DNS
Learn about managed DNS for Oracle Database@AWS.
DNS (Domain Name System) is the system that translates human-readable domain names (such as oracle.com) into machine-readable IP addresses which computers use to identify one another on a network. Instead of remembering complex numerical IP addresses, users can simply enter a domain name and DNS handles the lookup behind the scenes. DNS enables seamless access to websites and services, ensures scalability of the Internet, and allows traffic to be routed efficiently. Without DNS, we would need to memorize IP addresses for every online resource we want to access.
Oracle Database@AWS allows customers to choose from either default DNS (oraclevcn.com) or a custom domain name in the ODB Network creation step. When an ODB network is created with a custom domain name, a default domain is also created in addition to the custom domain name. While the default domain name can be used by both Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure and Oracle Autonomous AI Database on Dedicated Exadata Infrastructure services, the custom domain name can only be used by the Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure service. Oracle Autonomous AI Database on Dedicated Exadata Infrastructure always uses the default name.
During the ODB network creation flow, both Forwarder Endpoint and Listener Endpoints are created automatically. When you create an Oracle Database@AWS database, you receive a corresponding connection string that uses the DNS name to connect to the database.
By using the domain name instead of the IP address, you can manage the database connection easily and directly.
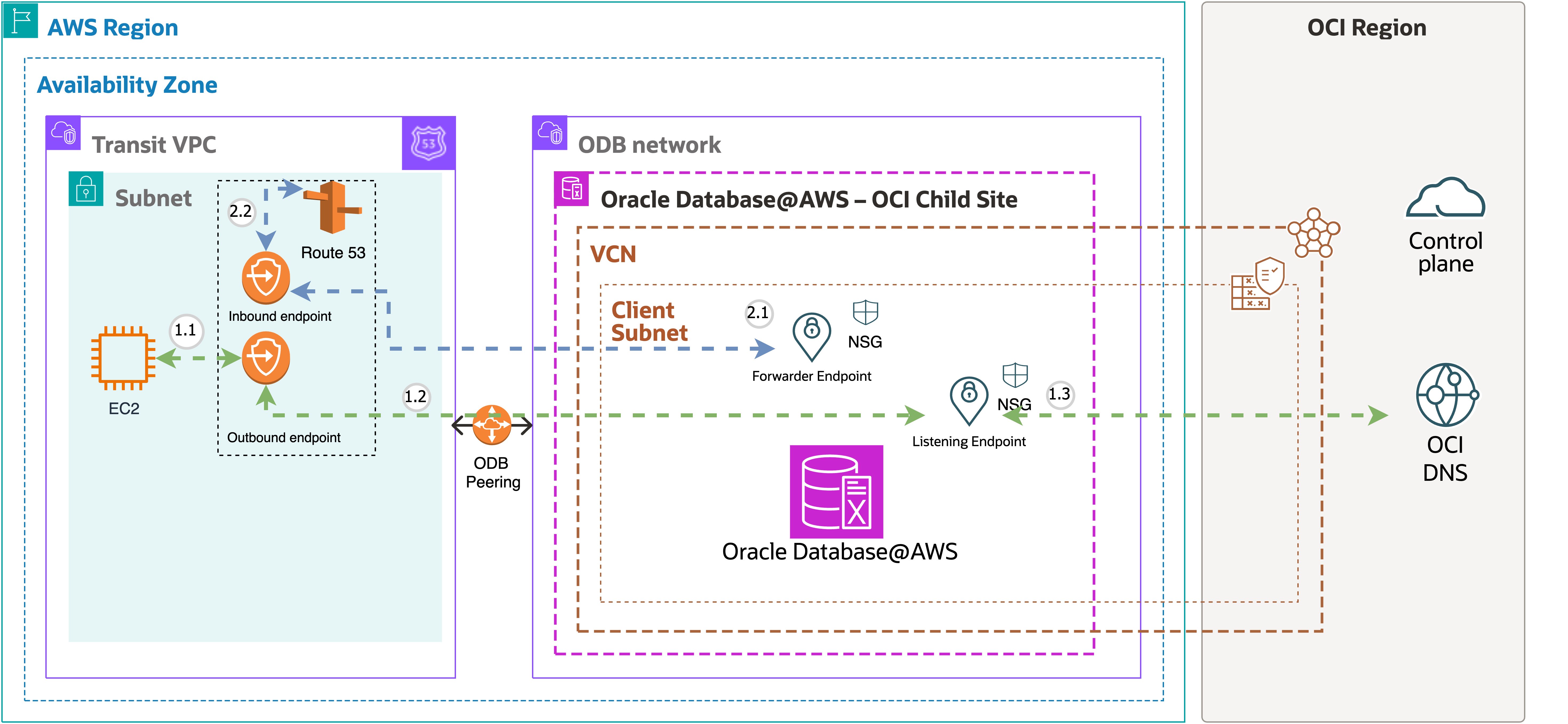
Let's learn using the following diagram how DNS resolution from AWS to OCI and from OCI to AWS is performed:
- AWS to OCI DNS Resolution: A database client running on an Amazon EC2 instance resolves the hostname in the database connection string using DNS.
- 1.1 The database client initiates a connection using the hostname.
- 1.2 The DNS query is handled by Route 53 DNS outbound endpoint of the VPC and matches the Route 53 resolver rule to forward the query to the OCI Private DNS listener endpoint.
- 1.3 The OCI Private DNS listener endpoint resolves the query to OCI DNS and returns the IP address to the database client.
- OCI to AWS DNS Resolution: An agent installed on the database host needs to resolve the host zone in AWS.
- 2.1 The database query a hostname, the query is handled by OCI Private DNS forwarder endpoint.
- 2.2 The DNS query is forwarded to AWS Route 53 private hosted zone linked to the VPC and the IP address is returned to the database.
1. Domain Name: The DNS domain names are defined during the creation of the ODB network.
2. Domain Resolution: The DNS resolution must be configured before connecting to the database.