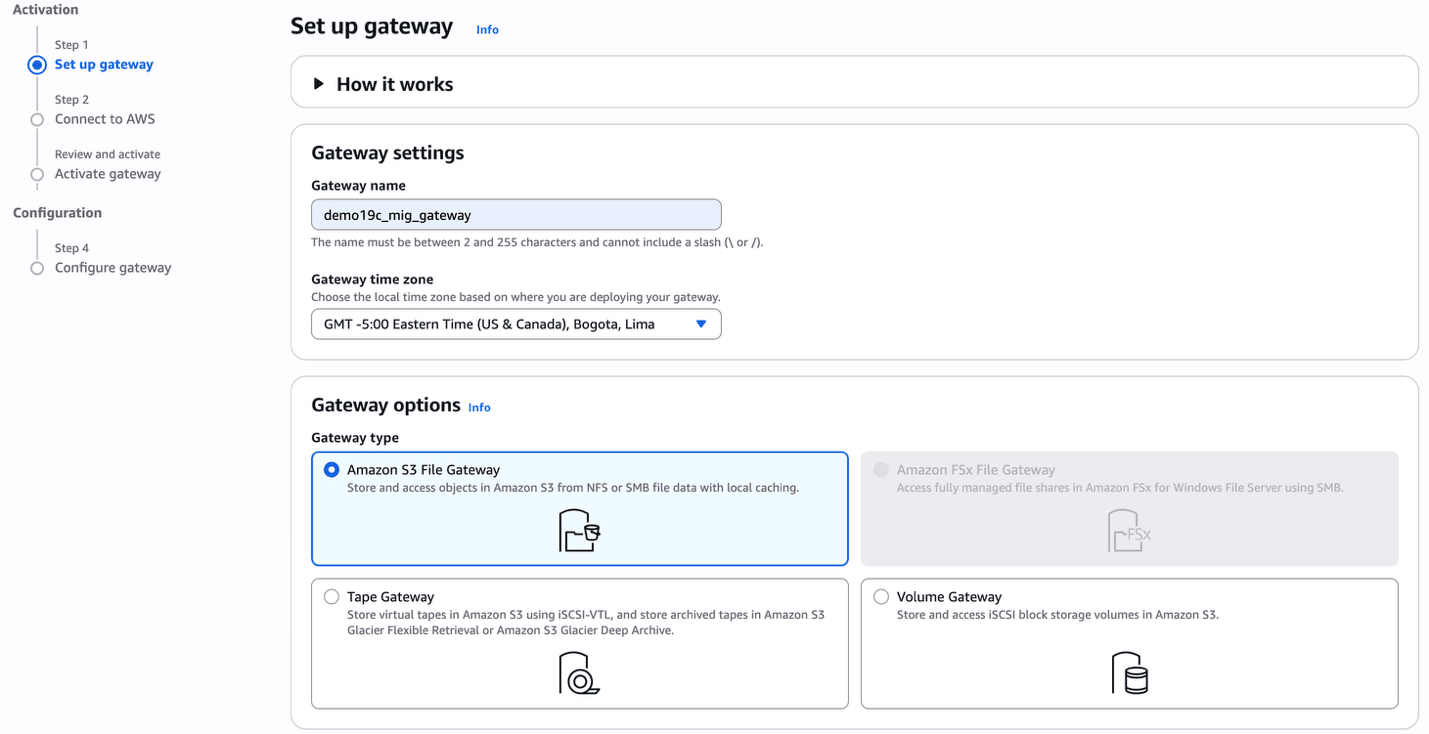
- From the AWS console, navigate to Storage Gateway.
- Click on the Create gateway button.
- In the Set up gateway section, enter the following information.
- Enter a descriptive name in the Gateway name field. The name must be between 2 and 255 characters and cannot include a slash (\ or /).
- From the dropdown list, select the Gateway time zone. Choose the local time zone based on where you want to create your gateway.
- From the Gateway options section, choose the Amazon S3 File Gateway option.
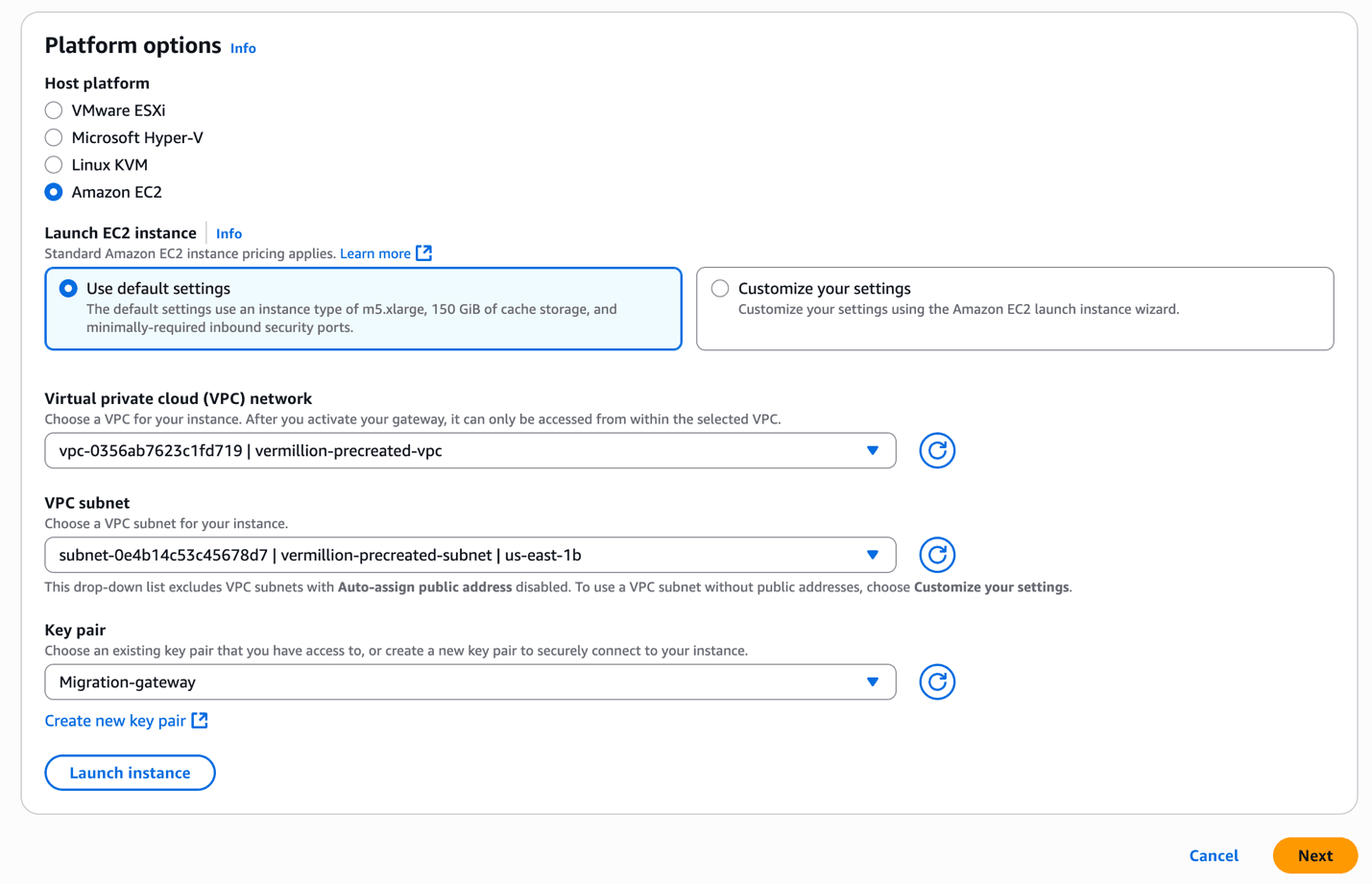
- From the Platform options section, choose the Amazon EC2 as the host platform.
- Choose the Use default settings if you want to create an EC2 instance with default settings. Alternatively, you can click on Customize your settings to select the EC2 instance size and shape .
- From the dropdown list, select the Virtual private cloud (VPC) network.
- From the dropdown list, select the VPC subnet.
- From the Key pair dropdown list, select the existing key pair. If you do not have an existing one, select the Create new key pair link to create one.
- Select the Launch instance button to launch the EC2 instance with default settings. If you select the Customize your settings option, the instance will be launched in EC2 instance console.
- Select the Next button to proceed.
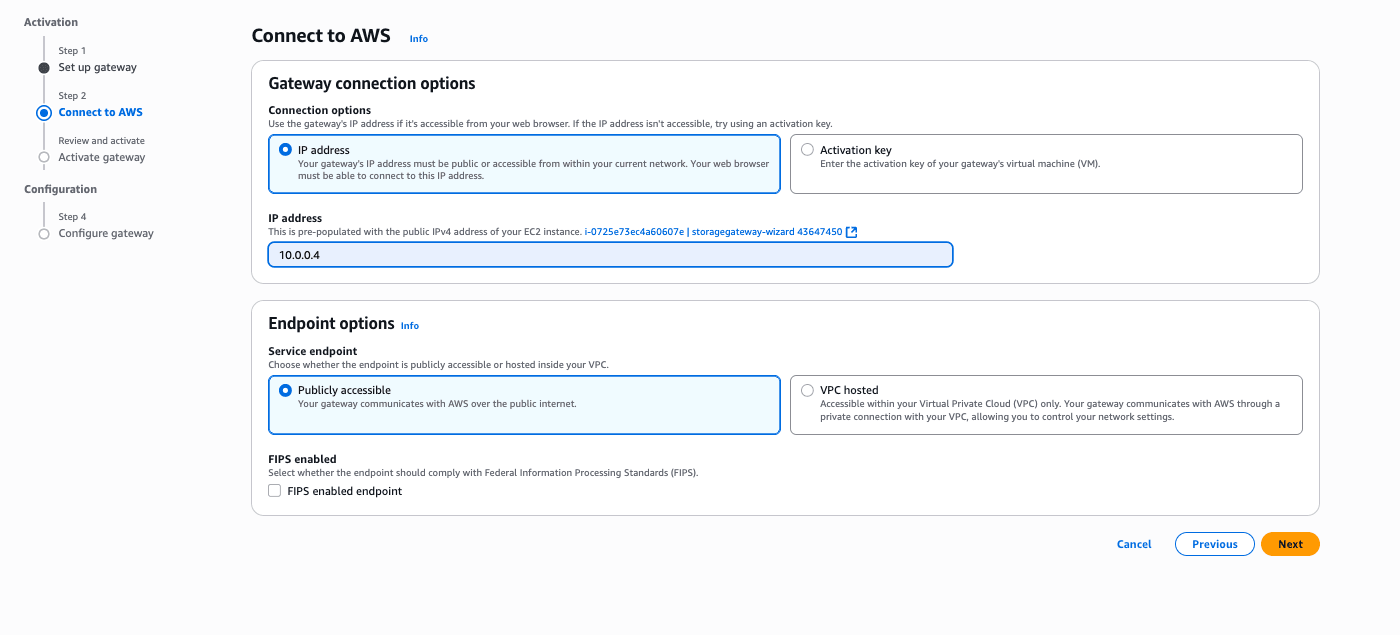
- In the Connect to AWS section, enter the following information.
- From the Connection options section, choose the IP address option.
- The IP address automatically populates from the previous step where you created an EC2 instance.
- From the Service endpoint section, choose either the Publicly accessible option or VPC hosted option.
- Select the Next button to continue the creation process or select the Previous button to go back.
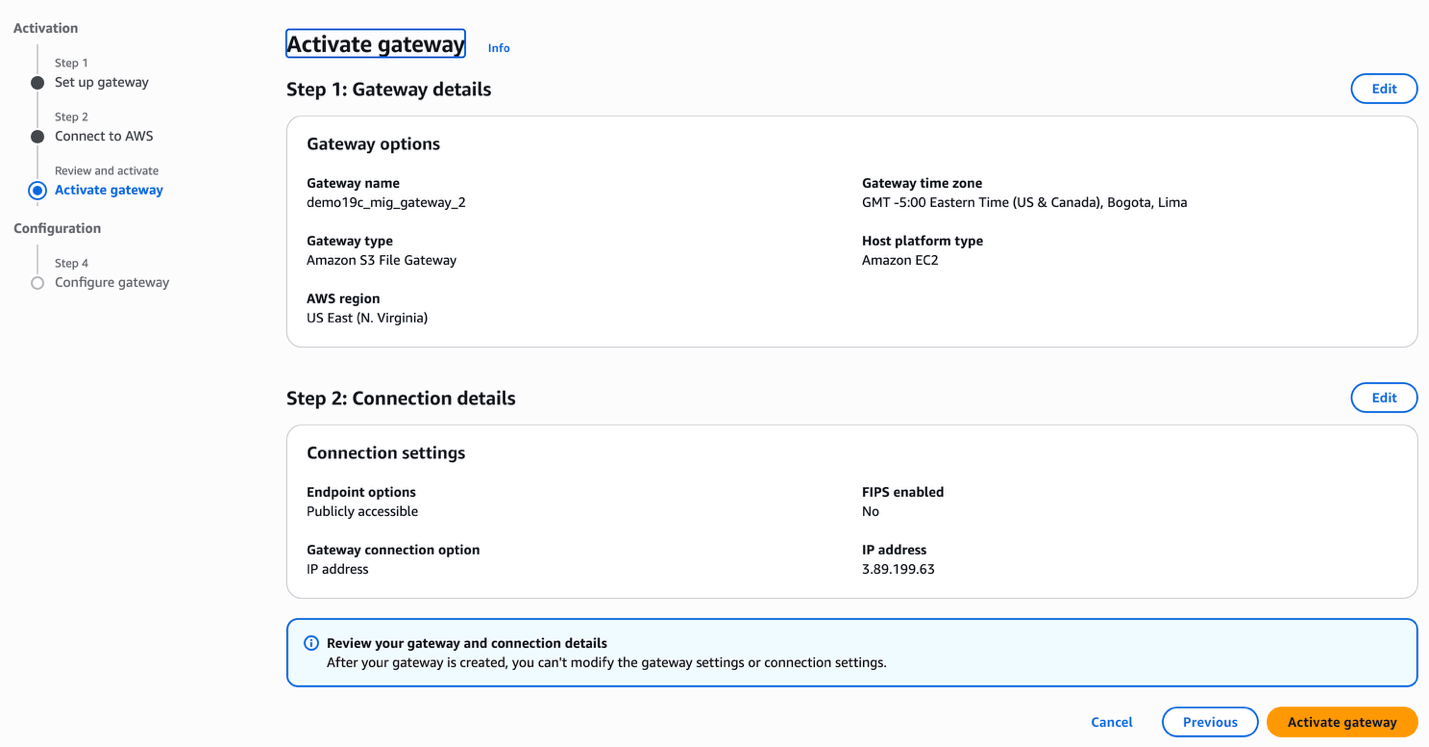
- In the Activate gateway section, enter the following information.
- Review the Gateway details and Connection details, and then click on the Activate gateway button to continue the creation process or select the Previous button to go back.
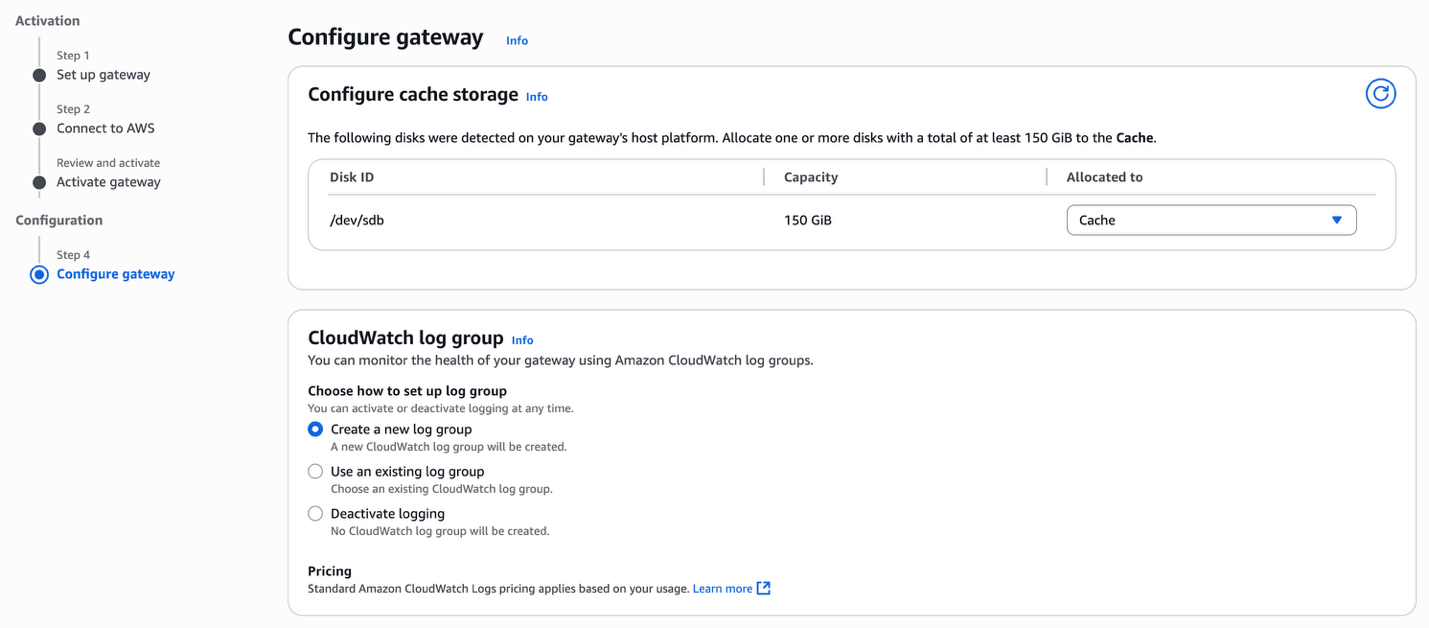
- In the Configure gateway section, enter the following information.
- From the Configure cache storage section, allocate one or more disks.
- From the CloudWatch log group section, choose either the Create a new log group option or the Use an exsiting group option. The Deactive logging option is not recommended.
- From the CloudWatch alarms section, choose the Create Storage Gateway's recommended alarms option.
- Based on your requirements, you can add Tags by selecting the Add new tag button.
- Select the Configure button.
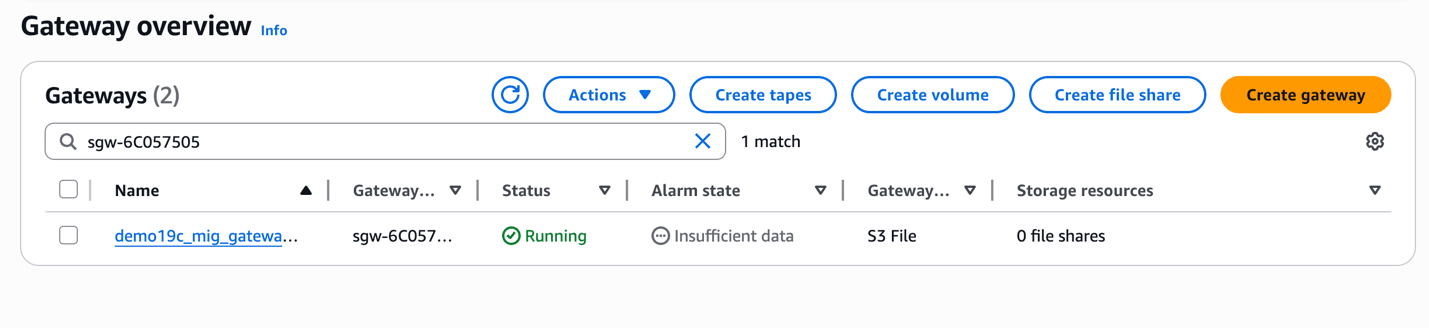
- Once your gateway is created, the status will change to Running.
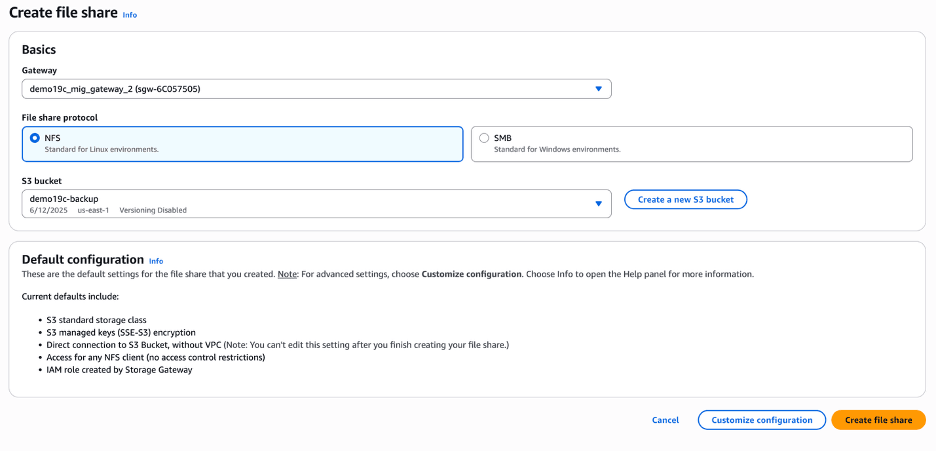
- Create a File ShareNote
Once the gateway is created, you can create a file share.- From the AWS console, navigate to Storage Gateway.
- From the Storage resources section, select File shares.
- Select the Create file share button, and then complete the following substeps.
- From the Create file share page, select the Gateway that you created previously.
- From the File share protocol section, choose the NFS option.
- From the S3 bucket dropdown list, select your existing S3 bucket. If you do not have one, you can create one by clicking the Create a new S3 bucket button.
- Select the Create file share button.
- Mount NFS Share in the Oracle AI Database EC2 Instance
- Use the following bash commands in the database EFS instance and mount the S3 bucket as NFS mount points. The NFS parameters used are specific to Oracle AI Database and RMAN.
- Create a directory with the required mount name. For example, the
s3_mountdirectory was created. - Run the following command.
mount -t nfs -o nolock,hard [ip-address]:/demo19c-backup /s3_mount/
- Backup Oracle AI Database
You can now use the NFS file share that is mounted on the database server to take backups on either using Oracle Data Pump or RMAN. For this example, RMAN is being used.
Oracle Recovery Manager provides a robust utility for backing up Oracle AI Databases. When storing backups in Amazon S3, ensure that the
db_recovery_file_destparameter is set to the NFS mount point established in previous steps. Additionally, to enforce a strict storage limit, define thedb_recovery_file_dest_sizeparameter, which controls the maximum space allocated for files within the recovery destination. For more information about RMAN backup types and best practices, see RMAN basic concepts.- Set the parameter
db_recovery_file_destto point the NFS share mounted in the previous steps, and definetgedb_recovery_file_dest_sizeby using the following command.alter system set db_recovery_file_dest='' scope=both; alter system set db_recovery_file_dest_size='<size limit for nfs share mount point>' scope=both; - This is an example output after setting up the parameters
db_recovery_file_destanddb_recovery_file_dest_size.alter system set db_recovery_file_dest='/s3_mount' scope=both; alter system set db_recovery_file_dest_size='1000G' scope=both; - Run RMAN backup on the database server using the following command:
rman target / <<EOFrun {CONFIGURE DEFAULT DEVICE TYPE TO DISK;CONFIGURE DEVICE TYPE DISK PARALLELISM 3;BACKUP DATABASE PLUS ARCHIVELOG;}EOF
- Set the parameter
- Verify Backup Upload to Bucket
For Oracle AI Database backups utilizing parallel processing via RMAN or Data Pump, configuring multiple cached disks in Amazon S3 File Gateway significantly improves performance. Instead of relying on a single disk, distributing the workload across multiple cache disks enhances throughput by leveraging parallelism, optimizing storage efficiency and backup speed.
All the backup files are uploaded into Amazon S3 in the background as the Storage Gateway writes the files to the shares. Transport Layer Security encryption protects the data while in transit and Content-MD5 headers are used for data integrity.
Depending on the backup file size and network bandwidth between your Amazon S3 File Gateway and AWS, the backup file can take time to transfer from the local cache of Amazon S3 File Gateway to Amazon S3 bucket. You can use CloudWatch metrics to monitor the traffic.
Restore an Oracle AI Database on the Target Oracle Exadata VM Cluster- Create Amazon S3 File Gateway in the ODB Peered VPC
- Follow the steps from above to create a S3 file gateway in the AWS VPC which is peered to the Exadata using ODB peering.
- When you create the file share make sure you are using the same S3 bucket that you have used for the RMAN backups.
- Mount NFS Share in the Exadata Virtual Machine
- Enter the following bash commands in the database EC2 instance and mount the S3 bucket as NFS mount points. The NFS parameters used are specific to Oracle AI Database and RMAN.
- Create a directory with the required mount name in this case we created the
s3_mountdirectory.mount -t nfs -o nolock,hard [ip-address]:/demo19c-backup /s3_mount/ - After the NFS is mounted, the RMAN backup will be available on Exadata Database.
- Restore the Backup
Using RMAN restore, databases can be restored on the same server or different server. RMAN backups can be used for disaster recovery scenarios across different regions in AWS as well.
- Use the following command to complete the restore on Exadata Database:
sqlplus / as sysdba<<EOFstartup mountexitEOF rman target / <<EOFrun {CONFIGURE DEFAULT DEVICE TYPE TO DISK;CONFIGURE DEVICE TYPE DISK PARALLELISM 3;RESTORE DATABASE;RECOVER DATABASE;alter database open;}EOF
- Use the following command to complete the restore on Exadata Database:
- Validation
- Run the validation steps to ensure the RMAN restore completed successfully.
Table 1-1 Validation Commands
Check Area Command Expected Result RMAN Log - No errors, restore complete DB Status select status from v$instance;OPEN Datafiles select * from v$datafile;All ONLINE Tablespaces select * from dba_tablespaces;All ONLINE Alert Log Tail the alert log Opened successfully Application Data select count(*) from known tablesReturns rows
- Run the validation steps to ensure the RMAN restore completed successfully.
Conclusion: Leveraging Amazon S3 File Gateway for migrating from on-prem Exadata Database to Exadata Database on Oracle Database@AWS offers a strategic, secure, and scalable bridge for hybrid cloud workflows. It simplifies data transfer by presenting Amazon S3 as an NFS mount, enabling seamless integration with existing Exadata environments while reducing operational overhead. The key AWS resources for Amazon S3 File Gateway include:- Official Product Page: Overview, benefits, and use cases of Amazon S3 File Gateway.
- Best Practices: Guidance on performance tuning, security, and lifecycle management.
- Cache Disk Sizing
Oracle AI Database Migration Using Amazon Elastic File System (EFS)
Migrating an on-premises Oracle AI Database to Oracle Exadata Database within AWS can be a complex process as it requires an efficient data transfer mechanism. Amazon Elastic File System provides a scalable, serverless, and highly available file storage solution that simplifies migration workflows. By integrating Amazon Elastic File System with your databases, you can streamline data movement, reduce storage overhead, and enhance migration efficiency.
There are several advantages that Amazon Elastic File System offers, making it an ideal choice for migration.- Scalability and Elasticity
Amazon Elastic File System automatically scales from gigabytes to petabytes which eliminates the need for manual storage provisioning. This ensures that migration workloads can handle large datasets without storage constraints.
- Seamless Integration with Oracle AI Database
Amazon Elastic File System supports Network File System (NFS) protocols, allowing Oracle AI Databases to read and write directly to the EFS file system. This is particularly useful for Data Pump exports and imports, RMAN backups, and transportable tablespaces.
- Cost Optimization
Amazon Elastic File System follows a pay-as-you-go model, reducing upfront costs. It eliminates the need for dedicated storage provisioning, making it a cost-effective choice for temporary migration workloads.
- High Availability and Durability
Amazon Elastic File System is designed for Multi-Availability Zone (Multi-AZ) replication, ensuring high availability and data durability. This minimizes the risk of data loss during migration.
- Enhanced Security
Amazon Elastic File System supports encryption at rest and in transit, ensuring that sensitive database files remain protected throughout the migration process.
Solution Overview
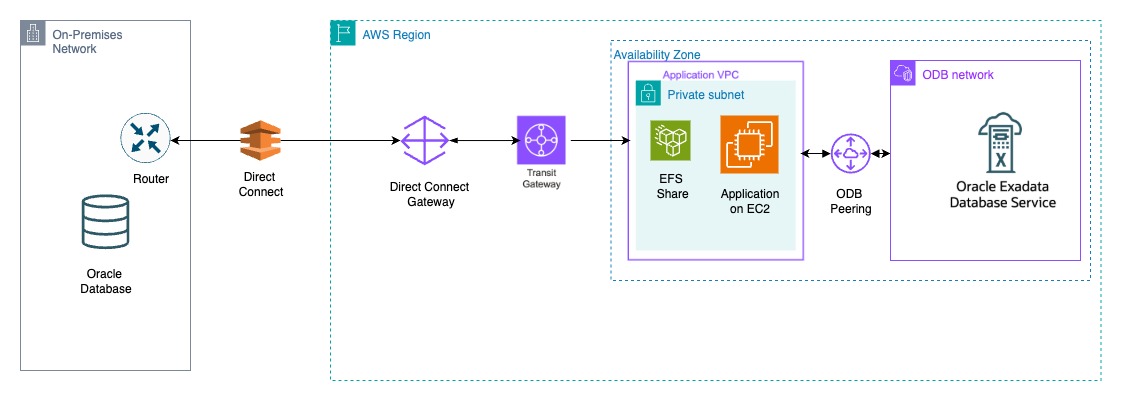
This solution demonstrates how an Amazon Elastic File System file share can serve as a landing zone for RMAN backups, simplifying the database migration process.
The architecture diagram below illustrates the workflow, where the source is an Oracle AI Database running on Linux or Oracle Exadata Database, and the target is an Oracle Exadata Database Service created in the Oracle Database@AWS environment. The EFS share is set up and used both on the on-premises systems and within the Oracle Exadata Infrastructure in the Oracle Database@AWS.
 Prerequisites The following prerequisites are required to complete this solution.
Prerequisites The following prerequisites are required to complete this solution.- Source database running on compatible Oracle AI Database such as Exadata Database, RAC or database instance.
- Target Exadata Database as part of Oracle Database@AWS.
- EFS mount point.
- Network connectivity and routes established between the On-Prem and AWS region.
Using Amazon Elastic File Systemfor Oracle AI Database Migration: Complete the following steps.- Setting Up Amazon Elastic File System
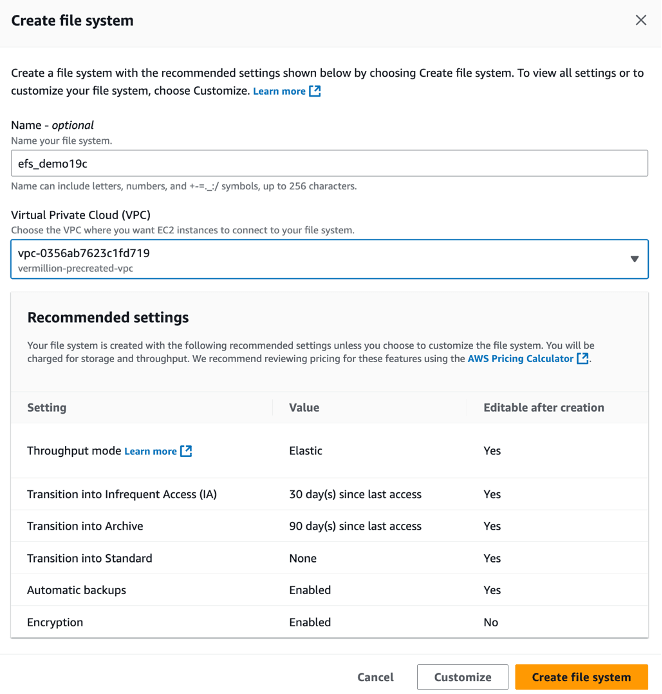
- From the AWS console, navigate to Elastic File System.
- Click on the Create file system button.
- In the Create file system section, enter the following information.
- The Name field is optional. If you want, you can enter a descriptive name for your file system. The name must include letters, numbers, and
+-=._:/symbols and it can up to 256 characters. - From the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) section, choose the VPC where you want EC2 instances to connect to your file system.
- From the Recommended settings section, review the settings. If you want to change the default settings, click on the Customize button and make required changes.
- Select the Create file system button to create a file system.
- The Name field is optional. If you want, you can enter a descriptive name for your file system. The name must include letters, numbers, and
- Configure mount targets within the same VPC as your Oracle AI Database.
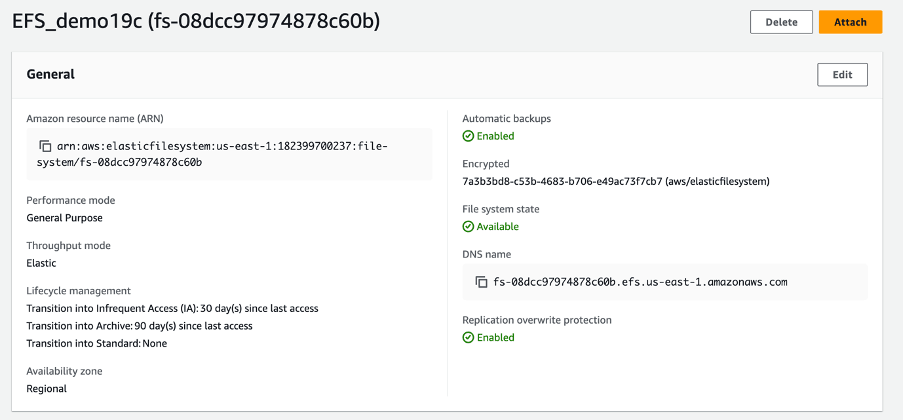
- Select the previously created file system, and then select the Attach button which provides you the sample commands to attach the EFS to the database server.
- From the Attach page, select the Mount via IP option.
- From the dropdown list, select the Availability zone.
- Copy the commands located under the Using the NFS client section.
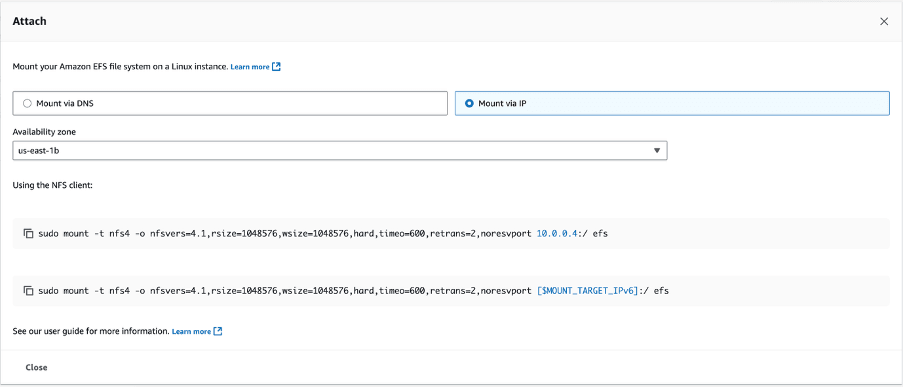
- Mounting EFS on Oracle AI Database Server
- Create a directory on the database server.
[oracle@vm-q9rk11 backup]$ mkdir -p /home/oracle/backup/efs_backup - Use the following command to mount EFS on an EC2 instance running Oracle:
[root@vm-q9rk11 ~]# sudo mount -t nfs4 -o nfsvers=4.1, rsize=1048576, wsize=1048576, hard, timeo=600, retrans=2,noresvport \ >10.0.0.4: /home/oracle/backup/efs_backup - Verify the mount using the following command:
df -k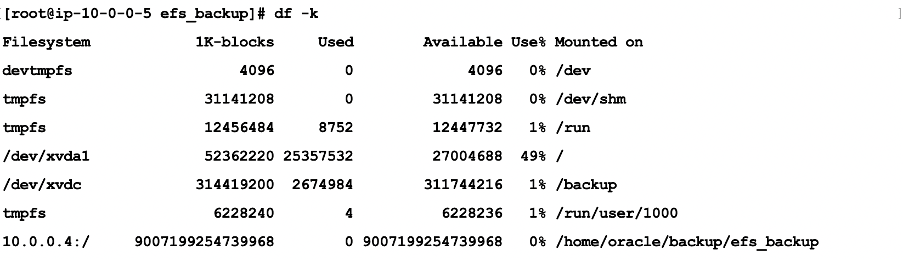
- You can use Data pump export / import or RMAN, or any other backup and restore method to migrate where EFS can be used as a staging area for the files. In this example, the RMAN option is used as the migration tool.
- RMAN Backups: Use EFS as a backup staging area before transferring data to Exadata Database.
- Create a directory on the database server.
- Migrating Oracle AI Database Files
A key advantage of using Amazon Elastic File System for Oracle Recovery Manager backups is its ability to provide a shared, highly available storage layer between the on-premises Oracle environment and the Exadata system. This eliminates the need for complex data movement processes.
- Configure RMAN to store backups on EFS.
CONFIGURE CHANNEL DEVICE TYPE DISK FORMAT '/home/oracle/backup/efs_backup/rman_backup_%U'; - Run RMAN backup for container database
ORCLPDB1.
- Verify RMAN backups are stored on EFS.
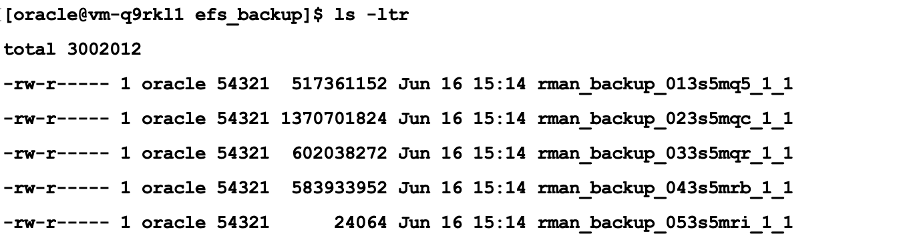
- Configure RMAN to store backups on EFS.
Restore an Oracle Exadata Database at Oracle Exadata VM Cluster
Since Amazon Elastic File Systemis a shared storage solution, the same backup files stored in EFS on-premises will be accessible from EFS Oracle Exadata Database.- Mount the EFS on Oracle Exadata VM Cluster using the following command.
[opc@vm-q9rk11 ~]$ sudo mount -t nfs4 -o nfsvers=4.1, rsize=1048576, wsize=1048576, hard, timeo-600, retrans=2,noresvport \ >10.0.0.4://home/oracle/backup/efs_backup - Validate RMAN backup availability at the EFS location
/home/oracle/backup/efs_backup. - Restoring the database on Oracle Exadata Database Pluggable Database (PDB) Complete Recovery.
$ rman target=/ RUN { CONFIGURE CHANNEL DEVICE TYPE DISK FORMAT '/home/oracle/backup/efs_backup/rman_backup_%U'; ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE orclpdb1 CLOSE; RESTORE PLUGGABLE DATABASE orclpdb1; RECOVER PLUGGABLE DATABASE orclpdb1; ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE orclpdb1 OPEN; } - Since EFS maintains consistency across all mounted instances, there is no need to manually transfer files, they are readily available for recovery on Oracle Exadata Database.
Key Benefits- Eliminates manual file transfer between environments.
- Ensures high availability and durability of RMAN backups.
- Accelerates migration timelines by leveraging shared storage.
Conclusion- Amazon Elastic File System provides a scalable, cost-effective, and secure solution for migrating Oracle AI Databases from on-premises environments Oracle Exadata Database at AWS. By leveraging EFS integration, organizations can simplify data movement, reduce storage overhead, and accelerate migration timelines.
- For more information about mounting EFS across regions, and different VPC’s, see Mounting EFS file systems from a different AWS Region.
- Scalability and Elasticity